Algebra II
1/334
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
335 Terms
CHAPTER Consider the numbers 1/2 and 9. Which of the following statements is completely true regarding the most specific classification of these two numbers?
1 1/2 is a rational number and 9 is a natural number. The most specific classification for the number 1/2 is a rational number as it is not an integer. The number 9 is an integer, but can be more specifically classified as a natural number.
Which of the numbers in the following set are rational numbers?
500, -15, √2, 1/4, 0.5, -2.50, π
500, -15, 1/4, 0.5, -2.50 Rational numbers include integers, natural numbers and whole numbers. √2 and π are not rational numbers. The rest are.
Which of these statements is FALSE regarding the number 0?
0 is the smallest natural number. 0 is a real, rational number. It is also the smallest whole number. It is not a natural number, though.
Which family of numbers begins with the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, …?
Whole numbers Whole numbers include the counting numbers 1, 2, 3, and so on plus the number 0.
Which is NOT a rational number?
√2 The √2 is NOT a rational number. All the others are rational numbers. A rational number is a number that is made by dividing two integers, meaning it can be written as a fraction, such as 1/3, 0.25 (25/100), 0.666... (2/3), 1000 (1000/1).
What numbers are graphed on the number line?

63, 85, 96 The graph shows increments of 5. From left to right, it shows 50, 55, 60, 65, 70....and so on. Based on this information, we know the numbers graphed on the line are 63, 85, and 96.
Which number is graphed on the number line?

65 Remember that you can graph rational numbers on a number line by drawing a line with the appropriate scale and then placing a dot at the correct position on the number line. The number on the line is 65.
Graph the following daily high temperatures on a number line.
Monday - 78
Tuesday - 72
Wednesday - 65
Thursday - 80

Which number line would be best for creating a timeline depicting major events of the 1700s?

Because the 1700s is an entire century of events, the image showing a 100 year period starting at 1700 and going to 1800 is correct. The other models show too large of a span of time or incorrect labeling of the time period.
Convert the following fraction to a decimal: 9/10
0.9 Remember that the line in a fraction is the same as a division symbol. 9 over 10 is the same as 9 divided by 10. So, one method is to divide the numerator by the denominator. 9 divided by 10 is 0.9. And that's our decimal.
Convert the following fraction to a decimal: 2/3
0.667 Divide 2 by 3
2 /3 = 0.667
Convert the following fraction to a decimal: 35/70
0.5 35 over 70 is the same as 35 divided by 70.
35 / 70 = 0.5
Convert the following decimal to a fraction: 0.07
7/100 0.07 = 7/100
Convert the following decimal to a fraction: 0.25
¼ We have 25 hundredths and we can write it as 25/100.
So 25/100 can be simplified by dividing the numerator and denominator by 25, which gives us 1/4.
Which statement is INCORRECT about inequalities?
One of the inequality symbols is = An equal sign is not an inequality.
Which of the answer choices is an INCORRECT statement?
-2 < -4 Everything is correct except the -2 one because the -2 is greater than the -4.
Fill in the blank
-3 _____ -√11
> The square root of 11 is 3.316. So -3 is greater than, >, the negative square root of 11.
Fill in the blank
2 + √5 _____ 7 - √10
> 2 + √5 = 4.236 and 7 - √10 = 3.8377 so the first number is greater than, >, the second number.
Which set of numbers make this inequality true?
a < b
a = pi
b = 3.5 The only one where the a number is less than or smaller than the b number is 3.14, pi, for a and 3.5 for b.
Simplify |1 - 3|
2 Remember that absolute value is always positive, and whatever number or variable is inside the absolute value symbols, the result will be positive. We know that 1-3 usually equals -2, but because it is in between the absolute value symbols, we know that the correct answer is 2.
Which of the following is not a real number?
infinity The imaginary numbers are the square root of -1 and infinity.
Solve |17|
17 Keep in mind that the absolute value of a number is its distance from zero on a number line, so the correct answer is 17.
Solve -(-|-5|)
5 Since the absolute value of negative 5 is positive 5, we end up with negative 5 in the parentheses. Because there is a negative sign outside of the parentheses, and two negatives equal a positive, the correct answer is 5.
Which statement is true about the absolute value?
It is notated by |x| It is TRUE that absolute value is designated by a set of straight vertical lines - |x|.
What do you multiply by to rationalize this denominator?

sqrt(6)/sqrt(6) To rationalize the denominator, you multiply both numerator and denominator by the square root of 6.
Rationalize the denominator.

sqrt(5) Multiplying both numerator and denominator by the square root of 5 and simplifying gives us the square root of 5.
What do you multiply the numerator and denominator with to rationalize the denominator?

5 + sqrt(2) To rationalize this denominator, we multiply by the conjugate, 5 + sqrt(2) where the only difference is the sign between the two terms in the denominator.
Rationalize the denominator.

sqrt(14)/2 Multiply both the numerator and denominator by the square root of 14 and then simplify to get the square root of 14 divided by 2.
Rationalize the denominator.

(2 - sqrt(2))/2 Multiplying both the numerator and denominator by 2 - sqrt(2) gives us (2 - sqrt(2))/(4 - 2) which simplifies to (2 - sqrt(2))/2.
An algebraic number is what to a polynomial?
a solution An algebraic number is any number that is the solution to a polynomial with rational coefficients.
Algebraic numbers are _.
countable Algebraic numbers can be radicals, irrational numbers and even the imaginary number i. And even though they're infinite, they are countable and definable.
Which of these numbers is transcendental?
Pi
Transcendental numbers are _ .
uncountable Transcendental numbers are infinite and uncountable because there are far more transcendentals than there are algebraics.
Which of these numbers is a transcendental number?
pi pi is a proven transcendental number.
Which of the following is a Pythagorean Triple?
(3, 4, 5)
What formula must all Pythagorean Triple obey?
a^2 + b^2 = c^2
Which of the following is a Pythagorean Triple?
(9, 40, 41) (9, 40, 41) follows the formula a^2 + b^2 = c^2.
9^2 + 40^2 = 41^2
81 + 1600 = 1681
Which of the following is a scaled up version of (5, 12, 13)?
(10, 24, 26) (10, 24, 26) are all the numbers in the original multiplied by 2. It is scaled by a factor of 2.
Which of the following is NOT a Pythagorean Triple?
(5, 10, 11)
CHAPTER Which of the following is an imaginary number?
2 2i 2i is an imaginary number. Infinity is not an imaginary number or really a number at all. It is a concept or idea of something without end.
What is the simplified value of the expression below?

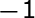
√-110 equals -1
Which of the following expressions is written as a complex number?
-1 + i When you combine an imaginary number with a real one you get a complex number: -1 + i.
When solving a quadratic equation, under what circumstances would the result be two answers that are imaginary numbers?
When the discriminant is negative When the discriminant is negative, a quadratic equation will result in two answers that are imaginary.
In math, i equals _____.

In math, i equals √-1.
Subtract and simplify the following expression:


Remember (a + bi) - (c + di)=(a - c) + (b - d)i.
Therefore, (-1 + 4i) - (-2 + i) = 1 + 3i.
Add and simplify the following expression:


Remember a + bi and c + di gives us an answer of (a + c) + (b + d) i.
So (2 - i) + (-5 -3i) = -3 - 4i.
Multiply and simplify the following expression:


The FOIL method can be used to multiply. This will give:
8 - 4i + 12i - 6i^2
= 8 + 8i - (-6) (since i^2 = -1)
= 8 + 8i + 6
= 14 + 8i
Which of the following is a complex number with a non-zero real part and a non-zero imaginary part?
8 + 4i When we take an imaginary number and add a real number to it, we end up with a complex number, often denoted by a+bi, where a represents the real and b the imaginary portion of the number.
Simplify the following expression:

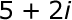
First simplify (1 + i)(1 - i) by using FOIL:
This gives (1 - i^2) but since i^2 = -1 this can be simplified
(1 - i^2) = (1 - (-1)) = 1 + 1 = 2
Now put this back into the original problem:
3 + 2i + 2 = 5 + 2i.
What is the first step in dividing these complex numbers?

Multiply the top and bottom of the fraction by 3 + 4i. Similar to multiplying a fraction by its bottom term to find a common denominator, multiply both the top and bottom of the fraction by the complex conjugate of the bottom number. The conjugate of 3 - 4i is 3 + 4i.
What is the complex conjugate of the expression below?


A conjugate is a binomial where the sign for the second term has been switched.
Simplify the following expression:


Begin by multiplying the top and bottom of the fraction by the complex conjugate of the denominator.
Using FOIL multiply the numbers in the parentheses.
By definition i2 equals (-1).
Any term multiplied by -1 equals its opposite, yielding 18 plus 18i plus 6i minus 6 over 9 plus 9.
Calculate the sums of like terms, which gives 12 plus 24i over 18.
Reduce the fraction by 6 and separate the real numbers from the imaginary numbers: 2 over 3 plus 4 over 3 times i.
Simplify the following expression.


Starting by multiplying both the top and bottom of the fraction by the complex conjugate of the denominator.
Use FOIL to expand the fraction.
By definition, i2 equals -1, which can be multiplied to eliminate the parenthesis, resulting in the equation 3 minus 3i plus 5i plus 5 over 1 plus 1.
Collect like terms, the 8 and 5 on top and the 1's on the bottom.
Factor the expression 8 plus 2i over 2, and simplify: 4 + i.
Which two complex conjugates would multiply to equal 13?

Multiplying these two complex numbers using FOIL yields 4 - 6i + 6i - 9i^2.
When we combine the like terms, the two groups of i's in the middle cancel out.
Substituting -1 for i^2 and then adding 4 + 9 gives 13.
Which complex number would look like it was located at the coordinates (-2, 4) if it was graphed?
-2 + 4i Since graphing complex numbers are essentially the same as real numbers, the set would look like -2 + 4i.
Which number is represented by the graph below?

4 The dot is located at (0,4). Any point on the x-axis, (or the real axis) is a complex number without any imaginary value. Therefore, the answer is 4.
Which number is represented by the graph below?

3 - 5i The dot is located at (3,-5), so the complex number would be 3 - 5i.
Which of the following graphs represents the complex number -i on the complex plane?

The complex number for -i would look like 0 + -1i, so the dot has to be located at x = 0 and then move down to -1.
Which of the following graphs represents the complex number 3 + 2i on the complex plane?

Since both numbers are positive, the dot would have to be located in the first quadrant.
How many roots does the equation below have?

2 real roots Converting the standard form to the discriminant gives you, [(-2)2 - (4*-1*6)]. The answer is 28. When the discriminant is positive, you will get two real answers.
Find the roots of the equation below:


When solving the problem, begin by subtracting 1 from both sides. Then find the square root of both numbers. The square of a negative number must be signified by a plus/minus sign, making it a complex number. As both sides are 1, x = ±'i.
When it comes to solving quadratics with complex solutions, which one of the following statements is FALSE?
If the discriminant is zero, the result will be no real answers. This statement is false: If the discriminant is zero, the result will be no real answers. If the discriminant is zero, there will only be one real answer.
What is the most simplified form of the expression below?

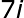
When solving for the square root of a negative number, you must add an imaginary number, typically denoted with an italic lower case i (i). The i will allow you to remove the negative and work the problem as a complex number giving you ±7i.
√-49 = √-1 x √49
Solve the equation below:


Begin by converting the equation to the quadratic formula, we have: x =-(3) ± √ 32-4 1 5 / 2(1). Working the formula, we're left with x = -3±i√11 / 2.
CHAPTER Write using exponential notation
9 x 9 x 9
3 93 You have 3 nines being multiplied together, so you get 93.
Simplify
C x C x C x C x C x C
c6 This C is being multiplied by itself 6 times, so it is being taken to the 6th power: c6.
Simplify
2 x 2 x 2 x 2
24 This 2 is being multiplied by itself 4 times, so it is being raised to the 4th power: 24.
Which term corresponds to the exponent?

y The exponent is the number that's raising the base, so in this case, it is y.
Which number is the base?

5 The base number is the number being raised to a certain power, so in this case, it is 5.
Convert 1.763 x 10^2 to standard notation.
176.3 An exponent of 2 means the decimal moves 2 spaces to the right, so 176.3.
Convert 36,098,000 to scientific notation.
3.6098 x 10^7 Moving the decimal to right after the first digit, you have to move it 7 spaces to the left, so you have to multiply your new decimal by 10^7: 3.6098 * 10^7.
Convert 0.00028 to scientific notation.
2.8 x 10^-4 Moving the decimal to right after the first non-zero digit, you have to move it 4 spaces to the right, so 2.8 x 10^-4. Note that 28 x 10^-5 does not qualify for being scientific notation as it breaks the rule to "move the decimal place from its current location to the space directly behind the first non-zero digit in the number." In this case, it is behind the second non-zero number.
Convert 8.06 x 10^-1 to standard notation.
0.806 A -1 in the exponent of the 10 means the decimal moves 1 space to the left: 0.806.
Which of the following is written in proper scientific notation?
3.009 x 10^-4 Proper scientific notation has the decimal right after the first non-zero digit followed by a multiplication by 10 to a power.
Simplify the following expression:

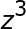
Both have the same bases, so you can subtract the exponents to get z to the third power.
Solve the following expression:

729 Multiplying 9 x 9 x 9, you get 729.
Solve the following expression:

-128 Multiplying the -2 seven times, you get -128.
Simplify and solve the following expression:

8 The bases are the same, so you can subtract the exponents to get 8.
Solve the following expression:

625
Which of the following operations are performed together from left to right?
Which of the following operations are performed together from left to right? Multiplication and division are to be done together from left to right. Addition and subtraction follow the same rule.
Solve:

-94 Following the order of operations:
Clearing parenthesis first gives:
5 - 4^3 * 2 + 3^3 - (-2)
Next do the exponents leading to:
5 - 64 * 2 + 27 - (-2)
Now do multiplication and division from left to right which gives us:
5 - 128 + 27 - (-2)
Finish with addition and subtraction from left to right:
5 - 128 + 27 - (-2) = -94
To double check, enter the numbers into your scientific calculator EXACTLY as written, including parenthesis.
Solve

-24 First work through the exponent:
3 - 14/7 * 2 + 13 - 36
Next work from left to right and do the multiplication and division. We will do the division of 14/7 first as we move from left to right:
3 - 2 * 2 + 13 - 36
Now go back through and do the multiplication of 2 * 2:
3 - 4 + 13 - 36
Now go from left to right and do the addition and subtraction:
3 - 4 + 13 - 36 = -24
Solve

3 Performing the operations inside the parentheses first beginning with the multiplication, you get 12/3 - (2) + 3*1 - 2. Then going through and performing both multiplication and division, you get 4 - 2 + 3 - 2. Now, going from left to right again with addition and subtraction, you get 3.
Which operation comes second in the order of operations?
exponents Exponents come in second in the order of operations.
Why is it always important to anticipate and refute possible opposing views in your argumentative paper?
Otherwise, your reader may not let go of the opposing views that he or she may have about your essay topic Because the success of this type of essay is so tied up with your audience - with convincing your readers that your position on the subject is the right one - you have to really pay special attention to your audience. What views and opinions do they already hold before they read your essay? Are they open and receptive to your point of view? Or are they more skeptical of your position?
It's particularly important to consider your audience when you write an argumentative paper because _____.
you need to be mindful of the views that members of your audience might have in order to effectively persuade them. Your purpose when writing this type of essay is to persuade the reader to accept your point of view on your chosen subject. Therefor, it is important to understand the views of your audience.
Which of the following is NOT an appropriate place to present an opposing view and your counterargument to that view?
During the writing of your thesis, at the end of the introduction Place these opposing views and counterarguments either where they blend together with your own points in your paper or cluster them together at the start or end of the body of your essay. Do NOT place your opposing view in your thesis or in the introduction.
What key method can you use to determine major opposing views?
Conducting research on your topic Research plays an important role in refuting any opposing views and being able to fully articulate your argument.
Why can it be useful to outline your own major argumentative points before writing your persuasive paper?
Because you can consider the strength of each point, and determine how much time you'll spend arguing your points and how much time you'll spend refuting opposing views Performing this assessment will help you gain a sense of whether the bulk of your paper will be spent trumpeting your own solid points or knocking down the weak ideas of the opposing side.
Simplify
(a^2)*(a^7)*(b^3)
(a^9)(b^3) The a's can be combined to get (a^9)(b^3).
Simplify
(5^6)*(5^-4)
5^2 The bases are the same, so you can go ahead and add the exponents to get 5^2.
Which statement is TRUE about multiplying exponential expressions?
You can only multiply exponential expressions if the exponents have the same base. The only true statement here is the one about only being able to multiply exponential expressions if the bases are the same.
Simplify
(y^4)*(y^4)
y^8 Since the base y is the same in both, you can multiply them by adding the exponents to get y^8.
Simplify
(y^4)*(2^3)
This cannot be simplified The bases are not the same so they cannot be combined.
Simplify
x2/x-3
x5 The bases are the same, so you subtract the bottom exponent from the top: 2 - (-3) = 5. Your answer then is x5.
Simplify
25/22
23 This becomes 23. You subtract the bottom exponent from the top exponent since they share the same base.
Simplify

35 x7 Simplifying the like bases, you get 35 x7.
Simplify

The expression can not be simplified. This expression has no like bases, so it is already as simplified as it can be.
Which of the following is true when dividing expressions with exponents?
If the bases are not the same, you can't simplify. You can only simplify division expressions with exponents if the bases are the same.
What is 0^0?
undefined The number 0 has its own rules and 0 to the 0th power is undefined because there is no consistent proof for it.