week 11 DICOM, PACS etc.
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
DICOM (digital imaging and communications in medicine)
an international standard (ISO) for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting information in medical imaging
includes a file format definition and a network communication protocol
communication protocol is an application protocol that uses TCP/IP to communicate between systems
what does a single DICOM file contain?
a header (which stores information about the patients name, type of scan, image dimension, etc.)
image data (in compressed or uncompressed form)
PACS (picture archiving and communication system)
an integrated computer system for the storage, transfer and display of radiological images
consists of
a digital archive to store medical images
display workstations to permit physicians to view the images
a computer network to transfer images and related information between the imaging devices and the archive and between the archive and the display workstatio
point spread function (PSF)
most basic measure of the resolution properties of an imaging system
response of the imaging system to a point input
a two dimensional function, described in the x and y dimension
line spread function (LSF)
an imaging system is simulated with a signal in the form of a line is used to evaluate LSF
a profile measured perpendicular to the line gives LSF(x)
most common method for measuring blur and system resolution (FWHM)
magnification
results in increased penumbral blurring (geometric unsharpness)
magnification = source to image distance / source to object distance
depends on focal spot size, SOD, SID, OID
focal spot size effect on magnification / spatial resolution
the smaller the focal spot, the sharper the image - better spatial resolution
but with smaller focus, only smaller mA can be used - long exposure time
fourier transform (FT)
FT breaks any arbitrary signal down into the sum of a set of sine waves of different phase, frequency, and amplitude
transforms spatial domain signal to frequency domain
used for filtering procedure in filtered back projection for CT reconstruction
modulation transfer function (MTF)
provides the most complete characterisation of the resolution of an imaging system
how well the contrast is transferred from object to image
MTF = image contrast/object contrast
limiting resolution
characterises the approximate resolution limit (a single number) of an imaging system
considered to be the frequency at which the MTF crosses the 10% level
what is the nyquist frequency?
highest frequency that can be accurately measured on the imaging system
for an imaging system, FN =1/ 2Δ, where Δ (mm) is the centre-to-centre spacing between detector elements
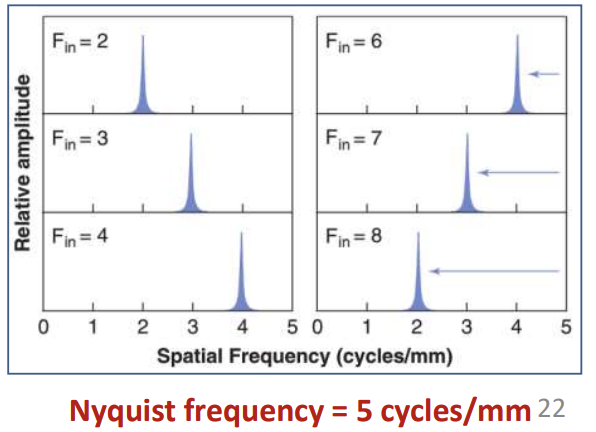
what happens if the input frequency is higher than the nyquist frequency (FN)?
the true frequency will not be recorded - it would be aliased, and the frequency recorded will be lower than the incident
the measured frequency will be lower than FN by the same amount which the input exceeds FN
what is contrast resolution characterised by?
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) - number of photons (mA)
what types of noise is contrast resolution affected by?
quantum - fluctuation in x-ray, photons, electrons, etc
electronic - exists in all electronic circuits
anatomical - unwanted anatomy
signal to noise ratio (SNR)
as signal increases, SNR increases (image quality increases)
SNR = N (square root)
i.e. if the signal is doubled, dose is doubled but SNR increases by square root of 2
to double SNR, dose must be increased by a factor of 4
what is a good measure of the dose efficiency of an x-ray detector system?
detective quantum efficiency (DQE)
what does the DQE describe?
how effectively an x-ray imaging system can produce an image with high SNR