Reconstruction Vocab( AICE US HISTORY)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms

10 Percent(%) Plan
A proposal by President Abraham Lincoln during the Civil War that allowed Southern states to rejoin the Union if 10% of their voters pledged allegiance to the Union and accepted the end of slavery.

Southern Black Codes
Laws passed in Southern states after the Civil War to restrict the rights and freedoms of newly freed African Americans.
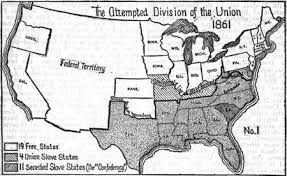
Wade Davis Bill
A Reconstruction plan requiring a majority of white males in Southern states to take a loyalty oath for readmission to the Union. Passed by Congress in 1864 but pocket-vetoed by Lincoln.

Freeman’s Bureau
A federal agency established in 1865 to assist freed slaves and poor whites in the South by providing food, housing, education, and medical care.

Civil Rights Act of 1866
Legislation aimed at protecting the civil rights of African Americans, granting them citizenship and equal protection under the law.

13th Amendment
Constitutional amendment that abolished slavery in the United States, ratified in December 1865.

14th Amendment
Constitutional amendment that granted citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the United States, including former slaves, and provided equal protection under the law, ratified in July 1868. It also aimed to prevent states from denying any person the rights of life, liberty, or property without due process.
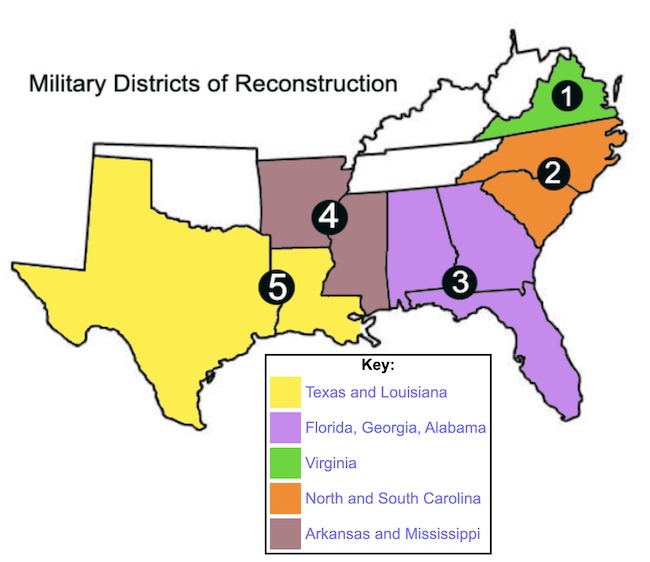
1867 Reconstruction Act
Legislation that divided the South into military districts and set conditions for readmission to the Union, including ratifying the 14th Amendment.

Tenure of Office Act
Legislation that restricted the president's power to remove certain officeholders without the Senate's approval, enacted in March 1867.

Impeachment trial of Andrew Johnson
A political process initiated by the House of Representatives against President Andrew Johnson in 1868, primarily over his violation of the Tenure of Office Act, which resulted in his acquittal by the Senate.

Credit Mobilier Scandal
A major political scandal involving the Union Pacific Railroad and Congress in the 1870s, where profits were skimmed from government contracts. It involved bribery and corruption among politicians and businessmen, leading to a significant loss of public trust in the government.

15th Amendment
Prohibits the federal and state governments from denying a citizen the right to vote based on "race, color, or previous condition of servitude." Ratified in 1870. This amendment aimed to secure voting rights for African American men following the Civil War.

Carpet Baggers
Northerners who moved to the South after the Civil War, often seeking economic opportunities and political power during Reconstruction. They were often perceived negatively by Southerners, seen as exploiting the region's post-war madness for personal gain.

Scalawags
Southern whites who supported Reconstruction and the Republican Party, often viewed as traitors by other Southerners. They sought to promote economic recovery and social change in the South after the Civil War. They were often former Whigs or individuals who opposed the Democratic Party's dominance in the South.

Ku Klux Klan
A secret society formed in the South during Reconstruction that used terror and violence to intimidate African Americans and their allies, aiming to restore white supremacy.

The Compromise of 1877
An agreement that resolved the disputed 1876 presidential election, resulting in the withdrawal of federal troops from the South and effectively ending Reconstruction. It also included concessions to Southern Democrats, such as promises for economic support and the appointment of a Democrat to the cabinet.

Seward’s Folly
The purchase of Alaska from Russia in 1867, which was initially criticized as a foolish investment but later proved valuable due to its natural resources. This acquisition was orchestrated by Secretary of State William H. Seward, and it significantly expanded U.S. territory.