Energy, power and resistance
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Ohm’s Law
The potential difference across a component is directly proportional to the current in the component as long as its temperature remains constant
Electrical Resistance
A property of a component calculated by dividing the potential difference across it by the current in it (ratio)
Resistance equation
R = V/I
What is the sequence of events if the EMF in a circuit is increased?
Temperature increases, the positive ions in the wire vibrate more, increasing the resistance of the wire
Resistivity
A property of a material, measured in Ωm, defined as the product of the resistance of a component made of the material and its cross-sectional area dived by its length
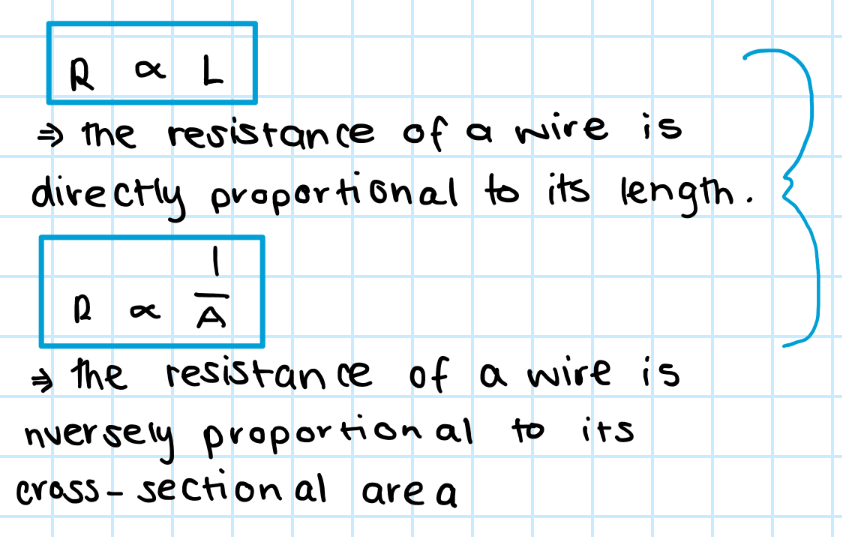
Relationships between resistance and length or cross-sectional area
R is directly proportional to length
R is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area
Resistivity equation (at constant temp)
ρ = RA/L
4 factors that affect resistance of a wire
Temperature
Material
Length
Cross-sectional Area
Resistivity order of magnitude in different types of conductors
Good conductors - 10^-8 Ωm
Semiconductors
Insulators 10^16 Ωm
NTC
Negative Temperature Coefficient
resistors where the as the resistance decreases, the temperature increases
Resistance in series
R = R1 + R2 + …
Resistors in parallel
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + …
I-V Graph of a fixed (ohmic) resistor

I-V Graph of a filament lamp (non-ohmic component)

I-V Graph of a Diode (non-ohmic component)

I-V Graph of a thermistor (non-ohmic resistor)

Power Equation excluding R
P = VI
Power equation excluding V
P = I²R
Power equation excluding I
P = V²/R
Electrical power definition
the rate of energy transfer by each electrical component
Calculation for energy transferred (work done)
P = W/t → W = Pt
P = VI
∴ W = VIt
2 factors affecting energy transferred to a device
the power of the device
how long the device is used for
The kilowatt-hour
the energy transferred by a device with a power of 1kW operating for a time of 1hour
What is 1kWh in joules
1000 × 3600
= 3.6MJ
SI units equation for energy transferred (J)
power of device (W) x time for which device is used (s)
kWh equation for energy transferred (kWh)
power of device (kW) x time for which the device is used (h)