Ovarian Neoplasms ~ Stromal Tumors
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Solid adnexal masses that arise from the sex cords of the embryonic gonadal or ovarian stroma.
Sex-cord Stromal Tumors
Sex cord {stromal tumors} types:
Granulosa cell tumor
Thecomas
Fibromas
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors
Sex cord {stromal tumors} are ___________ but _________ on ultrasound.
Hypoechoic, solid
What age group is it most common to find Fibroma in?
Middle age
Menopausal
Postmenopausal
Characteristics that describe a Fibroma.
Solid
Unilateral
Variable size
May be pedunculated – torsion factor
What is the ultrasound appearance of a Fibroma?
Variable attenuation (fibroid)
Hypoechoic mass with substantial attenuation
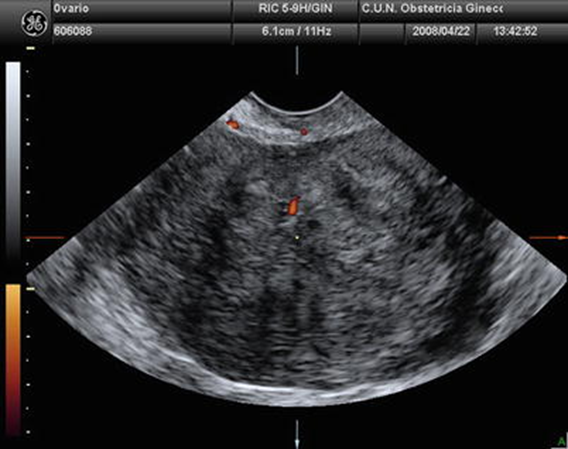
What is this US image?
Ovarian Fibroma
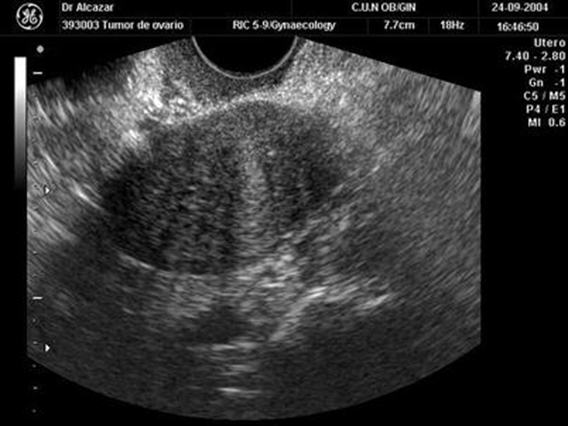
What is this US image?
Ovarian Fibroma
What is Meig’s Syndrome?
Fibroma associated with:
Massive ascites
Pleural effusion {R side}
What is a different diagnosis for Meig’s Syndrome?
Ovarian CA with ascites and pleural effusion
Pseudo-Meig’s syndrome
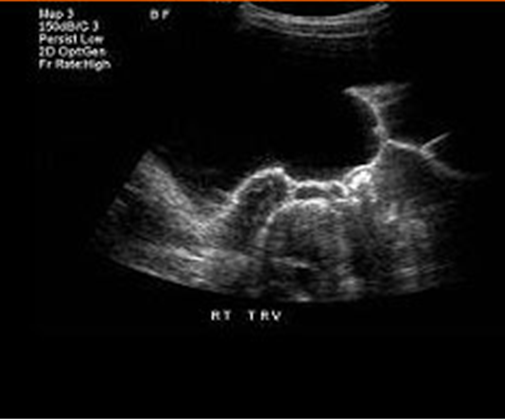
What is this US image?
Meig’s Syndrome
Considered most common hormonally functioning ovarian tumor (estrogen).
Thecomas
Thecomas are usually _______.
Benign
What age group is it most common to find Thecomas in?
Postmenopausal w/ bleeding
Thecomas are occasionally associated with _________ or ______ ___________.
Ascites
Meig’s syndrome
What is the sonographic appearance of a Thecomas?
Hyperechoic
Posterior shadowing
May show areas of necrotic degeneration
Granulosa tumors are ______.
Rare
Granulosa tumors are __________ neoplasms.
Feminizing
Cells resembling the Graafian follicle
Hormone-active estrogenic ovarian tumor
Granulosa tumors are ____ to _____% associated endometrial CA.
5-15%
What age group is it most common to find Granulosa in?
Postmenopausal
What is the sonographic appearance of Granulosa?
Small - predominately solid (Fibroid appearance)
Large – multiloculated and cystic
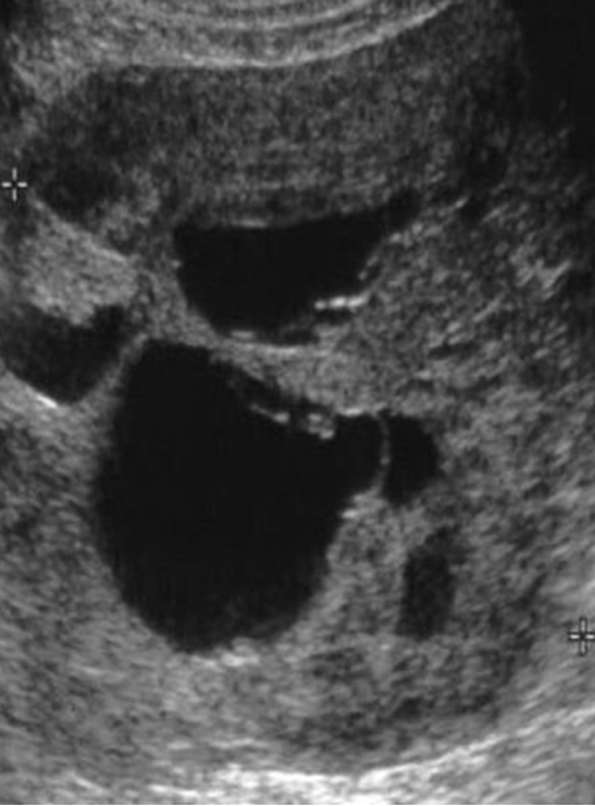
What is this US image?
Granulosa
What are other names for Sertoli - Leydig Cell Tumor.
Arrhenoblastomas
Androblastomas
Androblastomas is a __________ ovarian tumor.
Masculinizing
What age group is it most common to find Sertoli - Leydig Cell Tumor in?
Peak is 25-45 years old
Androblastomas are found _________ and can vary in size.
Unilaterally
What may be a result of Androblastomas?
Amenorrhea
Infertility
What is percentage for malignant potential of an Androblastoma?
22%
What is the sonographic appearance of Androblastomas (Sertoli – Leydig Cell)?
Solid mass
Cystic components
Lobulated – well encapsulated
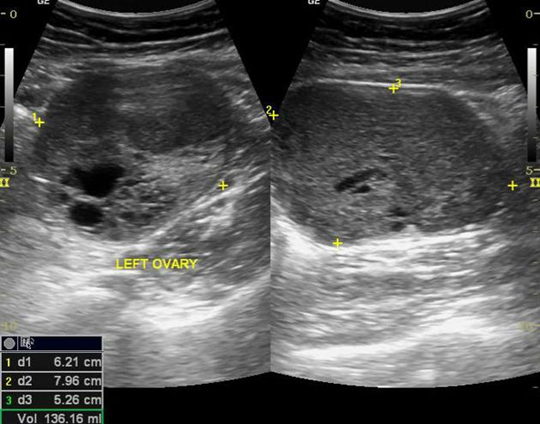
What is this US image?
Sertoli - Leydig Cell Tumor
Metastatic Disease can have spread from:
Bowel
Breast
Endometrium
Melanoma
Lymphoma
What is the sonographic appearance of Metastatic Disease?
Bilateral
Ascites
Solid or “moth eaten” appearance
When mets has spread to bowel, the tumor is known as __________ _______.
Krukenberg’s tumor
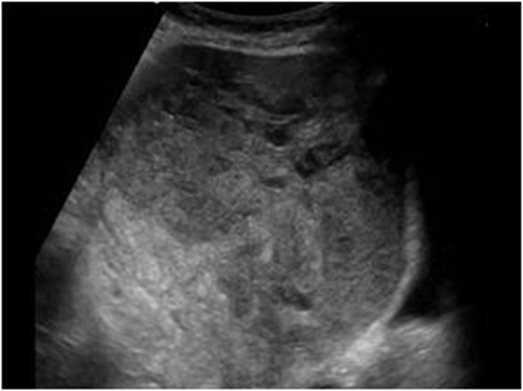
What is this US image?
Metastatic Disease