Peace and Conflicts!!
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IB SL Global Politics - Peace & Conflict
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Negative Peace
Absence of war/violent conflict
BUT there is still tension (structural or cultural or both)
Positive Peace
Absence of war/violent conflict
Tensions/contradictions are resolved
Stage 1 of Peace
Absence of war
negative peace
Stage 2 of Peace
Balance of forces
Prevents war through stability
Note: Hegemonic stability theory → single dominant power creates stability
Stage 3 of Peace
No structural violence (positive peace)
Stage 4 of Peace
Feminist peace (removal of discrimination)
Stage 5 of Peace
Humans living sustainably and harmoniously with environment
Stage 6 of Peace
Individual
Spiritual/religious
What is violence?
a manifestation of conflict due to incompatible goals. Thus resulting in harm to one or more of the parties involved
Misconceptions of conflict
caused by single factors
conflict parties are unitary actors
it’s always visible
always undesirable
needs to be settled
requires a third-party intervention
Realist focus on conflict
only focus on “state”/inter-state conflict & alliences
Liberal focus on conflict
increase in NSAs (non-state actors) means that it’s no longer just about “states”
Typology 1: COW
Correlates of War (Project of the University of Michigan)
inter-state conflict
extra-state conflict
internationalized internal conflict
intra-state conflict
NSA conflict
Inter-state conflict
between states/governmental parties
Extra-state conflict
between state and a non-state group outside its territory
(usually colonial/imperial wars)
after de-colonisation is uncommon
Internationalized internal conflict
between the govt. of a state and internal opposition WITH international intervention from other states
Intra-state (internal) conflict
beweetn govt. of a state and internal opposition WITHOUT intervention from other states
Non state conflicts
the groups involved are not under the govt./state
Typology 2: Fr Christopher Moore (MOORE)
relationship
data
interest
structural
value
Relationship conflict
when parties are upset with e/o
one party has a negative stereotype of the other
poor communication damaging relations
Data conflict
inadequate/untrustworthy data
when parties distort/hide/downplay/exaggerate information
Interest conflicts
real/perceived competitive interests
over land/resources/markets/influence
Structural conflict
structural violence
tension between those trying to solve issues & those resisting
Value conflicts
similar to structural conflicts
different criteria used to evaluate ideas/behaviours
focused on ideology/religion/culture
Why is conflict good/needed?
inevitable of human social interations (can’t always agree w e/o)
natural/constructive for human interaction
is important for a functioning democracy - political parties alw argue about how to govern a state
it’s only bad if it results in violence
Types of violence
Direct
structural
cultural
Direct violence
Physical force that leads to harm (lethal/non-lethal)
most visible
eg. armed conflict, terrorist attacks, riot police dispersing protesters
Structural violence
responsibility of the govt.
social injustice & inequality
people are harmed bc of the social/political/legal structures created within the state
results in - lack of healthcare, housing, employment opportunities etc.
less noticable
Cultural violence
embedded in all levels of society
beliefs & values
committed anywhere
driven in the mindset, so hard to remove
Just war theory
when should war be allowed and how to conduct it. (usually abt inter-state)
Just cause in war
should be fought for moral purposes
Just manner of conduct in war
the war itself should be fought justly
(no POWs, avoid civilian casualties, violence shld be proportional)
Jus ad bello
having just cause
being a last resort
being declared by a proper authority
possessing right intention
having a reasonable chance of success
the end being proportional to the means used.
Jus in bello
the law that governs the way in which warfare is conducted
Jus post bello
deals with the morality of the termination phase of war, including the responsibility to rebuild.
Humanitarian intervention
3rd party using military force to intervene in an armed conflict to protect civilians and stop violatins of human rights (ie. war crimes, genocide, crimes against humanity)
Has implications to sovereignty
Manifestation of conflict
direct violence
direct, can be seen, visible
Latent conflicts
Cultural & structural
indirect, usually not visible
What does Galtung say about conflict?
due to incompatible goals
What does Gerstandt say about conflict?
referring to latent conflicts which leads to “tension of difference”
Most conflicts begin before they manifest
observable actions taken by conflict parties are the manifestations of the underlying conflicts (structural/cultural)
Examples of Conflict manifestations
resolutions
avoidance
activism
discrimination
demonstration
civil disobedience
violent protests
arms proliferation
nuclear deterrence
guerilla warfare
terrorism
genocide
intrastate war
interstate war
Conflict party
any actor directly/indirectly involved in a conflict is a conflict party
state actors
non-state actors
transnational actors
IGOs/NGOs
militias/freedom fighters/terrorists
protesters/activists
individuals
social identity theory
Derives esteem from a group that they positively identify with, therefore they favor it. However, they view the opposition negatively even if their situations are similar
In-groups/out-groups
we judge people similar to us (in-group) better than people different to us (out-group)
Dehumanisation
However, due to in/out group mindsets, we tend to normalize or even glamorize harming the out-groups, even if we won’t be happy with the same harm done to us.
we think it’s okay to dehumanize them just because they are not like us
Unitary actor
treats state as a single entity with the aim to max national interest
Rational actor
decisions are made due to calculated benefits
Galtung’s conflict triangle
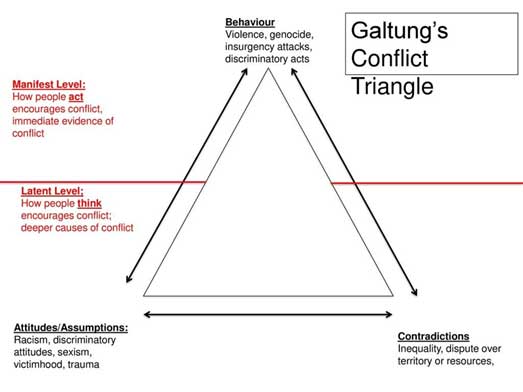
Greed
“how do I benefit?”
people fight over opportunistic reasons, cost-benefit calculations, alternative income etc.
Grievance
“how have they wronged me?”
people fight over inequality, discrimination, authro
Peacekeeping
3rd party breaking up the conflict parties and separating them
Peacemaking
coming up with a solution to solve the conflict
Peacebuilding
3rd party monitoring the conflict parties to make sure that they follow through with the negotiation/peace settlement
Ways that 3rd parties intervene
humanitarian intervention
direct military assistance
financial/economic assistance
weapon sales/embargos
trade sanctions/freezes/embargoes
treaty organisation (eg. NATO) involvement
election observation
brokering (mediator)/negotation of peace treaties or ceasefires
multilateral (more than the conflict parties involved) agreements
6 fold typology (before conflict climax)
conciliation
consultation
pure mediation
power mediation
arbitration
peacekeeping
6 fold typology: conciliation
trusted 3rd party gets the conflict parties to negotiate the problem
6 fold typology: consultation
3rd party brings out the expertise and tries to find a problem to the solution
6 fold typology: pure mediation
using persuasion/reasoning/etc. to convince both parties to settle on a negotiated settlement
6 fold typology: power mediation
uses coercion (not actual force, more like promised rewards or punishment)
may involve a third party to monitor agreement
6 fold typology: arbitration
3rd parties gives a binding judgement to impose a settlement that is fair and just
6 fold typology: peacekeeping
3rd party provides military personnel to monitor a ceasefire/agreement
might also engage in humanitarian activities/assist the management of political decision-making processes (ie. elections)
Contingency approach
conflicts are a mixture of objective and subjective interest
when conflict escalates, usually subjective interest increases, later resulting in both parties seeing different realities
Conflict escalation
discussion
polarisation
segregation
destruction
Conflict escalation: discussion
parties maintain a respectful relationship & are both wanting to find a joint gain on objective interests
Conflict escalation: polarisation
relationship deteriorate and negative perceptions (stereotypes) and emotions (hostitility) emerge
Conflict escalation: segregation
subjective interests increases, high levels of mistrust, limited direct communication, threats, increased “good vs evil”
Conflict escalation: destruction
conflict parties sees e/o as subhuman
if the losing end feels hopeless, they resort to just settle for losing