Computer science AS
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Denary numbers
Base-10 number system
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
Binary number
The binary number system is base-2. Each binary digit is written with either of the symbols 0 and 1.
Bit
A digit in the binary number system written using either of the symbols 0 and 1
Byte
A group of eight bits treated as a single unit
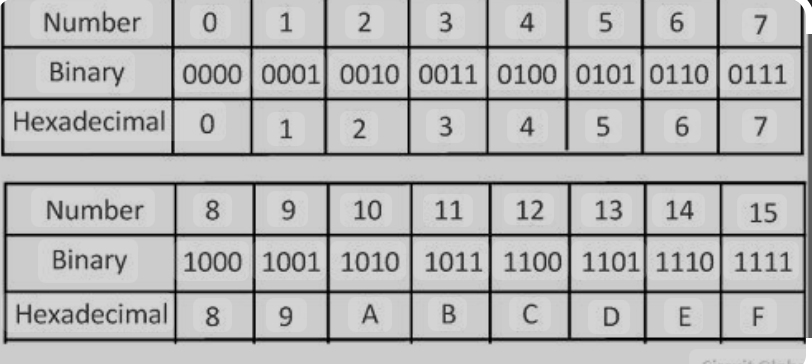
Hexadecimal
These are base-16 numbers and each digit is represented by the symbols: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F
Nibble
A group of four bits
Binary, denary and hexa conversions
Binary prefix
Examples are kibi, Mebi, gibi,and tebi representing factors of 2^10, 2^10, 2³0 and 2^40 respectively to define the magnitude of a value

two’s complement
Two's complement is a method for representing signed (positive, negative, and zero) integers in binary, and is the most common way computers handle these numbers. It uses the most significant bit (leftmost bit) as a sign bit, where 0 indicates a positive number or zero, and 1 indicates a negative number.
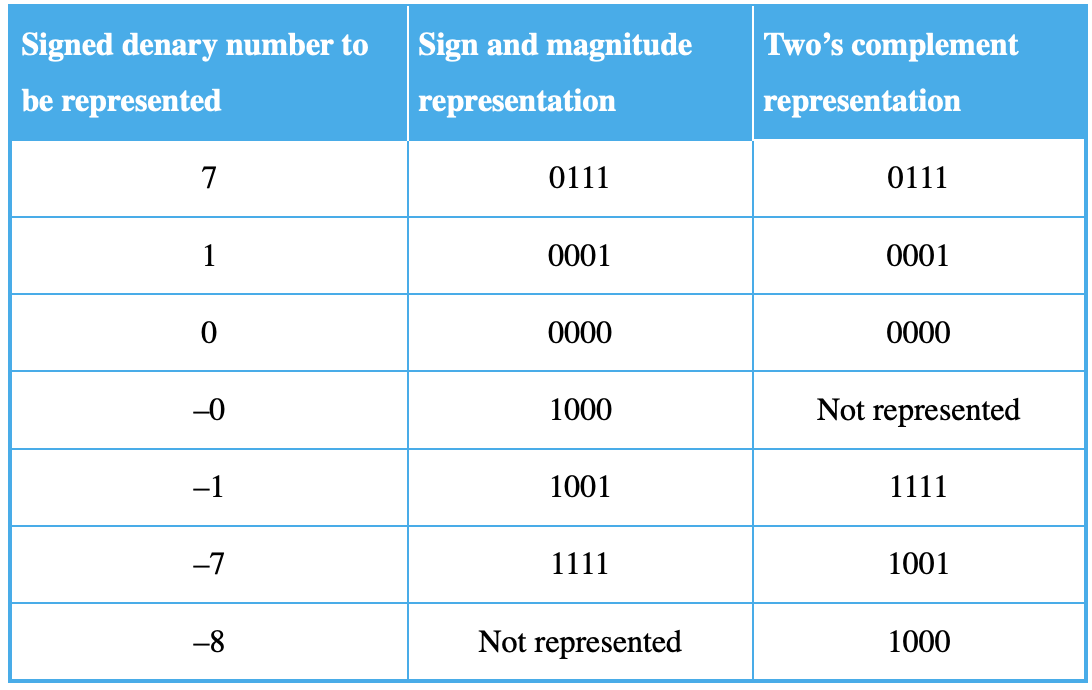
One’s complement
One's complement is a method of representing negative binary numbers where each bit of the number is inverted
Binary arithmetic
Binary arithmetic refers to the mathematical operations performed on binary numbers, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, using the base-2 numeral system. goes from right to left.

overflow
In computer science, an overflow occurs when a calculation produces a result that exceeds the maximum value that a variable or data type can hold. This often leads to unexpected behavior in programs, potentially causing crashes, incorrect results, or even security vulnerabilities.
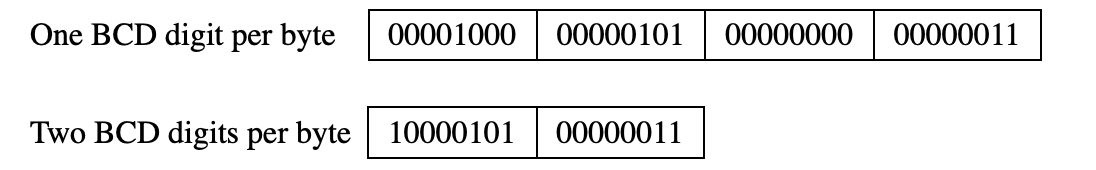
Binary coded decimal
Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) is a way to represent decimal numbers in a digital system using binary digits (bits). Each decimal digit (0-9) is encoded with a four-bit binary number.BCD is often used in applications requiring precise decimal arithmetic, such as calculators, cash registers, and accounting systems.
packed BCD
Packed Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) is a way to represent decimal numbers in binary format where two decimal digits are stored within a single byte (8 bits). Each 4-bit nibblewithin the byte represents a single decimal digit, allowing for more efficient storage compared to unpacked BCD,where each digit occupies a full byte.
BCD arithmetic

ASCII code(American standard Code for information Interchange)
a character encoding standard for electronic communication that uses numeric codes to represent alphabetic and control characters. ASCII assigns a unique numerical value to each character, allowing computers and devices to communicate text.

Unicode
a standard for character encoding that aims to provide a unique number for every character in every language, enabling consistent text representation across different systems. Unicode is designed to be comprehensive and includes characters from various writing systems, symbols, and emoji, enhancing global communication.
drawing object
a graphical element in computer graphics that can be manipulated, such as shapes, text, or images, often used in design software and presentations.
vector graphic
a type of digital image created using mathematical equations rather than pixels. Vector graphics are scalable without loss of quality, making them ideal for logos, illustrations, and graphic design. They maintain clarity at any size, allowing for precise adjustments and edits.
drawing list
a collection of drawing objects used in computer graphics to organize and manage graphical elements, enabling efficient rendering and manipulation in design applications.
property
a defined characteristic or attribute of a drawing object, such as its position, size, color, or style, that affects its appearance and behavior in a graphical context.
Bitmaps
are digital images composed of pixels, where each pixel represents a color. Bitmaps are resolution-dependent, meaning they can lose quality when scaled.
picture element (pixel)
the smallest unit of a digital image, representing a single point in the graphic, with a specific color and intensity.
colour depth
the number of bits used to represent the color of each pixel in a bitmap image, determining the range of colors that can be displayed.
bit depth
refers to the number of bits used to represent each pixel's color information in a digital image. Higher bit depth allows for more colors and smoother gradients.
image resolution
describes the amount of detail an image holds, typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or as the total pixel dimensions (width x height) of the image. The number pixels in an bitmap file. as product of its height and width values.
Screen resolution
the product of width and height values for the number of pixels that the screen can display.

file header
A file header is a set bytes at a bitmap file which identifies a file and contains information about the coding used

analogue data
data obtained by measurement of a physical properties which can have any value from continuous range of values
digital data
data that has been stored as a binary value which can have one of a discrete range of values
sampling
taking measurements at regular intervals and storing the value
sampling resolution
the number of bits used to store each sample
sampling rate
the number of apples taken per second
lossless compression
coding techniques that allow subsequent decoding to recreate exactly the original file.a type of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data, without any loss of information.
lossy compression
coding techniques that cause some information to be lost o that the exact original file cannot be recovered in subsequent decoding.a data compression technique that reduces file size by permanently discarding some of the original data.
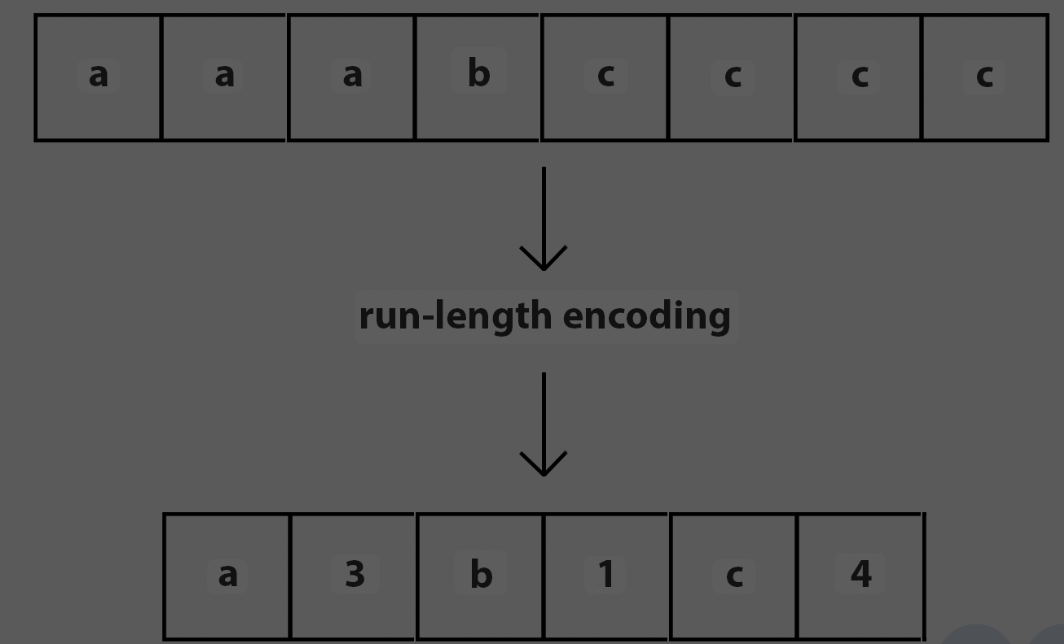
RLE(run length encoding)
a common lossless compression technique.It works by replacing sequences of identical data values (runs) with a single instance of the data value and a count of its occurrences.This method is particularly effective on data with many repeating consecutive characters or symbols.
text file compression
Lossless Compression: Common techniques include:
Huffman coding: Assigns shorter codes to frequently occurring characters, reducing overall file size.
Run-length encoding (RLE): Replaces sequences of identical characters with a count and the character itself (e.g., "AAAA" becomes "4A").
Lempel-Ziv (LZ) algorithms: Builds a dictionary of repeating patterns and replaces them with references to the dictionary.
bitmap image compression
Lossy Compression (e.g., JPEG):
Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT): Transforms image data into frequency components, allowing for discarding less important high-frequency data.
Quantization: Reduces the precision of DCT coefficients, further decreasing file size.
Color space reduction: Limits the number of colors used, reducing the amount of data needed to represent each pixel.
Lossless Compression (e.g., PNG):
Predictive coding: Uses previously encoded pixel data to predict the value of the current pixel, storing only the difference.
Deflate algorithm: A combination of LZ77 and Huffman coding.
vector graphic compression
Lossless Compression:
Primarily focuses on compressing the mathematical descriptions of the shapes and paths that make up the graphic.
Reduced storage of points and curves:
Instead of storing color information for every pixel, vector graphics store the coordinates of control points and mathematical equations that define lines, curves, and shapes.
sound file compression
Lossy Compression (e.g., MP3, AAC):
Perceptual coding: Exploits the limitations of human hearing to discard inaudible or less noticeable audio data.
Psychoacoustic modeling: Analyzes the audio signal and removes frequencies that are masked by louder sounds.
Lossless Compression (e.g., FLAC):
Predictive coding: Similar to image compression, predicts future audio samples based on past samples.
Variable-length coding: Assigns shorter codes to frequently occurring audio patterns.
WAN(wide area network)
a network connecting computers on different sites, possibly thousands of kilometres apart
benefits of having the computers connected by aa WAN
a data archive that was stored on a remote computer could be accessed.
a message could be transmitted electronically to user on a remote computer
a ‘job’ could be run on a remote computer that had the required application software
WAN Characteristics
it will not be owned by organisations or company
it will be used by an organisation Orr a company to connect sites or branches
the transmission medium will be fibre optic cable
it will be leased from a public switched telephone network company(PSTN)
a dedicated communication link will be provided by the pstn
Local area network
a network connecting computer in a single room, in a single building Orr on a single site
benefits of connecting computers by LAN