Nutrient Catabolism
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BHCS1003 - CA05
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Key Concepts
Catabolic Pathways: Energy- yielding breakdown reactions
Amphibolic pathways: serves both catabolic and anabolic roles
Oxidative phosphorylation: ATP generation usinf electrons from NADH and FADH2
Cellular Respiration
Nutrient Oxidation → NADH/ FADH2
Electrons donated to the electron transport chain
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor → H2O
Proton gradient drives ATP synthesis
Carbohydrate Catabolism - Glucose Catabolism
Gluocose is broken down via glycolysis to pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH
Key glycolytic itermediates:
Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P)
Fructose-6-phosphate (F6P)
Glyceraldehyde-3-phophate (G3P)
Pyruvate
Pyruvate is further oxidised via the TCA cycle and the OXPHOS
Fructose Metabolism
General features:
Metabolised more rapidly than glucose
Uptake is Insulin- independent
Metabolic fate depends on nutritional state and organ type
In muscle:
single step conversion to a glycolytic intermediate
In liver:
Requires multiple enzymatic steps
Disorders:
Fructokinase deficiency → benign, fructose accumulates in blood and urine
Hereditary Fructose intolerance (Aldolase B Deficiency) → severe liver damage if untreated
Galactose Metabolism
Occurs via Leloir Pathway → converted to glucose-6-phosphate
Disorder → Galactosemia (defect occurs in step 2)
Fatty acid Catabolism
Faty acids are a major energy source and are catabolised bia mitochondrial B-oxidation.
Main stages:
1) activation to fatty acyl-CoA
2) Transport into mitochondria
3) B-oxidation
4) Acetyl-CoA oxidation in the TCA cycle
Fatty Acid Activation
Key points:
Catalysed by acyl-CoA synthetase
Driven by pyrophosphate Hydrolysis
Enzymes show chain length specificity
Transport into Mitochodria
Requires Carnitine shuttle
Catalysed by Carnitine Palmitoyltansferase (CPT)
2 cpt isozymes involved
Mitochondrial B-Oxidation
Oxidation occurs at the beta-carbon of the fatty acyl-CoA
each cycle yields:
→ Acetyl-CoA
→ NADH
→FADH2
→ fatty acyl-CoA shortened by 2 carbons
processes repeats until fatty aid is fully degraded
Special Mechanisms exist for:
very long chain fatty acids
unsaturated fatty acids
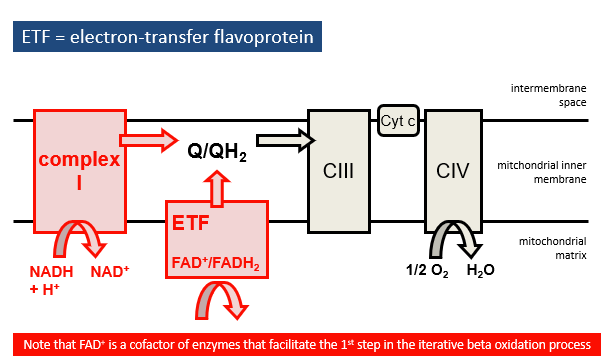
Reoxidation of NADH and FADH2
NADH feeds electrons into complex I
FADH2 donates electrons via:
electron-tranfers flavoprotein (ETF)
Complex II (succinate dehydrogenase)
electrons pass through Q, complex III, cytochrome c and complev IV
OXGYEN IS REDUEED TO WATER
Amino Acid Catabolism
Amino acids come from dietary protein or muscle breakdown
Important during fasting or disease states
Associated conditions:
sarcopenia: age-related muscle loss (ageing, CKD, liver disease)
Cachexia: severe muscle wasting
Deamination and Nitrogen Disposal
Amino acid catabolism involves deamination
produces ammonia (NH3) which is toxic
Urea Cycle (krebs-Henseleit cycle)
Converts toxic ammonia into urea for excretion
Functionally linked to the TCA Cycle
Discovered by Hans Krebs
Glucogenic vs Ketogenic Amino Acids
Glucogenic Amino Acids: form glucose via TCA Cycle intermediates
Ketogenic amino acids: form acetyl-CoA or ketone bodies
Some amino acids are both
Metabolic Convergence
Carbohydrates→ glycolysis → TCA cycle
Fatty acids→ acetyl-CoA → TCA cycle
Amino Acids → TCA cycle intermediates
All major nutrients converge on the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP