Psychology keywords (more terms will be added as we learn more)
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For practicing important terms for psychology exam. There are terms and the terms have either a definition or how they fit with psychology because obviously you're not studying the definition of change but rather how its applied in psychology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
External validity
Ecological validity + population validity = external validity
How/if you generalize your findings outside the experiment
Internal validity
How/if you are sure that the independent variable affected the dependent variable
Construct validity
If the test or manipulation actually represents the concept you’re studying
Quantitative research
Using numerical data and statistical methods to study behavior and cognition
Qualitative research
Collecting and analyzing non-numerical data to understand behavior and cognition in a more detailed and subjective way
True experiment
Manipulates an IV and measures a DV and controls all other variables
Participants are randomly allocated
Test a hypothesis
Most of the time quantitative data
Highly stanardized procedure
Quasi experiment
Participants assigned to group based on existing characteristics
IV naturally changes; no manipulation
High ecological validity because IV is not manipulated
Repeated measures design
One sample of participants receive all conditions of the experiment
Independent sample design
Participants are randomly allocated a condition of the experiment
Cross-sectional design
Researchers study multiple groups (e.g., age groups) within the population
Purpose: understand the differences and similarities between the groups
Longitudinal cohort design
Repeated observations or measurements of the same participants at multiple points in time
Purpose: track developmental changes and patterns across different life stages
Matched pairs design
Matching participants based on a certain trait
Order effects
Order effects are changes in participants' responses that result from the order that the conditions are presented to them
Bias
Key concept
Systematic errors in thinking, research, and practice that can affect the validity and reliability of findings
Causality
Key concept
The cause of something
Patterns: Linear, domino, and cyclic causality
Change
Key concept
What changes can us and what can we change
Measurement
Key concept
How you measure data (e.g., quantitative vs. qualitative)
Perspective
Key concept
How you view psychological behaviours and approaches
Responsibility
Key concept
Legal, ethical and professional responsibilities of psychologists
Dependent variables (DV)
The variable that you measure
Independent variables (IV)
The variable that you manipulate
Control variables
The variables that are controlled to stay the same
Hypothesis
A specific, testable statement that predicts the relationship between variables or predicts the outcome of a study
Null hypothesis
The null hypothesis argues that the IV has no effect on the DV
One-tailed hypothesis
Predicts that the effect will go in a specific direction
Two-tailed hypothesis
Predicts that there will be a difference, but it could go either way
Confounding variable
A variable that was not controlled and could potentially make the experiment unreliable
Participant bias
Participants in a study consciously or subconsciously act in a way that they think the experimenter wants them to
Expectancy effect
When a researcher’s expectations are inadvertently conveyed to participants and influence their responses
Social desirability effect
When participants answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others
Researcher bias
When the researcher's beliefs or expectations influence the research design, data collection, or interpretation of the findings
Confirmation bias
The tendency to search for, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms one's preconceptions
Interviewer bias
When the interviewer behavior leads to participants to answer in a certain way
Sampling (selection) bias
When the sample studied is not representative of the population intended to be analyzed
Cultural bias
Judging phenomena through the lens of one's own culture
Ecological fallacy
Assuming that because someone is a member of a cultural group, they share all the traits of the culture
WEIRD samples
Western
Educated
Industrialized
Rich
Democrats
Gender bias
Judging phenomena through the lens of gender
Alpha bias
The exaggeration of the differences between men and women
Beta bias
Minimising differences between the sexes
Publication bias
When journals mostly publish positive findings rather than null or negative results
P-hacking
Various techniques that researchers can use to increase the chances of finding statistically significant results, even if the results are not actually meaningful
Can lead to false reports
Recall bias
When participants do not accurately remember a past event or experience or leave out details
Optimism bias
When you believe that your behavior is better than it is and that you are at a lower risk of health problems than others
Peak-end rule
When people judge an experience based on the peak moment rather than the sum of the experience
Counterbalancing
One group of participants do condition A then condition B. The second group will do condition B then condition A
Single-blind approach
Either the researchers or the participants are unaware of certain details
Double-blind approach
Both the researchers and the participants are unaware of certain critical details
Emic approach
Striving to avoid imposing one's own cultural values and beliefs on other culture
Linear causality
An independent variable is manipulated, and its direct effect on a dependent variable is measured
Domino causality
Cause-and-effect relationships where an effect becomes the cause of another effect
Cyclical causality
Feedback loop for cause-and-effect
The cause leads to an effect that causes the "original cause"
Locus of control
How individuals perceive their control over events in their lives
Interpretivism
Philosophical approach that emphasizes understanding human behavior from the subjective perspective of individuals
Positivism
Advocates for the application of the scientific method to study behavior
Holism
Uses case studies to the bigger picture of a person’s life to understand their behavior
Reductionism
Uses experiments to determine cause-and-effect relationships
Cultural competence
Understanding and effectively interacting with people from different cultures
Reflexivity
When psychologists examine their own biases and preconceptions so that they do not influence their work
Socially sensitive research
Studies in which there are potential consequences or implications, either directly for the participants in the research or for the class of individual represented by the research
Biological perspective
Emphasizes the influence of biological factors on behavior
Cognitive perspective
Examines how mental processes such as thinking, memory, perception, and problem-solving, information processing influences behavior
Psychodynamic perspective
Emphasizes the influence of unconscious processes, early childhood experiences, and interpersonal relationships on behavior (Sigmund Freud)
Humanistic perspective
Focuses on individual potential and stresses the importance of growth and self-actualization.
Emphasizes subjective experiences and the inherent goodness of people
Sociocultural perspective
examines how social and cultural influences affect behavior
Evolutionary perspective
Explores how evolutionary principles, shape behaviors and mental processes that enhance survival and reproduction
Ecological perspective
Emphasizes how environmental factors influence behavior, development, and mental processes
Cross-cultural perspective
(Through the lens of cultural diversity) Explores how culture affects thought patterns, behaviors, and mental health
Inductive research
Gather data then look for patterns then develop theory
Deductive research
Theorize/hypothesize then analyze data then the null hypothesis is disproven or not
T.E.A.M.
Evaluating theories:
Testable
Empirical evidence
Application
Measurable
Duty of care
Psychologists’ legal and moral responsibility to provide quality care to clients
Client autonomy
Psychologists avoid imposing their personal values or influencing the client's decision-making inappropriately
Cultural sensitivity
Psychologists must be sensitive to their clients' cultural, social, and personal contexts
Stratified samples
The sample matches the makeup of the population
Participants from various subgroups of the population are randomly selected
Random samples
Each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected
Opportunity (convenience) samples
Participants are selected based on naturally occurring groups (based on based on their availability e.g. people shopping at your local supermarket)
Snowball sampling
Participants recommend other participants for a study
Self-selected (volunteer) samples
Volunteers responding to an advertisement
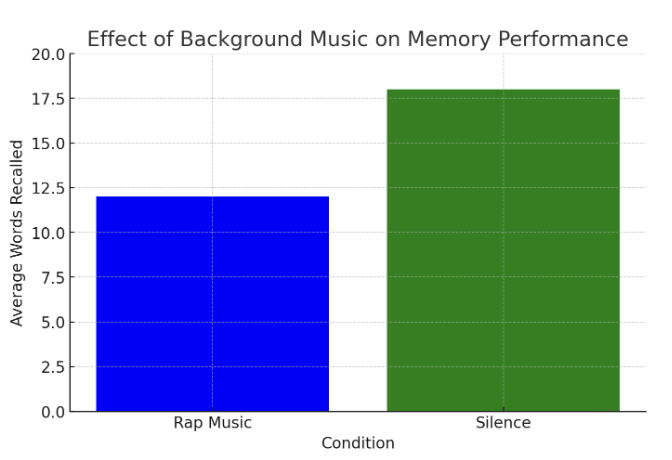
Bar graph
Use bars of different lengths to compare conditions and represent differences in the data
Box and whisker plot
They show the distribution of a dataset
The "box" is the interquartile range [IQR], which is the middle 50% of the data
The line inside is the median.
The "whiskers" go from the box to the smallest and largest data points within 1.5 times the IQR
![<p><span>They show the distribution of a dataset</span></p><p><span>The "box" is the interquartile range [IQR], which is the middle 50% of the data</span></p><p><span>The line inside is the median.</span></p><p><span>The "whiskers" go from the box to the smallest and largest data points within 1.5 times the IQR</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff817c22-5c31-4223-9f1c-d9f06573bb41.png)
Histogram
They look similar to bar graphs but show the distribution of the data
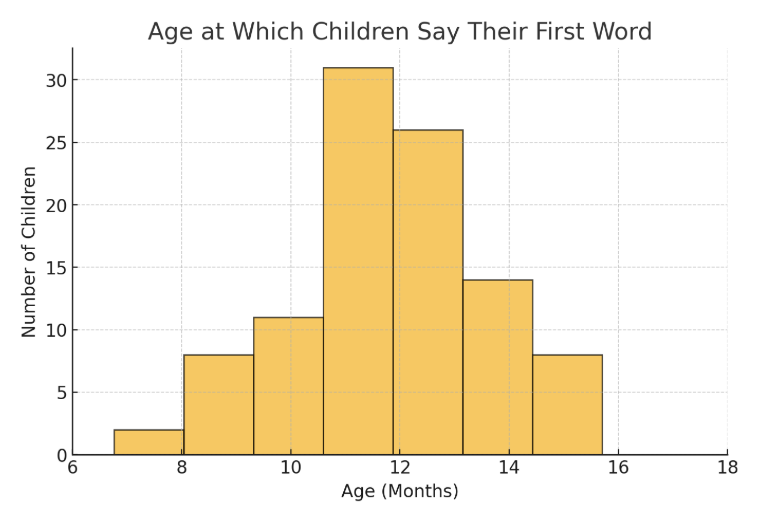
Inferential statistics
Infers properties of a population
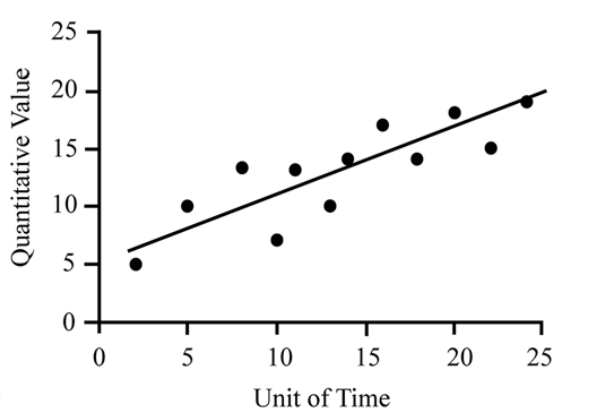
Line graph
Displays the relationship between two variables
Outliers (in data)
Data points that differ significantly from other values in a dataset
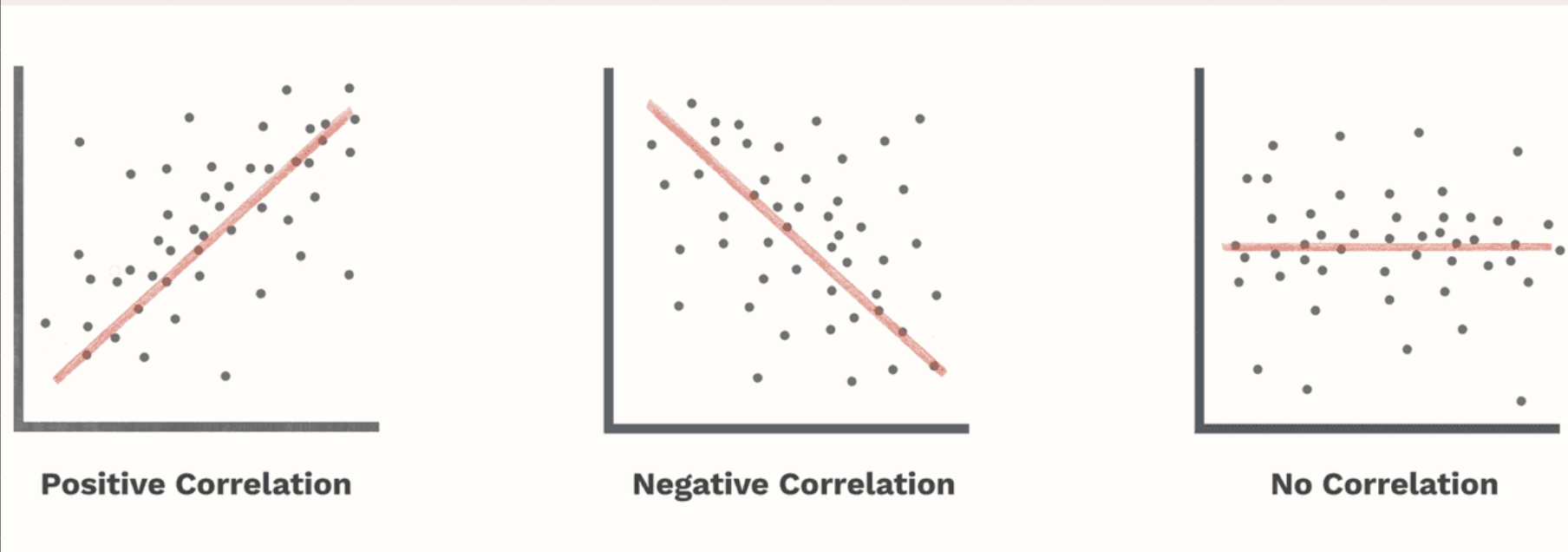
Correlation
The measurement of the extent to which pairs of related values of two variables tend to change together or co-vary
Scatterplot
Graph that shows the relationship between two variables by displaying each data point as a dot
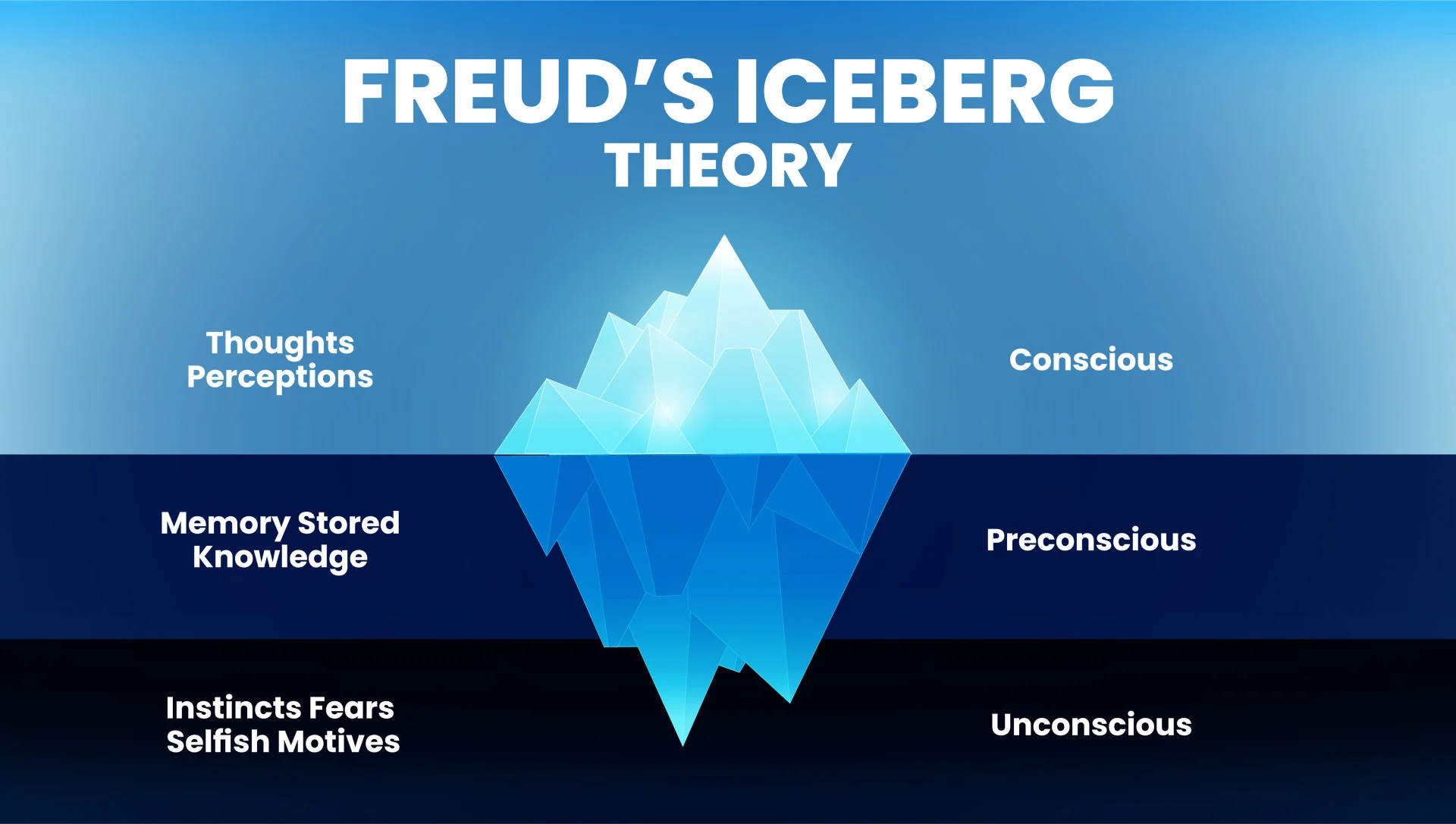
Sigmund Freud
Considered one of the Founding Fathers of psychology
Practiced interpretivism
Founded the iceberg model
Collected qualitative data
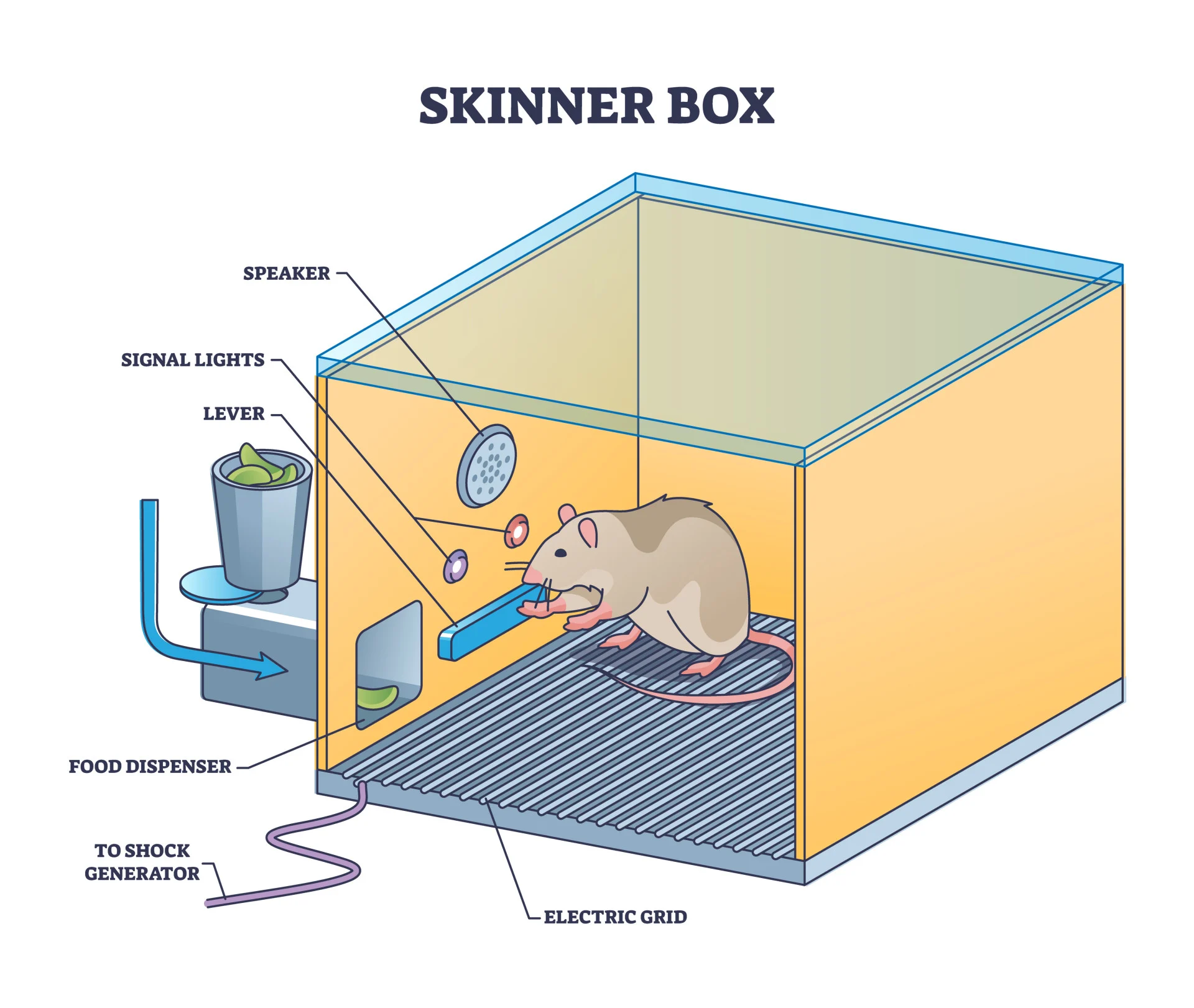
B.F. Skinner
Practiced positivism
Collected quantitive data
Made the Skinner box
Practice effect
When people get better at something because they keep doing it
Fatigue effect
When participants are asked to take part in several conditions of the same experiment and they get tired or bored
Placebo effect
Participants may experience changes in behavior, symptoms, or outcomes simply because they believe they are receiving a treatment
Nocebo effect
Expectation that negative effects will come from a treatment causing them to feel the effects with the effects being real
Screw-you effect
When a participant attempts to figure out the researcher's hypotheses, but only to destroy the study's credibility
Interference effect
When the fact that you have taken part in one condition affects your ability to take part in the next condition
Anecdotal data
Information based on personal stories, individual experiences, or isolated observations
Empirical data
Information obtained through systematic observation or experimentation
Research triangulation
Multiple researchers or investigators independently analyze the data and compare their interpretations
Help minimize bias
Method triangulation
Using multiple research methods or techniques to investigate the same phenomenon
Data triangulation
Using multiple sources of data to study a single phenomenon