Psych Unit 4 Exam (Biological Bases of Behavior)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mrs. Rivera's Unit 4 exam— good luck everyone :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

36 Terms
Lobes of the brain
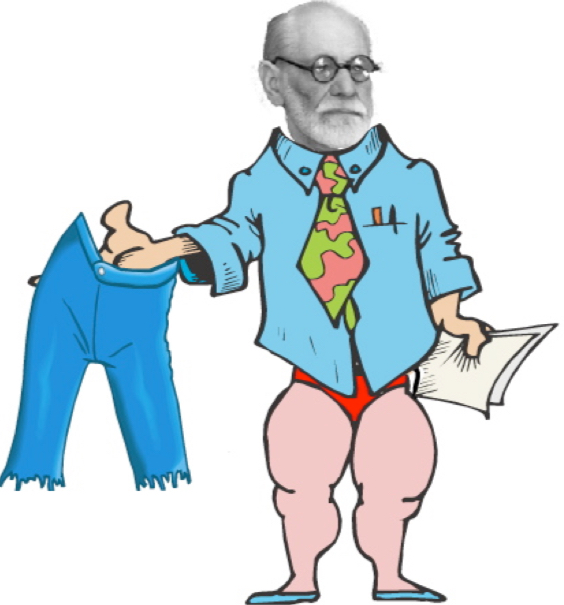
Freud Took Off his Pants
Frontal, Temporal, Occipital, Parietal

Occipital Lobe
processes visual information
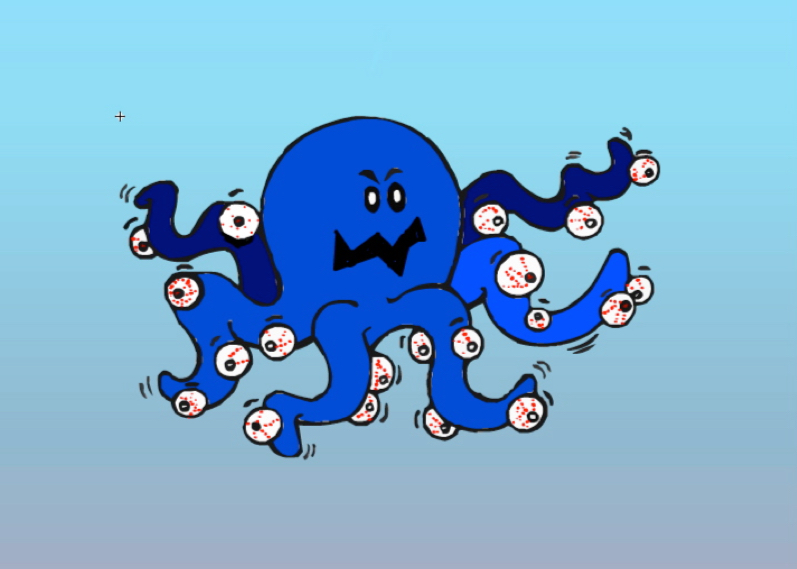

Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory information…
Use a “piranha” fish as your mnemonic. The piranha bites you on the top of the head (where the parietal lobe is located). That’s a sensation the parietal lobe would process.

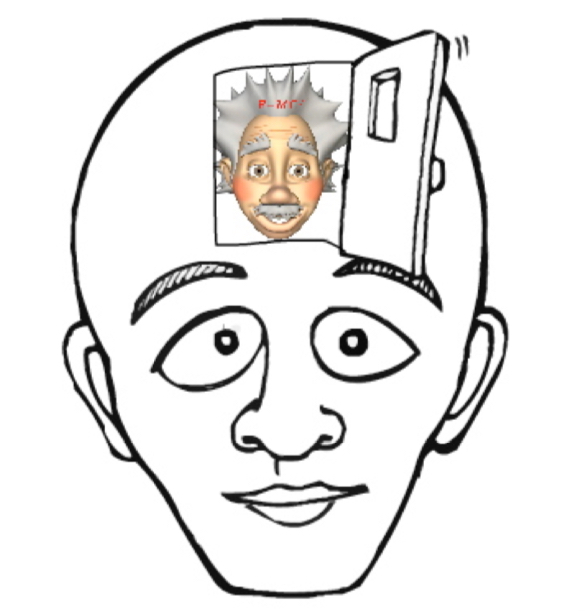
Frontal Lobe
where complex thinking occurs…
Use “front door” as your mnemonic. Put the front door on your forehead and put Einstein (complex thinker) behind the door.
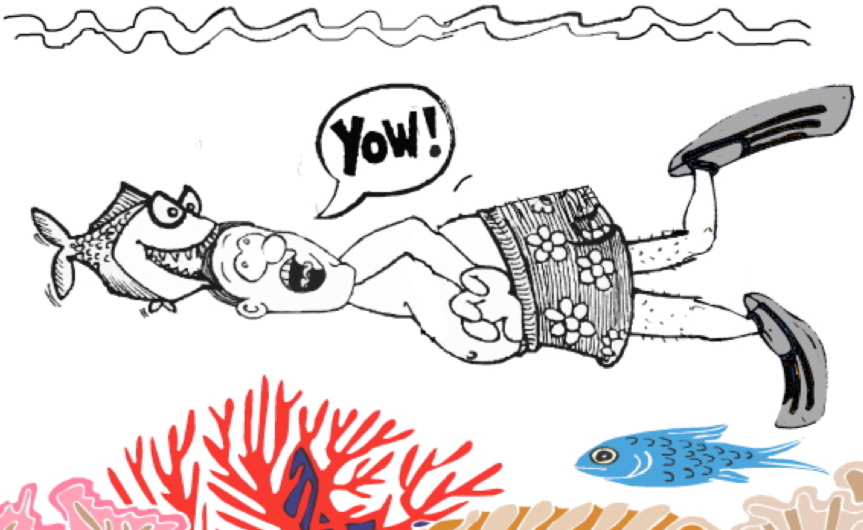
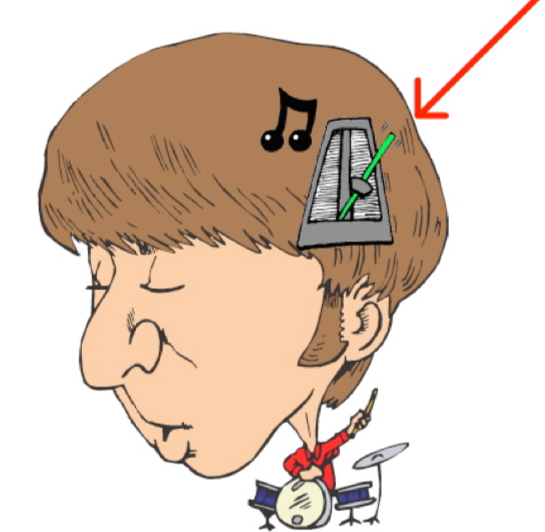
Temporal Lobe
where auditory processing occurs…
Use “tempo” as your mnemonic and picture a metronome above your ear (where the temporal lobe is located)
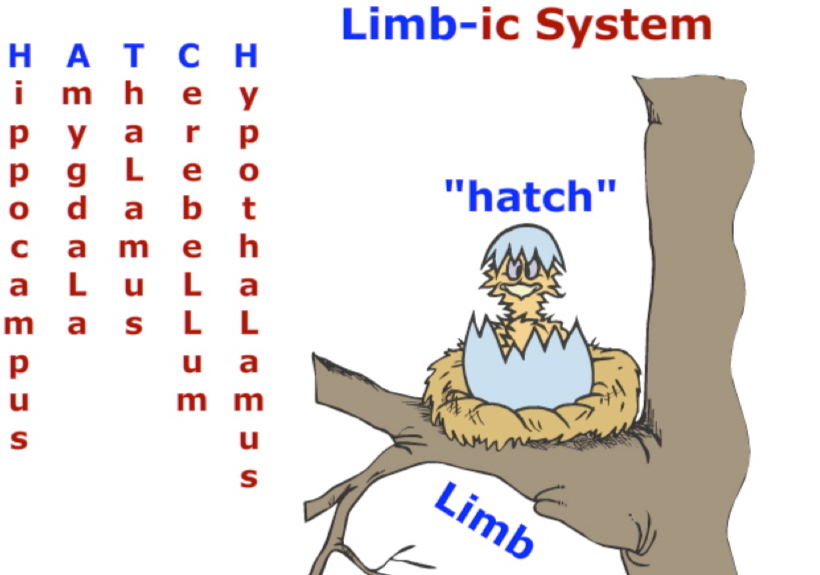
Limbic System
HATCH
Hippocampus, Amygdala, Thalamus, Cerebellum, Hypothalamus
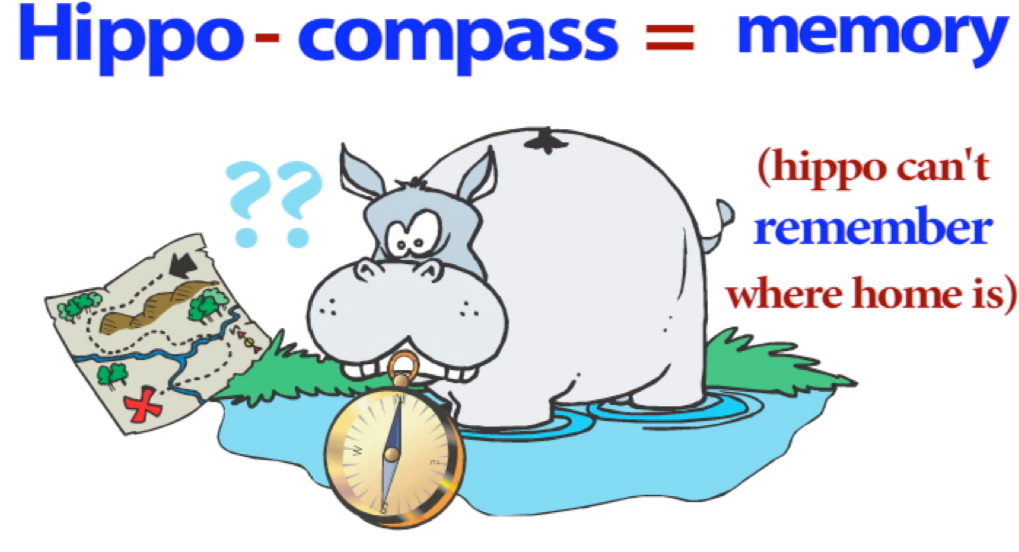
Hippocampus
Involved in memory.
Amygdala
Involved in your fear responses

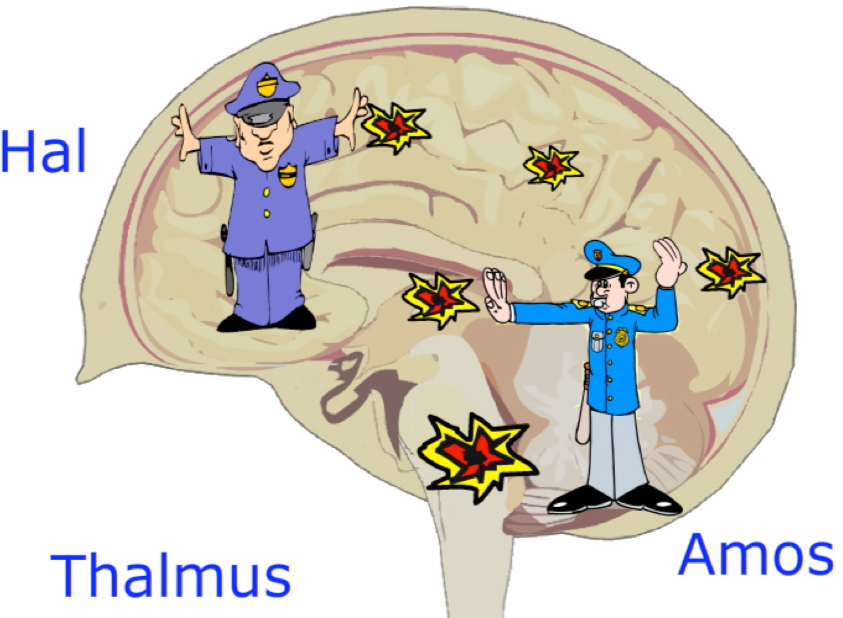
Thalamus
relays information from the body to different areas of the brain for processing…
Picture Hal and Amos as traffic cops.
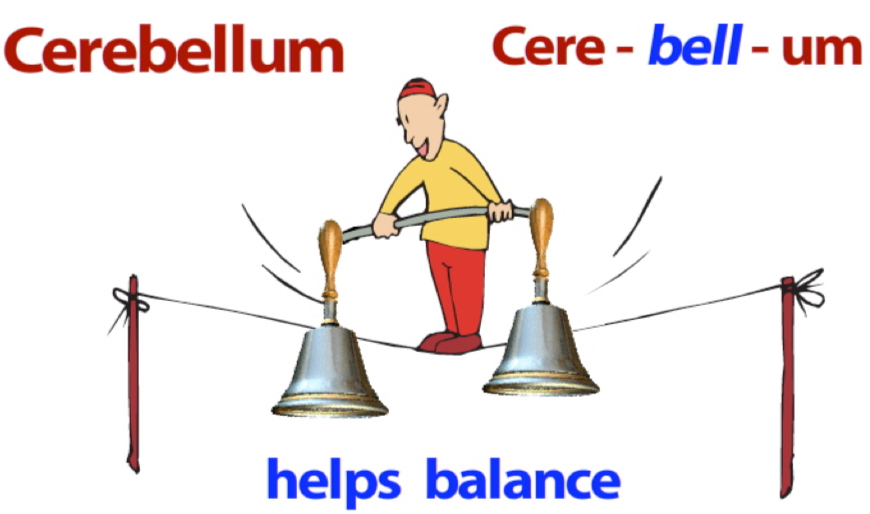
Cerebellum
Involved in helping you maintain balance.
Hypothalamus
regulates many of the body’s metabolic processes, thirst, hunger and body temperature.

The Brain stem
Pavlov’s Really Frickin’ Mad
Pons, Reticular Formation, Medulla

Pons
the part of the brain that regulates waking and relaxing.

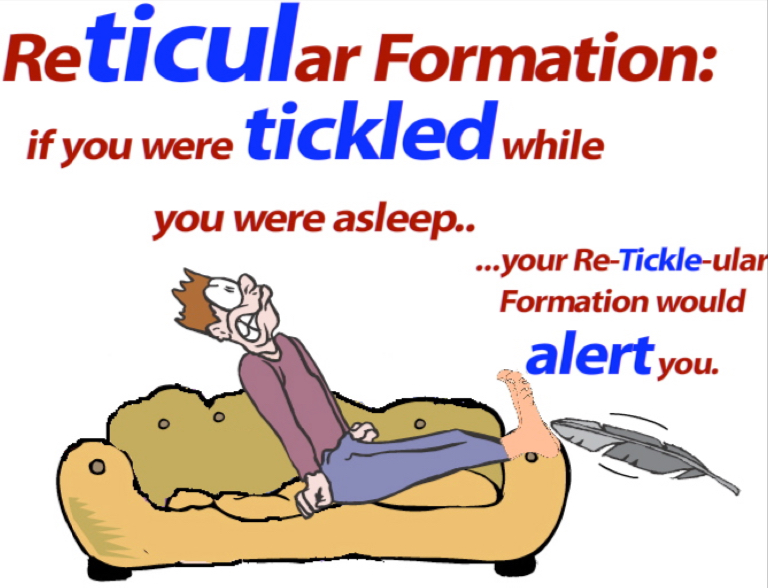
Reticular Formation
involved in motivation and alertness.
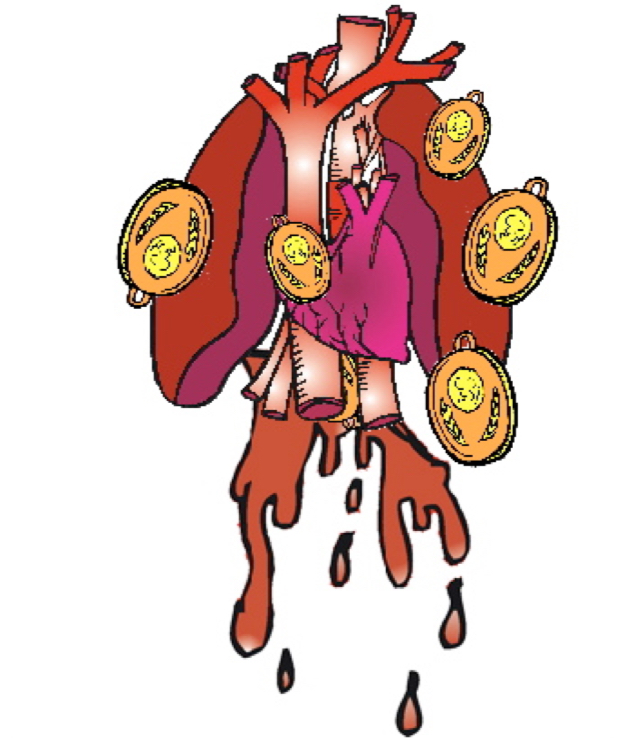
Medulla
regulates the autonomic activity of the heart and lungs.
The Neurons
Damn! Skinner Ate Mice?? Not Very Smart
Dendrites, Soma, Axon, Myelin Sheath, Nodes of Ranvier, Synaptic Vesicles, Synapse
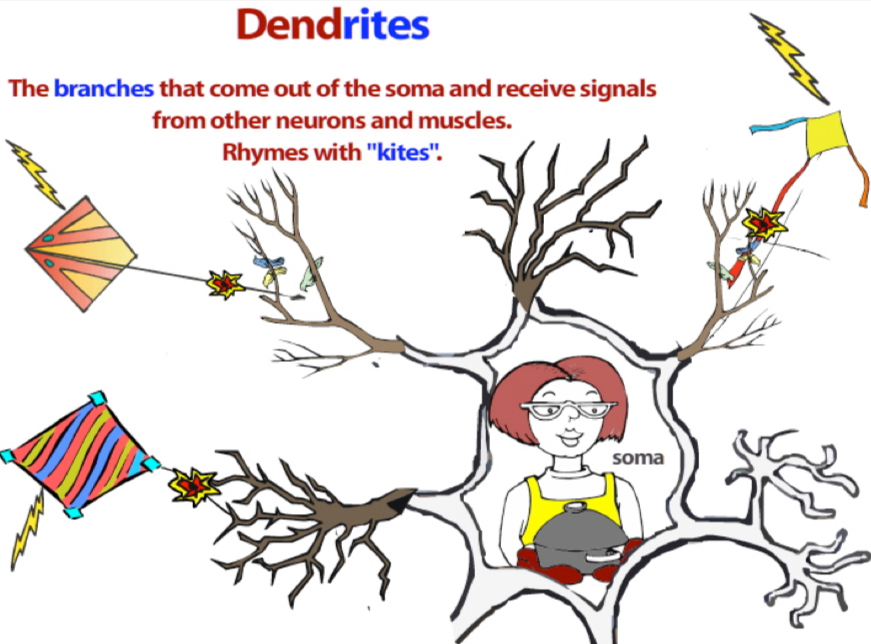
Dendrites
Signals from muscles and other neurons enter the neuron through branches called dendrites.
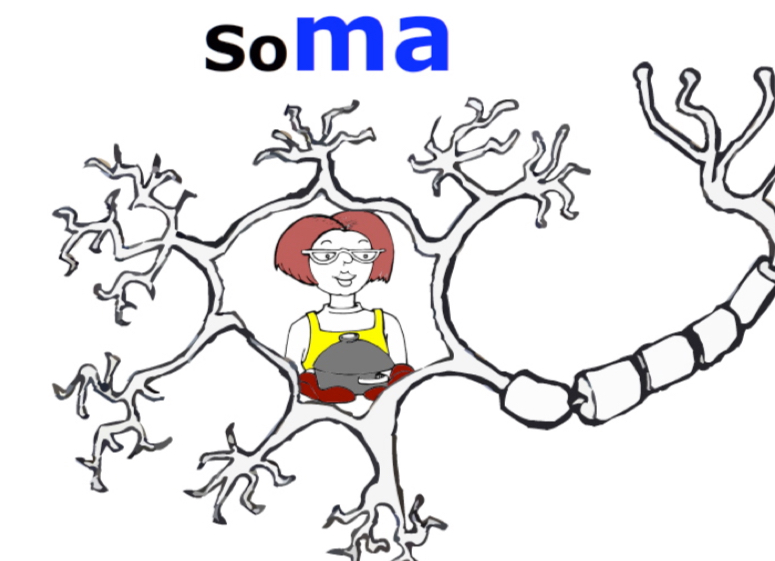
Soma
the cell body of the neuron...
Use “ma” or “someone’s ma” as your mnemonic. Picture your mother inside the cell body.
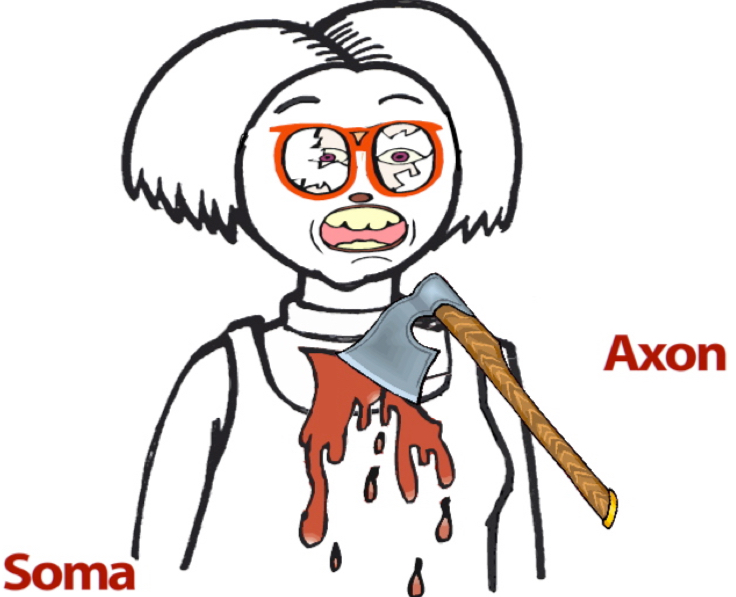
Axon
extends out from the soma.
Myelin Sheath
protects the axon and speed the signal down the axon.

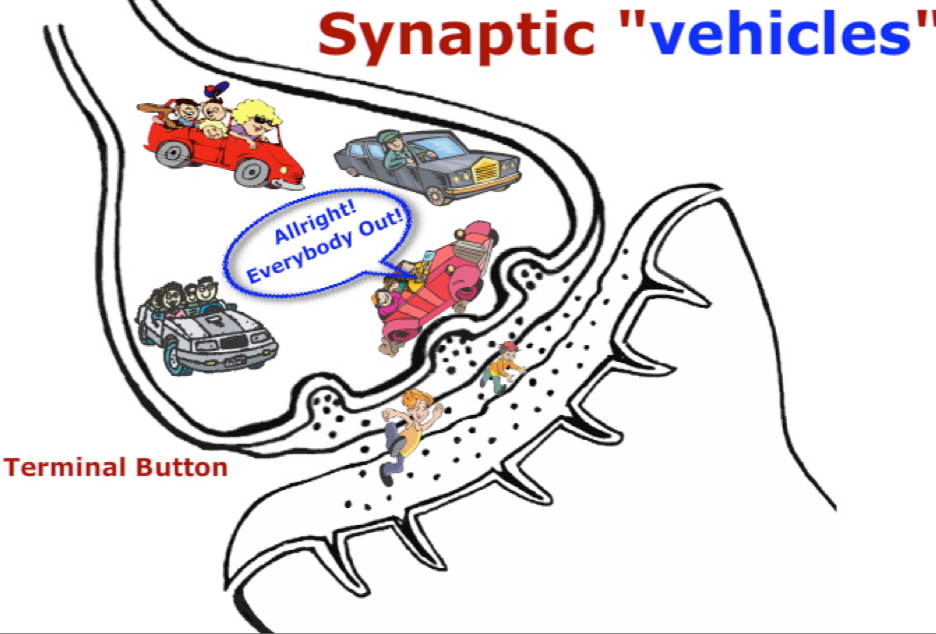
Synaptic Vesicles
found at the end of the axon (which is sometimes called the terminal button). They contain the neurotransmitters.
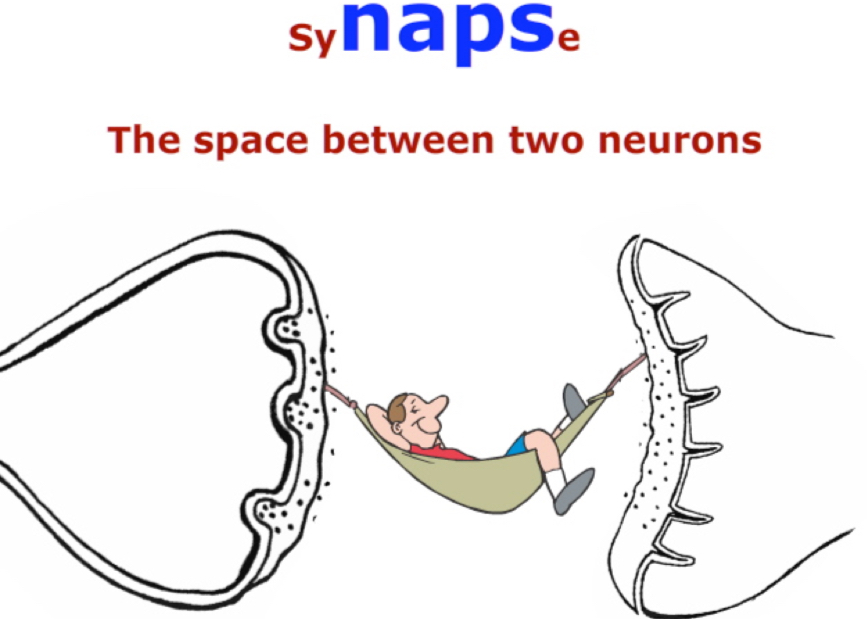
Synapse
found at the end of the axon. It is the space between one neuron and another or between one neuron and a muscle.
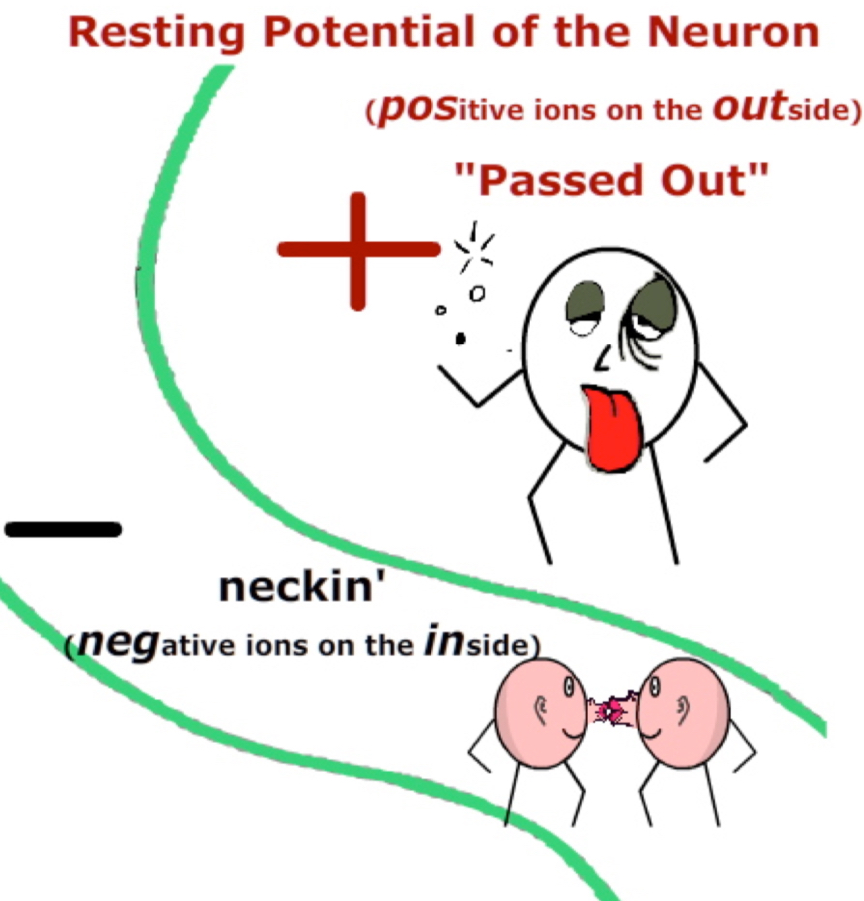
Resting and Action Potential
When the neuron is in its resting state the majority of the ions inside the neuron are negatively charged and the majority of the ions outside the neuron are positively charged.
Neurotransmitters
DASE
Dopamine, Acetylcholine, Serotonin, Endorphins
Serotonin
Low levels of this in the brain are associated with depression.

Acetylcholine
Involved in helping you contract your muscles.

Dopamine: low levels
Associated with Parkinson’s disease.

Dopamine: high levels
Associated with schizophrenia.

Endorphins
involved in blocking pain sensations and in producing “runner’s high”.

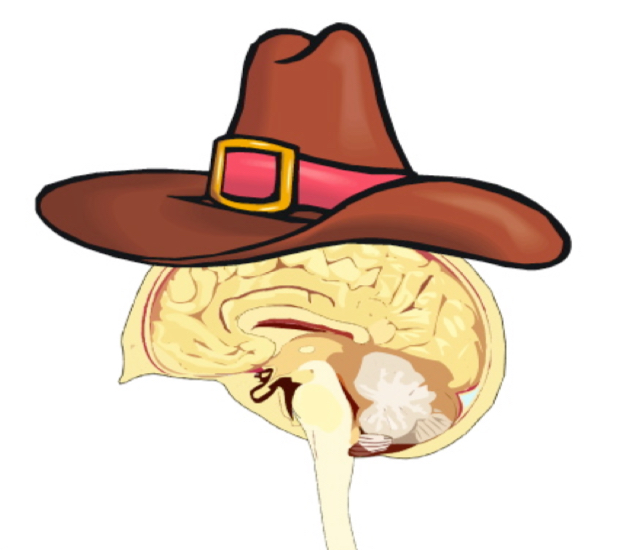
Cortex
Imagine a Texas hat on your head which is covering the outermost part of your brain – the cor"tex".
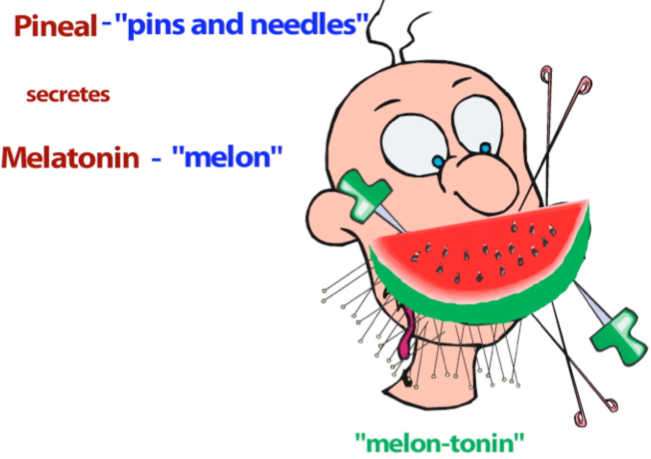
Pineal Gland
secretes melatonin.
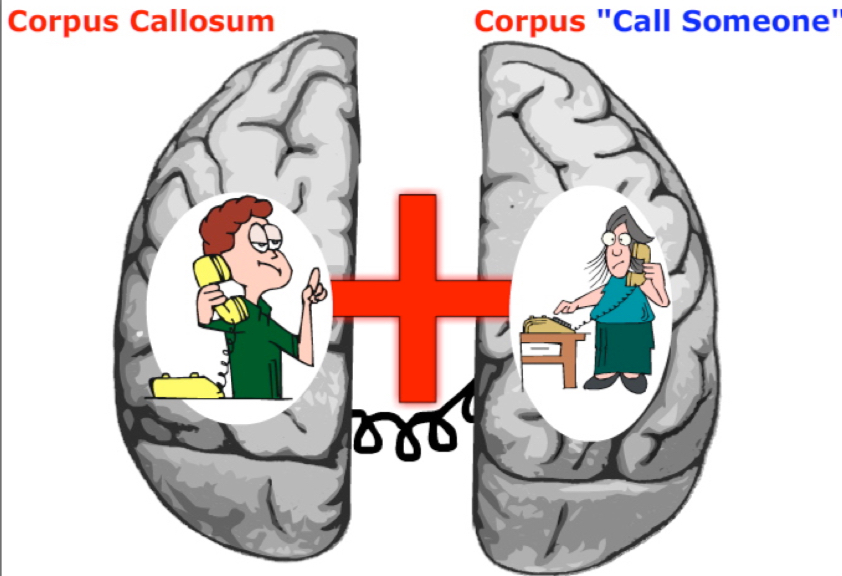
Corpus Callosum
connects the two hemispheres, and it is through the corpus callosum that the two hemispheres communicate.
Thus, the corPLUS CalloSUM and you could also picture “corpus CALL SOMEONE”.
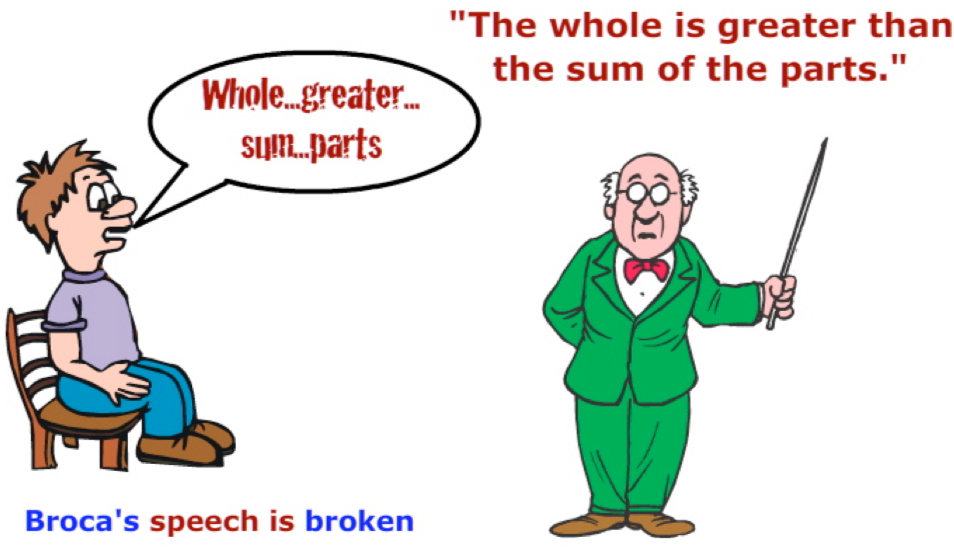
Broca’s area
the area of the brain responsible for producing speech. If it is damaged, you can understand what someone says, but your speech is disjointed.
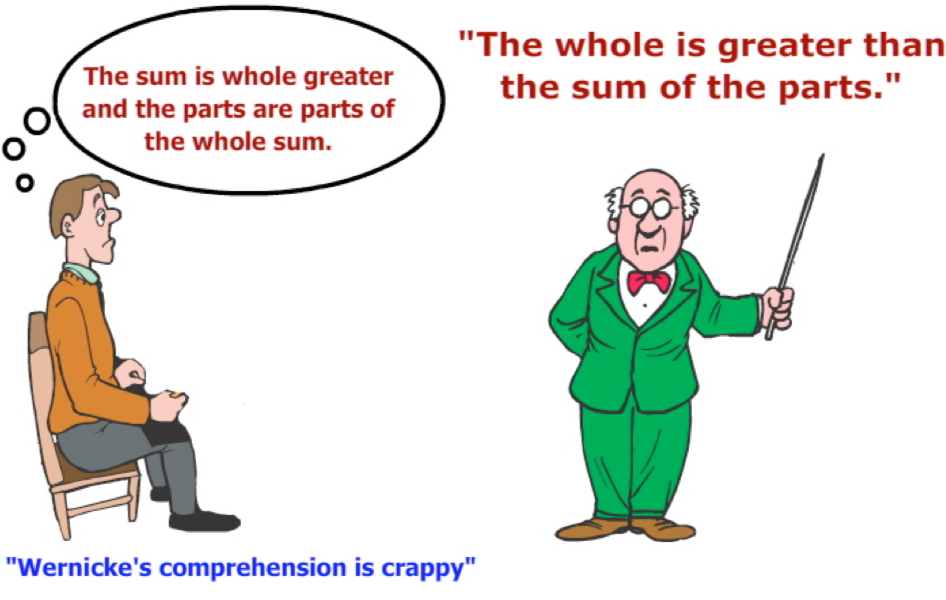
Wernicke’s area
responsible for the comprehension of speech. If you have an aphasia in this area of the brain you are unable to understand and respond to what people are saying to you.
Antagonist Drugs
Have an inhibitory effect in neurotransmitters
Agonist Drugs
Have an excitatory effect in neurotransmitters