Pituitary and Thyroid Gland
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Where is the pituitary gland located?
- On the ventral surface of the brain, connected to it by a thin stalk and cradled and protected by the sphenoid bone
Describe the development of the anterior pituitary
- Made up of endocrine cells (derived from rathke's pouch, which is an upgrowth from the epithelium of the pharynx towards the base of the brain) This wraps around the posterior pituitary
Describe the development of the posterior pituitary
- Extension if the hypothalamus (neural ectoderm) into the anterior pituitary: the cell bodies remain in the hypothalamus, the axons from the stalk of the posterior pituitary and the nerve ending of the posterior lobe itself
What form the pituitary?
two fused glands surrounded by the sphenoid bone
What connects the pituitary to the brain?
Infundibulum
What hormones are released by the posterior pituitary?
Oxytocin and ADH
(released but not synthesised here)
Where are Oxytocin and ADH synthesised?
in the cell bodies within the hypothalamus
What is the mechanism for hormone release?
- released from their axons terminals into capillaries in the posterior pituitary
What is a portal system?
two capillary networks connected in series
Describe the release of hormones using the capillary portal system in the pituitary gland
- Neurones synthesising tropic hormones release them into the first capillary system of the portal system
- Portal vessels carry the tropic neurohormones to the anterior pituitary where they act on the endocrine cells
- Endocrine cells release their peptide hormones into the second set of capillaries for distribution to the rest of the body.
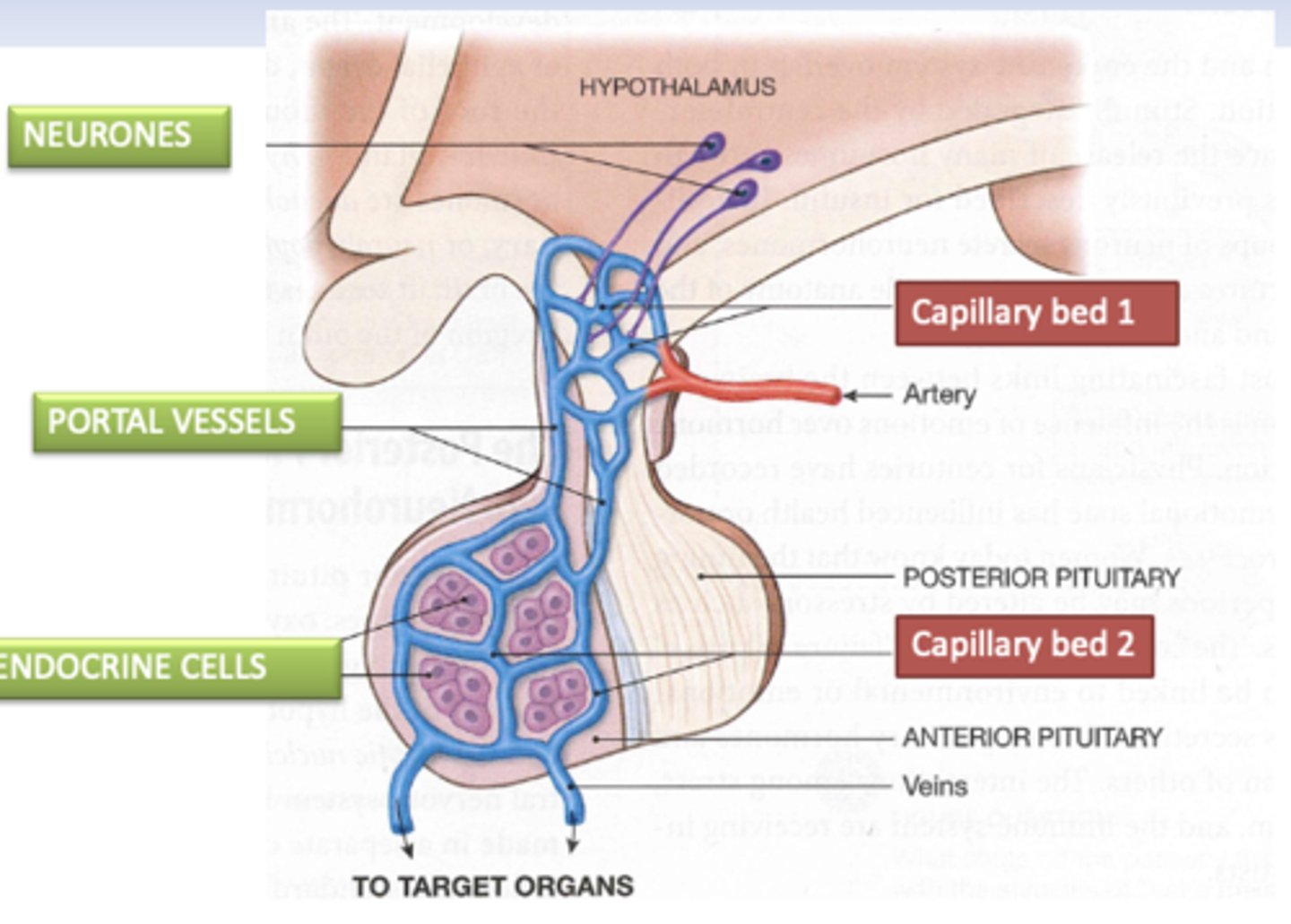
What is the purpose of the portal system?
amplifies the system
What 6 hormones are released by the anterior pituitary gland?
FLAT PiG
-FSH
-LH
-ACTH
-TSH
-Prolactin
-GH
What is the difference between a tropic and a trophic hormone?
- Trophic hormones regulate the growth and development of a target organ
- Tropic hormones are ones that cause the release of another hormone
- Words are unrelated, anterior pituitary hormones are both.
What are the two types of feedback of trophic hormones?
long and short loop negative feedback
Describe the short pituitary hypothalamic loop
- Stimulus causes the hypothalamus produce a releasing hormone which travels to the anterior pituitary where it is released as a tropic hormone
- This hormone then inhibits the hypothalamus, therefore completing the negative feedback loop
Describe the long end organ loop of negative feedback
- Stimulus causes hypothalamus to produce releasing hormone, which is then transported to the anterior pituitary via the portal system where they act on endocrine cells
- Endocrine cells release their peptide hormones
- These hormones stimulate the endocrine glands to release different hormones which will cause a response in the body
- It is these hormones that inhibit both the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to prevent further release of the releasing and tropic hormones, thus preventing the endocrine glad from releasing more of it's hormones
Describe the intermediate lobe of the pituitary
same embryological origin as the anterior lobe of the pituitary
-- secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormones, known collectively as MSH
How many lobes does the thyroid gland have
2
where is the thyroid glad located?
the lobes are located either side of the trachea just below the larynx
Briefly describe the histological appearance appearance of the thyroid gland
- Mostly composed of spherical groups of epithelial follicular cells surrounding a non-cellular filling
What is the significance of the parafanicular C cells?
have a lot o do with metabolism
how and where are the thyroid hormones produced?
- The raw materials are trapped or synthesised by the follicular cells
--Trap iodide via a NaI symporter and oxidise it to iodine and transport it to the colloid
--Synthesis and transport thyroglobulin, tyrosine and enzymes etc into the colloid
what are the two types of thyroid hormone?
- T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine)
Describe he storage of thyroid hormone
- In Colloid or protein bound
- Free fraction in the plasma will bind to target receptors (this provides a depot that will last several days)
How are the thyroid hormones regulated?
- Secretion of TRH from the hypothalamus is largely driven by the CNS
- Both long and short loop feedback exists but the dominant regulatory pathway is TSH
--Increased concentration of thyroid hormones in the plasma inhibit TSH
- In the absence of the TSH thyroid follicular cells are inactive
- If the concentration of TSH increases for prolonged period, follicular hyperplasia and hypertrophy is induced
Which hormone is the main hormonal product of the thyroid gland?
- T4, it is converted to T3 in peripheral tissues as T3 is much more biologically active.
Describe the role of thyroid hormones in metabolism
- Increases metabolic rate in all tissues (except gonads, brain and spleen)
- Leads to increased O2 consumption and thermogenesis
What are the main roles of the thyroid hormones?
- Increases metabolic rate in ALL tissues
- Required for normal growth and development
-- Increased protein synthesis and increased cell division
- Required for normal development of the CNS
- Promotes target responsiveness to sympathetic nervous system
- Promotes axonal conductivity
- Required for normal gonadal function
Why would iodine deficiency cause an enlarged thyroid?
- Lack of iodine in diet substances inhibit uptake
- Therefore can't make thyroid hormones
- Continually high TSH binds to its specific receptor and stimulates thyroid follicular cell growth
- No negative feedback
- Causes enlarged thyroid