Anatomy Unit 1 Test
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Gray Matter
Contains non-myelinated fibers, cell bodies.
Inner region of the spinal cord (butterfly-shaped).
Outer region of brain.
White Matter
Contains myelinated axons.
Actual shiny, white appearance.
Inner region of the brain.
Outer region of the spinal cord.
Meninges
The brain and spinal cord are wrapped in protective membranes
3 Layers:
Dura Mater
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater
Dura Mater
Outer layer.
White, tough, fibrous connective tissue.
Inside the skull, the dura mater has 2 layers fused together.
Superficial layer adheres to the skull.
In some places, the layers separate and form dural venous sinuses.
Collects venous blood and excess CSF and returns both to the cardiovascular system.
Arachnoid Mater
Middle layer.
“Spider-web” like connective tissue.
No space between dura.
Adheres via thin strands to the deeper layer.
Pia Mater
Deepest meninx.
Directly attaches to brain/spinal cord.
Space between arachnoid and pia mater is filled with CSF.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Clear tissue fluid.
Protective cushion within and around CNS.
Formed from blood plasma.
Lower protein, glucose, and pH.
Formed by the choroid plexus in the ventricles.
Hollow, interconnecting cavities in the brain.
CSF fills the ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord.
Can build up in babies and cause hydrocephalus.
“water in the brain.”
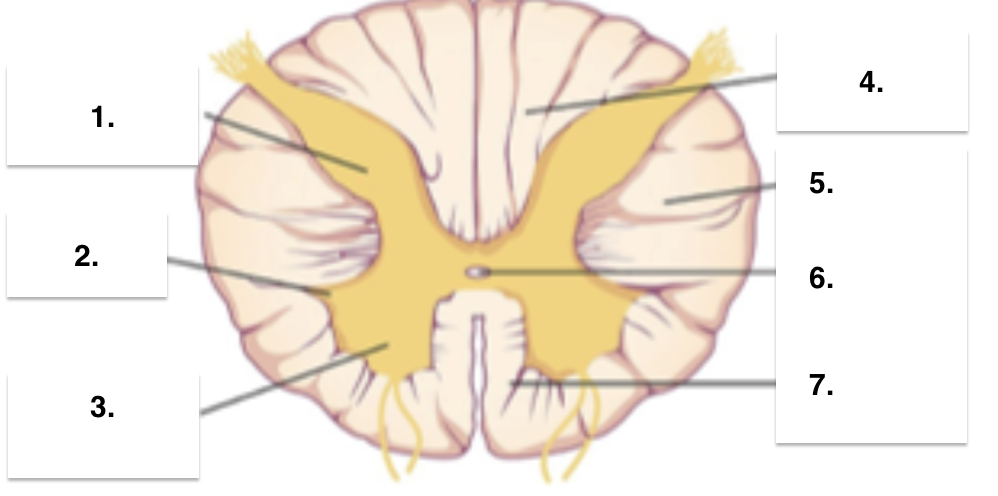
Gray matter: posterior (dorsal) horn
Lateral horn
Anterior (ventral) horn
White matter: posterior (dorsal) columns
Lateral columns
Central canal
Anterior (ventral) columns
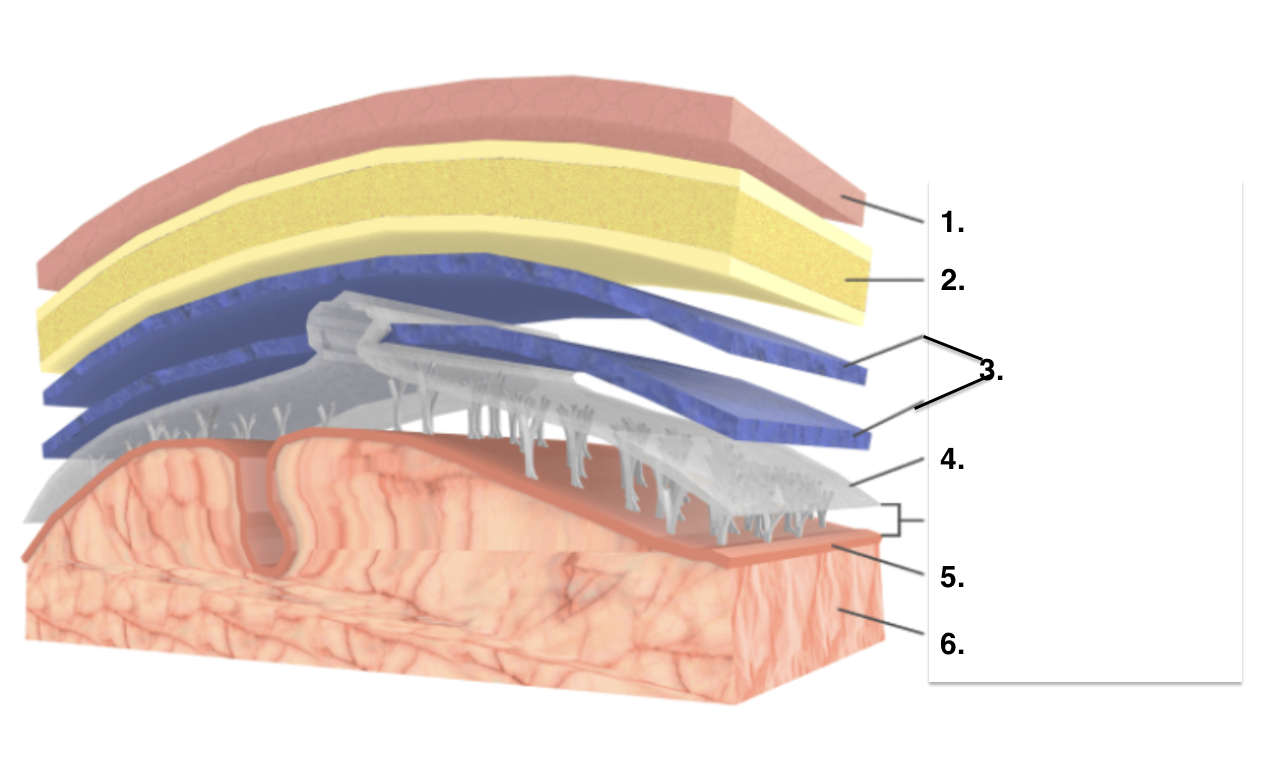
Scalp
Skull
Dura Mater
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebrum
General Function: receives sensory input, processes, and commands a response.
Communicates with and coordinates activities in other parts of the brain.
Carries out higher thought processes: memory, learning, and language.
General Structure:
2 cerebral hemispheres:
Separated by longitudinal fissure.
Connected by a bridge called the corpus callosum.
Ridges and shallow groves.
Gyri (bump) and sulci (groove)
Divided into 4 lobes: Frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal.
Cerebral Cortex
Thin, highly convoluted layer of gray matter.
Covers each hemisphere.
Contains over 1 billion cell bodies.
Processes sensation, voluntary movement, and consciousness.
Cerebellum
Consists of 2 cerebellar hemispheres.
Coordinates muscle movements to create smooth motion.
Regulates posture and balance.
Brain Stem
Midbrain:
Help cerebellum coordinate muscle movement, movement of eyes, neck and head in response to visual stimuli, startle reflex.
Pons (means bridge):
Controls breathing and acts as a relay site.
Medulla Oblongata:
Controls breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Swallowing, vomiting, coughing, hiccuping, and sneezing.
Production and processing of language.
Broca’s Area
Monitors and regulates motor behavior or movements, including posture, balance and coordination.
Cerebellum
Controls autonomic nervous system and the pituitary gland, hunger, thirst, sleep, and body temperature.
Hypothalamus
Controls emotions, pleasure, and anger.
Limbic System
Relays motor and sensory impulses from the spinal cord to the brain, alertness, awareness, consciousness, and arousal.
Medulla Oblongata
Secretes hormone melatonin.
Pineal Gland
Vision
Occipital lobe
Hearing
Temporal Lobe
Relays info to the cerebral cortex, perception of touch, pressure, and pain.
Thalamus
Amygdala function and associated problems
Functions:
learning
fear-processing
emotion processing
fight-or-flight response
reward-processing
Problems:
disruption of short-term memory
deficits in recognizing emotions
irritability
loss of control of emotion
aggression
Brain Stem function and associated problems
Functions:
maintaining homeostasis by controlling autonomic functions
alertness
sleep
balance
startle response
Problems:
organ failure
sleep disorders
difficulties balancing and moving
Cerebellum function and associated problems
Functions:
coordination of voluntary movement
motor-learning
balance
reflex memory
posture
timing
sequence learning
Problems:
loss of fine coordination
inability to walk
tremor
slurred speech
dizziness
Corpus Callosum function and associated problems
Functions:
allows info to move between hemispheres and is therefore a very important integrative structure.
Problems:
schizophrenia
psychotic episodes
alzheimer’s
children w/ ADHD
non-cognitive disorders
Frontal Lobe function and associated problems
Functions:
“higher” cognitive functions like executive processes, voluntary control, cognition, intelligence, attention, and language processing.
Problems:
paralysis
loss of spontaneity in social interactions
mood changes
inability to express language
atypical social skills and personality traits
Hypothalamus function and associated problems
Functions:
hunger
circadian rhythms
body temperature
blood pressure and heart rate
sexual activity
sleep
Problems:
weight gain/loss
hypersomnia
hypothermia
chronic stress
over/under active sex drive
lethargy
Occipital lobe function and associated problems
Functions:
vision
Problems:
hallucinations
blindness
inability to see color, motion, or orientation
Parietal lobe function and associated problems
Functions:
Integrating info from different senses to build a coherent picture of the world.
Problems:
Inability to attend to people, objects, or one’s own body on the side opposite the damaged area.
Pons function and associated problems
Functions:
regulates breathing, taste, and autonomic functions
Problems:
screaming, thrashing arms, punching, and kicking during violent and vivid dreams
Temporal Lobe function and associated problems
Functions:
perception
face recognition
object recognition
memory acquisition
understanding language
emotional reactions
Problems:
difficulties in understanding speech, faces, and objects
inability to attend to sensory input
persistent talking
long and short-term memory loss
increased/decreased interest in sexual behavior
aggression
Thalamus function and associated problems
Functions:
relaying motor and sensory information
memory
alertness
consciousness
contributes to perception and cognition
Problems:
impaired processing of sensory info
impaired movements and posture
amnesia
dementia
loss of alertness and activation
sleepiness
inattention
coma
difficulty speaking
apathy
pain
Ventricles function and associated problems
Functions:
cushions and protects the brain
Problems:
schizophrenia
bipolar disorder
dementia
Taste Buds
Sensory receptors are embedded in taste buds.
Found mainly in the epithelium of the tongue.
Along the raised papillae.
Others on the hard palate (roof), pharynx, and epiglottis.
5 primary taste sensations.
Sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami.
Scattered throughout the tongue.
How the brain receives taste information
Each taste bud opens at a taste pore.
Microvilli of taste cells project through taste pore.
Microvilli have receptor proteins for molecules that allow the brain to distinguish between 5 tastes.
When molecules bind to the proteins, a nerve signal is sent to the brain (gustatory regions).
Olfactory Cells
In the epithelium of the nasal cavity.
Modified neurons.
Ends with 5 olfactory cilia.
Contains protein receptors for odor molecules.
How the brain perceives odor
Each olfactory cell has only 1 type of 1000+ different protein receptors.
Nerve fibers travel to the olfactory bulb (cranial nerve).
Multiple signals combined to create the smell signature.
Example: a certain food may contain multiple odor molecules that combine.
Connect directly with the limbic system.
Memory and emotion centers.
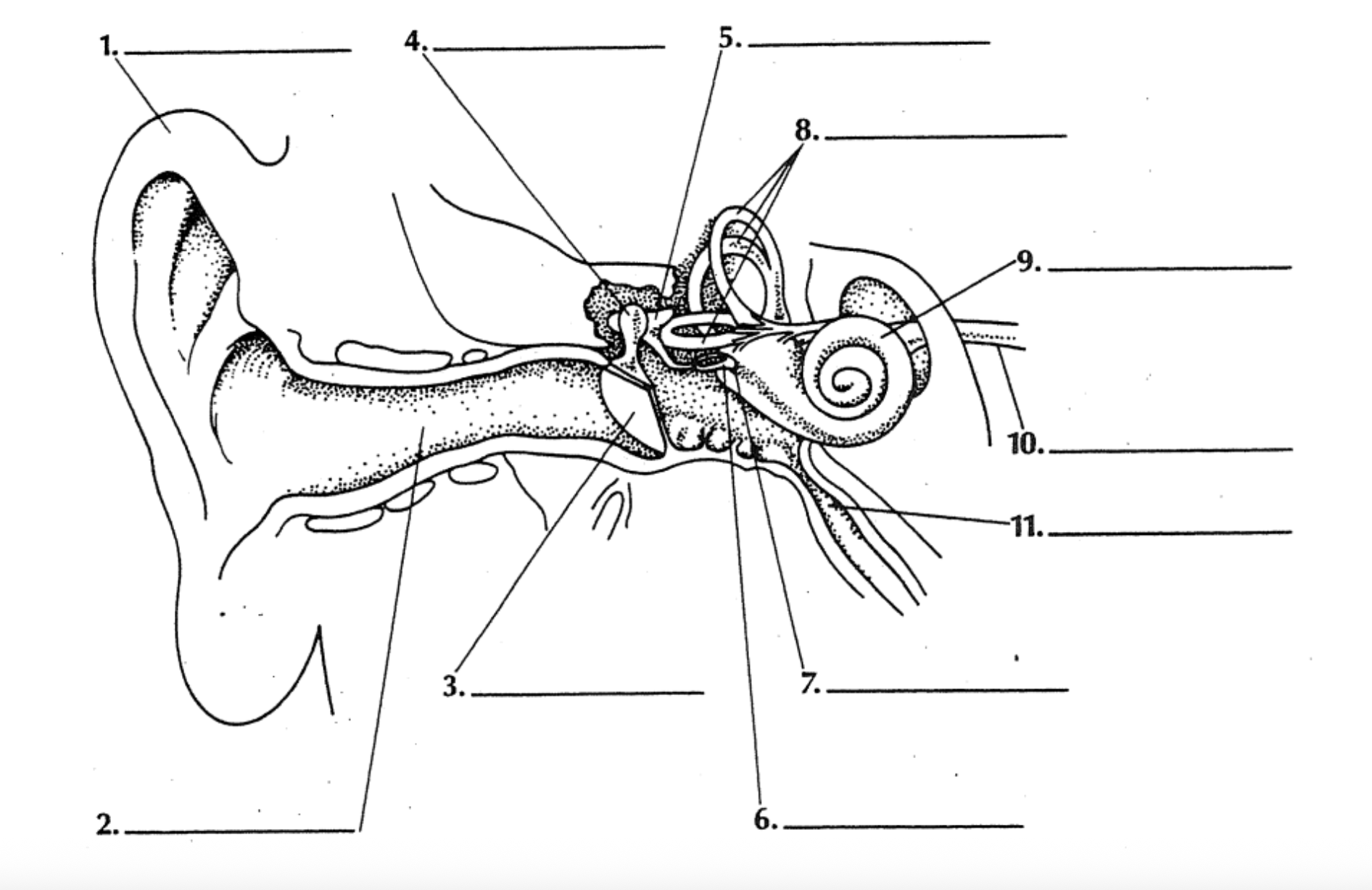
Auricle/Pinna
Auditory canal
Tympanic membrane
Malleus
Incus
Stapes
Oval window
Semicircular canals
Cochlea
Auditory nerve
Eustachian tube
Outer ear
Pinna: outer flap made of skin, cartilage (auricle).
Auditory canal
Passes through the temporal bone.
Opening lined with fine hairs and sweat glands.
Upper wall contains modified sweat glands.
Secrete cerumen or wax.
Guard against foreign materials like dust or air pollutants.
Middle Ear
Tympanic membrane
Eardrum.
Sound waves hit the membrane and vibrate.
Vibrations passed to each ossicle.
Auditory ossicles
Malleus (hammer)
Incus (anvil)
Stapes (stirrup)
Vibration increases 20x as it moves from bone to bone.
Oval window
Small membrane-covered opening in the bone of the inner ear.
Passes vibrations to the inner ear.
Auditory tube (Eustachian tube)
Connects to the nasopharynx and equalizes air pressure.
Inner ear
Found in the bony labyrinth.
Carved cavity in the temporal bone.
Lined with the membranous labyrinth.
Contains 2 fluids:
Perilymph and Endolymph.
3 areas:
Semicircular canals → balance
Vestibule → balance
Cochlea → hearing
Sound Pathway
Through the auditory canal and middle ear.
From cochlea to auditory cortex.
Contains 3 ducts.
Vestibular and tympanic duct filled with perilymph.
Cochlear duct filled with endolymph.
Spiral organ - sense organ for hearing.
Organ of Corti.
Contains tiny hair cells in the basilar membrane.
Above is the tectorial membrane connected to nerves.
When the oval window vibrates.
Pressure waves travel through ducts.
Basilar membrane moves up and down.
Hairs affect signals to the auditory nerve → brain.
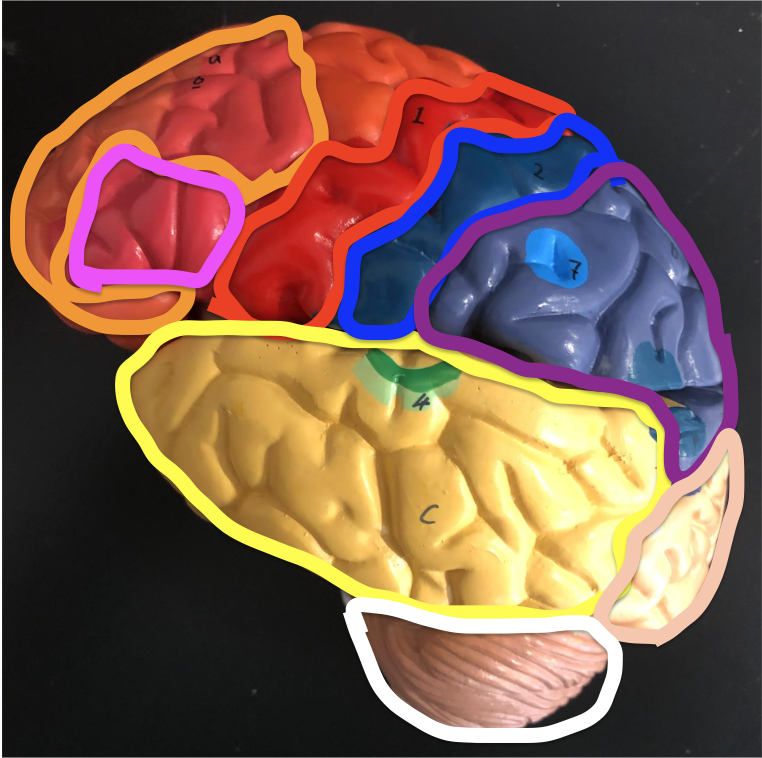
Orange - Frontal lobe
Red - Motor cortex
Yellow - Temporal lobe
Blue - Somatosensory cortex
Purple - Parietal lobe
Peach - Occipital lobe
Green - Wernicke’s area
Pink - Broca’s area
White - Cerebellum
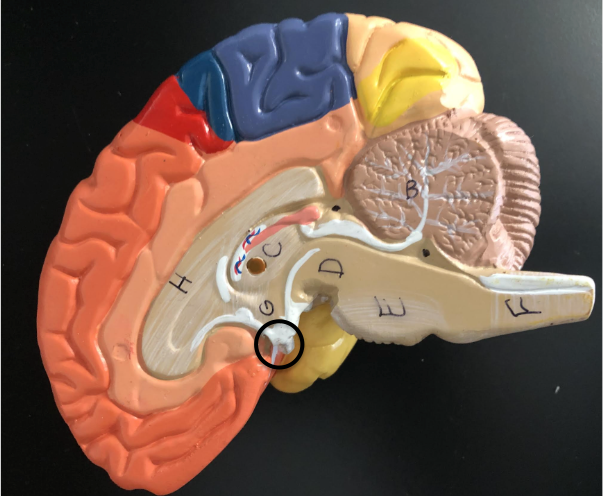
B - Cerebellum
C - Thalamus
D - Midbrain
E - Pons
F - Medulla Oblongata
G - Hypothalamus
H - Corpus Callosum
Black circle - Pituitary gland
Black dots - Ventricles
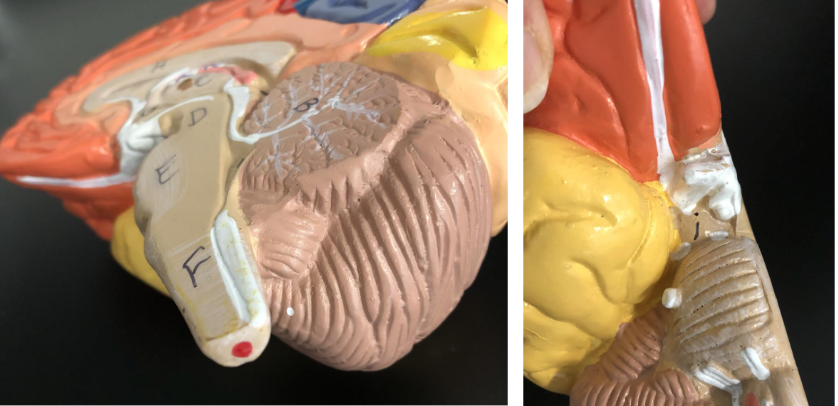
Red dots - Spinal cord
i - Pituitary gland
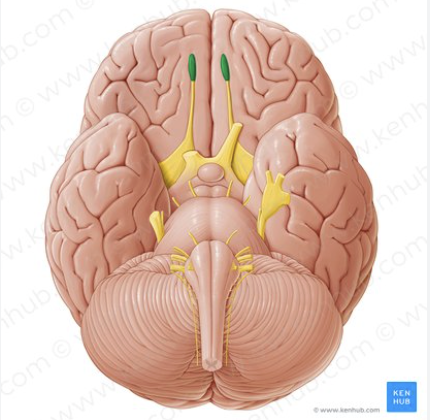
Olfactory bulb/tract
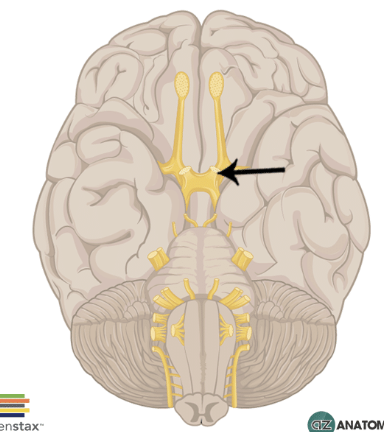
Optic nerve