AQA GCSE Physics Paper 2
1/259
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set should (hopefully) contain everything you need to know for AQA GCSE Physics Paper 2. Made using the specification and Freesciencelessons on YouTube. This is designed to be used in Term → Definition mode. You can do it the other way around for extra revision, but it will not be framed as a question. Topic 5 - Forces: Cards 1-109 Topic 6 - Waves: Cards 110-199 Topic 7 - Magnetism and electromagnetism: Cards 200-245 Topic 8 - Space physics: Cards 246-260 (Topics 1-4 are in the Paper 1 flashcards) (Note: Questions in paper 2 may draw on an understanding of energy changes and transfers due to heating, mechanical and electrical work and the concept of energy conservation.) Cards starting with ᵀ are triple/separate/physics only. Cards starting with ᴴ are Higher tier only. (Cards starting with ᵀᴴ are both.) If you want to remove these cards, star all the other cards and then study with starred cards only.
Physics
Newton's Laws
GCSE Physics
AQA
aqa
gcse
physics
science
higher
foundation
HT
triple
separate
combined
trilogy
paper 2
required practical
topic 5
topic 6
topic 7
topic 8
forces
waves
magnetism and electromagnetism
space physics
forces and their interactions
scalar and vector quantities
contact and non-contact forces
gravity
resultant forces
work done and energy transfer
forces and elasticity
moments, levers and gears
pressure and pressure differences in fluids
pressure in a fluid
pressure in a fluid 1
pressure in a fluid 2
atmospheric pressure
forces and motion
describing motion along a line
distance and displacement
speed
velocity
the distance-time relationship
acceleration
forces, accelerations and Newton’s Laws of motion
Newton’s First Law
Newton’s Second Law
Newton’s Third Law
forces and braking
stopping distance
reaction time
factors affecting braking distance 1
factors affecting braking distance 2
momentum
momentum is a property of moving objects
conservation of momentum
changes in momentum
waves in air, fluids and solids
transverse and longitudinal waves
properties of waves
reflection of waves
sound waves
waves for detection and exploration
electromagnetic waves
types of electromagnetic waves
properties of electromagnetic waves 1
properties of electromagnetic waves 2
uses and applications of electromagnetic waves
lenses
visible light
black body radiation
emission and absorption of infrared radiation
perfect black bodies and radiation
permanent and induced magnetism, magnetic forces and fields
poles of a magnet
magnetic fields
the motor effect
electromagnetism
Fleming’s left-hand rule
electric motors
loudspeakers
induced potential, transformers and the National Grid
induced potential
uses of the generator effect
microphones
transformers
solar system; stability of orbital motions; satellites
the life cycle of a star
orbital motion, natural and artificial satellites
red-shift
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
260 Terms
What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
Scalar quantities have magnitude only. Vector quantities have magnitude and an associated direction.
What is a force?
A push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
What is the difference between contact and non-contact forces?
Contact forces – the objects are physically touching
Non-contact forces – the objects are physically separated
Give four examples of contact forces.
Friction, air resistance, tension and normal contact force
Give three examples of non-contact forces.
Gravitational force, electrostatic force and magnetic force
Is force a scalar quantity or a vector quantity?
Vector quantity
What is weight?
The force acting on an object due to gravity
What is the force of gravity close to the Earth due to?
The gravitational field around the Earth
What does the weight of an object depend on?
The gravitational field strength at the point where the object is
What is the unit of weight?
Newtons (N)
What is the unit of mass?
Kilograms (kg)
What is the unit of gravitational field strength (g)?
Newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
What is an object’s ‘centre of mass’?
A single point at which the weight of the object may be considered to act
What is used to measure weight?
A calibrated spring-balance (a newtonmeter)
What is a resultant force?
A single force that has the same effect as all the forces acting together on an object
Draw a free body diagram to describe an aeroplane flying with constant velocity.
(You could be asked to draw a free body diagram for other situations.)
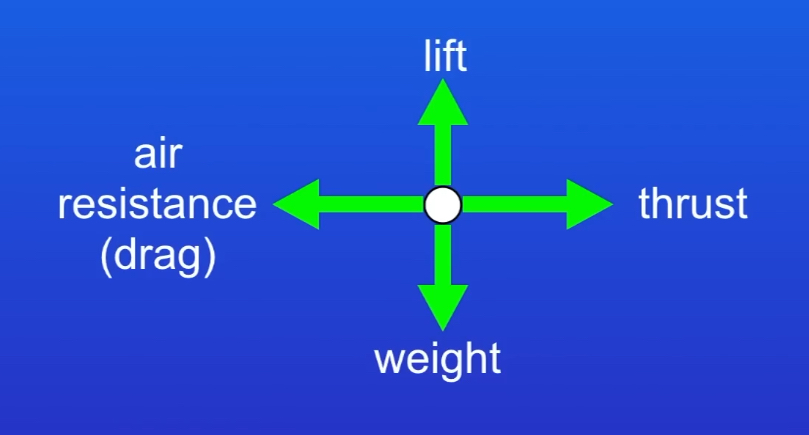
What is the resultant force when the forces acting on an object are balanced?
0 N
ᴴ What can a single force be resolved into?
Two components acting at right angles to each other. The two component forces together have the same effect as the single force.
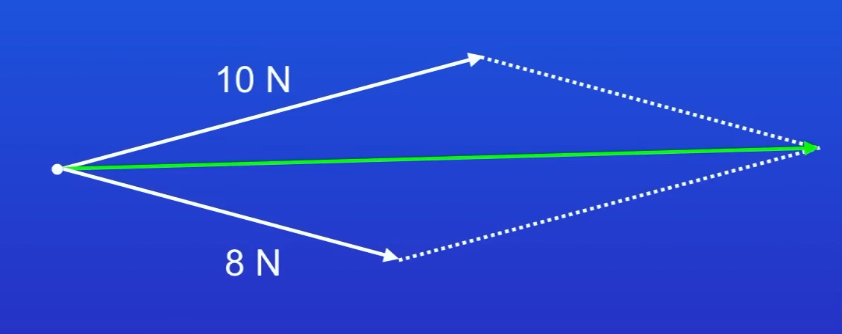
ᴴ Use a vector diagram to illustrate the resolution of a force.
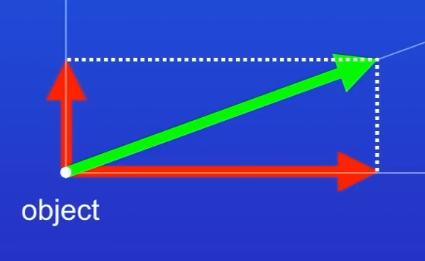
ᴴ Use a vector diagram to determine the resultant of two forces with magnitudes 10 N and 8 N respectively, acting on the same object with an angle of 30° between them.
(You could be asked a variation of this question with different numbers. Draw a scale diagram, create a parallelogram, and measure the resultant force.)
What happens when a force causes a displacement of an object (causing it to move through a distance)?
Work is done on the object
What is the unit of work done?
Joules (J)
What is the unit of force?
Newtons (N)
What is the unit of distance?
Metres (m)
Convert 1 joule into newton-metres.
1 joule = 1 newton-metre
What does work done against the frictional forces acting on an object cause?
A rise in the temperature of the object
Why does more than one force have to be applied to change the shape of a stationary object?
If only one force was applied, the forces would no longer be balanced and the object would move instead of changing shape.
What is the difference between elastic deformation and inelastic deformation?
In elastic deformation, the object returns to its original shape and length if the forces are removed. In inelastic deformation, the object does not return to its original shape and length when the forces are removed.
What is the unit of extension (of a spring)?
Metres (m)
How could the equation F = ke apply to the compression of an elastic object?
‘e’ would be the compression of the object
Provided a spring is not inelastically deformed, what is the relationship between the work done on the spring when a force stretches or compresses it and the elastic potential energy stored in the spring?
They are equal
What is the unit of energy?
Joules (J)
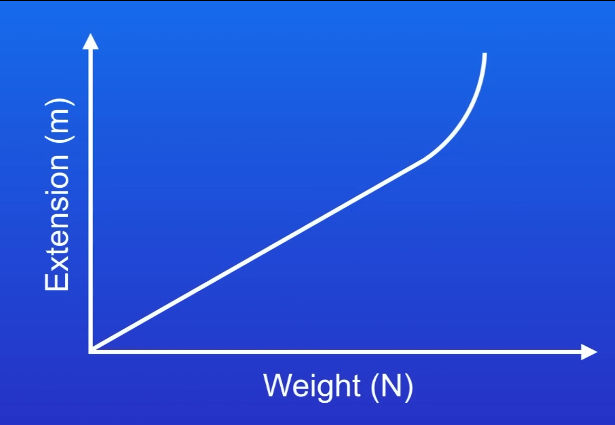
Why does this graph show a non-linear relationship between force and extension for a spring?
Too much weight has been added to the spring and it has been overstretched. If all the weight was taken away, the spring would still show an extension. The spring has been inelastically deformed and it has exceeded its limit of proportionality.
Describe how to investigate the relationship between force and extension for a spring.
- Set up a clamp stand with two bosses and two clamps. Place a heavy weight on the clamp stand to stop it from falling over.
- Attach a metre rule and a spring to the clamps. The top of the spring must be at the zero point on the metre rule. The metre rule must be vertical, and there must be a horizontal wooden splint attached at the bottom of the spring.
- Read the position of the pointer on the metre rule. This is the unstretched length of the spring.
- Hang a 1 N weight on the spring and read the new position of the pointer on the metre rule.
- Repeat step 4 multiple times.
- Calculate the extension produced by adding each weight by subtracting the length of the unstretched spring from each reading.
- Plot a graph of extension against weight.
ᵀ What may cause an object to rotate?
A force or a system of forces
ᵀ Give some examples in which forces cause rotation.
e.g. wheelbarrows, crowbars, seesaws, cranes
ᵀ What is the turning effect of a force called?
The moment of the force
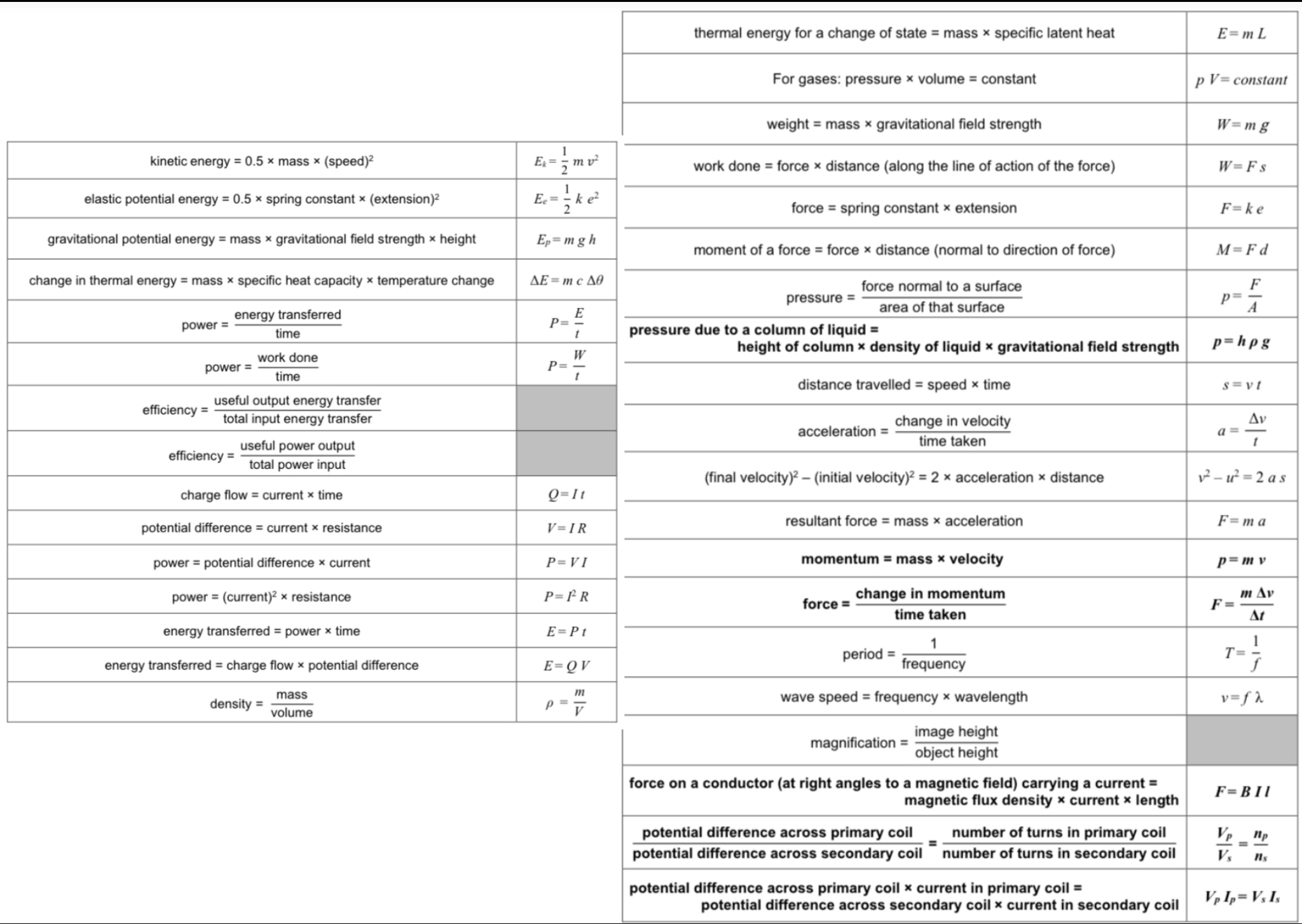
ᵀ What is the unit of moment (of a force)?
Newton-metres (Nm)
ᵀ What is true about moments when an object is balanced?
If an object is balanced, the total clockwise moment about a pivot equals the total anticlockwise moment about that pivot
ᵀ What can be used to transmit the rotational effects of forces?
A simple lever and a simple gear system
ᵀ How do levers transmit the rotational effects of forces?
Levers transmit the turning effect of the force from one side of the pivot to the other. Levers are force multipliers - if the distance from the input force to the pivot is larger than the distance from the output force to the pivot, the output force will be greater than the input force as the clockwise and anticlockwise moments must be balanced. This means that levers allow us to lift a heavy object by applying a relatively small amount of force.
ᵀ How do gears transmit the rotational effects of forces?
When one gear turns, it applies a force onto the other. The turning effect depends on the distance between the edge of the gear and the centre. If the radius of the second gear is larger than the first, it will have a larger turning effect. It will also rotate more slowly, so the work done by the two gears is the same.
ᵀ What states of matter can fluids be?
Liquids or gases
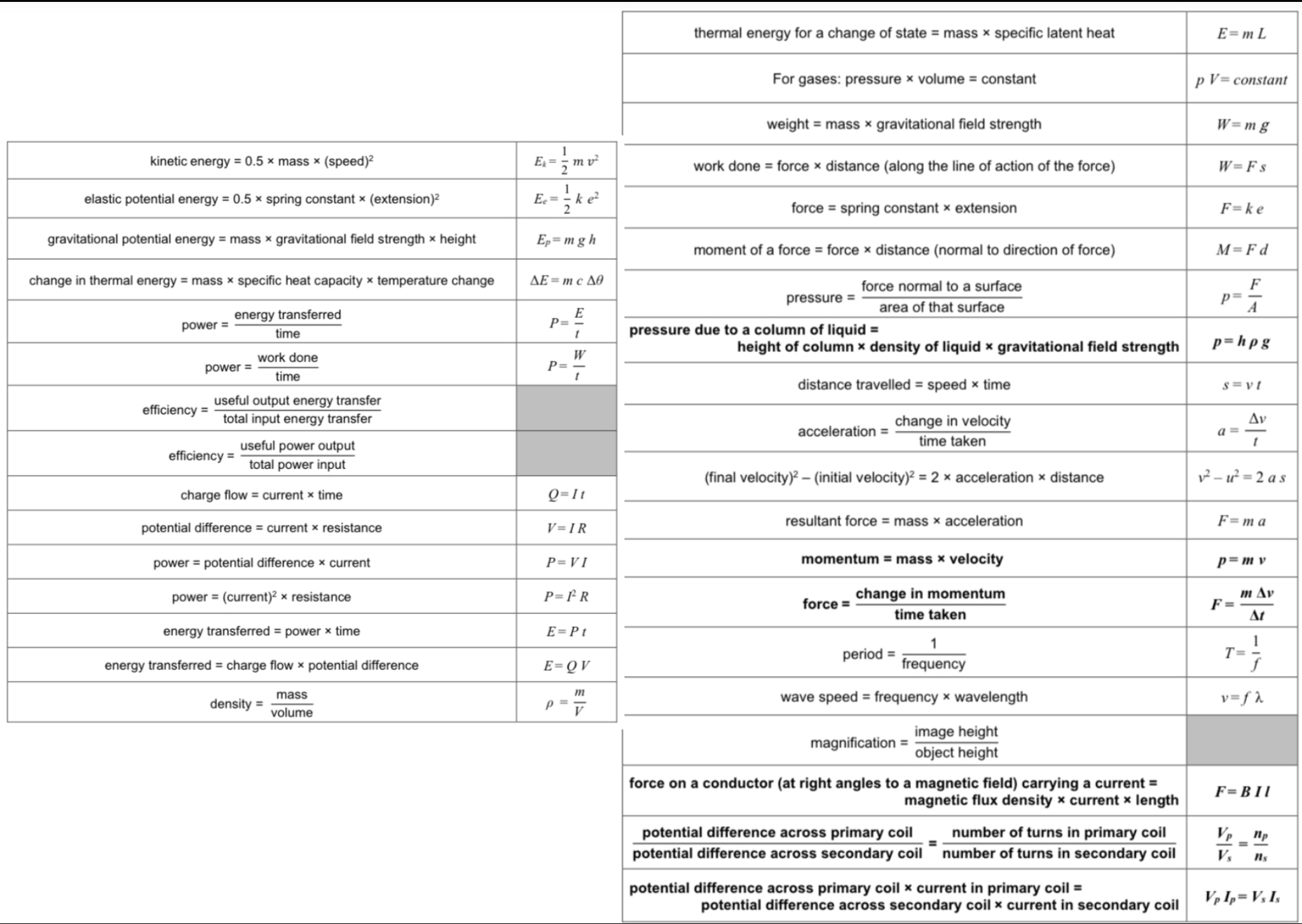
ᵀ What does the pressure in fluids cause?
A force normal (at right angles) to any surface
ᵀ What is the unit of pressure?
Pascals (Pa)
ᵀ What is the unit of area?
Metres squared (m²)
ᵀᴴ What is the unit of height?
Metres (m)
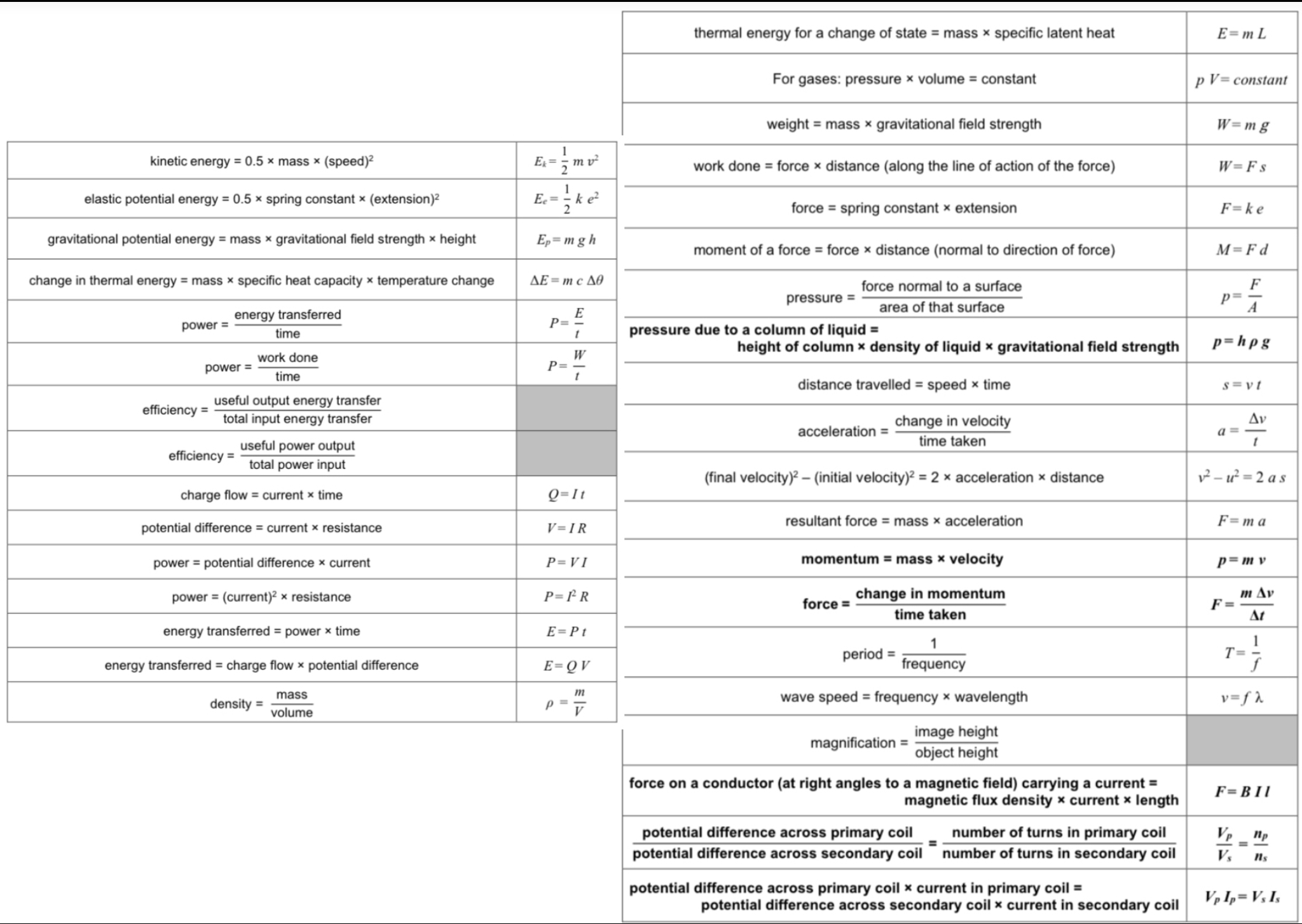
ᵀᴴ What is the unit of density?
Kilograms per metre cubed (kg/m³)
ᵀᴴ In a liquid, why does pressure at a point increase with the height of the column of liquid above that point and with the density of the liquid?
As they increase, there is a greater weight of liquid acting downwards
ᵀᴴ What is upthrust?
A resultant force upwards created when a partially (or totally) submerged object experiences a greater pressure on the bottom surface than on the top surface
ᵀᴴ What factors influence floating and sinking?
When an object is submerged in a liquid, the size of the upthrust acting on the object is the same as the weight of the liquid displaced by the object. If an object can displace its own weight of the liquid, the upthrust will equal the object’s weight and the object will float.
An object less dense than the liquid only has to displace a small volume of the liquid before the weight of the liquid displaced equals the weight of the object, so the object floats high in the liquid.
An object with the same density as the liquid has to displace its own volume of the liquid in rider for the weight of liquid displaced to equal the weight of the object. The upthrust equals the weight of the object, so the object floats at the surface of the water.
An object more dense than the liquid cannot displace a volume of the liquid equal to its own weight. The weight of the water is greater than the upthrust acting on it, so it sinks.
ᵀ What is the atmosphere?
A thin layer (relative to the size of the Earth) of air round the Earth
ᵀ What happens to the density of the atmosphere as altitude increases?
It decreases
ᵀ Why does atmospheric pressure decrease with an increase in height?
Air molecules colliding with a surface create atmospheric pressure. The number of air molecules (and so the weight of air) above a surface decreases as the height of the surface above ground level increases. So as height increases there is always less air above a surface than there is at a lower height.
What is distance?
Distance is how far an object moves. Distance does not involve direction.
Is distance a scalar quantity or a vector quantity?
Scalar quantity
What is displacement?
Displacement includes both the distance an object moves, measured in a straight line from the start point to the finish point and the direction of that straight line.
Is displacement a scalar quantity or a vector quantity?
Vector quantity
Is speed a scalar quantity or a vector quantity?
Scalar quantity
Is the speed of a moving object usually constant?
No
What factors does the speed at which a person can walk, run or cycle depend on?
Age, terrain, fitness and distance travelled
What is a typical value for the speed of a person walking?
~1.5 m/s
What is a typical value for the speed of a person running?
~3 m/s
What is a typical value for the speed of a person cycling?
~6 m/s
What is a typical value for the speed of a car on a main road?
~13 m/s
What is a typical value for the speed of a fast train in the UK?
~50 m/s
What is a typical value for the speed of a cruising aeroplane?
~250 m/s
What is a typical value for the speed of sound in air?
330 m/s
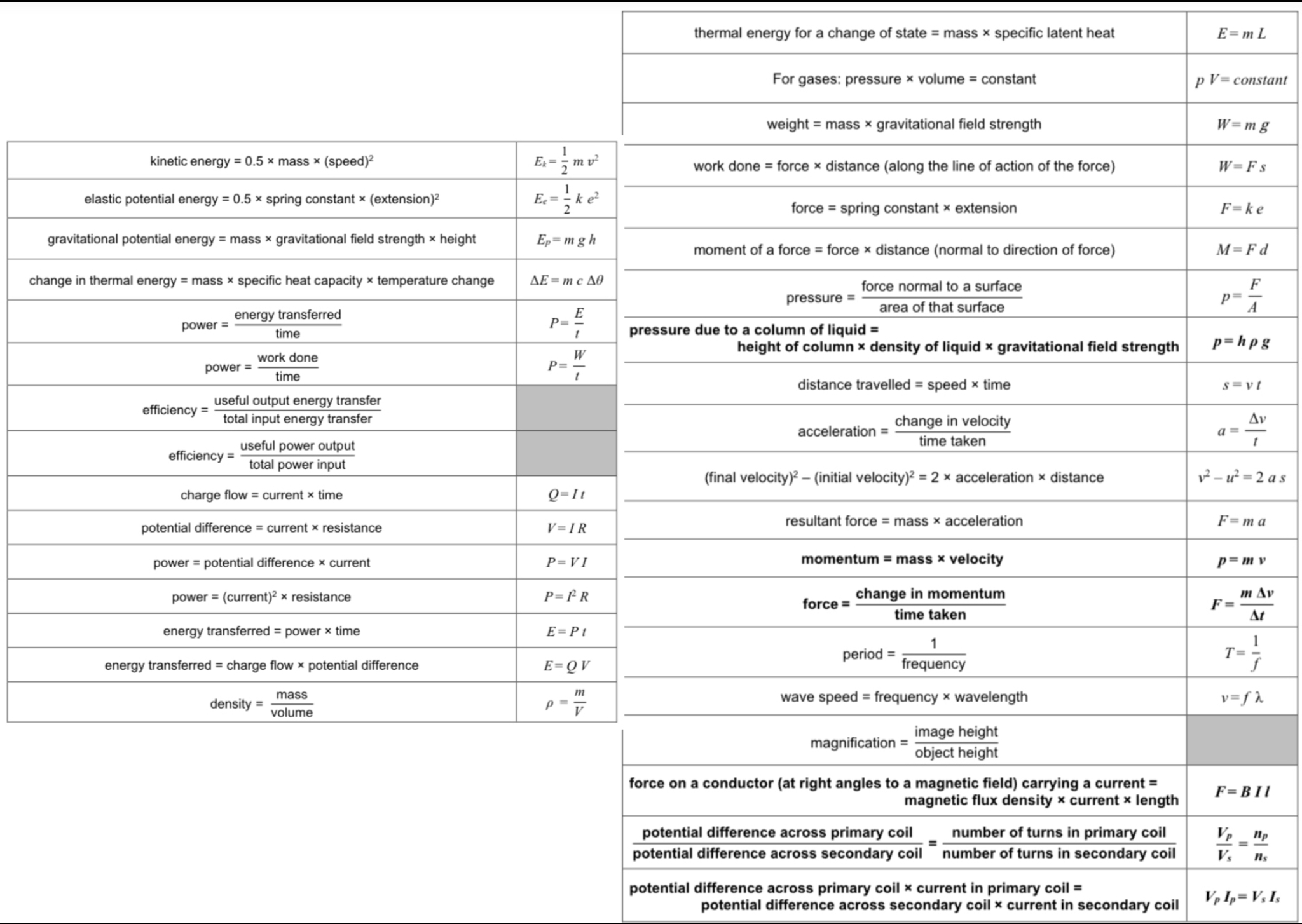
What is the unit of speed?
Metres per second (m/s)
What is the unit of time?
Seconds (s)
What is velocity?
The velocity of an object is its speed in a given direction
Is velocity a scalar quantity or a vector quantity?
Vector quantity
ᴴ Why does motion in a circle involve constant speed but changing velocity?
The object’s direction is constantly changing
How can the distance travelled of an object moving along a straight line be represented?
By a distance-time graph
How can the speed of an object be calculated from its distance time graph?
It is equal to the gradient
ᴴ If an object is accelerating, how can its speed at any particular time be determined using a distance-time graph?
By drawing a tangent and measuring its gradient at that time
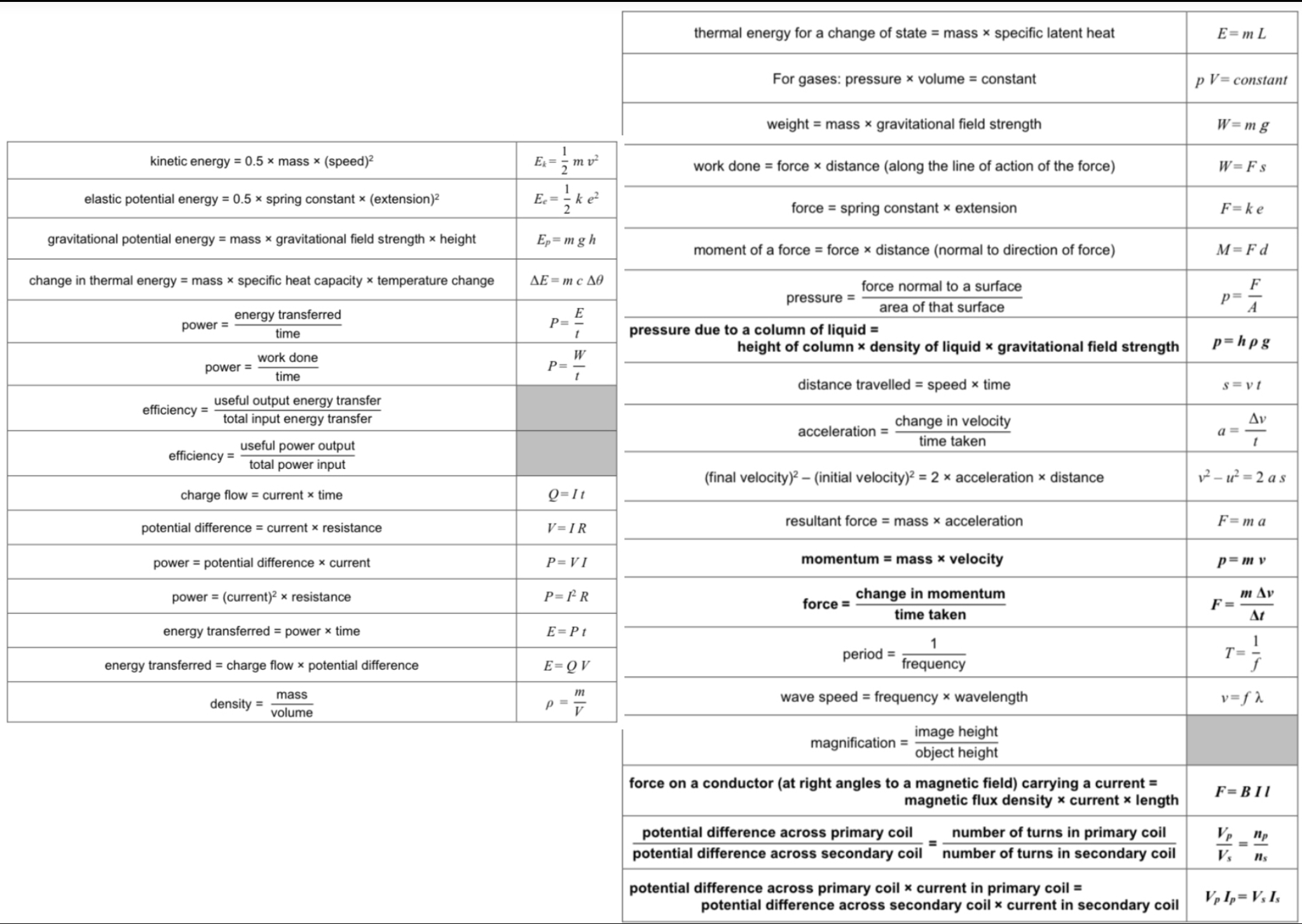
What is the unit of acceleration?
Metres per second squared (m/s²)
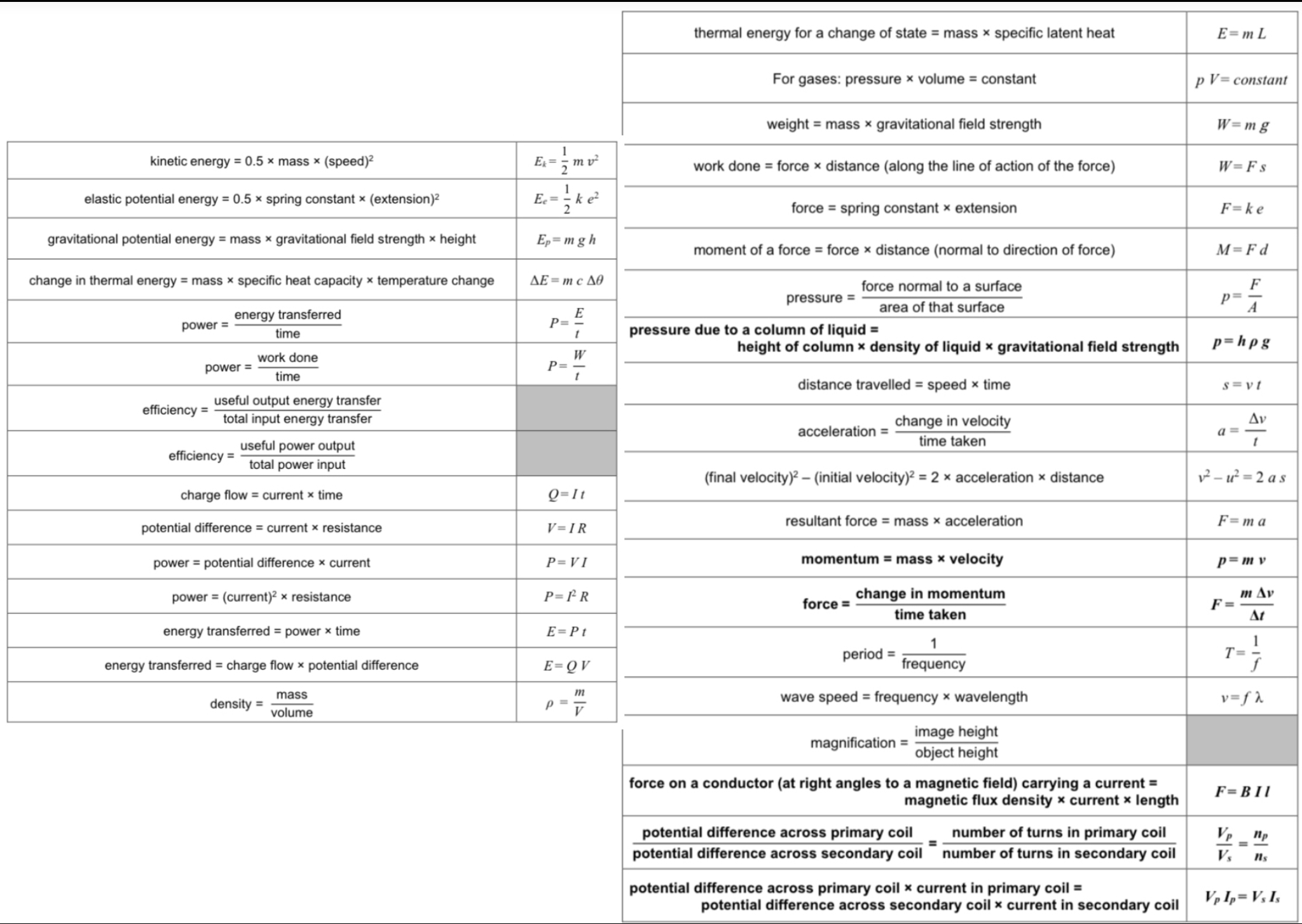
What is the unit of velocity?
Metres per second (m/s)
How can the motion of an object that is slowing down be described in other words?
The object is decelerating
How can the acceleration of an object be calculated using a velocity-time graph?
It is equal to the gradient
ᴴ How can the distance travelled by (or displacement of) an object be calculated using a velocity-time graph?
It is equal to the area under the graph
ᴴ How can the area under a velocity-time graph be estimated when the acceleration is constantly changing?
By counting squares
What acceleration does any object falling freely under gravity near the Earth’s surface have?
About 9.8 m/s²
Describe the motion of an object falling through a fluid.
(Note: If you are doing triple/separate science, you can ignore this card.)
It initially accelerates due to the force of gravity. Eventually the resultant force will be zero and the object will move at its terminal velocity.
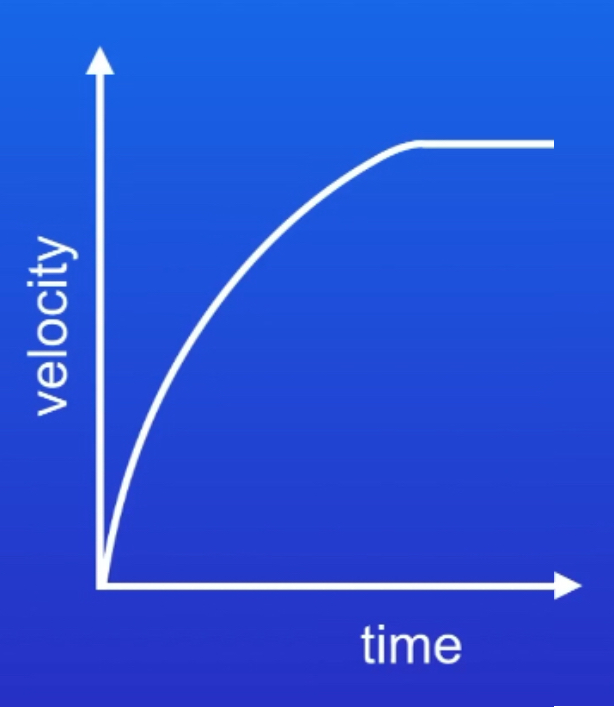
ᵀ Draw a velocity-graph for an object reaching terminal velocity. Interpret the changing motion in terms of the forces acting.
As the object begins to fall, the only force is weight. The object accelerates towards the ground. As the object falls, air resistance acts upwards. Weight is still greater than air resistance so the object continues to accelerate. As the velocity increases, air resistance also increases. When air resistance balances weight, the resultant force is zero and the velocity stays constant. This is the terminal velocity.
What is Newton’s First Law?
If the resultant force acting on an object is zero and:
• the object is stationary, the object remains stationary
• the object is moving, the object continues to move at the same speed and in the same direction. So the object continues to move at the same velocity.
What is true about the forces acting on a vehicle driving at a steady speed?
The resistive forces balance the driving force
What must happen for the velocity of an object to change?
A resultant force must act on the object
ᴴ What is inertia?
The tendency of objects to continue in their state of rest or of uniform motion
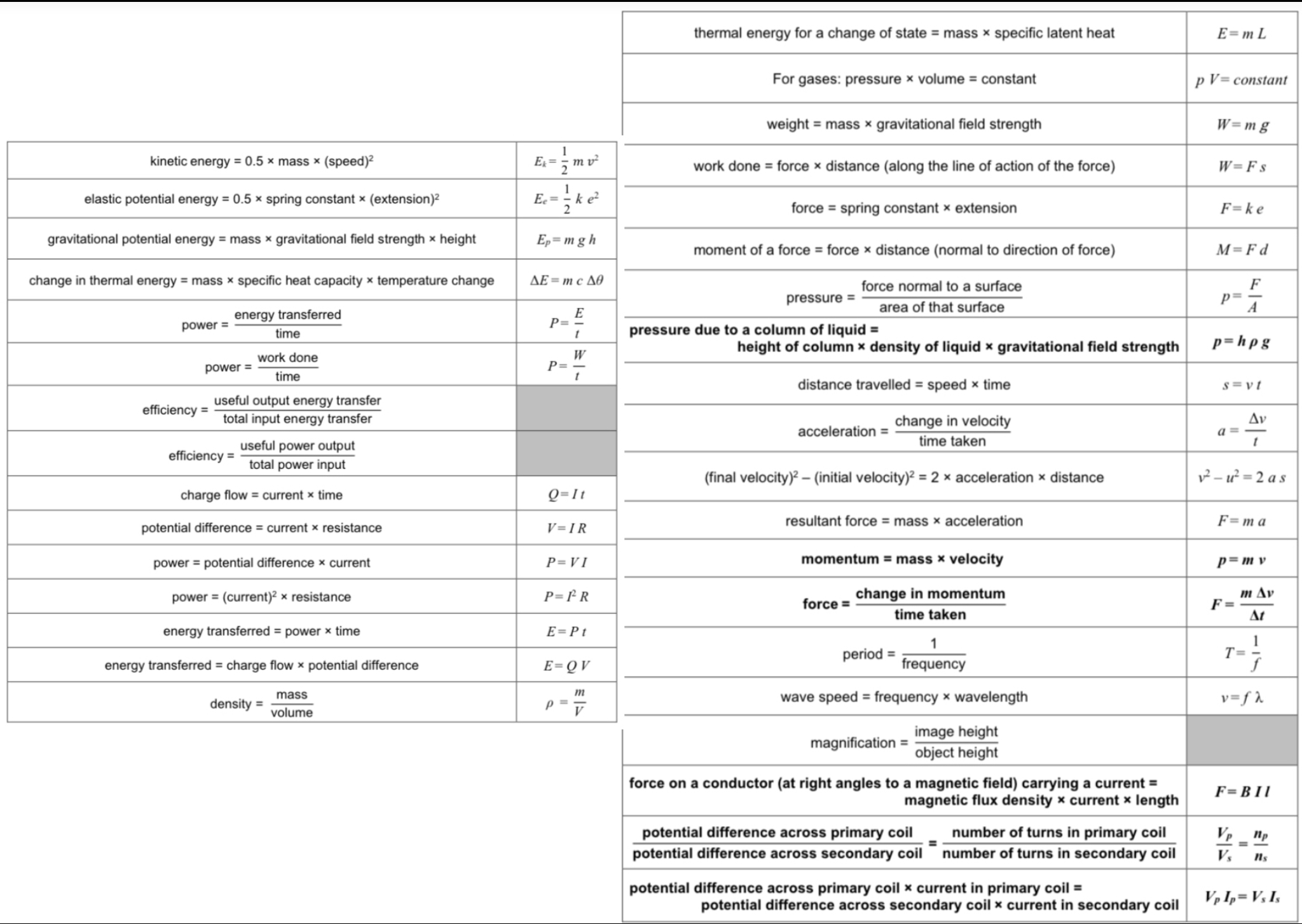
What is Newton’s Second Law?
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. As an equation: resultant force = mass × acceleration (F = ma).
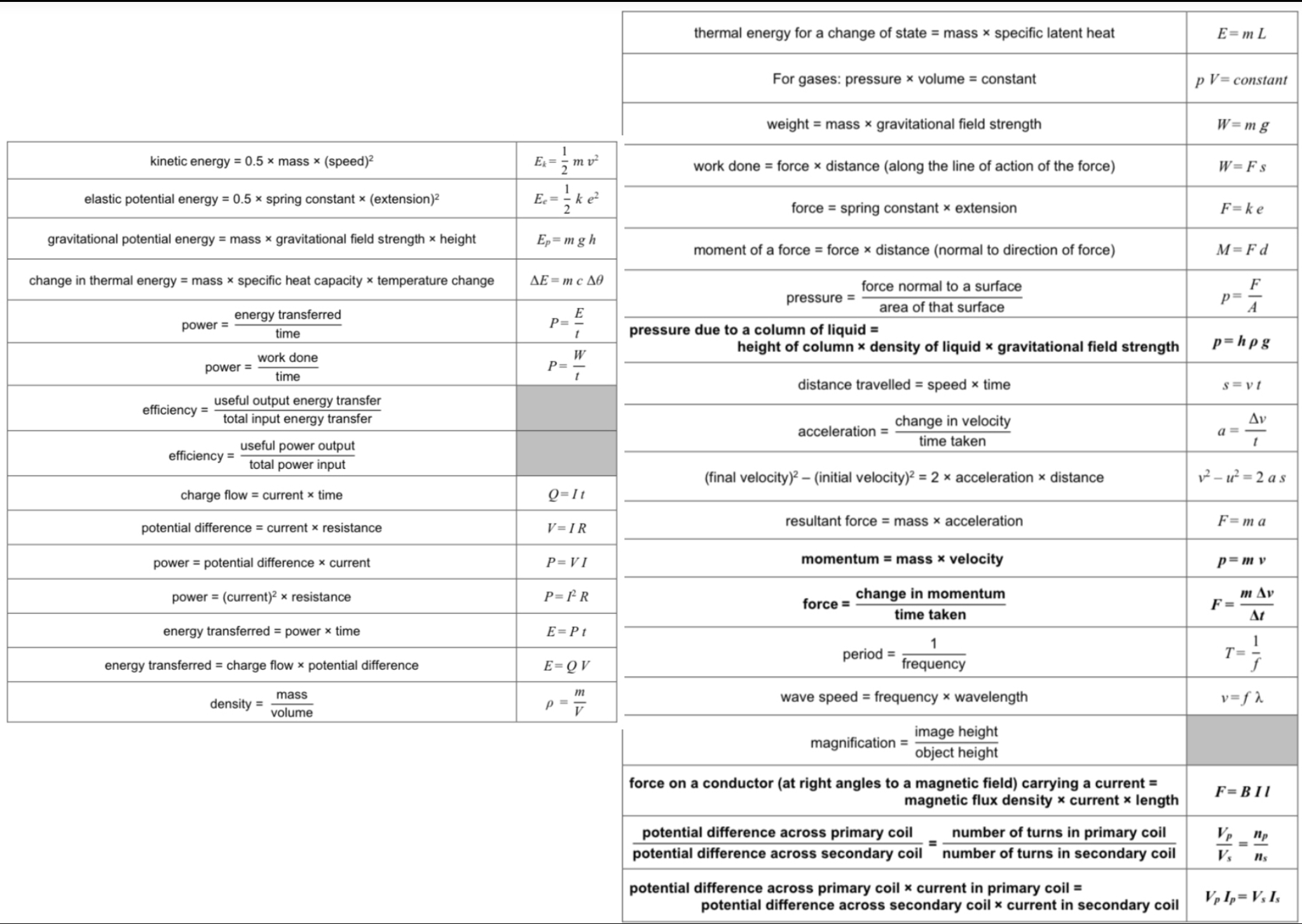
ᴴ What is inertial mass? How is it defined?
Inertial mass is a measure of how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object. It is defined as the ratio of force over acceleration.
What is the symbol that indicates an approximate value or approximate answer?
~
Describe how to investigate the effect of varying the force on the acceleration of an object of constant mass.
- Attach a toy car to a piece of string which is looped around a pulley and has a 100 g mass attached to it on the other end. (The weight of the mass will provide the force acting on the toy car.)
- Draw chalk lines at equal intervals (e.g. every 10 cm) on the desk, and hold the toy car at the starting point.
- Let go of the car. (Because there is a resultant force acting through the string, the car will accelerate along the bench.) Record the experiment, including a timer, using a mobile phone.
- Record the time that the car passes each distance marker - if needed, play the video back and record the times accurately.
- Repeat the experiment several times, but decrease the mass on the end of the string each time and transfer it onto the toy car.
Describe how to investigate the effect of varying the mass of an object on the acceleration produced by a constant force.
- Attach a toy car to a piece of string which is looped around a pulley and has a 100 g mass attached to it on the other end. (The weight of the mass will provide the force acting on the toy car.)
- Draw chalk lines at equal intervals (e.g. every 10 cm) on the desk, attach a mass (e.g. 200 g) to the toy car, and hold it at the starting point.
- Let go of the car. (Because there is a resultant force acting through the string, the car will accelerate along the bench.) Record the experiment, including a timer, using a mobile phone.
- Record the time that the car passes each distance marker - if needed, play the video back and record the times accurately.
- Repeat the experiment several times, but increase the mass attached to the toy car each time.
What is Newton’s Third Law?
Whenever two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal and opposite.
What is the stopping distance of a vehicle?
The sum of the distance the vehicle travels during the driver’s reaction time (thinking distance) and the distance it travels under the braking force (braking distance)
For a given braking force, if the speed of a vehicle is greater, will the stopping distance be smaller or greater?
Greater
Are reaction times the same for everyone?
No
What is the typical range of human reaction times?
0.2 s to 0.9 s
What can affect a driver’s reaction time?
Tiredness, drugs, alcohol and distractions