Human Anatomy Structures, Systems, and Motions
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of the body—what it’s made of, where things are, and how they’re arranged.
Physiology
The study of function—how biological structures work and what they do.
Levels of Organization
Biological organization spans from atoms to organ systems.
Respiratory System
One of the 11 systems of the body, responsible for the exchange of gases.
Digestive System
One of the 11 systems of the body, responsible for processing food and extracting nutrients.
Urinary System
One of the 11 systems of the body, responsible for waste removal and regulating water balance.
Reproductive System
One of the 11 systems responsible for producing offspring.
Endocrine System
One of the 11 systems that controls bodily functions through hormones.
Lymphatic/Immune System
One of the 11 systems that helps in defending the body against pathogens.
Integumentary System
One of the 11 systems that includes the skin and its derivatives.
Skeletal System
One of the 11 systems that provides structure and support to the body.
Muscular System
One of the 11 systems that enables movement through muscle contraction.
Cardiovascular System
One of the 11 systems responsible for transporting blood and nutrients throughout the body.
Nervous System
The body system responsible for sending signals between different parts of the body.
Body Cavities
Spaces within the body that house and protect internal organs.
Cranial Cavity
The space within the skull that contains the brain.
Vertebral Cavity
The space that houses the spinal cord.
Thoracic Cavity
The cavity within the chest that contains the heart and lungs.
Abdominal Cavity
The cavity that contains digestive organs.
Pelvic Cavity
The cavity that contains reproductive organs and urinary bladder.
Diaphragm
A dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
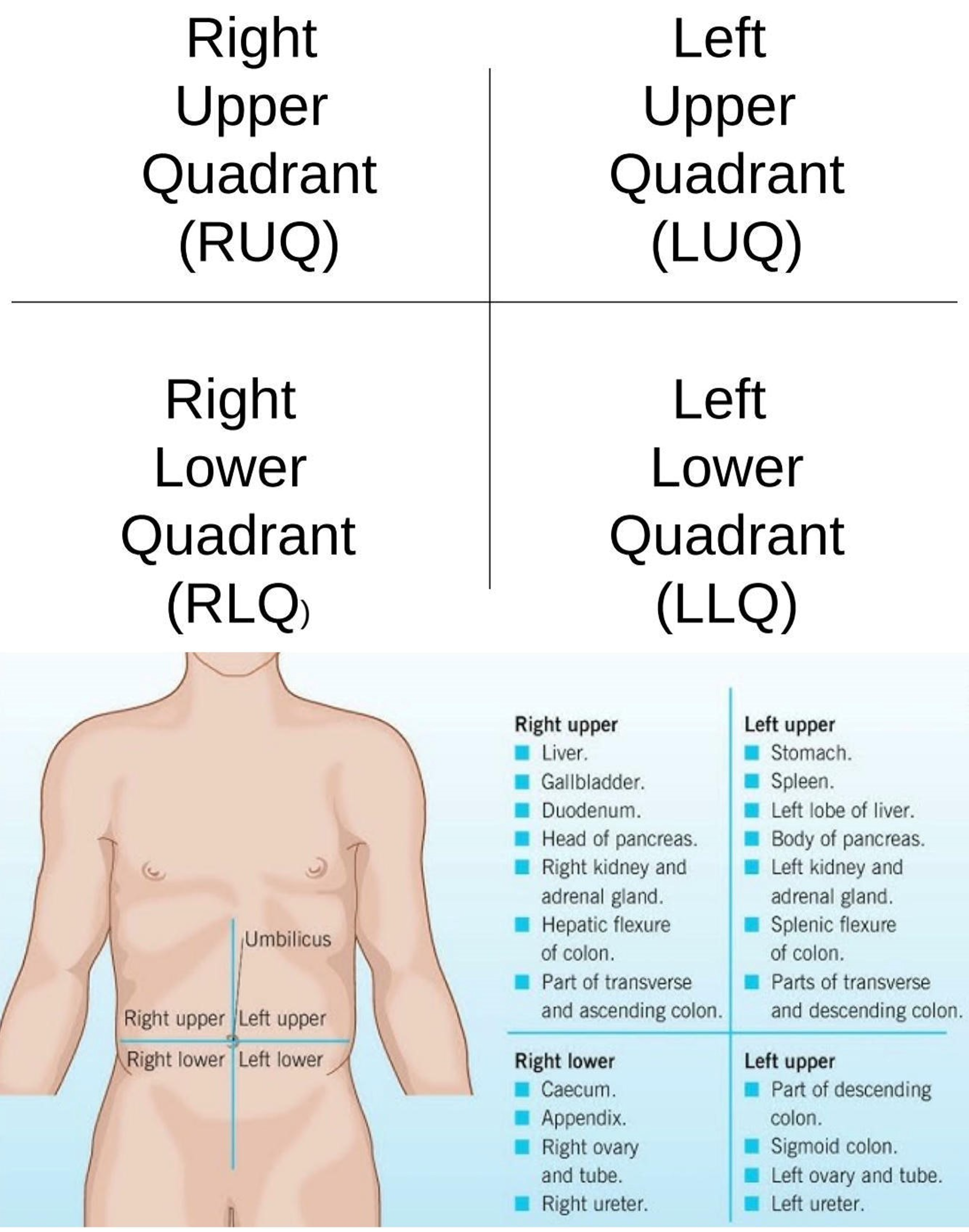
Right Hypochondriac Region
Upper right region of the abdominopelvic area.
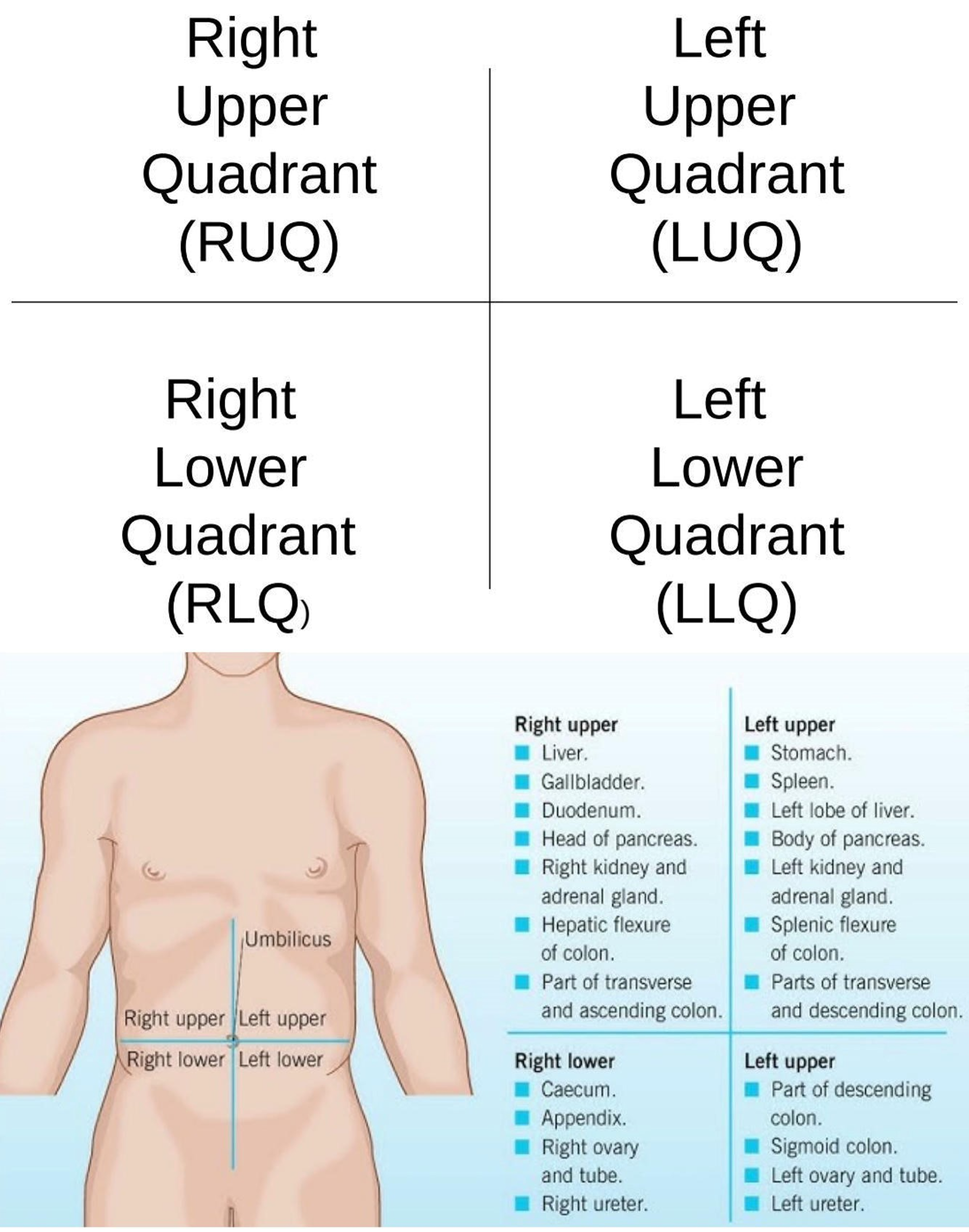
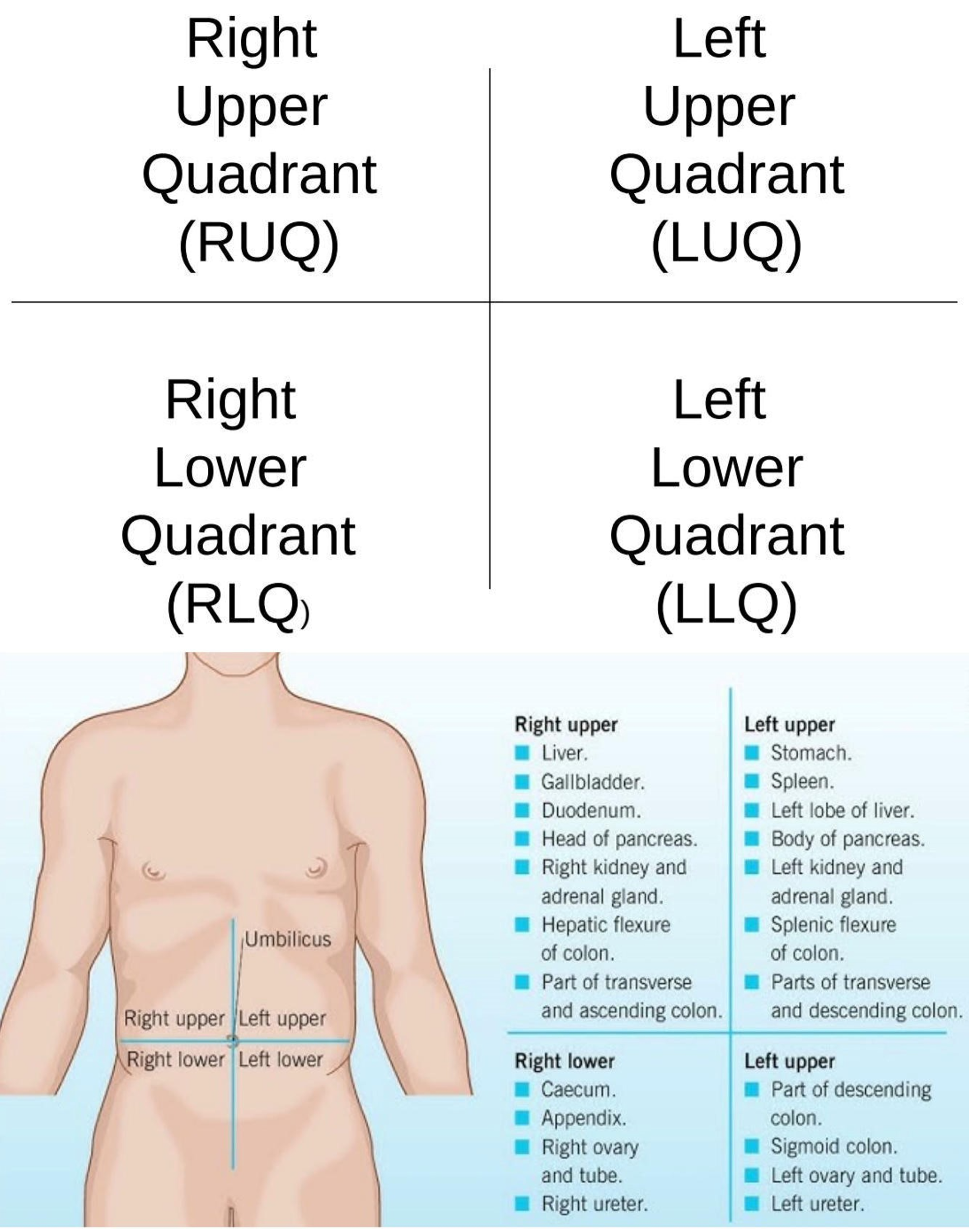
Epigastric Region
Upper center region of the abdominopelvic area.
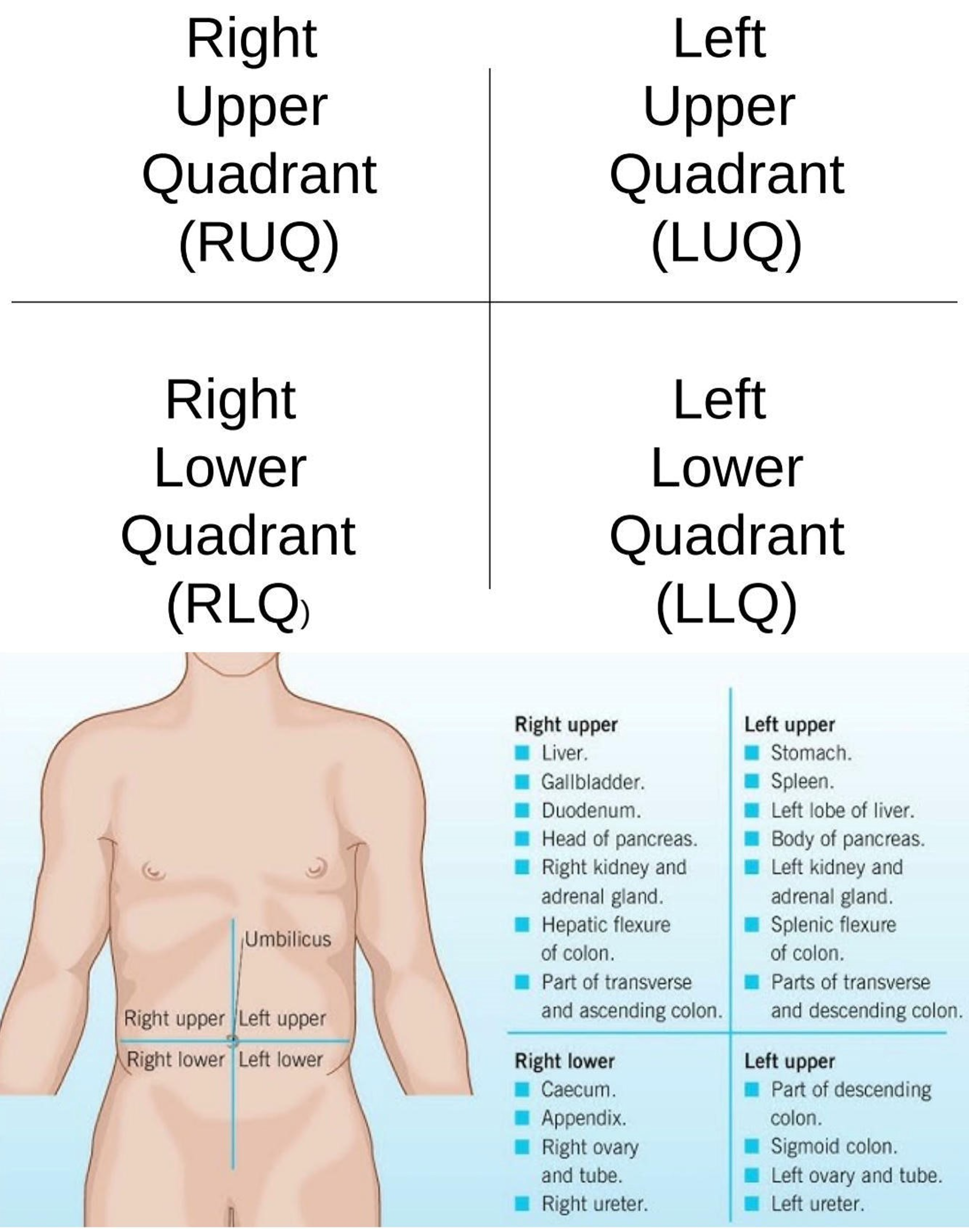
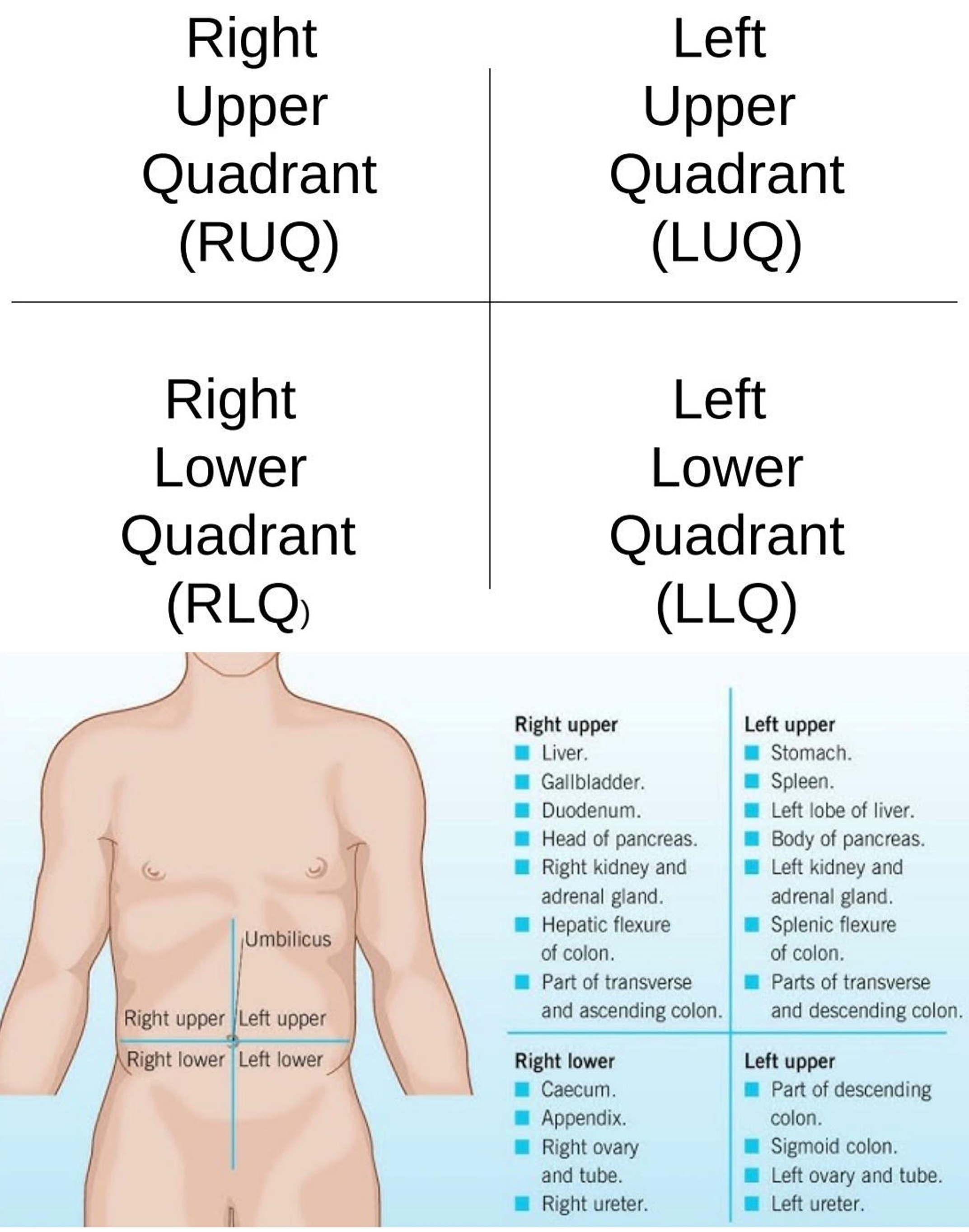
Left Hypochondriac Region
Upper left region of the abdominopelvic area.
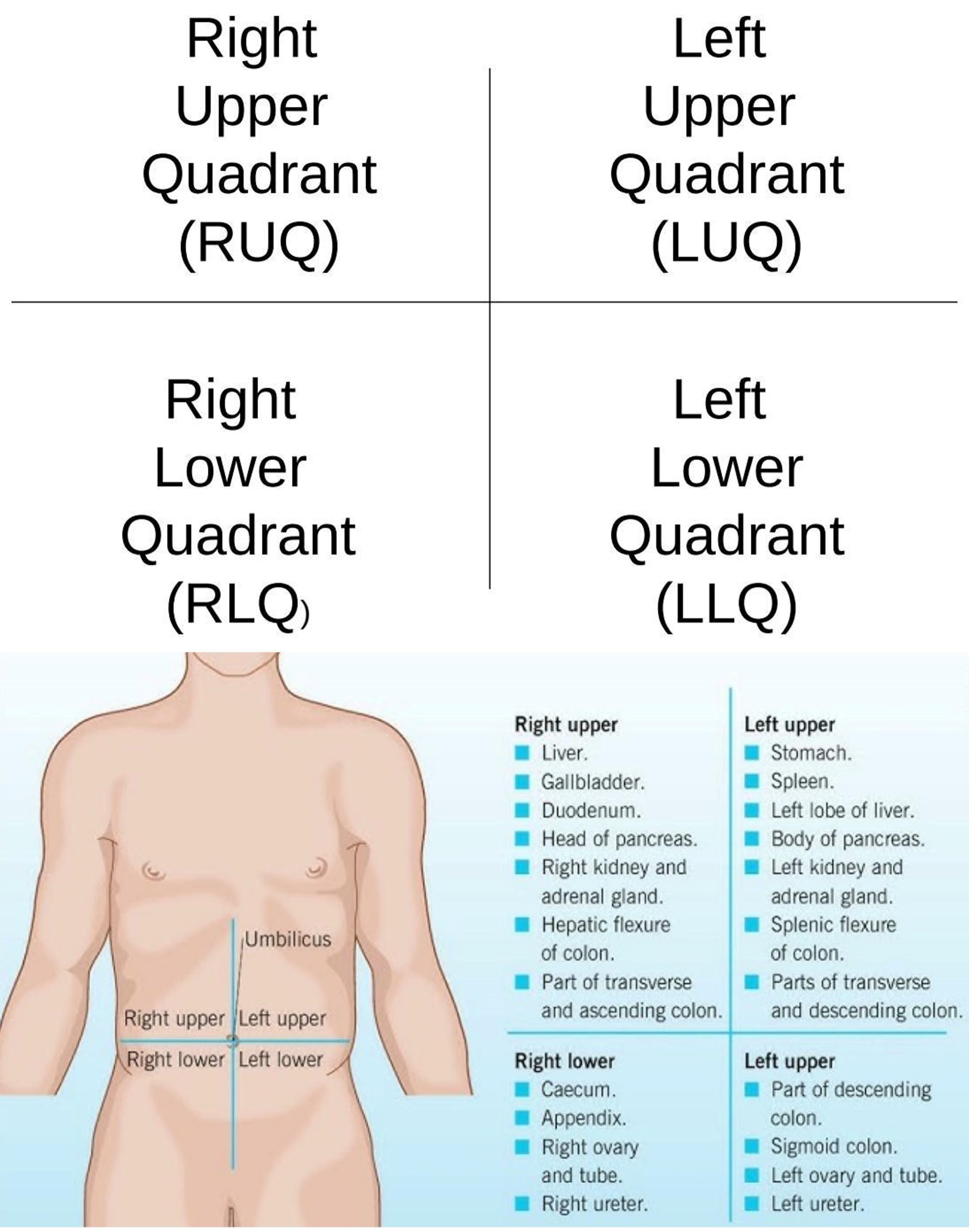
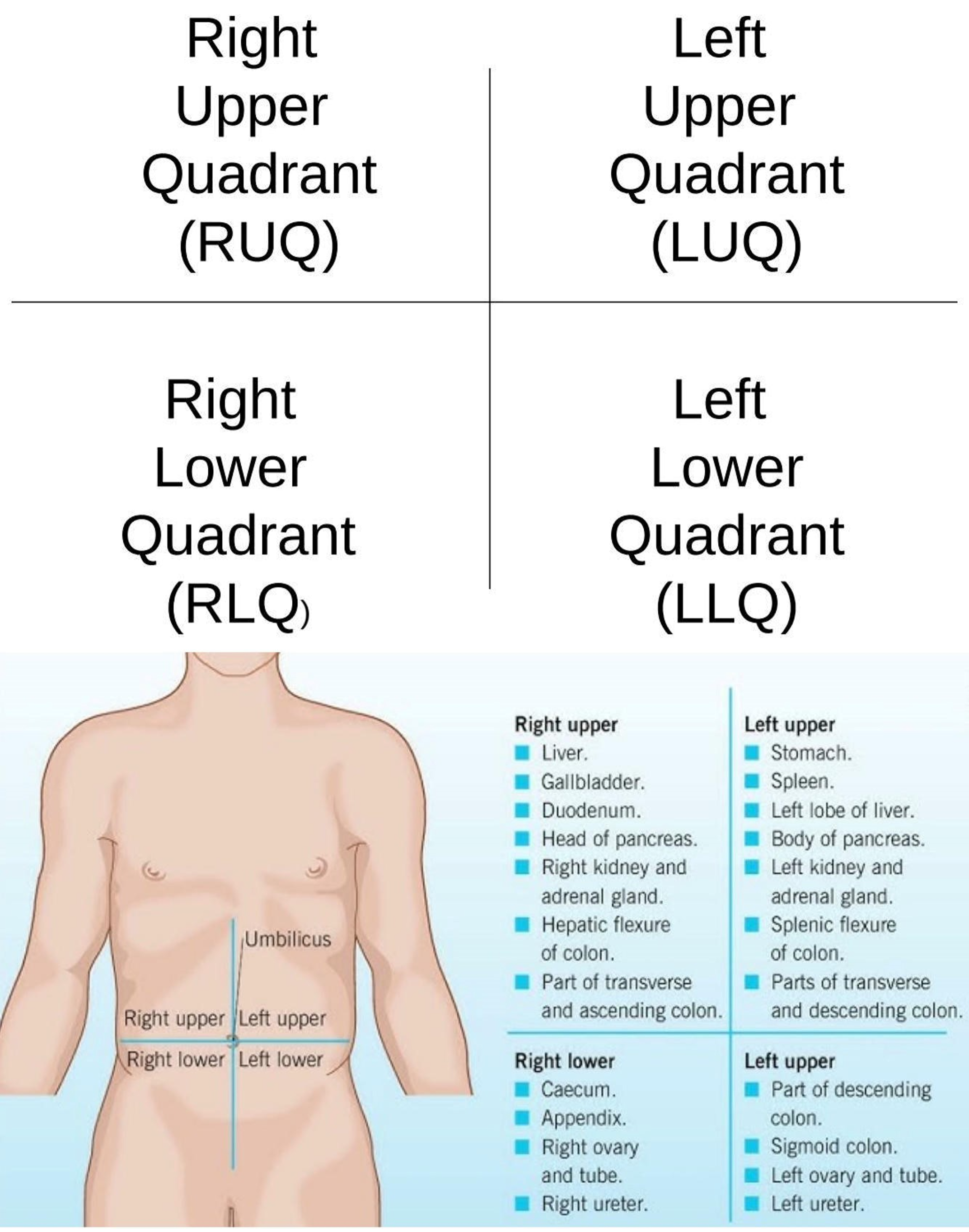
Right Lumbar Region
Middle right region of the abdominopelvic area.
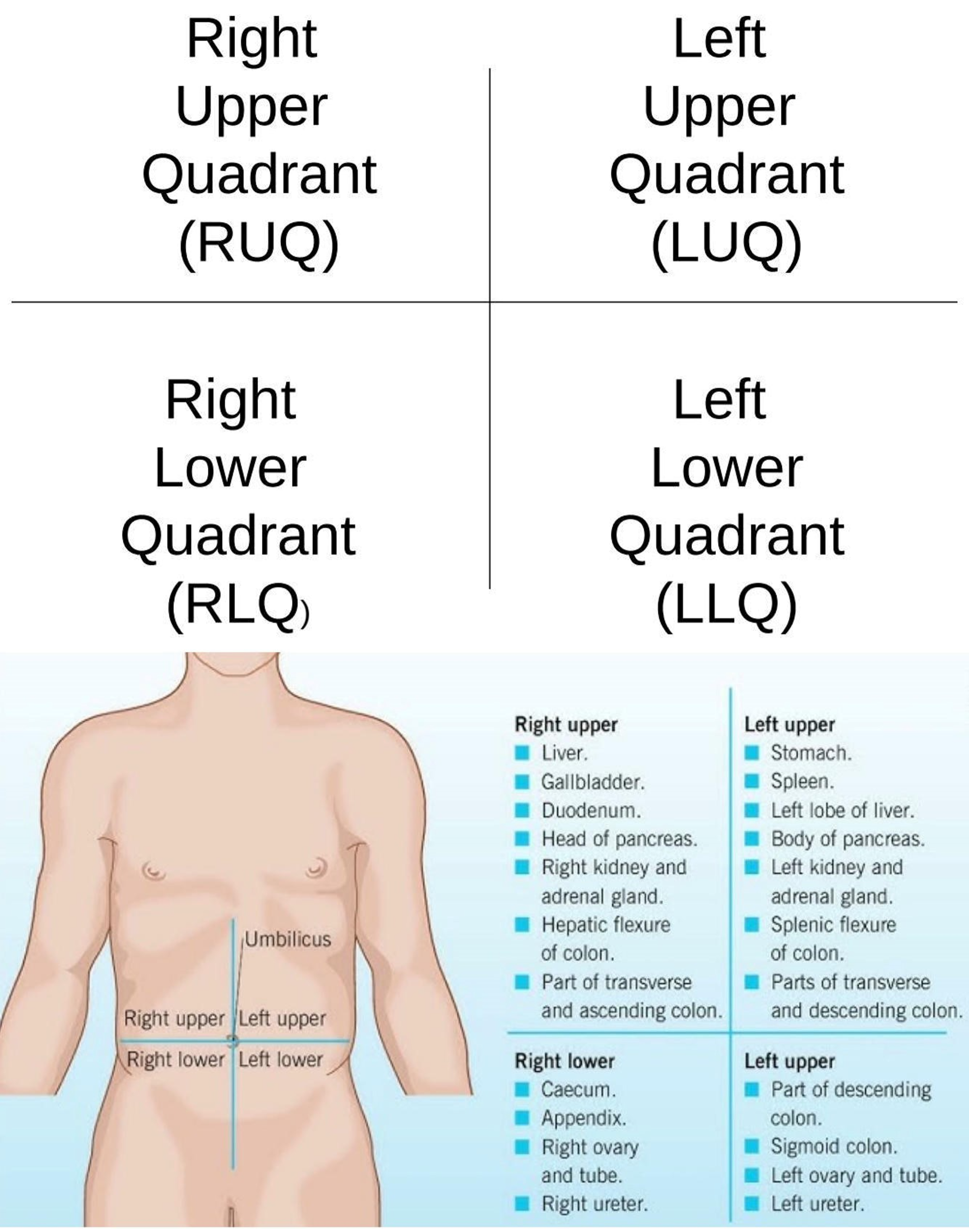
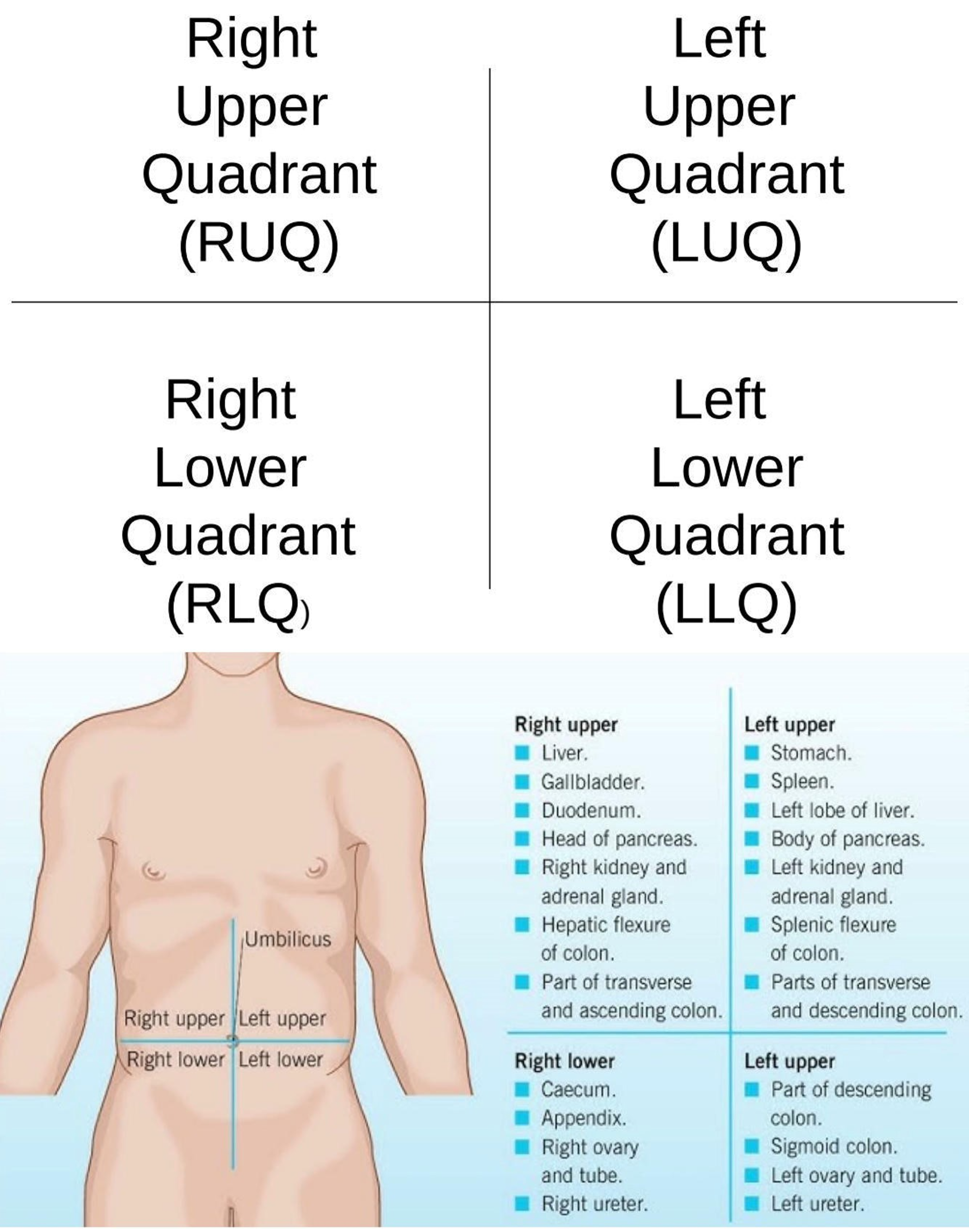
Umbilical Region
Center region of the abdominopelvic area.
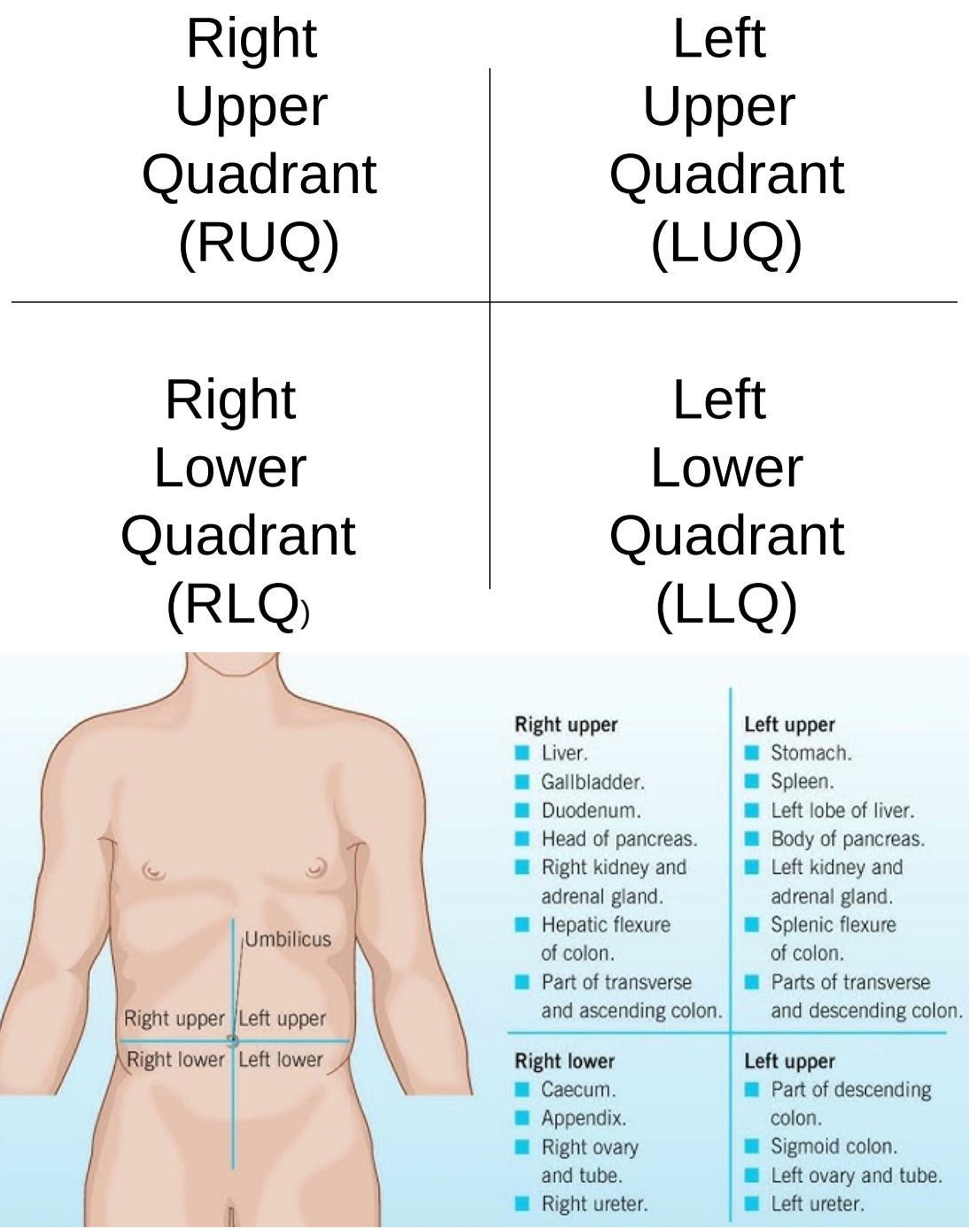
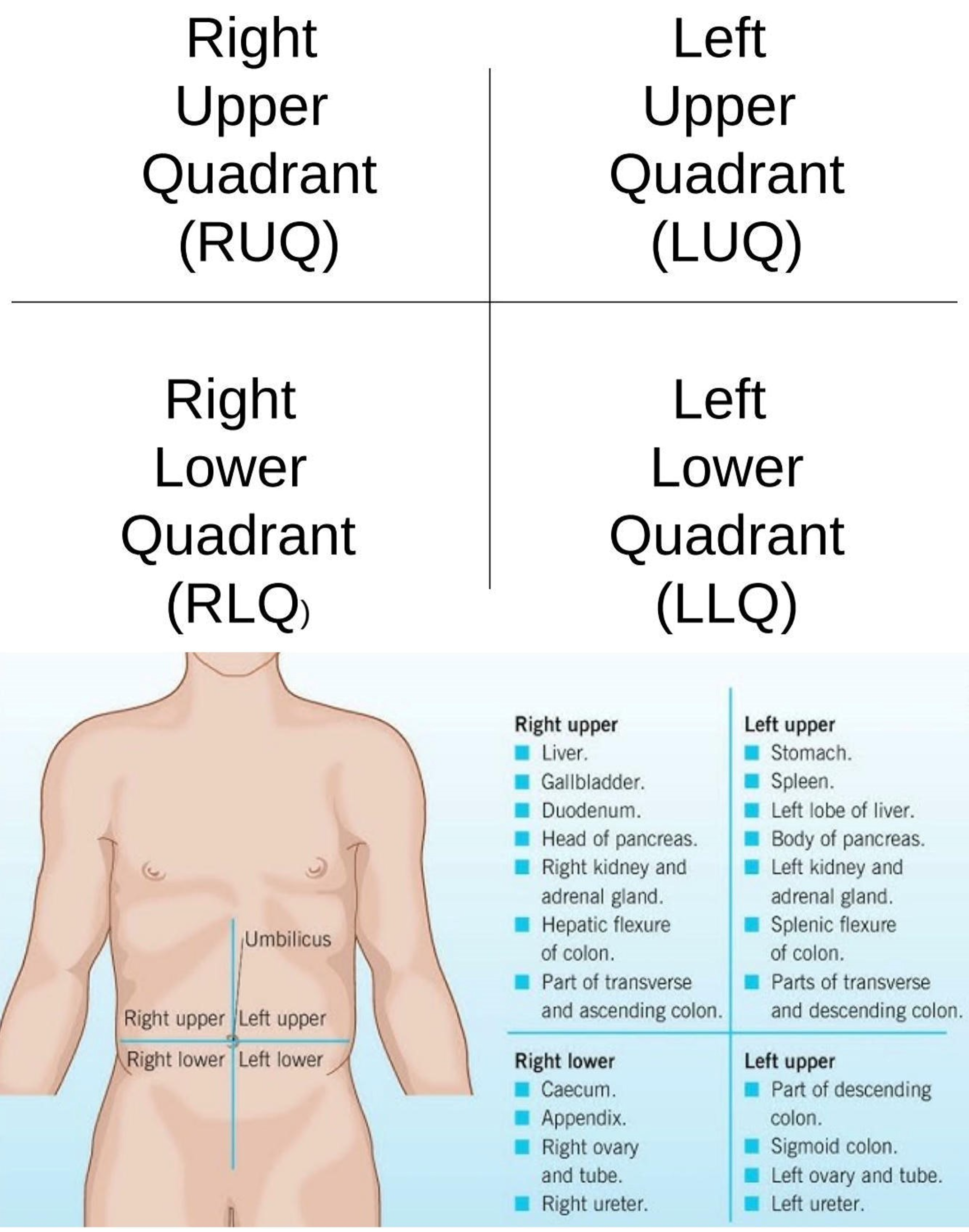
Left Lumbar Region
Middle left region of the abdominopelvic area.
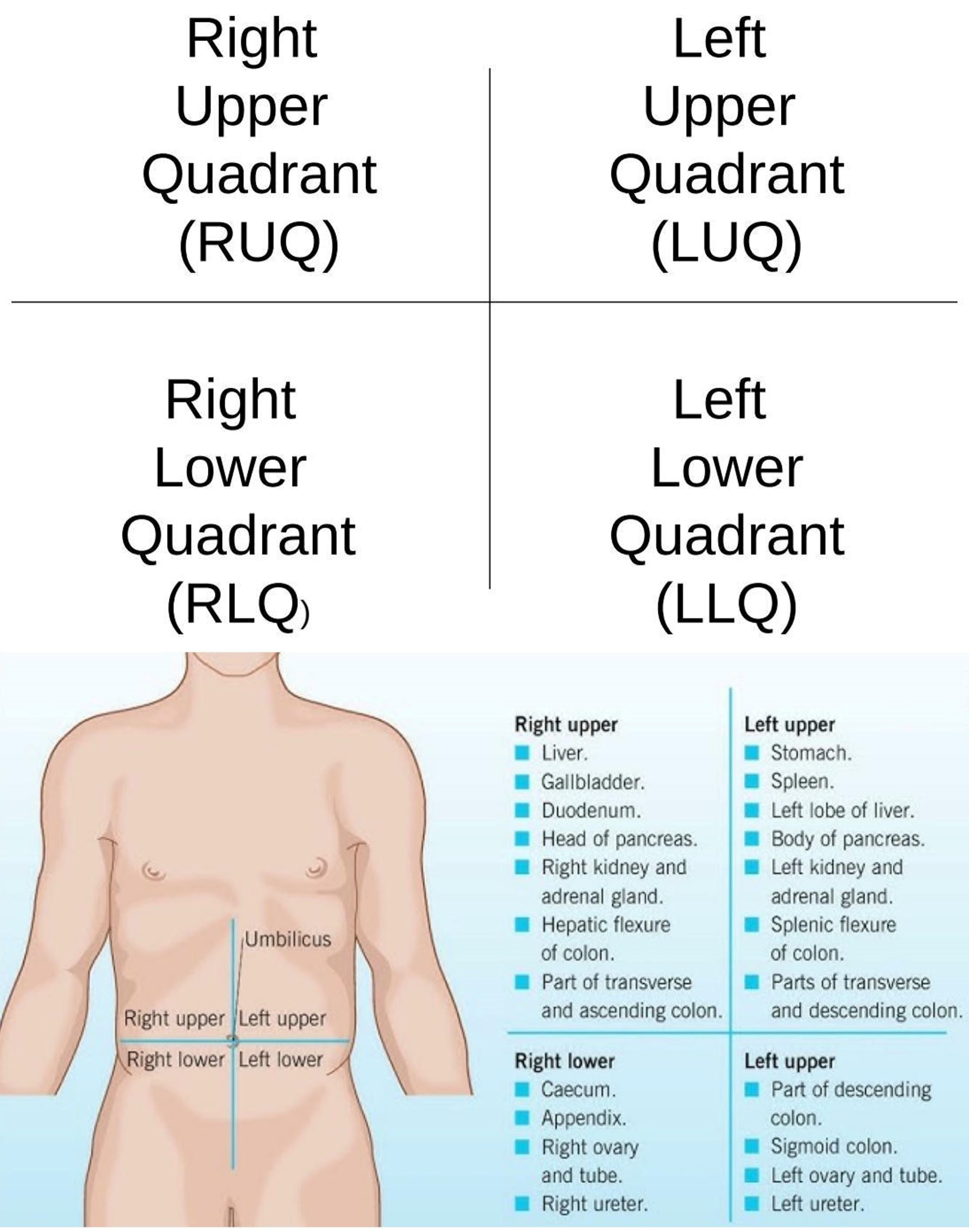
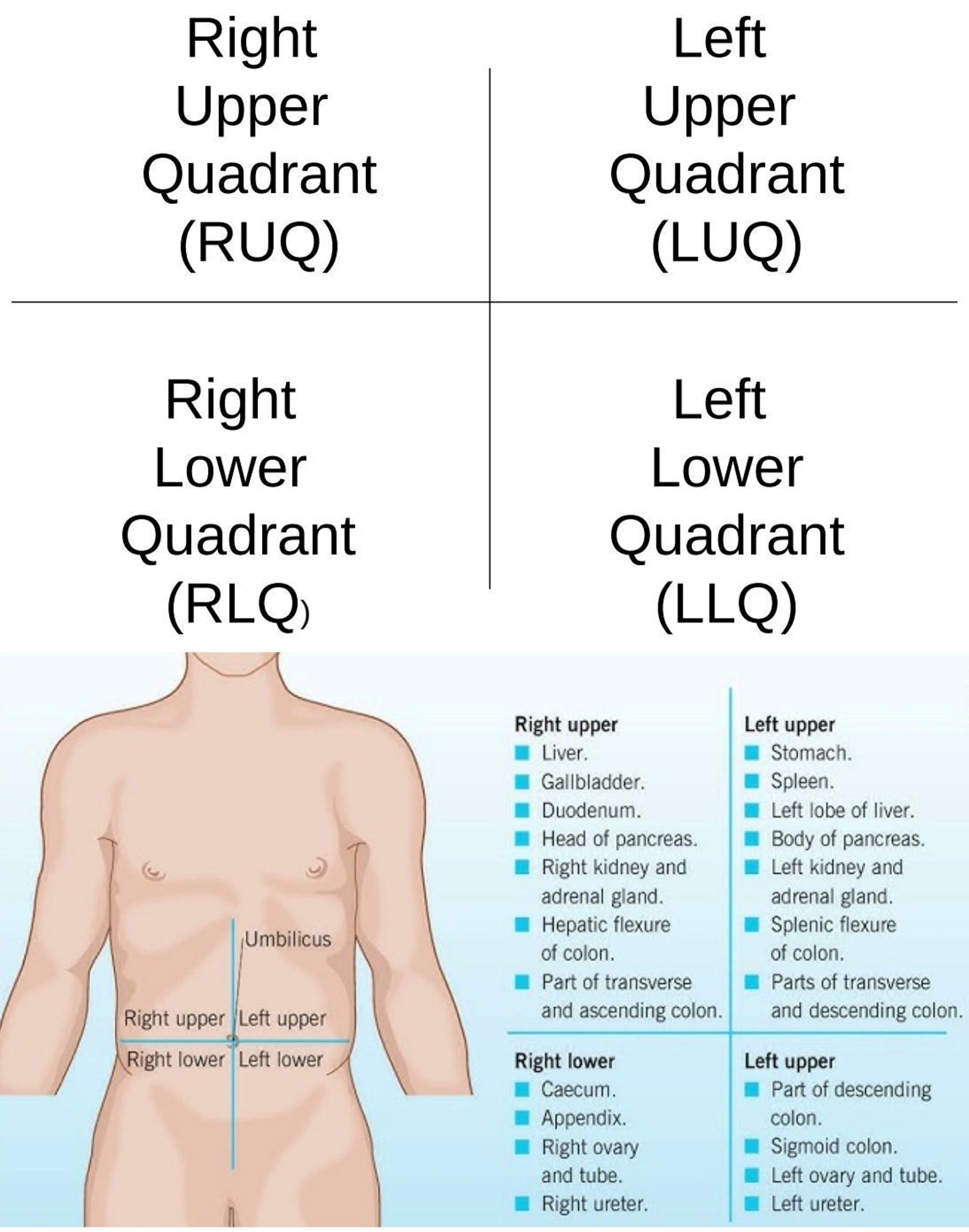
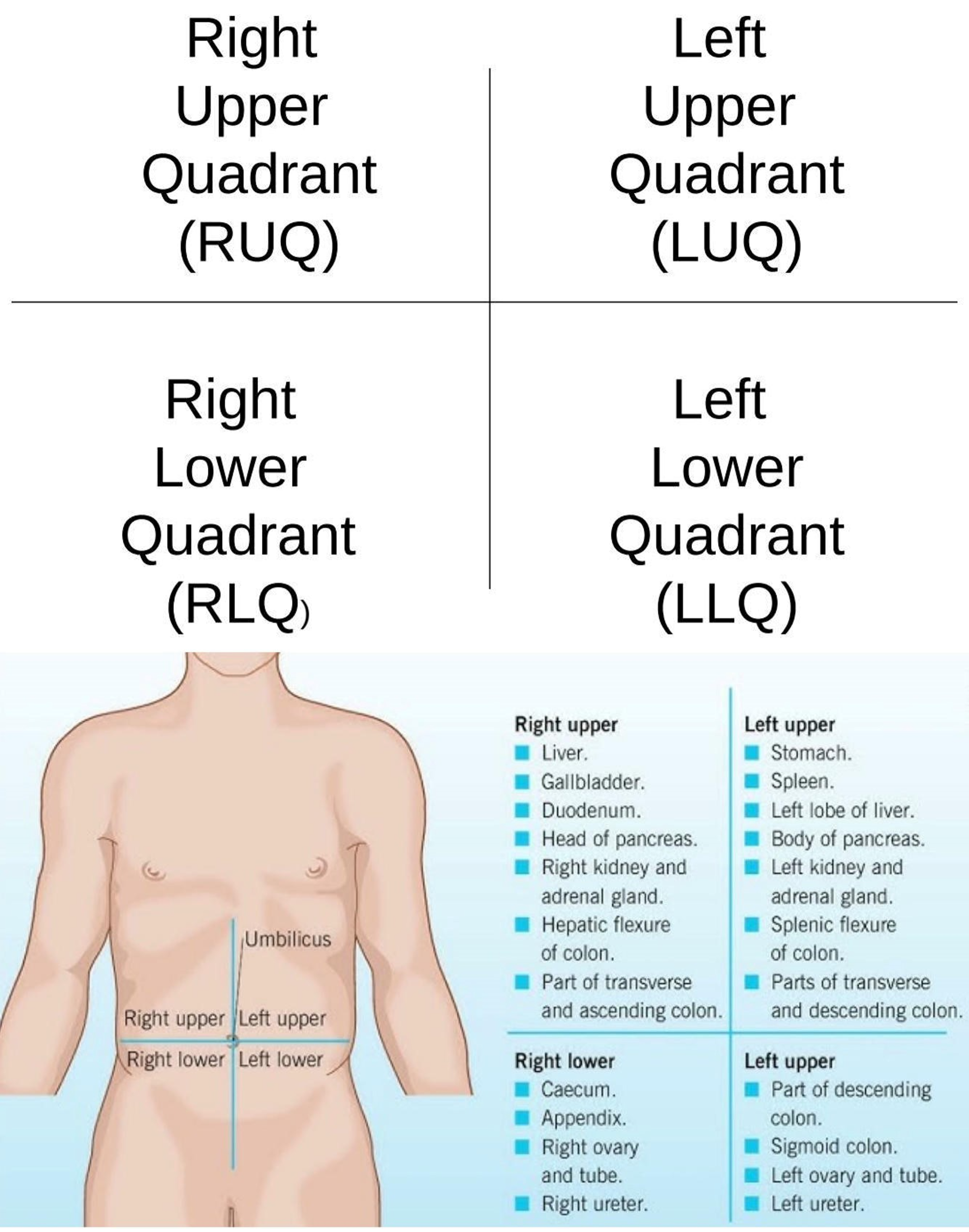
Right Iliac Region
Lower right region of the abdominopelvic area.
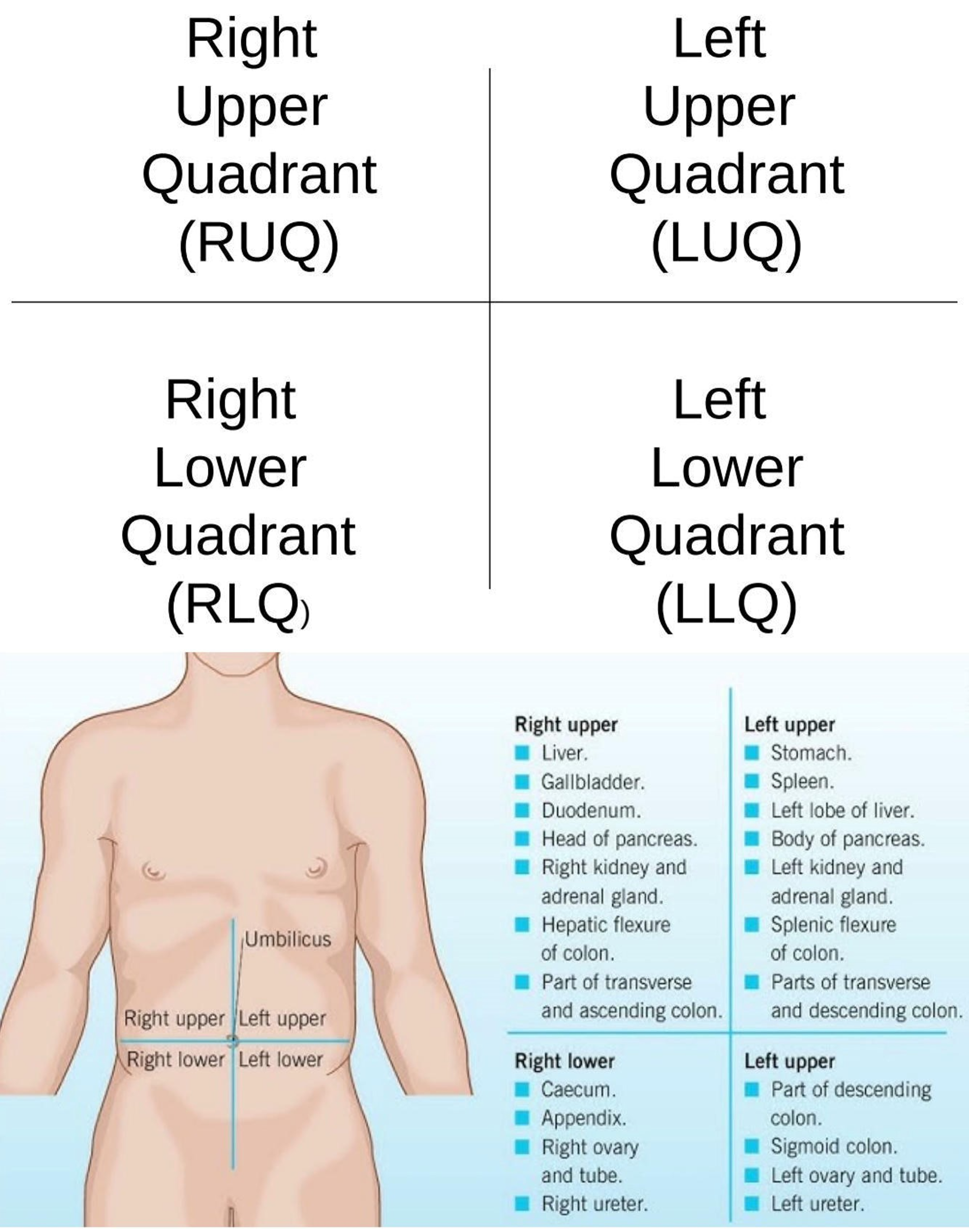
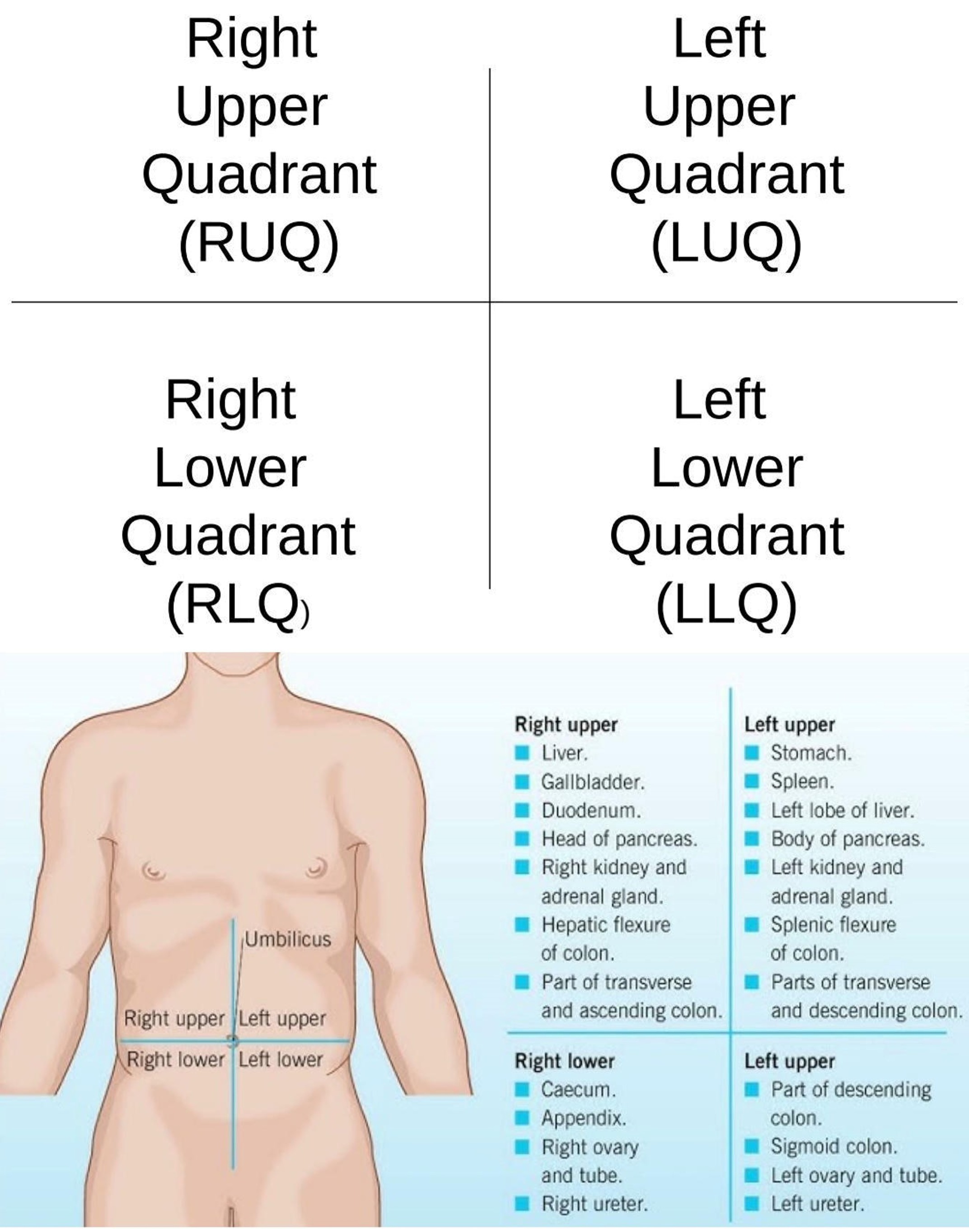
Hypogastric Region
Lower center region of the abdominopelvic area.
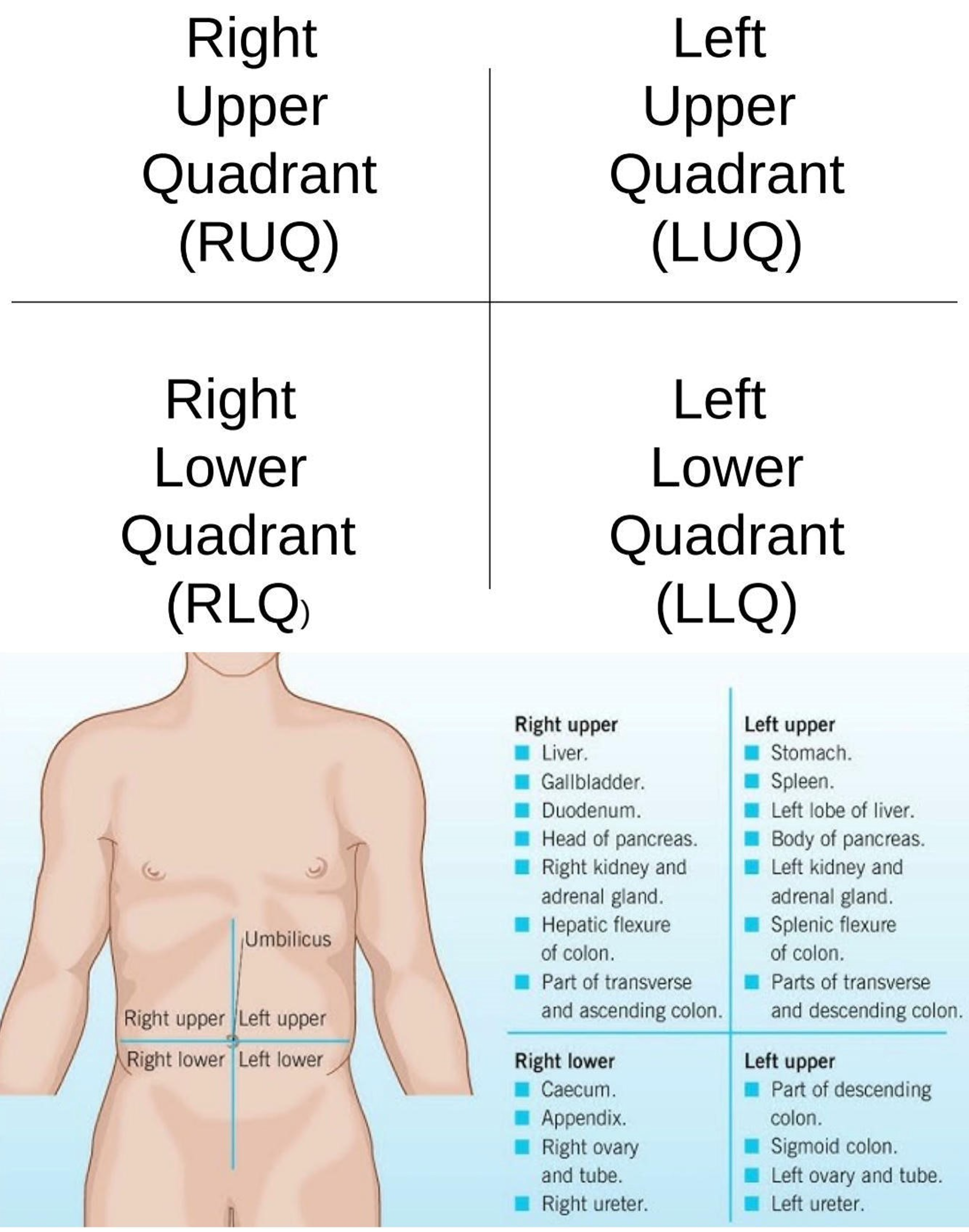
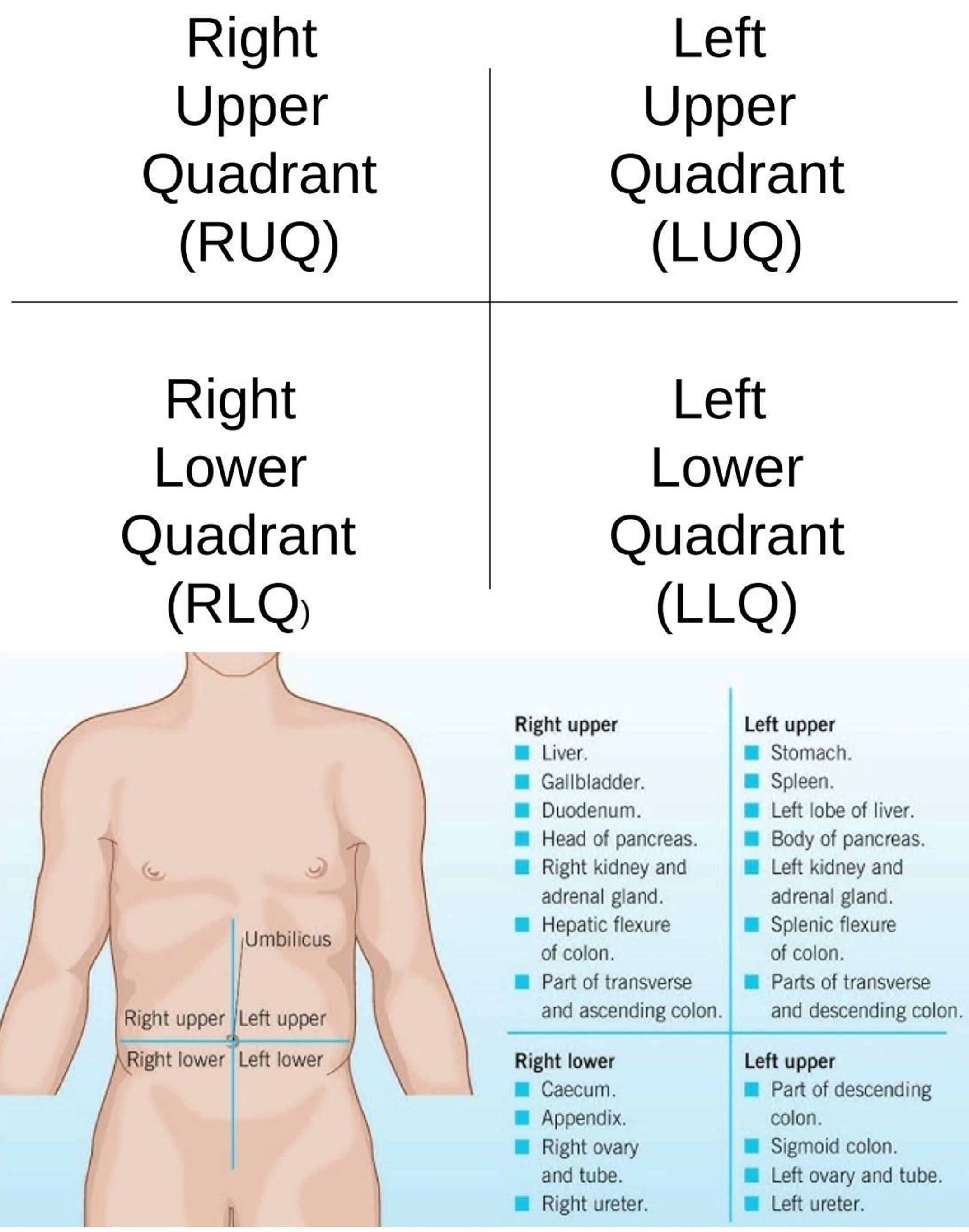
Left Iliac Region
Lower left region of the abdominopelvic area.
Anatomical Position
A standard position where the body is standing upright, facing forward, with palms forward.
Proximal
Closer to the trunk of the body.
Distal
Farther from the trunk of the body.
Medial
Closer to the midline of the body.
Lateral
Farther from the midline of the body.
Anterior
The front side of the body.
Posterior
The back side of the body.
Superior
Towards the head.
Inferior
Towards the feet.
Cranial (Directional)
Towards the head.
Caudal
Towards the tail.
Superficial
Closer to the surface of the body.
Deep
Farther from the surface of the body.
Plantar
Refers to the bottom of the foot.
Dorsal (Foot)
Refers to the top of the foot.
Palmar
Refers to the palm side of the hand.
Dorsal (Hand)
Refers to the back of the hand.
Ipsilateral
On the same side of the body.
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body.
Varus
A condition where the distal segment deviates toward the midline.
Valgus
A condition where the distal segment deviates away from the midline.
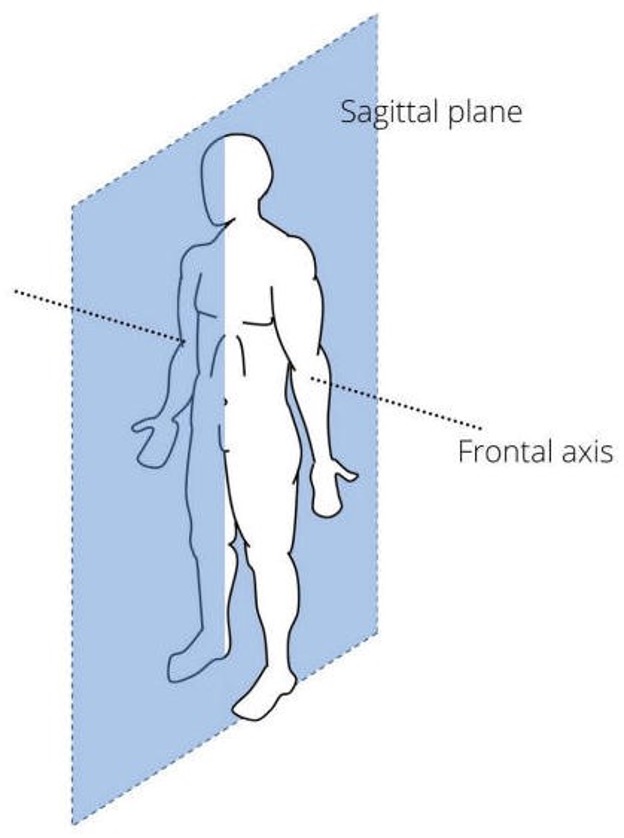
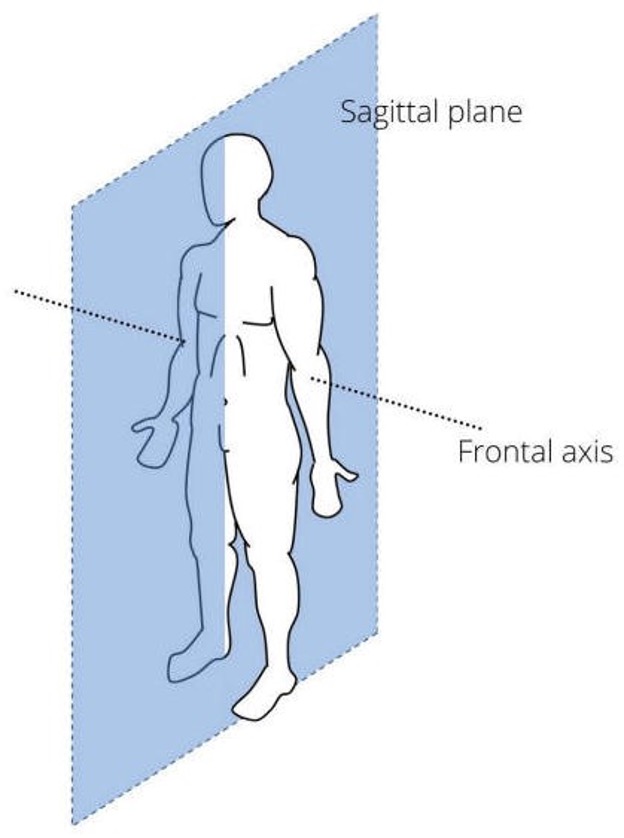
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body into left and right halves.
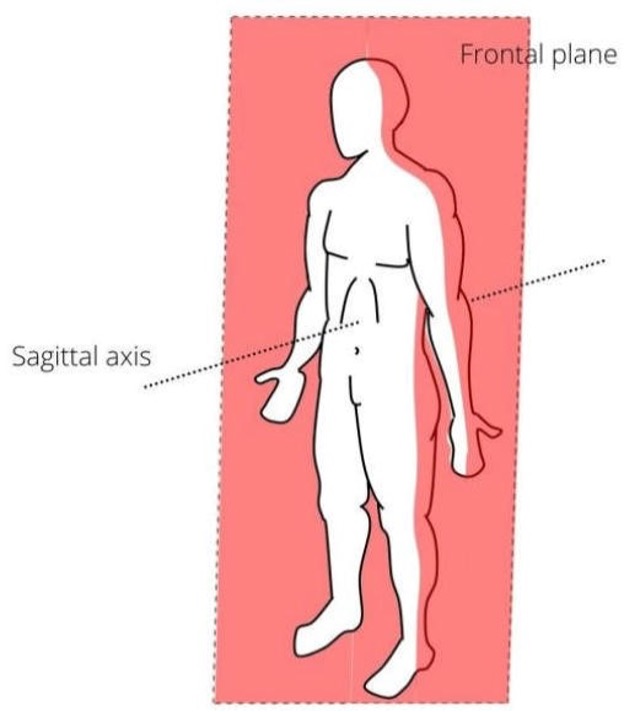
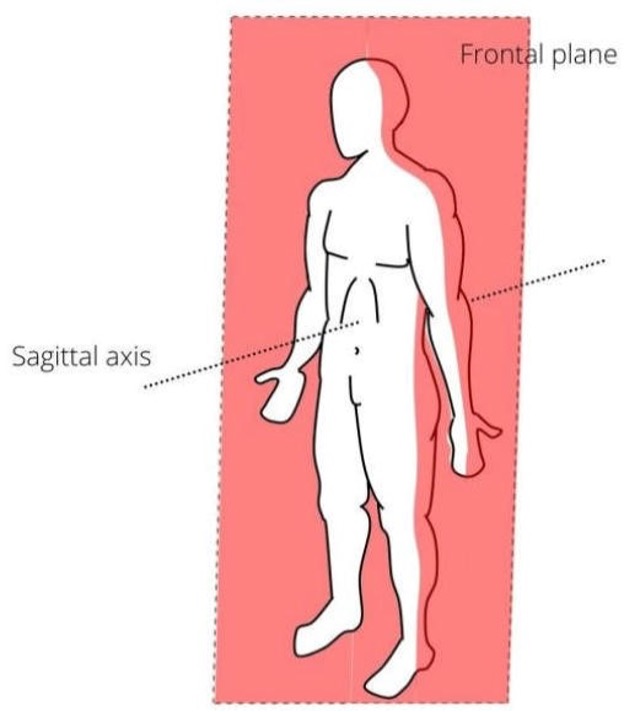
Frontal Plane
Divides the body into front and back halves.
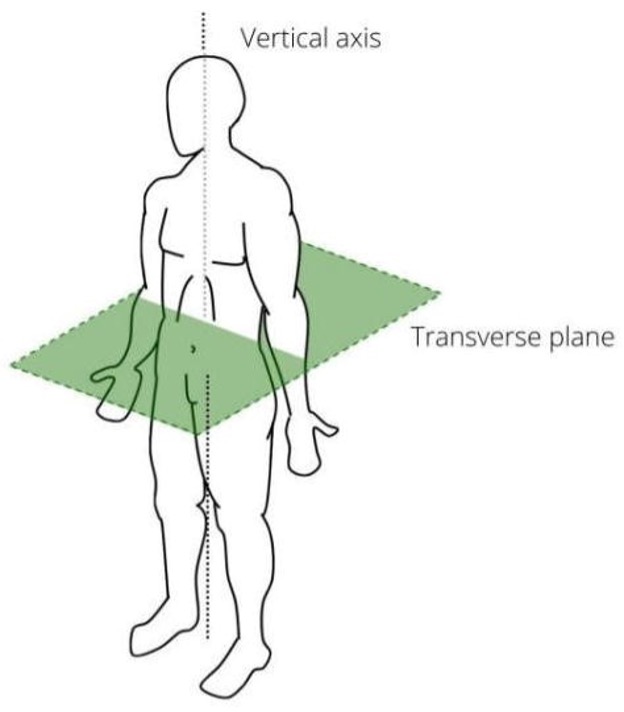
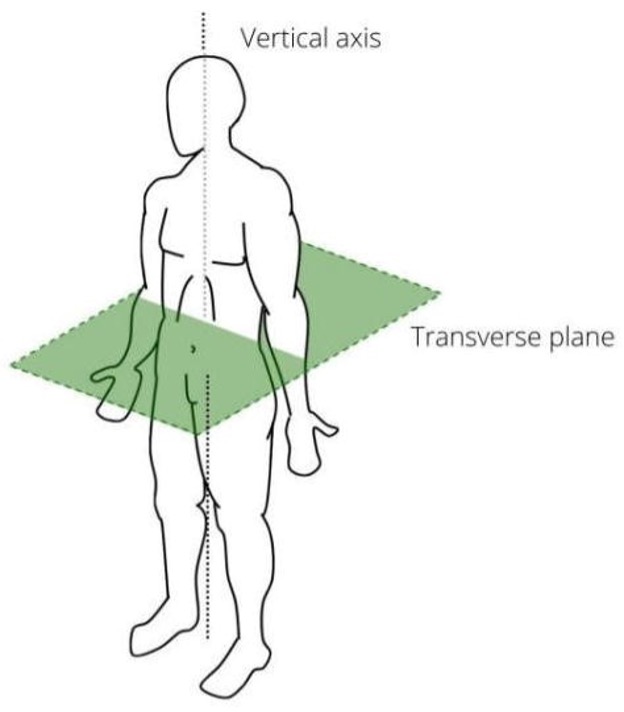
Transverse Plane
Divides the body into top and bottom halves.
Flexion
A movement that decreases the angle between body parts.
Extension
A movement that increases the angle between body parts.
Circumduction
A circular movement that combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.