MCAT Behavioral Sciences - Sensation and Perception
1/155
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
sensation
a raw signal, which is unfiltered and unprocessed until it enters the central nervous system; performed by receptors in the peripheral nervous system, which forward the stimuli to the central nervous system in the form of action potentials and neurotransmitters
transduction
taking the physical, electromagnetic, auditory, and other information from our internal and external environment and converting this information into electrical signals in the nervous system
Perception
processing this information within the central nervous system in order to make sense of the information’s significance; include both the external sensory experience and the internal activities of the brain and spinal cord
Sensory receptors
are neurons that respond to stimuli by triggering electrical signals that carry information to the central nervous system; may encode multiple aspects of a stimulus
distal stimuli
Physical objects outside of the body that can be sensed
proximal stimuli
Photons, sound waves, heat, pressure, etc. are frequently produced by objects and directly interact with sensory receptors
psychophysics
relationship between the physical nature of stimuli and the sensations and perceptions these stimuli evoke
threshold
the minimum amount of a stimulus that renders a difference in perception
absolute threshold
minimum of stimulus energy that is needed to activate a sensory system
e.g. sweetness (a teaspoon of sucrose dissolved in two gallons of water); light (naked eye may see one candle burning thirty miles away)
threshold of conscious perception
level of intensity that a stimulus must pass in order to be consciously perceived by the brain or reach the higher-order brain regions that control attention and consciousness
subliminal perception
information that is received by the central nervous system but that does not cross this threshold
just-noticeable difference (jnd) threshold
to the minimum change in magnitude required for an observer to perceive that two different stimuli are, in fact, different
e.g. pitch (~3Hz)
discrimination testing
A participant is presented with a stimulus. The stimulus is then varied slightly, and researchers ask the participant to report whether they perceive a change. The difference continues to be increased until the participant reports they notice the change, and this interval is recorded as the just noticeable difference.
Weber’s law
observation that difference thresholds are proportional and must be computed as percentages; discovered by Ernst Heinrich Weber (1795–1878)
Signal detection theory
studies how internal (psychological) and external (environmental) factors influence thresholds of sensation and perception.
noise trials
trials in which the stimulus is presented
catch trials
trials in which the stimulus is not presented
hit (signal detection)
a trial in which the signal is presented and the subject correctly perceives the signal
miss (signal detection)
a trial in which the subject fails to perceive the presented signal
false alarm (signal detection)
a trial in which the subject indicates perceiving the signal, even though the signal was not presented
correct negative (signal detection)
a trial in which the subject correctly identifies that no signal was presented
adaptation
ability to detect a stimulus can change over time; physiological and psychological
eye
specialized organ used to detect light in the form of photons
sclera
white of the eye, thick structural layer that covers much of the exposed eye excpet the cornea
choroidal vessels
complex intermingling of blood vessels between the sclera and the retina
retinal vessels
blood vessels that go to and from the retina
retina
innermost layer of the eye; contains the actual photoreceptors that transduce light into electrical information
cornea
a clear, domelike window in the front of the eye, which gathers and focuses the incoming light
anterior chamber
lies in front of iris
posterior chamber
between iris and lens
iris
colored part of the eye; composed of muscle
dilator pupillae
muscle in iris that opens the pupil under sympathetic stimulation
constrictor pupillae
muscle in iris that contracts the pupil under parasympathetic stimulation
choroid
vascular layer of connective tissue that surrounds and provides nourishment to the retina
ciliary body
produces the aqueous humor that bathes the front part of the eye
aqueous humour
transparent water-like fluid similar to blood plasma, but containing low protein concentrations
canal of Schlemm
where aqueous humor flows into
lens
behind the iris; helps control the refraction of the incoming light
ciliary muscle
parasympathetic control; pulls on suspensory ligaments to change the shape of the lens to focus on image as distance varies
accomodation
focus on an image as the distance varies
vitreous humour
a transparent gel behind the lens that supports the retina
ganglia
collections of neuron cell bodies found outside the central nervous system
projection areas
areas in the brain that further analyse sensory input
photoreceptors
respond to electromagnetic waves in the visible spectrum (sight)
mechanoreceptors
respond to pressure or movement. Hair cells, for example, respond to movement of fluid in the inner ear structure (movement, vibration, hearing, rotational and linear acceleration)
nociceptors
respond to painful or noxious stimuli (somatosensation)
thermoreceptors
respond to changes in temperature (thermosensation)
osmoreceptors
respond to the osmolarity of the blood (water homeostasis)
olfactory receptors
respond to volatile compounds (smell)
taste receptors
respond to dissolved compounds (taste)
retina
a screen in the back of the eye consisting of neural elements and blood vessels; converts incoming photons of light to electrical signals
duplexity/duplicity theory of vision
the retina contains two kinds of photoreceptors: those specialized for light-and-dark detection and those specialized for color detection
cones
eye cells that sense color and fine detail; most effective in bright light, named for the wavelengths at which they have highest light absorption: short (S, blue), medium (M, green), and long (L, red)
rods
eye cells that sense light and dark; most effective in low light; highly sensitive to photons and is somewhat easier to stimulate than a cone cell
rhodopsin
pigment in rods
macula
central section of the retina; contains many cones
fovea
centermost region of the macula, only cones
blind spot/optic disk
region of the retina where the optic nerve leaves the eye, devoid of photoreceptors
bipolar cells
highlight gradients between adjacent rods or cones; synapsed with rods and cones; located in front of rods and cones
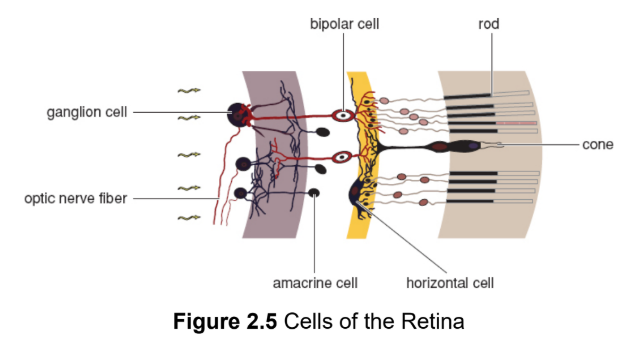
ganglion cells
axons group together to form optic nerve; synapsed with bipolar cells; located in front of rods and cones; output from each ganglion cell represents the combined activity of many rods and cones
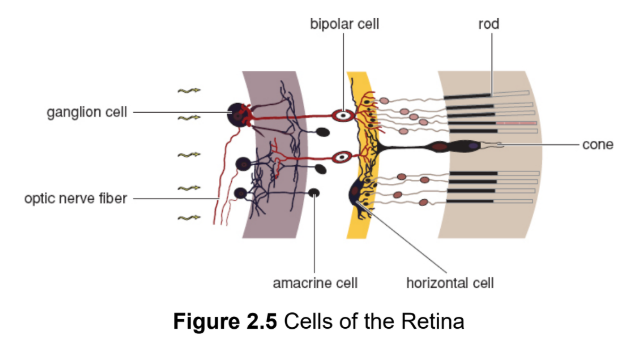
amacrine cells
receive input from multiple retinal cells in the same area before the information is passed on to ganglion cells (a); accentuate slight differences between the visual information in each bipolar cell (edge detection)
horizontal cells
receive input from multiple retinal cells in the same area before the information is passed on to ganglion cells (h); accentuate slight differences between the visual information in each bipolar cell (edge detection)
visual pathways
both the anatomical connections between the eyes and brain and to the flow of visual information along these connections
temporal/nasal retinal fibers
where the photons from an object travel to the opposite side to reach your eyes
left side stimulus → right temporal & left nasal → right side brain
right side stimulus → left temporal & right nasal → left side brain
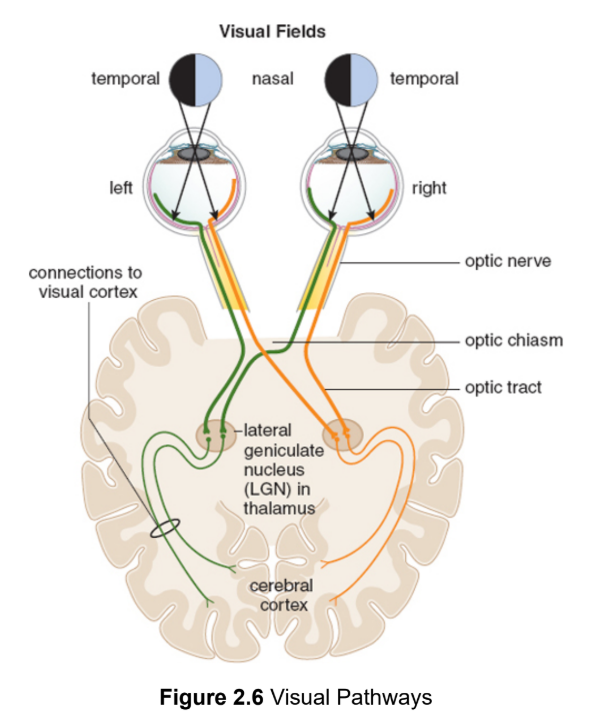
temporal/nasal visual fields
the placement of a stimulus in space relative to each eye is opposite of the retinal path they take
optic chiasm
nasal fibers from the left and right eyes cross paths to route apporpriate information to each side of the brain
optic tracts
reorganized pathways going to each side of the brain
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
in thalamus, synapse with nerves that then pass through radiations in the temporal and parietal lobes to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe
visual cortex
Region of the brain that processes visual information
occipital lobe
Part of the brain at the back of the head, contains visual cortex
thalamus
a well-known connecting and routing center of the forebrain
superior colliculi
control some reflexive responses to visual stimuli and reflexive eye movements; midbrain
parallel processing
the brain’s ability to analyze information regarding color, form, motion, and depth simultaneously, using independent pathways in the brain
form
the shape of an object, but also our ability to discriminate an object of interest from the background by detecting its boundaries
parvocellular (P) cells
in the lateral geniculate nucleus; high spatial resolution but low temporal resolution; colour and low contrast
magnocellular (M) cells
in the lateral geniculate nucleus; high temporal resolution but low spatial resolution; monochrome and high contrast
spatial resolution
ability to detect very fine detail when thoroughly examining an object
temporal resolution
ability to detect a fast-moving object
Depth perception
our ability to discriminate the three-dimensional shape of our environment and judge the distance of objects within it
binocular neurons
specialised cells repsonsibles for comparing the inputs to each hemisphere
feature detectors
detects a very particular, individual feature of an object in the visual field
vestibular sense
ability to both detect rotational and linear acceleration and to use this information to inform our sense of balance and spatial orientation
pinna/auricle
cartilaginous outside part of the ear; channel sound waves into external auditory canal
external auditory canal
directs the sound waves to the tympanic membrane
tympanic membrane/eardrum
vibrates in phase with the incoming sound waves
intensity
corresponds to an increased amplitude
ossicles
three smallest bones in body; in middle ear; help transmit and amplify the vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear
malleus (hammer)
ossicle 1; attached to tympanic membrane
incus (anvil)
ossicle 2
stapes (stirrup)
ossicle 3; rests on the entrance to cochlea
Eustachian tube
connects auditory canal to nasal cavity; helps equalize pressure
between the middle ear and the environment
bony labyrinth
hollow region of the temporal bone containing the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals
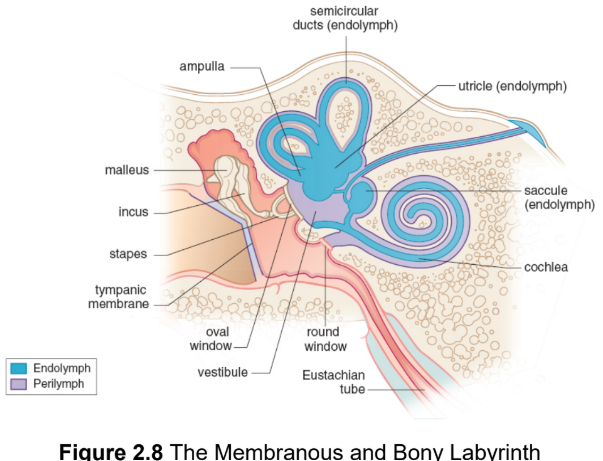
membranous labyrinth
a continuous collection of tubes and chambers inside the bony labyrinth; filled with endolymph
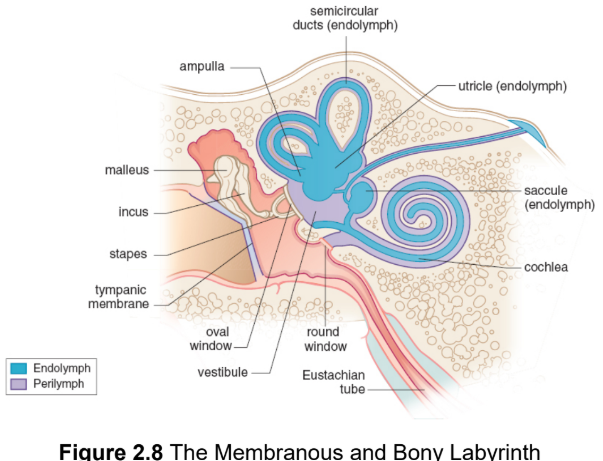
endolymph
a potassium-rich fluid that fills mebranous labyrinth
perilympth
suspends membranous labyrinth in bony labyrinth; transmits vibrations from the outside world and cushions the inner ear structures in scalae
cochlea
a spiral-shaped organ that contains the receptors for hearing, divided in three scalae
organ of Corti
hearing apparatus on basilar membrane in middle scala; composed of thousands of hair cells, which are bathed in endolymph; transduce the physical stimulus into an electrical signal
basilar membrane
stiff structural element within the cochlea of the inner ear that separates two scalae
tectorial membrane
relatively immobile membrane over the organ of Corti
round window
a membrane-covered hole in the cochlea, permits the perilymph to
actually move within the cochlea