EENT Trauma
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Globe rupture
A traumatic injury to the eye that typically occurs at the site of the greatest structural weakness directly behind the insertion of the rectus muscles
high velocity projectile, high impact blunt trauma, injury from sharp object
What is a globe rupture caused by?
Anything that puts pressure on the eye ball so eyelid retraction, IOP measure etc.
Patient presents to the ER after being stabbed by his ex-wife with an ice pick. On a physical exam you note markedly decreases visual acuity and an eccentric pupil. The IOP is low with decrease anterior chamber depth and there is an extrusion of vitreous humor and external prolapse of internal ocular structures. What are we not going to do on this patient?
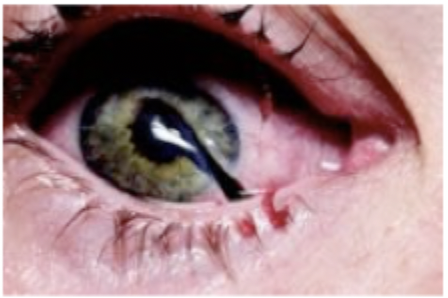
Emergent ophthalmologist eval, leave any foreign body, eye shield placement, aggressive pain control, anti-emetics to avoid extrusion of ocular contents
Concerning a globe rupture what is our treatment plan?
hyphema
Blood in the anterior chamber of the eye due to either blunt trauma (sports, MVCs, etc.) or penetrating trauma (BB, shrapnel, drills)
eye shield, bed rest and dim lighting, elevate the head of the bed, control the pain (No NSAIDs), treat nausea prevent vomiting, emergent ophthalmology eval
Patient presents to the ER after an elastic band popped back in her face. Patient reports vision loss and eye pain. Patient reports nuasea/vomiting. On a physical exam, you note anisocoria and iridodialysis, as well as blood in the anterior chamber and increased IOP. What’s our treatment plan?
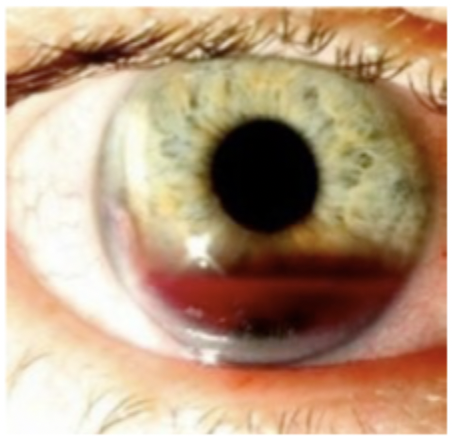
increased IOP, vessels spasm, clot formation
Why does bleeding normally stop pretty quick in hyphema
Measure visual acuity/extraocular movements, penlight exam, fluorescein stain, lid eversion to assess for foreign body
Patient presents to the ER for severe eye pain with a foreign body sensation. While collecting a history, your patient notes that he works with fiberglass, often without eye protection. What can you do to rule out open globe and hyphema?
Corneal abrasion
Eye trauma that is due a foreign body (such as rust, fiberglass, wood, glass, plastic, vegetable material) lodged under the lid or improper contact lens use (over-worn, improper fit, or unclean)
Corneal ulcer
Eye trauma that is typically evident as a white/opaque spot with a penlight or direct inspection, will be round on staining
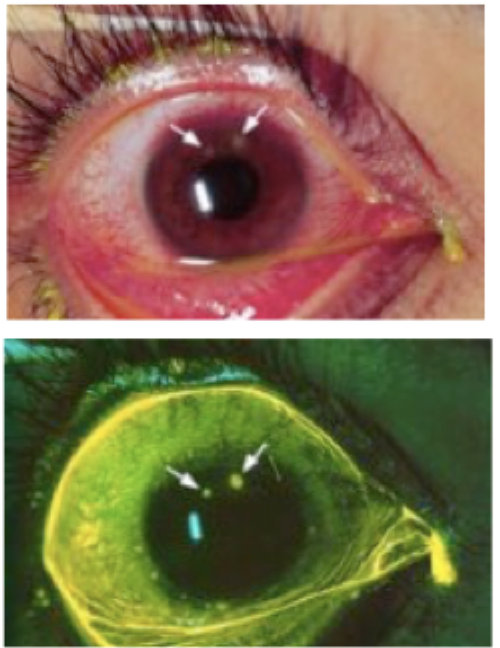
corneal infiltrate/white spot/opacity that suggest ulceration, foreign body that can’t be removed, hyphema/hypopyon, pus in anterior chamber, large epithelial defect, purulent discharge, drop in vision 1-2 lines, corneal abrasion that doesn’t heal in 3-4 days
When treating corneal abrasion or ulcers what are your referral indicators?
Cipro, Ofloxacin (cover for pseudomonas)
For small uncomplicated corneal abrasions, how are you treating contact lens wearers?
erythromycin ointment, DO NOT PATCH THE EYE
For small uncomplicated corneal abrasions, how are you treating non-contact lens wearers?
functions as lubricant and may decrease disruption of remaining/new epithelium
Why is ointment preferred over drops for corneal abrasions?
No (contraindicated)
Can you give a corneal abrasion patient steroids?
24 hours
Most abrasions heal fully within
oral NSAIDs, topical ophthalmic NSAID solutions
Pain control for corneal abrasions
ophthalmology IMMEDIATELY, plastic surgeon within 24 hours
Patient reports to the ER after getting into a bar fight. Patient reports double vision and N/V. Vitals are stable with the exception of HR with is 49 bpm. On a physical exam you note periocular ecchymosis (wicked shiner), infraorbital numbness, enophthalmos (eye receded into orbit), orbital dystopia. Who do we need to call?
Orbital floor fracture (blowout fracture)
A condition due to significant trauma, frequently a intracranial injury (frontal cerebral contusion, epidural/subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage) or intraocular injury (ruptured globe, hyphema retinal injury) typically due when a small round object strikes the eye.
ischemia due to entrapment of muscle within fracture fragment or edema and hemorrhage of muscle and extraocular fate that prolapse through fracture into maxillary sinuses
Complications of a blowout fracture
diplopia/upward gaze, infraorbital numbness (infraorbital nerve injury), periocular ecchymosis (black eye)
Orbital blowout fracture triad
pupillary reactivity, size, shape; extraocular movements, visual acuity, fundoscopic exam (retinal injury?), slit lamp whenever possible
Diagnostic test of an orbital blowout fracture
evidence of fracture on physical exam, limitation of extraocular movements, decreased visual acuity, severe pain, inadequate examination due to soft tissue swelling or AMS
A sinus CT is performed for patients with orbital trauma plus…
severe vagal symptoms associated with extraocular muscle entrapment (N/V bradycardia)
A blow out fracture patient needs to see an ophthalmologist IMMEDIATELY if
muscle entrapment due to orbital floor or medial wall fracture, enophthalmos or orbital dystopia that results in significant facial asymmetry
A blow out fracture patient needs to see an ophthalmologist and plastics within 24 hours if
1 week
All orbital blow fracture need to see ophthalmology within ________
Amoxicillin-clauvunate, azithromycin
What prophylactic antibiotics do you give orbital blowout patients to cover sinus pathogens
cold packs 1st 48 hours, sleep with head elevated, avoid nose blowing and sniffing.
Other ways to manage orbital floor fracture
Auricular hematoma
A collection of blood within the cartilaginous auricle due to blunt trauma during sports such as amateur wrestling, rugby, boxing, MMA, etc that requires QUICK drainage and prevention of reaccumulation of blood.
Cauliflower ear
A permanent deformity caused by fibrocartilage overgrowth that occurs then auricular hematoma isn’t fully drained, recurs, or is left untreated
drain that thing A$AP (no rocky)
Patient presents to the clinic with a tender, tense fluctuant collection of blood on the anterior aspect of the pinna with in the scaphoid fossa. While collecting a history your patient reports that this started last night after his MMA match. What needs to be done?
7 days
How long after the original auricular hematoma does the formation of granulation tissue occur?
re-eval every 24 for 3-5 days to watch for reaccumulation or signs of infection
After we drain the ears of Conor Mcgregor what do we need to do?
Nasal fracture
Occurs due a direct blow to the nose that results in fracture of the nasal skeleton leading to the depression of nasal bones/septum
nasal fracture with septal injury
Patient presents to the ER after catching an elbow to the face in a basketball game. Patient reports 10/10 pain and anosmia. On a physical exam you note profuse nasal bleeding and external nasal deformity along with edema and eccyhmosis. What type of nasal injury does this suggest?
frontal sinus fracture
In the case of nasal fracture, tenderness over frontal sinus may indicate
periorbital ecchymosis (black eye)
What sign/symptom in the absence of other orbital findings suggest a nasal fracture?
epistaxis
Concerning a nasal fracture, what should you manage 1st so the eval is not impaired?
tenderness/swelling is isolated to bony bridge, patient can breath through both nares, nose is straight, no septal hematoma
A X-ray is not needed for a nasal fracture IF
refer to ENT (3-5 days to reduce swelling), closed reduction with 7-14 days
For patients with a nasal fracture with NO septal heamatoma, what’s our game plan?
nasal bones will remain mobile so NO SPORTS for 2 weeks (no contact sports for 6)
Patient education measures for nasal fracture
tenderness, deformity, mobility, crepitus, step-off
In a internal exam of the nose for a nasal fracture what are you looking for
septal hematoma
Trauma to the nasal septum characterized by a tear in blood vessels adjacent to septal cartilage leading to a collection of blood between the cartilage and overlying mucoperichondrium causing pressure induced necrosis of nasal cartilage
Urgen surgical drainage by ENT, oral clindamycin, follow up in 12-18 to check for cosmetic defomity
Patient presents to the clinic for persistent and worsening nasal pain. They also report they feel like their nose is blocked and rhinorrhea. On a physical exam you note asymmetry of the nasal septum with red/blue discoloration and a swollen nasal mucosa that is obstruction a nasal passage. When you try a tropical application of Afrin (vasoconstrictor) you note the size of the mass doesn’t change. What’s our treatment plan.
septal perforation, irreversible damage
Complications of surgical drainage of a septal hemangioma after 3-4 days
accumulated blood/necrotic tissue can become infected, facial deformity due to the retraction of scar tissue (necrotic tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue)
Complications of surgical drainage of a septal hemangioma