Lecture 1
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1, Lecture 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Definition of soil quality
The capacity of a specific kind of soil to function physically, chemically, and biologically, within natural or managed ecosystem boundaries, so as to maximize provisioning and regulatory ecosystem services. Often considered in relative to this capacity in the undisturbed, natural state.
5 components of soil quality
Physically
Chemically
Biologically
Provisioning
Regulatory
Ecological Function/Services
Ability of a soil to carry out a particular ecological function
Soil Resilience
A function of a soils performance (productivity), and its ability to withstand or recover from minor degradation
3 types of soil properties
Physical
Chemical
Biological
Soil properties are essential for…
understanding soil quality and restoring functions of degraded ecosystems
1 acre =
a. 1 ha
b. 43,560 ft2
c. 10,000 m2
b. 43,560 ft2
How many ft2 in an acre?
43,560 ft2
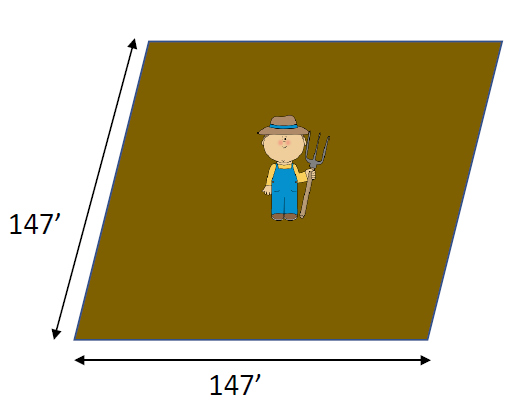
Arable land per person in 2020
0.49 ac/person
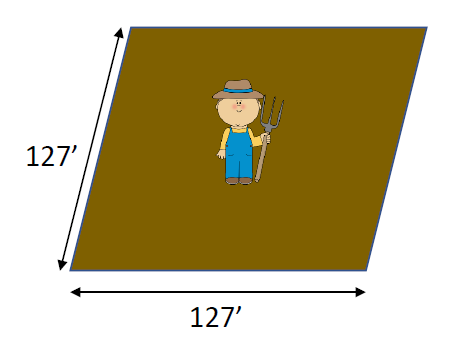
Project arable land per person by 2050
0.37 ac/person
3 regions in the world with high soil performance and resilience
Midwest
Ukraine
Southest South America (around Uruguay)
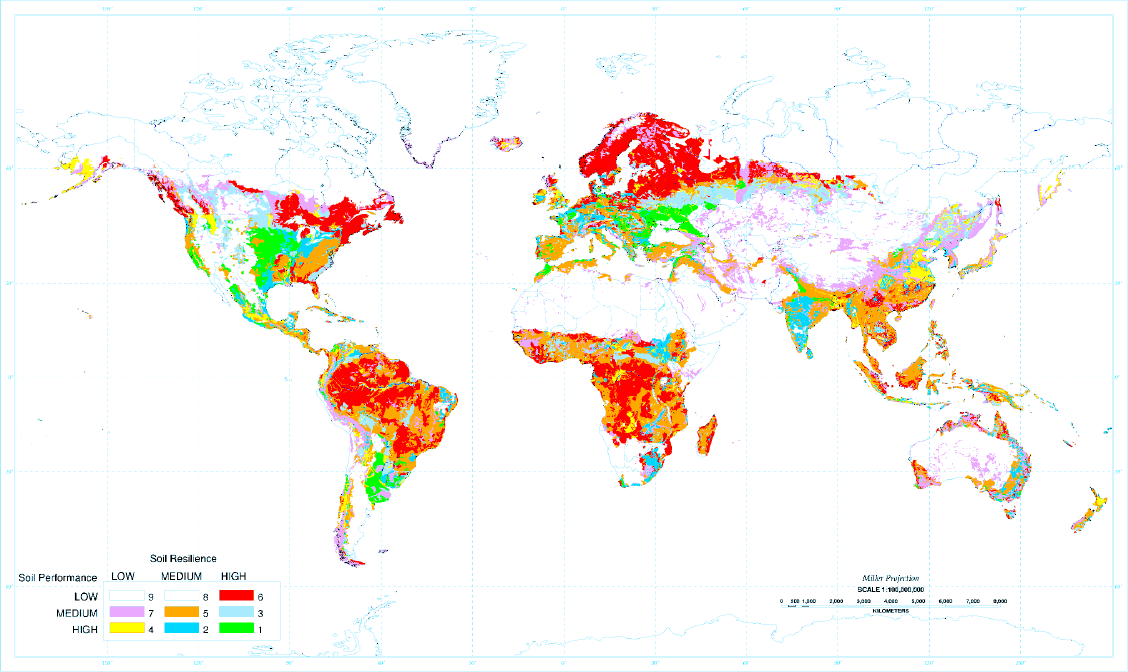
4 major processes contributing to soil degradation
Desertification
Water Erosion
Wind Erosion
Anthropic Tension
Desertification
Process by which soil loses its capacity to supply water to plants
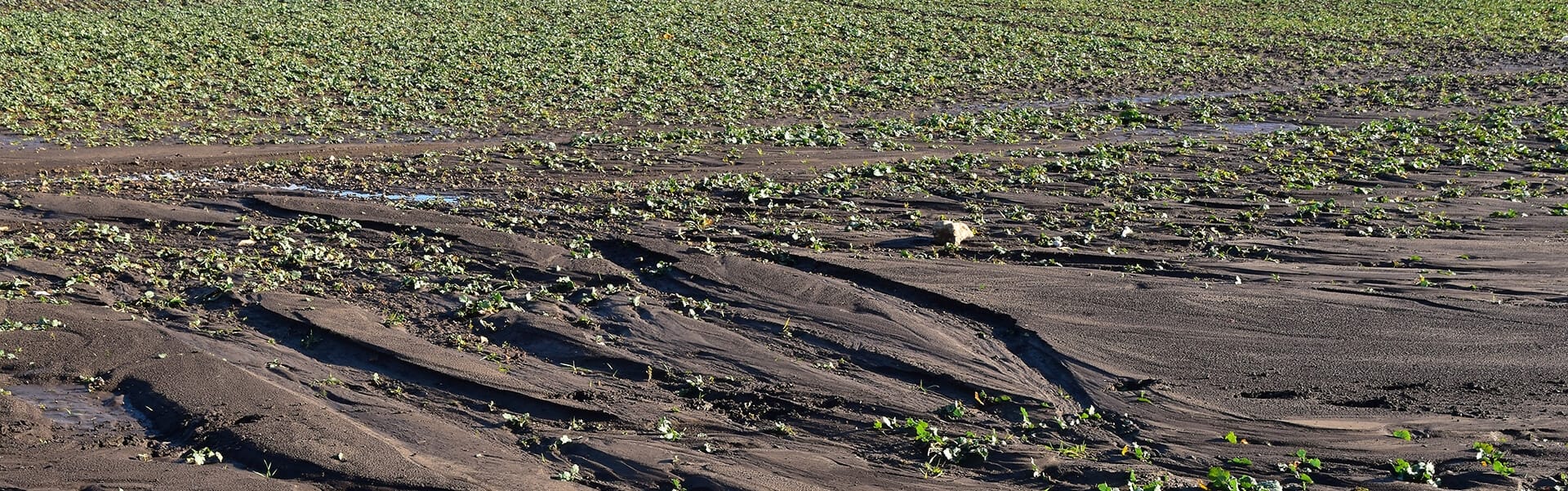

Water Erosion
Detachment and removal of soil particles by water
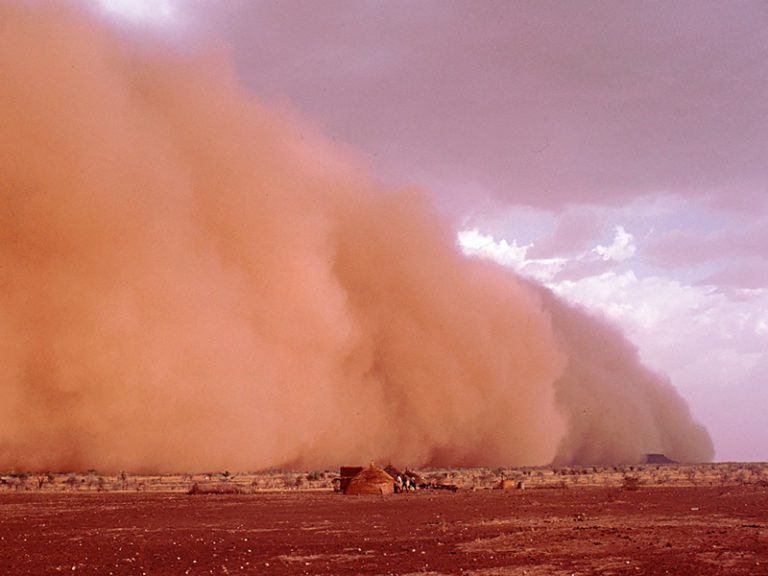

Wind Erosion
Detachment and removal of soil particles by wind
Anthropic Tension
Effects of humans