Cognitive Development in Childhood
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Self-Concept
The ability to understand and evaluate ourselves
gradually emerges
5-18 months, kids can recognize themselves in a mirror
school age, kids can name their own traits
8-10 years, self-image is stable (until you’re a teen)
Jean Piaget
Regarded as the godfather of cognitive development in children
made the most famous theory of cognitive development

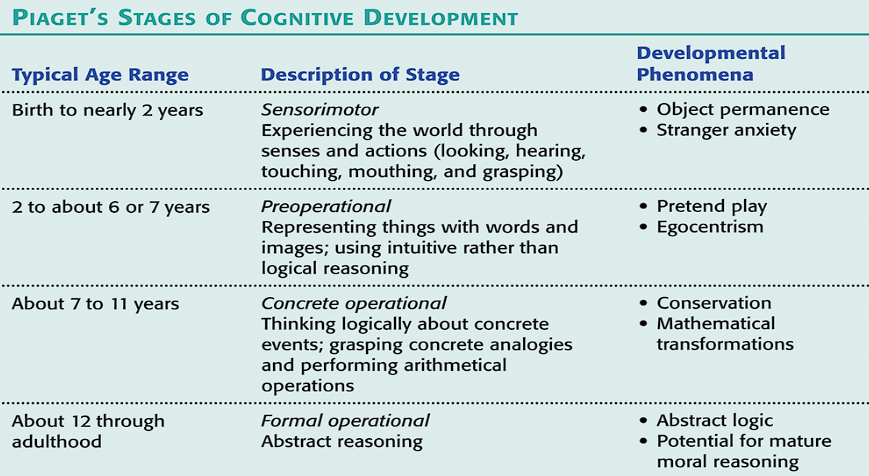
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development
Kid’s minds pass through an upward sequence of stages of cognition
Schemas
Piaget found out that children use ? to organize and interpret info
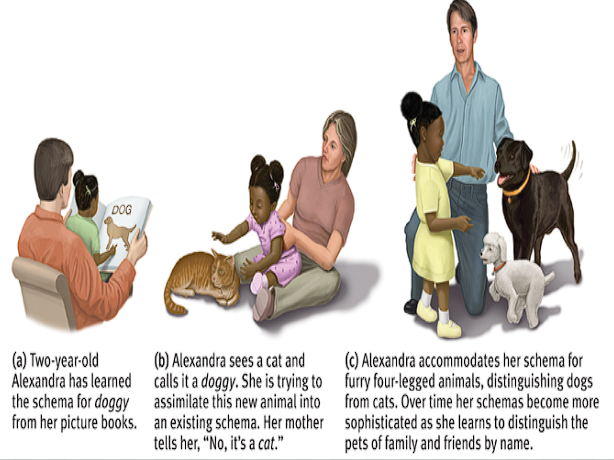
Assimilate
Interpreting new experience in the context of our existing schemas
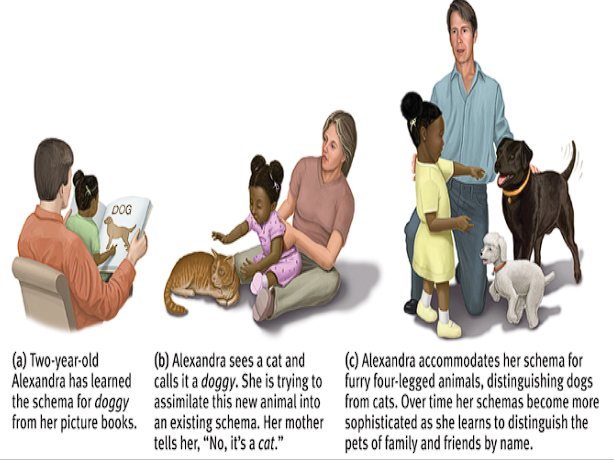
Accommodate
Changing our schemas to adapt to new experiences and info
Sensorimotor Stage
Piaget’s first stage of cognitive development theory
birth - 2 years
sensory, motor, circular
In the sensorimotor stage, kids learn mostly through ? impressions and ? activities
these methods of learning are called ? reactions
Primary Circular Reactions
Using one’s own body to learn
Secondary Circular Reactions
Responding to other people or objects
Tertiary Circular Reactions
Devising different activities to do with objects
kick a ball, put ball into a box, throw the ball, etc
Object Permanence
In the sensorimotor stage, there’s a lack of ?, or the awareness that things exist even when you can’t perceive them

underestimated
Piaget actually ? kid’s abilities since they actually show comprehension of
basic physics
sense of mathematics
and was slightly wrong about the stage being so sequential as they can be continuous
Preoperational Stage
Piaget’s second stage of cognitive development theory
2 years - 6/7 years
Logic
In the preoperational stage, children can use language, but lack ?
Conservation
In the preoperational stage, children lack the concept of ?, understanding that properties like mass and volume stay the same even if the form of the object changes

Egocentric
In the preoperational stage, children are ?, meaning they can’t see other pov’s other than their own
Theory of mind
In the preoperational stage, kids start to develop the ?, allowing them to recognize other’s mental states
Animism
In the preoperational stage, kids believe that inanimate objects have human characteristics, like a stuffed animal having feelings
Artificialism
In the preoperational stage, kids believe that natural events are man-made
Concrete Operational Stage
Piaget’s third stage of cognitive development theory
6/7 years - 12 years
concrete events
In the concrete operational stage, kids begin to be able to think logically about ?
conservation, seriation
In the concrete operational stage, kids begin to understand ? and also ?, or the ability to categorize objects
they also understand reversibility like how 5+6=11 and 6+5=11
less
In the concrete operational stage, kids become ? egocentric
Formal Operational Stage
Piaget’s fourth stage of cognitive development theory
12+ years
not everyone makes it to this stage…
abstract
In the formal operational stage, people can start to think logically about ? concepts, such as virtual reality, symbolism, art, etc
adolescent egocentrism
In the formal operational stage, people start to feel ?, the feeling that one is invincible
spotlight effect
In the formal operational stage, people fall victim to the ?, beliving that everyone is always paying attention to them
scientific thinking
In the formal operational stage, people start to show the ability to use ?
earlier
Most of the abilities Piaget suggested can actually be shown ? than he thought
safe
The fact that young kids are incapable of adult logic keeps them ? as they’re always sticking to their protective parents
Vygotsky
Made an underated theory of cognitive development focused more on social interaction
social environment
Vygotsky’s theory focused on how a child’s mind grows by interacting with their ?
scaffolds
Caretakers and teachers provide ?, or problems that get progressively more difficult
watching, help
Vygotsky believed that children learn best by ? others and receiving ? from peers and role models
words
By age 7, kids think in ? and use them to solve problems
Zone of Proximal Development
Area between what a kid can and can’t do, which forces the kid to just slightly push further beyond their current skill level to improve overall