Making Operational Decisions (EdExcel)
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Operations
The department managing production processes, suppliers, and operational efficiency to ensure goods and services are produced efficiently and meet quality standards.
Production Processes
The transformation of resources into finished goods or services, organized as job production, batch production, or flow production.
Job Production
Involves creating unique, custom products tailored to individual customer needs, made start-to-finish before the next job begins. Advantages include high customization, increased customer satisfaction, and higher prices, while disadvantages include higher costs, longer production times, and dependency on skilled labor.
Batch Production
Involves making a limited quantity of identical products in batches, allowing for economies of scale and flexibility to produce different products, but with drawbacks like downtime, storage costs, and risk of obsolescence.
Flow Production
Also called mass or continuous production, is the continuous manufacturing of standardized goods with high automation for consistency and speed. It offers advantages like high output rates, lower costs per unit, and consistent quality, but comes with drawbacks such as high initial setup costs, limited product design flexibility, and reliance on demand.
Purpose of Operations
Aiming to create or deliver goods and services efficiently, optimizing productivity and resource utilization.
Productivity
The quantity of output produced.
Efficiency
Making the most out of resources to achieve maximum output.
Labour Intensive
Relies more on human labor
Capital Intensive
Relies more on machinery and automation.
Impact of Technology
Technology can reduce costs, increase productivity, quality, and flexibility in operations.
Supplier Management
Involves working with suppliers for timely and quality deliveries, including procurement and Just in Time (JIT) stock management.
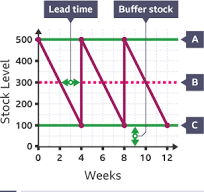
Bar Gate Stock Graph
A graphical representation of stock levels over time, including maximum and minimum stock levels, buffer stock, reorder points, and lead times.
Procurement
Involves finding the right suppliers, and ordering the right quantities at the right time and to the right standard.
Just in Time (JIT) Stock Management
A process in which raw materials are not stored on-site but ordered as required and delivered by suppliers 'just in time' to be used
Quality Management
Ensures products meet customer expectations and regulatory standards through quality control and quality assurance methods.
Quality Control
Inspection and testing of products at the end of the production process to ensure they meet standards. It ensures that finished products meet quality standards before reaching customers.
Quality Assurance
Continuous monitoring and improvement of processes to ensure consistent product quality throughout production. It prevents defects and ensures quality standards are met at every stage of production.
Sales Process
Involves stages from initial contact to post-sales support, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and drive business growth.
Importance of Customer Service
Good customer service generates loyalty, repeat purchases, and reduces marketing costs for businesses.