Calvin-Zyklus (lichtunabhängige Reaktion)
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Calvin-Zyklus Definition
beschreibt die Sekundärreaktion der Fotosynthese
hierbei wird Glucose mithilfe der Produkte der Primärreaktion (ATP und NADPH +H+ ) und aufgenommenen CO2 synthesiert
Nebenprodukte
die dabei entstehenden Nebenprodukte NADP+ und ADP+Pi dienen wiederum als Edukte der Primärreaktion
Ort
Stroma der Chloroplasten
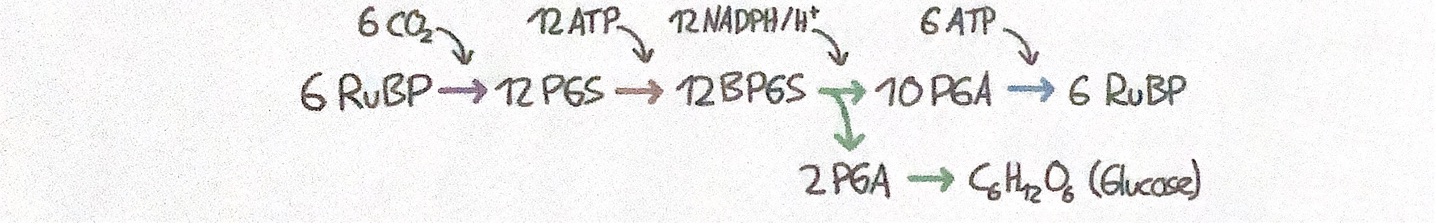
1.CO2-Fixierung (Carboxylierung)
durch das Enzym RUBISCO (Ribulosebiposphat-Carboxylase-Oxygenase)
Aufnahme von 6 CO2 → 12 PGS
6 Ribulosebiphosphat (RuBP, C5-Körper) + 6 CO2 + 6 H2O →12 Phosphoglycerinsäure (PGS, C3-Körper)
2.Aktivierung
Entstandenes PGS wird durch ATP zu BPGS aktiviert und auf Reduktion vorbereitet
12 PGS + 12 ATP → 12 Biphosphatglycerinsäure + 12 ADP (BPGS, C3- Körper)
3.Reduktion und Zuckersynthese
BPGS wird durch NADPH + H+ reduziert
Dadurch Erhöhung des Energieniveaus auf das von Glucose
Anschließend Zuckersynthese 2 PGS → Glucose
12 BPGS + 12 NADPH/H+ → 12 Phosphoglycerinaldehyd + 12 NADP+ + RPi+ 12 H2O PGA, C3- Körper
4.Regeneration
die 10 verbleibenden PGA (C3) werden unter Aufwendung von 6 ATP zu 6 RuBP (C5) in Komplexer Abfolge von Reaktionen regeneriert
Calvin-Zyklus beginnt erneut mit 6 RuBP
10 PGA + 6 ATP → 6 RuBP + 6 (ADP + Pi)
Übersicht und ergebnis der Sekundärreaktion
6CO2 + 12 NADPH/H+ + 18 ATP → C6H12O6 + 12 NADP+ + 18 (ADP+Pi) + 6 H2O
Gesamtsummengleichung der Fotosynthese
6CO2 + 12 H2O → C6H12O2 + 6O2 + 6H2O sekundär primär sekundär primär sekundär
Funktion der entstandenen Glucose
Kann
in form von Stärke (als Reserve) gespeichert
als Saccharose im Phloem transportiert
in Cellulose (Zellwand) umgewandelt
in Fructose (Nektar/Früchte) umgewandelt
in der Zellatmung verwendet
werden