Levers test
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
First class lever
Fulcrum in the middle
Second class lever
Load in the middle
Third class lever
Effort in the middle
MA > 0
1st class lever
MA > 1
2nd class lever
MA < 1
3rd class lever
Formula for MA
Length of effort arm/length of load arm
What amplifies force and does not amplify speed
Effort/load = MA > 1
What amplifies speed and does not amplify force
Effort/load = MA < 1
How is power transformed?
Power is transformed by a lever to amplify either force or speed
Where is effort exerted?
Effort (force) is where the muscle attaches
What levers are arm extension and flexion?
1st and 3rd class levers
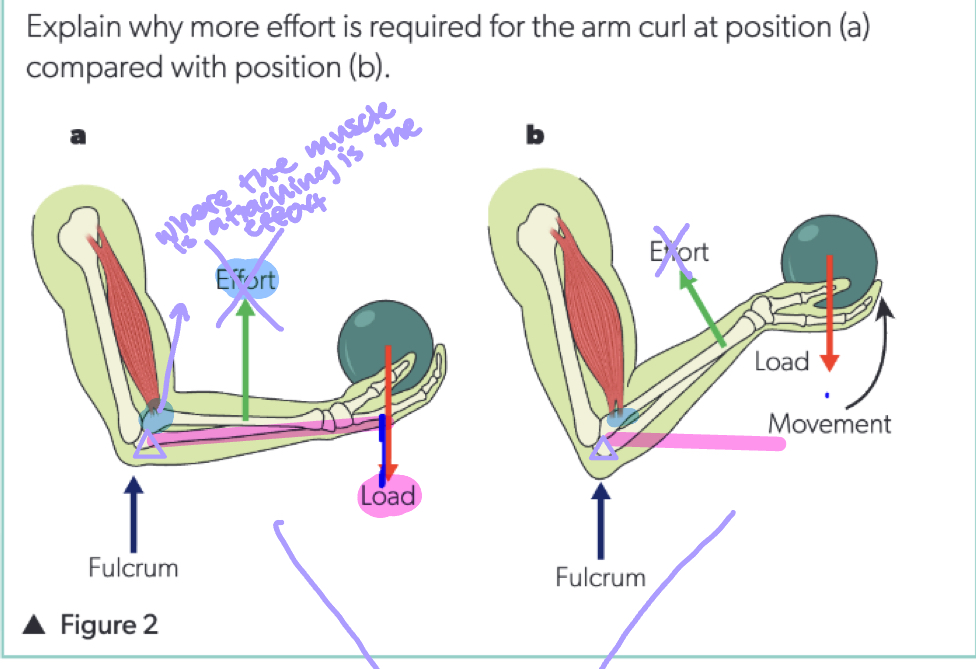
Explain why more effort is required for the arm curl at position (a) compared with position (b).
Load arms are both shortening, but position (b) is shortening more, in position (a) there is a smaller MA because there is a longer load arm
A. Explain why an athlete with shorter arms has an advantage compared with an athlete with longer arms when performing the dumbbell exercise in weightlifting.
B. Explain why an athlete with longer arms has an advantage compared with an athlete with shorter arms when throwing the discus.
A. An athlete with shorter arms means that they have a shorter load arms, that means there’s a greater MA, so less effort is required.
B. An athlete with longer arms, has a longer lever, this will increase how far the discus will go, so with this, the athlete can exert more force at the end of the lever.
When you flex your knee, where are the fulcrum and load? Where is the muscle that provides the effort located?
Fulcrum: knee joint
Load: foot and lower leg
Effort: hamstring muscles