IMH Exam 5 Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:50 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
1
New cards
Donor Selection - Malaria
* Deferrals:
* History of Malaria: 3 years
* Lived in endemic country: 3 years
* Travel to endemic area: 12 months
* ==(Update 3 months)==
* History of Malaria: 3 years
* Lived in endemic country: 3 years
* Travel to endemic area: 12 months
* ==(Update 3 months)==
2
New cards
Donor Selection - Babesiosis
* Deferrals:
* History of Babesiosis- indefinite deferral
* ==Update: 2 year==
* History of Babesiosis- indefinite deferral
* ==Update: 2 year==
3
New cards
Donor Selection - Chagas Disease
History of Chagas’ disease - indefinite deferral
4
New cards
Donor Selection - vCJD
Geographic deferrals ==removed (update)==
5
New cards
Donor Selection - CJD
* Deferrals:
* Pituitary-derived growth hormone, dura mater transplant, blood relatives with CJD - indefinite deferral
6
New cards
Donor Selection - Zika
* 4 week deferral
7
New cards
Donor Selection - Babesiosis
* Deferral: 2 years
8
New cards
12 month deferral
* Hepatitis B IgG
* Tattoo/piercing
* Exposure to blood
* Sexual contact with a person at high risk for HIV
* Imprisonment >72 hours
* Return from a malarial endemic area
* Post-blood transfusion
* Tattoo/piercing
* Exposure to blood
* Sexual contact with a person at high risk for HIV
* Imprisonment >72 hours
* Return from a malarial endemic area
* Post-blood transfusion
9
New cards
1 month deferral
* Accutane use
* Propecia use
* Propecia use
10
New cards
3 year deferral
* Malarial infection
11
New cards
48 hour deferral
* Aspirin and aspirin-containing drugs
12
New cards
Permanent deferral - Positive HBsAg
Human pituitary growth hormone injection
13
New cards
Permanent deferral - Positive HBc
Taken clotting factors
14
New cards
Permanent deferral - Positive HTLV
Sexual contact with anyone who used a needle to take illegal drugs
15
New cards
Permanent deferral - History of CJD
AIDS/ or HIV positive
16
New cards
Permanent deferral - History of Chagas’ or babesiosis
Males having sex with other males ==(Update: 3 months from last sexual contact)==
17
New cards
Permanent deferral
Had viral hepatitis
18
New cards
Donor criteria - minimum Hgb requirement
12\.5 g/dL
19
New cards
Donor criteria - minimum Hct requirement
38%
20
New cards
Donor criteria - Age
≥ 16 years of age
21
New cards
Donor criteria - Temperature
22
New cards
Donor criteria - Blood pressure
< 180/100
23
New cards
Donor criteria - Pulse
50-100 bpm
24
New cards
Donor criteria - Weight
110 lbs
25
New cards
Weight Exception - Autologous Donation
* Reduce amount of anticoagulant
* Reduce Volume Factor (A) = weight (lbs.)/ 110 lbs
* A x 63 mL = amount of anticoagulant needed (B)
* 63 mL – B = amount of anticoagulant removed
* A x 450 mL = amount of blood collected
* Example: 90 lb donor
* 90 lbs/110 lbs = 0.81 = A
* 0.81 x 63 mL = 51.5 mL (amount of anticoagulant needed)
* 63 mL – 51.5 mL = 11.5 (12) mL of anticoagulant removed
* 0.81 x 450 mL = 365 mL of blood collected
* Reduce Volume Factor (A) = weight (lbs.)/ 110 lbs
* A x 63 mL = amount of anticoagulant needed (B)
* 63 mL – B = amount of anticoagulant removed
* A x 450 mL = amount of blood collected
* Example: 90 lb donor
* 90 lbs/110 lbs = 0.81 = A
* 0.81 x 63 mL = 51.5 mL (amount of anticoagulant needed)
* 63 mL – 51.5 mL = 11.5 (12) mL of anticoagulant removed
* 0.81 x 450 mL = 365 mL of blood collected
26
New cards
Weight Exception - Autologous Donation
* Standard unit: 450 mL ± 45 mL
* Standard volume of anticoagulant: 63 mL
* Standard volume of anticoagulant: 63 mL
27
New cards
How often can you donate RBC’s?
8 weeks
28
New cards
How often can you donate Platelets/Granulocytes?
* 48 hours between donations
* No more than 2x a week or 24x/year
* 150,000/µL
* No more than 2x a week or 24x/year
* 150,000/µL
29
New cards
How often can you donate Plasma?
* Every 4 weeks
* Total protein-must be within normal limits (>6.0g/dL)
* Total protein-must be within normal limits (>6.0g/dL)
30
New cards
Anticoagulants - CPD and CP2D
Expiration: 21 days
31
New cards
Anticoagulants - CPDA-1
Expiration: 35 days
32
New cards
Anticoagulants - AS-I and AS-3
Expiration: 42 days
33
New cards
Preservatives - Dextrose
Supports RBC life
34
New cards
Preservatives - Adenine
Used in ATP synthesis; restores ATP
35
New cards
Preservatives - Citrate
Chelates calcium to prevent coagulation
36
New cards
Preservatives - Sodium biphosphate
Buffer to prevent decrease in pH
37
New cards
Storage Effects - Increases
Metabolic end products (K+, H+)
38
New cards
Storage Effects - Decreases
* ATP
* 2,3 DPG
* pH
* 2,3 DPG
* pH
39
New cards
PRBC
* Storage: 1-6°C
* Expires: 42 days
* Expires: 42 days
40
New cards
Frozen RBC
* Storage: ≤ -65°C
* Expires: 10 years
* Expires: 10 years
41
New cards
RBC deglycerolized
* Storage: 1-6°C
* Expires: 24 hours
* Expires: 24 hours
42
New cards
RBC irradiated
* Storage: 1-6°C
* Expires: 28 days or originally assigned expiration date - whichever comes first
* Expires: 28 days or originally assigned expiration date - whichever comes first
43
New cards
Platelets
* Storage: 20-24°C, agitated
* Expires: 5 days
* Expires: 5 days
44
New cards
Platelets (pooled)
* Storage: 20-24°C, agitated
* Expires: 4 hours
* Expires: 4 hours
45
New cards
Plateletpheresis
* Storage: 20-24°C, agitated
* Expires: 24-48 hours
* Expires: 24-48 hours
46
New cards
fresh frozen plasma (FFP)
* Storage: ≤ -18°C
* Expires: 1 year
* Expires: 1 year
47
New cards
thawed FFP
* Storage: 1-6°C
* Expires: 24 hours
* Expires: 24 hours
48
New cards
Cryoprecipitate
* Storage: ≤ -18°C
* Expires: 12 months
* Expires: 12 months
49
New cards
Granulocytes
* Storage: 20-24°C
* Expires: 24 hours
* Expires: 24 hours
50
New cards
Irradiated unit
* Unit drawn today: 4/21/2023
* Adsol: 6/2/2023
* Irradiate: 5/19/2023
* Adsol: 6/2/2023
* Irradiate: 5/19/2023
51
New cards
Platelet Refractoriness
* CCI = (Post transfusion - Pretransfusion plt count) x 10^11 x BSA / # of plts transfused (multiples of 10^11)
* ==CCI < 7500 after 1 hour = Refractory==
* ==CCI > 10,000/µL per m^2 10 min- 1 hour = Normal==
* ==CCI < 7500 after 1 hour = Refractory==
* ==CCI > 10,000/µL per m^2 10 min- 1 hour = Normal==
52
New cards
Refractoriness
* Patient BSA = 1.5 M^2
* Precount: 2000/μL
* Postcount: 29000/μL
* Platelets transfused: 4.5 x 10^11
* CCI = (29000 - 2000) x 10^11 x 1.5 / 4.5 x 10^11 = 9000
\
* Precount: 2000/μL
* Postcount: 29000/μL
* Platelets transfused: 4.5 x 10^11
* CCI = (29000 - 2000) x 10^11 x 1.5 / 4.5 x 10^11 = 9000
\
53
New cards
Refractoriness
* Patient BSA = 1.5 M^2
* Precount: 2000/μL
* Postcount: 29000/μL
* 6 random donor units transfused
* CCI = (29000 - 2000) x 10^11 x 1.5 / 6 x (0.55 x 10^11) = 12,272
* RDP = 5.5 x 10^10 = 0.55 x 10^11
* Precount: 2000/μL
* Postcount: 29000/μL
* 6 random donor units transfused
* CCI = (29000 - 2000) x 10^11 x 1.5 / 6 x (0.55 x 10^11) = 12,272
* RDP = 5.5 x 10^10 = 0.55 x 10^11
54
New cards
Refractoriness
* Patient BSA = 1.5 M^2
* Precount: 2000/μL
* Postcount: 29000/μL
* Apheresis platelet
* CCI = (29000 - 2000) x 10^11 x 1.5 / 3 x 10^11 = 13,500
* Precount: 2000/μL
* Postcount: 29000/μL
* Apheresis platelet
* CCI = (29000 - 2000) x 10^11 x 1.5 / 3 x 10^11 = 13,500
55
New cards
Bacterial Contamination Testing
* None of the methods listed are sensitive enough to detect bacteria directly after donation
* Most common methods (FDA approved methods)
* BacT/ALERT culture system (bioMerieux)
* Pall eBDS system (Pall Corp)
* ScanSystem (Hemosystem)
* Most common methods (FDA approved methods)
* BacT/ALERT culture system (bioMerieux)
* Pall eBDS system (Pall Corp)
* ScanSystem (Hemosystem)
56
New cards
Transport Temperatures
* PRBC: 1-10°C with ice in plastic bags
* Frozen components: transported with dry ice
* Frozen components: transported with dry ice
57
New cards
Apheresis - Centrifugation
* separation of blood components; removal of desired components and return of remainder of the blood to donor
* Plasma: 55% of total blood
* Buffy coat: leukocytes and platelets;
* Plasma: 55% of total blood
* Buffy coat: leukocytes and platelets;
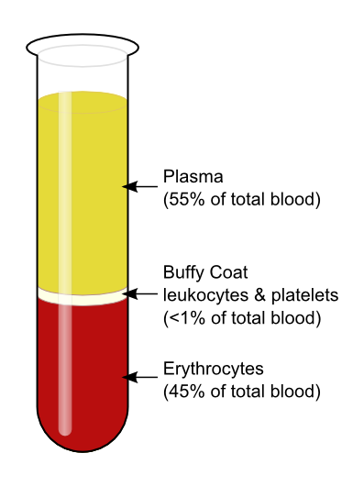
58
New cards
Plateletpheresis - donor requirements
* Same as whole blood, no aspirin w/in 3 days;
* Pre-platelet count: 150 x 10^9/L
* Pre-platelet count: 150 x 10^9/L
59
New cards
Plateletpheresis - quality control
* 3 x 10^11 in 75% of units tested
* pH > 6.0
* pH > 6.0
60
New cards
Plateletpheresis - uses
* Increase platelet counts
* Prevent HLA alloimmunization
* Prevent HLA alloimmunization
61
New cards
Plateletpheresis
Includes: green teas, ginseng, energy drinks
62
New cards
Leukapheresis - donor requirements
* Same as whole blood donations
* Absolute granulocyte count : 4.0 x 10^9/L
* Absolute granulocyte count : 4.0 x 10^9/L
63
New cards
Leukapheresis - quality control
* WBC > 1.0 x 10^10
64
New cards
Leukapheresis - uses
* Sepsis
* Removal of blasts from leukemic patients
* Neutropenia in cancer patients
* Removal of blasts from leukemic patients
* Neutropenia in cancer patients
65
New cards
Plasmapheresis
* Removal of plasma and returning cellular components to patient
66
New cards
Plasmapheresis - donor requirements
* same as platelet donors
67
New cards
Plasmapheresis - uses
* Multiple myeloma (remove abnormal protein)
* Lupus (immune complexes)
* Autoantibodies
* Toxins (barbiturate poisoning)
* Lupus (immune complexes)
* Autoantibodies
* Toxins (barbiturate poisoning)
68
New cards
Plasmapheresis
* Have to replace with another fluid to maintain intravascular compartment
* Antibodies- removes IgM antibody better b/c mostly in intravascular space and produced slowly; IgG evenly distrubuted in intravascular and extravascular spaces and body makes IgG quickly.
* Antibodies- removes IgM antibody better b/c mostly in intravascular space and produced slowly; IgG evenly distrubuted in intravascular and extravascular spaces and body makes IgG quickly.
69
New cards
Intermittent Flow Centrifugation (IFC)
* Blood drawn out and put back in “batches”
* One venipuncture site
* Repeats 6-8 cycle to obtain therapeutic dose
* Takes longer but more mobile
* One venipuncture site
* Repeats 6-8 cycle to obtain therapeutic dose
* Takes longer but more mobile
70
New cards
Continuous Flow Centrifugation (CFC)
* Blood is spun, separated continuously with desired product being removed, and remaining product returned uninterrupted
* 2 venipuncture sites
* Faster
* 2 venipuncture sites
* Faster
71
New cards
Anticoagulant
* Citrate
* Citrate Toxicity
* Citrate Toxicity
72
New cards
Acid Citrate Dextrose (ACD)
* Most common
* Citrate ions chelate free calcium (Ca2+) and blocks calcium-dependent coagulation cascade
* Ensures extracorporeal blood remains in fluid state
* Citrate ions chelate free calcium (Ca2+) and blocks calcium-dependent coagulation cascade
* Ensures extracorporeal blood remains in fluid state
73
New cards
Acid Citrate Dextrose (ACD) pros
* Found in all human cells, not foreign
* Metabolized quickly by liver to bicarbonate, little systemic effect
* Metabolized quickly by liver to bicarbonate, little systemic effect
74
New cards
Acid Citrate Dextrose (ACD) cons
* Can cause transient systemic hypocalcemia (citrate toxicity), presenting with numbness, tingly lips, cramping, EKC changes
75
New cards
HES
* Hydroxyethyl starch
* “Sedimenting agent”
* Promotes rouleaux
* “Sedimenting agent”
* Promotes rouleaux
76
New cards
Plasma apheresis
* Volumes vary based on weight of donor, max 600 mL
* Plasma may be used as FFP or as plasma for manufacture
* May be collected together with an apheresis platelet donation
* Plasma may be used as FFP or as plasma for manufacture
* May be collected together with an apheresis platelet donation
77
New cards
Platelets apheresis
* ==Minimum acceptable platelet count 3 x 10^11 platelets per component==
* Volume can vary from 100 to 500 mL
* One platelet apheresis is equivalent to one adult dose of platelets
* A high-yield apheresis platelet collection can be divided to 2 or more platelet apheresis components as long as each contains a minimum of 3 x 10^11 platelets
* Volume can vary from 100 to 500 mL
* One platelet apheresis is equivalent to one adult dose of platelets
* A high-yield apheresis platelet collection can be divided to 2 or more platelet apheresis components as long as each contains a minimum of 3 x 10^11 platelets
78
New cards
RBC apheresis
* Very similar to rbc components prepared from whole blood
* Normally contain about 60 g of hemoglobin per component
* May be collected together with an apheresis platelet or an apheresis plasma
* 2 rbc apheresis components can be collected from one donor if the donor meets eligibility requirements and no other apheresis components are collected during the same donation
* Normally contain about 60 g of hemoglobin per component
* May be collected together with an apheresis platelet or an apheresis plasma
* 2 rbc apheresis components can be collected from one donor if the donor meets eligibility requirements and no other apheresis components are collected during the same donation
79
New cards
Granulocytes apheresis
* ==Donors may be given drugs such as corticosteroids or growth factors (G-CSF) or precipitating agents, such as hydroxyethyl starch (HES), to increase the number of granulocytes that can be collected==
* ==Minimum number of granulocytes per component is 1 x 10^10==
* ==Minimum number of granulocytes per component is 1 x 10^10==
80
New cards
Component Preparation
* Whole blood unit is given a “soft-spin”
* PRBC + platelet-rich plasma
* Add adsol
* Separate RBC bag
* Hard-spin platelet-rich plasma
* Platelet concentrate (leave \~ 50 ml of plasma) + plasma
* Express off the plasma into separate bag; seal and freeze
* Platelets should “rest” prior to agitation
* PRBC + platelet-rich plasma
* Add adsol
* Separate RBC bag
* Hard-spin platelet-rich plasma
* Platelet concentrate (leave \~ 50 ml of plasma) + plasma
* Express off the plasma into separate bag; seal and freeze
* Platelets should “rest” prior to agitation
81
New cards
How long should it take to collect a whole blood unit?
15 min
82
New cards
When should FFP be separated/frozen?
Within 7 hours of collection
83
New cards
When should Platelets be separated?
Within 8 hours of collection
84
New cards
QC - Leukocyte-reduced Components
* 5.5 x 10^6
* 85% of original RBC mass
* 85% of original RBC mass
85
New cards
QC - Platelets
* 5.5 x 10^10 platelets/unit in 75% of units tested
* Apheresis unit: 3 x 10^11 platelets/unit
* Apheresis unit: 3 x 10^11 platelets/unit
86
New cards
QC - Cryoprecipitate
* 150 mg/dL of fibrinogen
* 80 IU Factor VIII
* 80 IU Factor VIII
87
New cards
QC - Granulocyte
1 x 10^10
88
New cards
Component Utilization - PRBC, whole blood, Leukocyte-reduced RBC, Irradiated RBC, Deglycerolized RBC, Washed RBC
* Oxygen carrying capacity
* Raise Hgb 1-1.5 g/dL; 3% increase in HCT
* Raise Hgb 1-1.5 g/dL; 3% increase in HCT
89
New cards
Component Utilization - FFP
* Replace coag factors
90
New cards
Component Utilization - Platelets
* Used to control bleeding
* Not indicated for patients with ITP
* Not indicated for patients with ITP
91
New cards
Component Utilization - Granulocytes
* Sepsis, immunodeficient patients
92
New cards
Component Utilization - Cryoprecipitate
* Used for patients with Factor XIII deficiency, fibrinogen deficiency, and as a fibrin sealant (mixed with thrombin)
93
New cards
Component Utilization - Leukocyte-reduced
chronically transfused, 5 x 10^6
94
New cards
Contraindications - RBC
* Compensated/nutritional anemias
* General fatigue
* Enhance a patient’s well-being
* Wound healing
* General fatigue
* Enhance a patient’s well-being
* Wound healing
95
New cards
Contraindications - Platelets
* Autoimmune disorders
* TTP
* Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
* TTP
* Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
96
New cards
A donor with a rare blood type weighs less than 110 pounds. The blood bank technologist calculates that less than 300 mL of blood can be drawn. What must be done prior drawing the unit.
The volume of anticoagulant in the bag must be reduced in proportion to the volume of blood drawn.
97
New cards
How often can person donate a unit of blood?
8 weeks
98
New cards
A donor reports that he just complete a 12 hour shift at work and was so busy that he had not eaten all day. What should he do before donating?
Eat a snack. This will decrease his chances of an adverse reaction.
99
New cards
A phlebotomist visits the blood mobile while it is at the hospital for a blood drive. During the donor history she relates that she had a needle-stick injury six months ago and was given HBIG. If she meets all other criteria, can she be accepted for donation?
No. She must be deferred for 12 months because of the needle stick.
100
New cards
How long must a prospective donor with a history of malaria be deferred?
3 years after becoming asymptomatic.