Magnetic Fields - Gravitational Potential Energy
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
satellite
obj or body that revolves around another body due to the grav attraction to the greater mass
ex. planets are NATURAL SATELLITES
artificial satellite
man-made obj’s orbiting earth or other solar bodies
GPS
a network of 24 satellites
stands for global posi sys
GPS cont’d
finds obj’s based on the intersections of the range of two or three or four satellites
orbital radius
dist from satellite to the center of the larger mass
motion of a satellite depends on
the centripetal force (the force of grav) and the orbital velocity
orbital velocity
the velocity a satellite needs to maintain its orbit
orbits are acc _______________
elliptical and deviates slightly from a circualr path
the orbital speed is the
same for all orbiting objects of the same large mass with the same orbital radius
orbital eccentricity
extent to which an obj is elliptical/deviates from a perf circ
four fundamental forces in nature
weak nuclear force
strong nuclear force
electromagnetic force
force of gravity
weak nuc force
responsible for radioactive decay; changes type of elementary particle (neutron → proton); vv short range
strong nuc force
strongest force but vv short range; holds nucleus together (repulsive forces of protons’ attraction, attraction between e- and p+)
electromagnetic force
responsible for everyday forces like friction (therefore contact forces); infinite range; opposites attract and like-like repels
force of gravity
weakest of all forces but infinite range; matter attracts matter; least understood of all forces
newton’s law of universal grav
there’s a grav attraction btwn any two objects
grav attraction is directly proportional to the masses individually and inversely proportional to the sqr of the radius dist between the centers)
newton’s law of gravitation related to his third law
magnitude of the Fg of mass one on mass two = mag of Fg of mass two on mass one → action rxn pair (therefore oppo directions)
newton’s law of gravitation related to inverse sqr law
Fg is inversely proportional to the sqr of the radius (therefore Fg decreases rapidly as radius increases and vice versa)
when is the grav force noticeable (newton’s law)
when at least one of the obj’s have a mass that is large compared to the dist bwteen the obj centers
[insert pic of earth w arrows that get smaller as it’s drawn further away from earth] what do the arrows represent
grav field vectors
(Fg are force vectors) → g is weaker as the radius increases
field
property of space
an obj influences the sapce around it
the obj producing the the change aka the field is the SOURCE
grav field
grav field is rep by the force/field vectors surrounding obj
a grav field exerts forces on any obj w mass
grav field strength
force of attraction per unit mass of an obj that is placed in a grav field
Fg/m, therefore N/kg (also the “acceleration” bc of newton’s 2nd law)
as dist increases, grav field strength ___
rapidly decreases
derivation of the grav field strength using newton’s uni law of grav
mg = Gm1m2/r² (see first worksheet)
explain how grav field strength can be measured from the center of one obj to another
center of mass can be considered at earth’s center that exerts Fg on a person or obj at dist r (the earth’s radius)
what is the g value dependent on
mass of central planet
dist to centre of mass
G constant
what does g not depend on?
the obj’s own mass
orbital speed formula derivation
see notes
Fc = Fg and isolate for v (Fg = newt formula NOT mg)
geosynchronous
describes an orbit that has an orbital speed that exactly matches Earth’s period of rotation
takes one day to travel around the earth and will appear to pass thru every 24 hours
geostationary
describes an orbit that is geosynchronous but orbits directly over the equator
would appear to remain fixed inthe same pt in the sky at all times
kepler’s three laws of planetary motion
law of ellipses
law of equal areas
law of harmonies
kepler’s laws: law of elipses
each planet moves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse.
BUT its a vv small deviation from circ path
kepler’s laws: law of eq areas
a straight line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in space in equal intervals of time
planet speeds up as it approaches sun and slows as it moves away
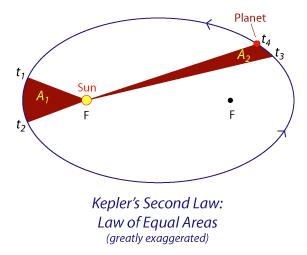
kepler’s laws: law of harmonies
the cube of the average radius r of a planet’s orbit is directly proportional to the square of the period T of the planet’s orbit
proportionality constant would be Cs (kepler’s constant)
Cs (proportionality constant)
tells us that the planet belongs to the solar system
the kepler’s constant
Cs for our sun is 3.35 × 10^18 m³ / s²
everything spins ________ bc of _____
counter clockwise; the big bang
finding velocity from period and vice versa
v = d/t therefore v = 2(pie)r/T
derivation of sun’s kepler’s constant
see notes
singularity
1D pt where the mass and density are infinite
schwarzschild radius
radius of black hole measured from the center to the event horizon
event horizon
the boundary b/w the edge of the black hole and the universe; the pt of no return
escape speed of a black hole
c (speed of light)
3 × 10^8 m/s
the area under a force distance graph
work done
as radius approaches infinity, Fg approaches
0
value for Eg is always negative since
at at infinity, the obj has no potential en since no work needs to be done to separate the bodies as Fg = 0
as r increase, Eg ___________
increases and becomes less negative as more work is done to separate the objects so more potential
as r appraoches infinity, Eg approaches
0 but from the negative direction so the Eg gets bigger
new Eg formula compared to old formula
past Eg formula did not account for the differing g value from higher elevations
at r infinity, Eg2 would be
0
as object ascends, you assume Eg2 is
0 bc it is propelling away from planet and makes change in Eg only equal to Eg1 which becomes positive
derive a formula for the escape speed
see notes
what changes of a rocket as it ascends into space
mass (as it uses up its propellent)
air resistance
for escape speed,
Ek and Eg2 are 0, bc obj will continue to drift off into infinity radius and v = 0 due to no further propulsion
proving that an object’s speed was not enough to escape the bounds of the grav field
if the mag of Eg is greater than the mag of Ek and Et is negative (Eg is neg)
proving that an object had the speed that would escape the bounds of the grav field w some speed left
mag of Ek is greater than mag of Eg and Et is pos
Et = ___ when you have the escape speed w no further propulsion
0
escape speed for balck holes
speed of light (c = 3.00 × 10^something)
bc grav pot en is neg, it is a
potential well and work must be done to get it out
why does Eg increase as the dist increases (unlike force)
bc MORE WORK WAS DONE TO SEPARATE THE MASSES. less work is done when the obj’s are closer toegther
GPE always increases with height either
by increasing positively or decreasing negatively (less and less negative) whether its measured from the perceived lowest pt or infinoity
if the velocity surpasses the escape speed, then
it would follow a curved path and then veer off
principle of equivalence
there’s no way to test whether acceleration occurs bc of a grav force or because their reference frame is accelerating
differences between theory of relativity and newtonian gravity
speed limit in general relativity (the speed of light) while newton says that a change in position of mass in one part of universe instantly changes its grav field in all other parts of universe
general relavity predicts that gravity affects light while newton says that light has no mass therefore exerts no force but light has been observed to bend and distort when passing super large masses
black hole
regions in space where the grav field is so strong that nothing including light can escape and form as one possible product of the end of a stars life
black holes are hard to study because
they are not visible as no light escapes however scientists can still detect them by observing how the surroundings behave
when material gets pulled into black hole, it emits xray and other particles that we can detect on earth
derive for the mass of the sun
use the orbital speed formulas