Chemistry of Life: Anatomy and Physiology Honors
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Define Element
The simplest form of matter, and cannot be broken down to other substances.
What are humans made of?
Elements
What six elements make up the majority of the human body?
CHONPS: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur
What is the significance of Oxygen?
Part of water, and is needed for cellular respiration
What is the significance of carbon?
It is the backbone of all organic molecules
What is the significance of hydrogen?
It is found in nearly all compounds in the body
What is the significance of Nitrogen?
It is a part of protein and nucleic acids
What is the significance of phosphorus?
In bones, teeth, nucleic acids and ATP
What is the significance of sulfur?
It is a part of some proteins
Define Trace Elements
A chemical element of a minute quantity, in a trace amount.
Define Atoms
The smallest components of elements, they are made of protons, neutrons and electrons
Protons
Has a positive charge and are in the nucleus.
Neutrons
Has no charge and is in the nucleus
Electrons
Has a negative charge and orbit the nucleus
What do protons determine?
They determine the elemental identity of the atom
What do neutrons determine?
They determine the mass of the atom
What do electrons determine?
They determine what chemical bonds the atom will have with other atoms
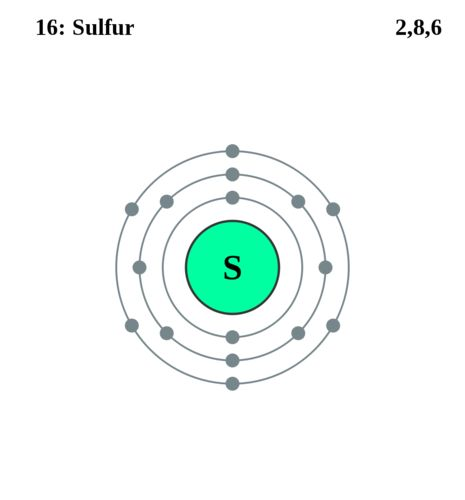
Electron shell
Used in chemistry. It shows electrons and how they interact during chemical bonding.
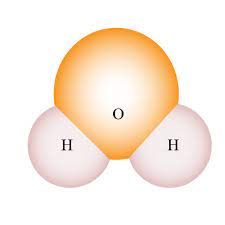
Space filling
Used in bio class. It shows the molecular shape and interactions between molecules. Draw as a cloud to depict electrons rapid movement
Neutral Atoms
Have an equal number of protons and electrons. The positive and negative charges cancel out.
Ions
An atom that loses or gains an electron, making it charged.
Cation
Losing an electron. Is positively charged.
Anion
Gaining an electron. Is negatively charged.
Electrolytes
An ion that is found in body cells or fluids.
Compounds
Single molecule made of two or more elements. Like water, and carbon dioxide
Mixtures
Compounds and elements are in the same place, but not chemically combined. Like urine and tears
Chemical bonding
A force of attraction between two atoms based on the sharing or transfer of electrons.
Ionic bond
An attraction between oppositely charged ions; formed when electrons are transferred
Covalent bond
Formed by two or more atoms sharing electrons
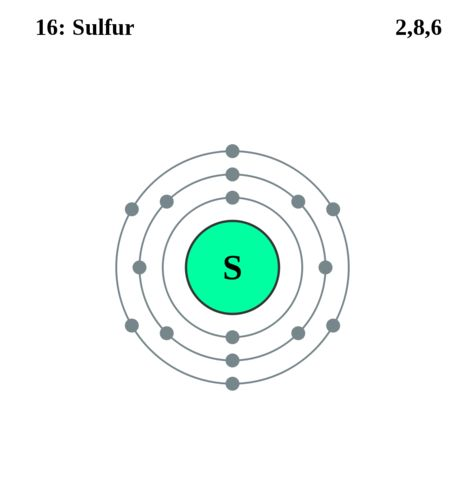
Electron shell
A way to draw a covalent bond.
The shared electrons are shown in a diagram
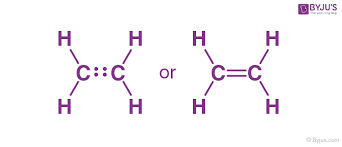
Structural
A way to draw a covalent bond.
The bonds are shown with lines
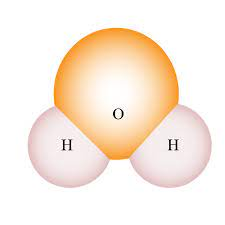
Space filling
A way to draw a covalent bond.
Electron clouds are merged together.
Single bond
A type of covalent bond. One pair of electrons are shared.
Double bond
A type of covalent bond. Two pairs of electrons are shared.
Triple bond
A type of covalent bond. Three pairs of electrons are shared.