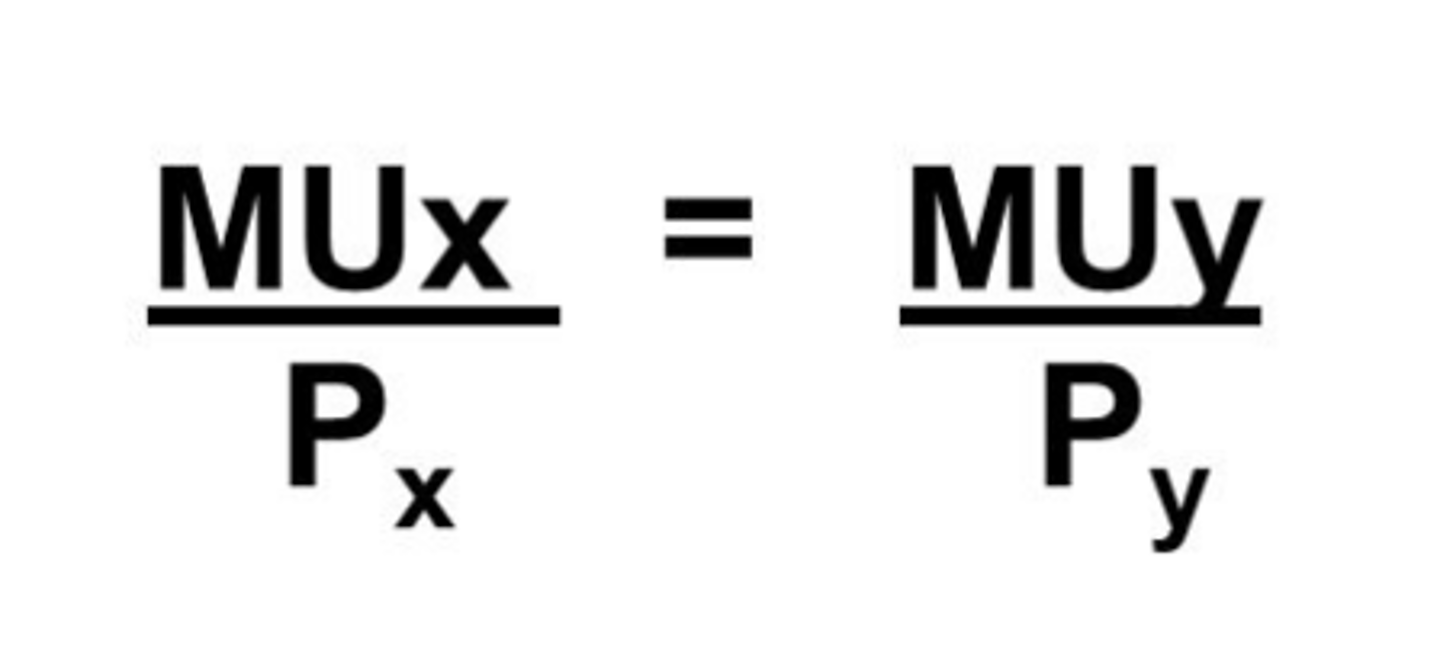unit 2 econ final review
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade ap microeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
demand
different quantities of goods that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices
law of demand
- inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
- occurs bc of substitution effect, income effect, and law of diminishing marginal utility
substitution effect
product price increases = consumer buys more of substitute product and less of that product (and vice versa)
income effect
produce price decreases = consumers buy more
law of diminishing marginal utility
consuming more units = additional satisfaction from each additional unit eventually decreases
utility
satisfaction
market demand
summation of the consumers' demand
shifters of demand
anything but price
substitutes
Px↑ = Dy↑ (direct relationship)
complements
Px↑ = Dy↓ (inverse relationship)
normal
income↑ = D↑ (direct relationship)
- goods you buy when you have money
inferior
income↑ = D↓ (inverse relationship)
- goods you buy when your poor
substitutes
- goods used in place of another
- ex: pepsi and coke
complements
- two goods that are bought and used together
- ex: skis and ski boots
supply
different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices
law of supply
direct/positive relationship between price and quantity supplied
shifters of supply
anything but price
subsidies
- gov payment that supports market
- supply of a good increases
consumer surplus
- difference between what you are willing to pay and what you actually pay
- CS = buyer's maximum - price
producer's surplus
- difference between the price the seller received and how much they were willing to sell it for
- PS = price - seller's minimum
unit elastic
consumer surplus and producer surplus is balanced
surplus
producers lower prices
shortage
producers raise prices
double shifts
either price or quantity will be indeterminate
elasticity of demand
- measurement of consumers responsiveness to a change in price
- helps firms determine prices and sales
- helps gov decide how to tax
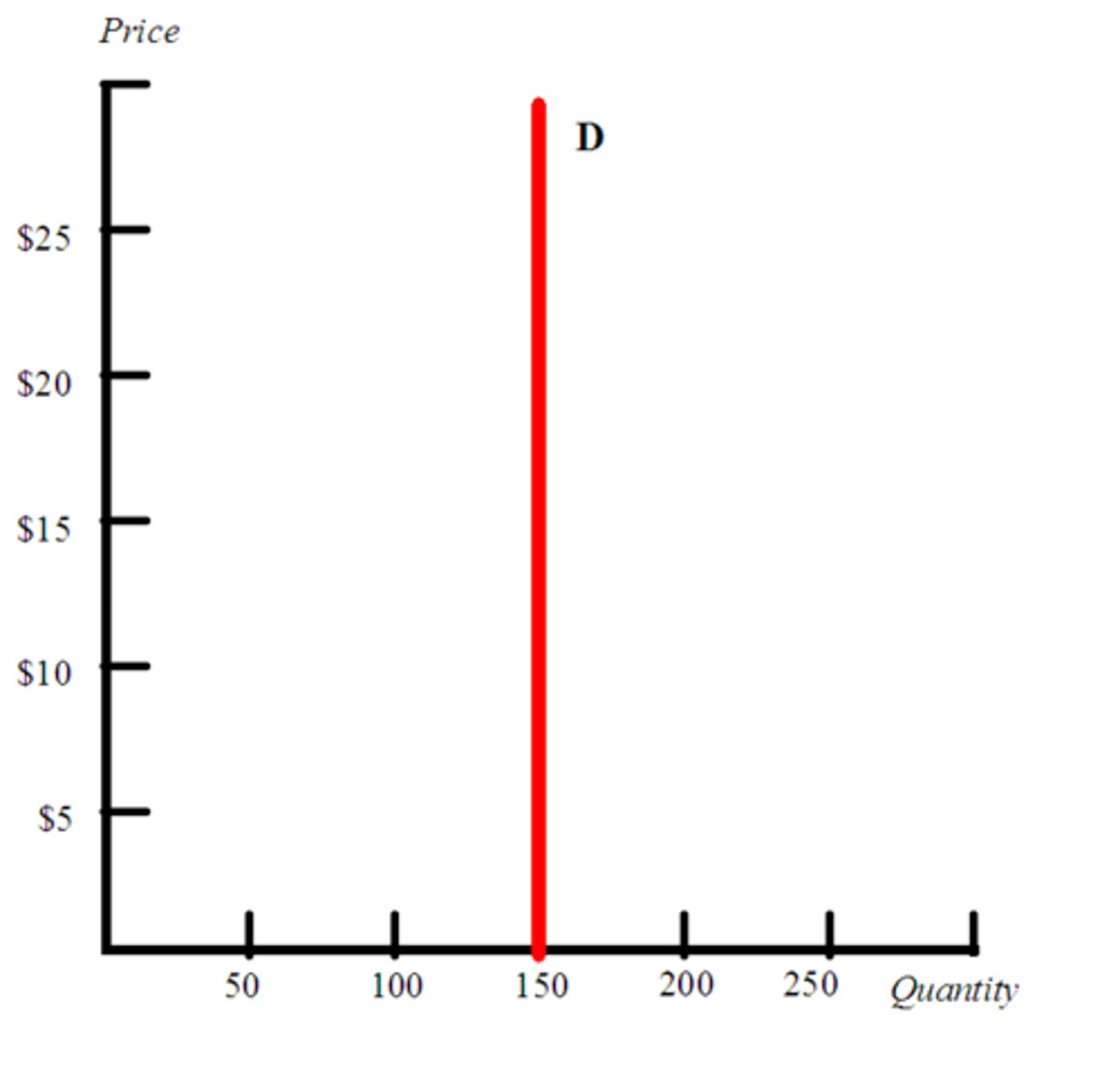
inelastic demand
- not sensitive to price change
- ppl will continue to buy it regardless of price
- elasticity coefficient <1
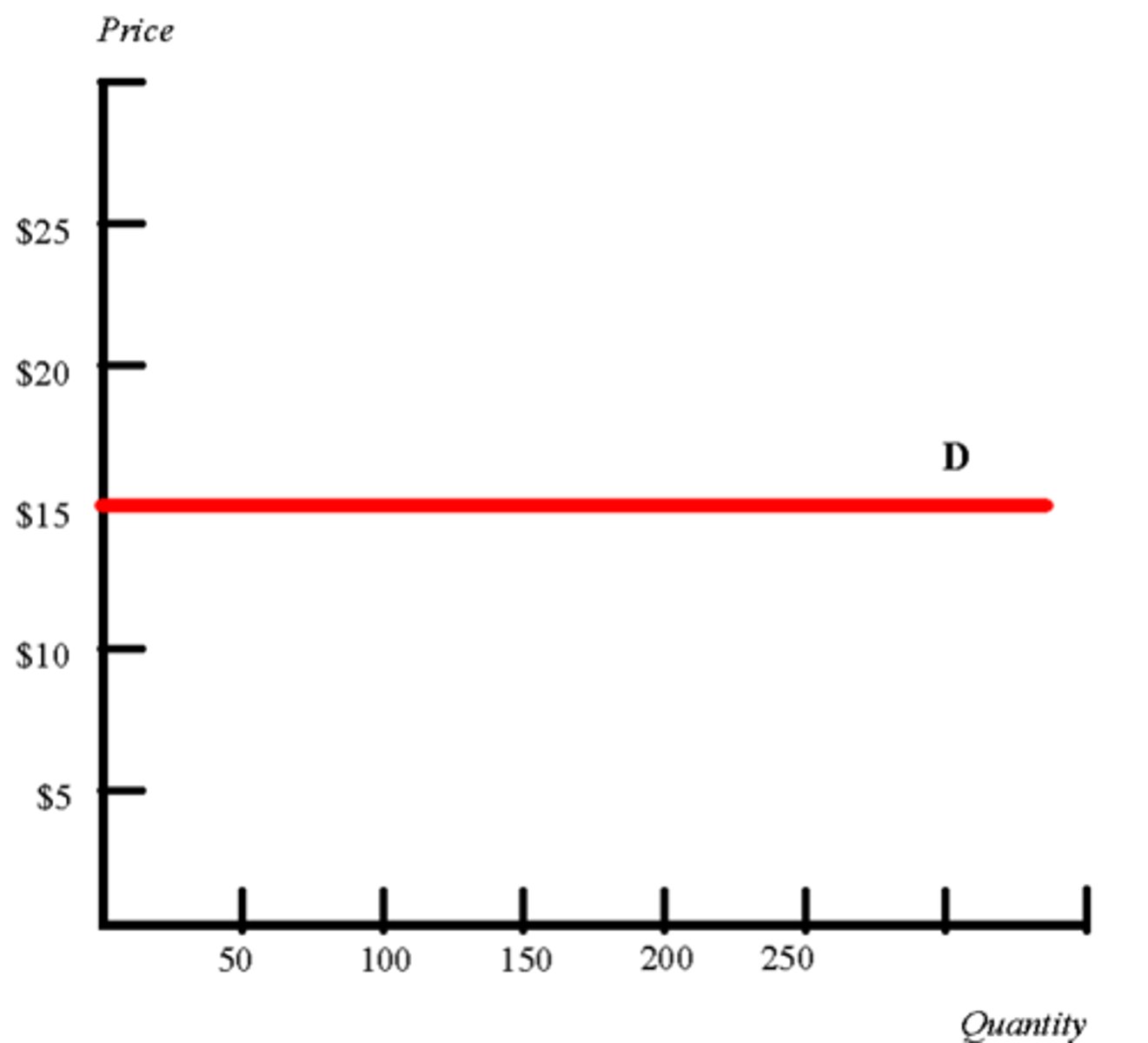
elastic demand
- sensitive to price change
- price change = quantity demanded changes a lot
elastic demand
P↑ = TR↓ (inverse relationship)
inelastic demand
P↑ = TR↑ (direct relationship)
unit elastic
P↑ = TR—
elastic
positive marginal revenue
total revenue
price x quantity
elastic demand
P↑ = TR↓ (inverse relationship)
- total revenue test
inelastic demand
P↑ = TR↑ (direct relationship)
- total revenue test
price elasticity of supply
how sensitive producers are to a change in price
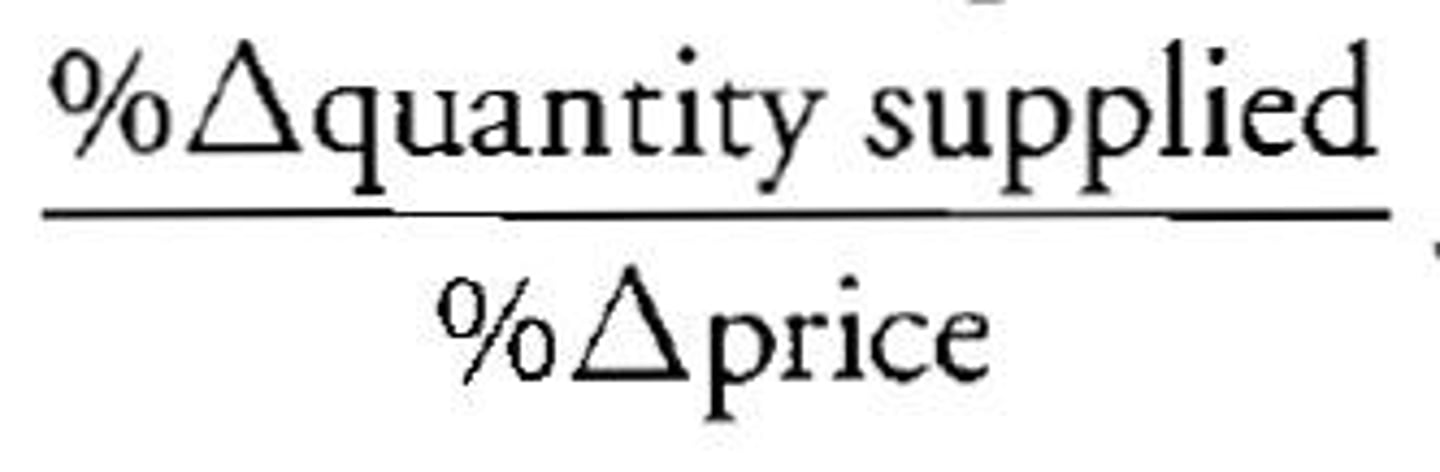
cross price elasticity of demand
- how sensitive a product is to a change in price of another good
- shows if goods are substitutes or complements
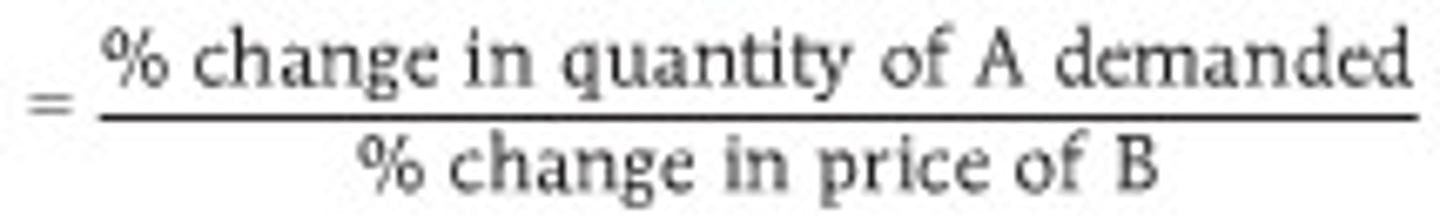
complements
coefficient = negative (shows inverse relationship)
- cross price elasticity
substitutes
coefficient = positive (shows direct relationship)
- cross price elasticity
income elasticity of demand
- how sensitive a product is to a change in income
- shows if goods are normal or inferior
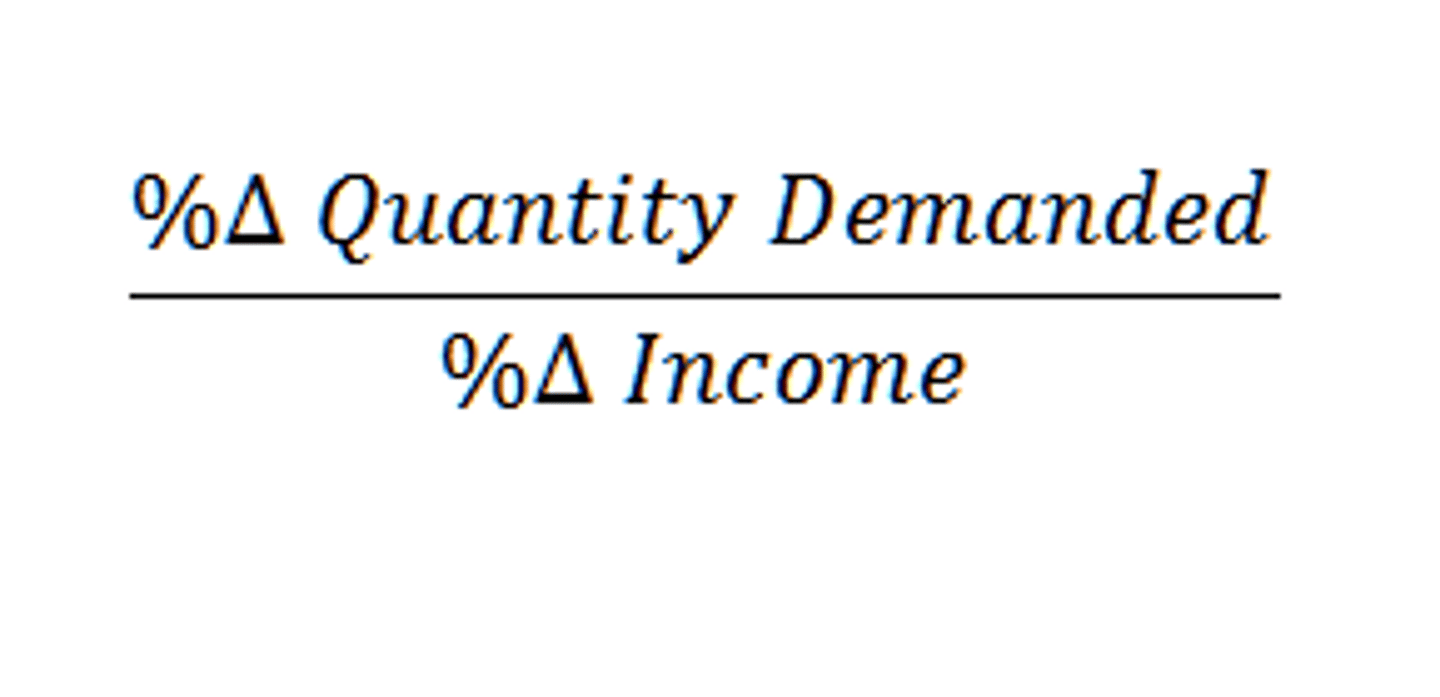
inferior
coefficient = negative (shows inverse relationship)
- income elasticity
normal
coefficient = positive (shows direct relationship)
- income elasticity
price ceiling
maximum legal price a seller can charge
price floor
minimum legal price a seller can sell
excise tax
per unit tax on producers
MB = MC
when to stop consuming
utility maximization