Electric circuits
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is static electricity?
A build up of electrical charge
What happens if a polythene rod is rubbed with a duster?
The friction causes electrons to gain energy and leave the atom
Polythene rod gains electrons → negative charge
Duster loses electrons → positive charge
What happens if an acetate rod is rubbed with a duster?
Electrons are rubbed off the acetate and onto the duster
Acetate rod loses electrons → positive charge
Duster gains electrons → negative charge
Define insulating materials?
Materials that does not allow charge or heat to pass through it easily
If a cloth rubs a plastic rod and the cloth is pulled away from the rod slightly, will the rod and cloth attract, repel or experience no force at all? Why?
The rod and cloth will attract
If electrons are rubbed off the cloth and onto the rod:
↳ cloth → positive rod → negative
If electrons are rubbed off the rod and onto the cloth:
↳ cloth → negative rod → positive
How does a Van De Graff generator work?
The generator removes electrons to produce a positive charge
↳ Touching the dome of the generator will cause the person's hair to stand up in all directions
↳ Each hair molecule is positively charged so they will repel from the head since like charges repel
What is an electric field?
A region where charged objects feel a force
Explain how electric fields can cause sparking
Larger the charge difference, stronger the electric field
Strong electric field → electrons from air particles are removed
↳ Air becomes more conductive → current can flow through it easier
Define electric current
A flow of charge (electrons)
What is current measured in?
Current (I) is measured in amperes (A)
What is charge measured in?
Charge (Q) is measured in coulombs (C)
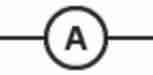
What is used to measure current? Where must it be placed?
With an ammeter
↳ Placed in series with the component
What is resistance?
How difficult it is for current to flow through
What is resistance meausred in?
Ohms (Ω)
What is potential energy?
The energy delivered by every coulomb of charge
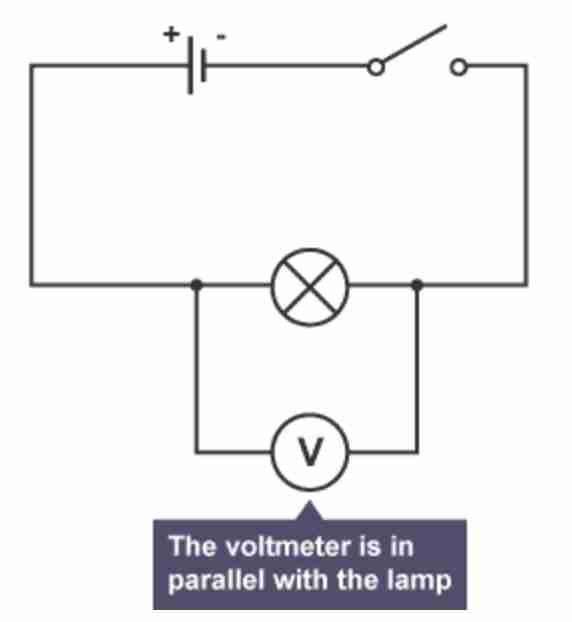
What is potential difference measured in? How is it connected in a circuit?
p.d (V) is measured in volts
↳ Must be connected in parallel to the component
Why do conductors have a low resistance but insulators have a high resistance?
Conductors have a high level of thermal conductivity so they are able to allow more energy through
What is the relationship between resistance and current?
As resistance increases, current decreases
↳ inversely proportional
What happens to resistance in series vs parallel?
Series- add the resistances
Parallel- total resistance is always less than the smallest resistor
What happens to current in series vs parallel?
Series- current is the same at all points
Parallel- current is divided at each junction
What happens to p.d in series vs parallel
Series- shared by each component
Parallel- same as the p.d of the supply
What happens to the resistance of a thermistor at low temperatures? What can they be used for?
The lower the temperature → the higher the resistance
↳ Can be used in thermostats or heat activated fire alarms
What happens to the resistance of an LDR at low light levels? what are its uses?
Low light intensity → High resistance
↳ Automatic lights
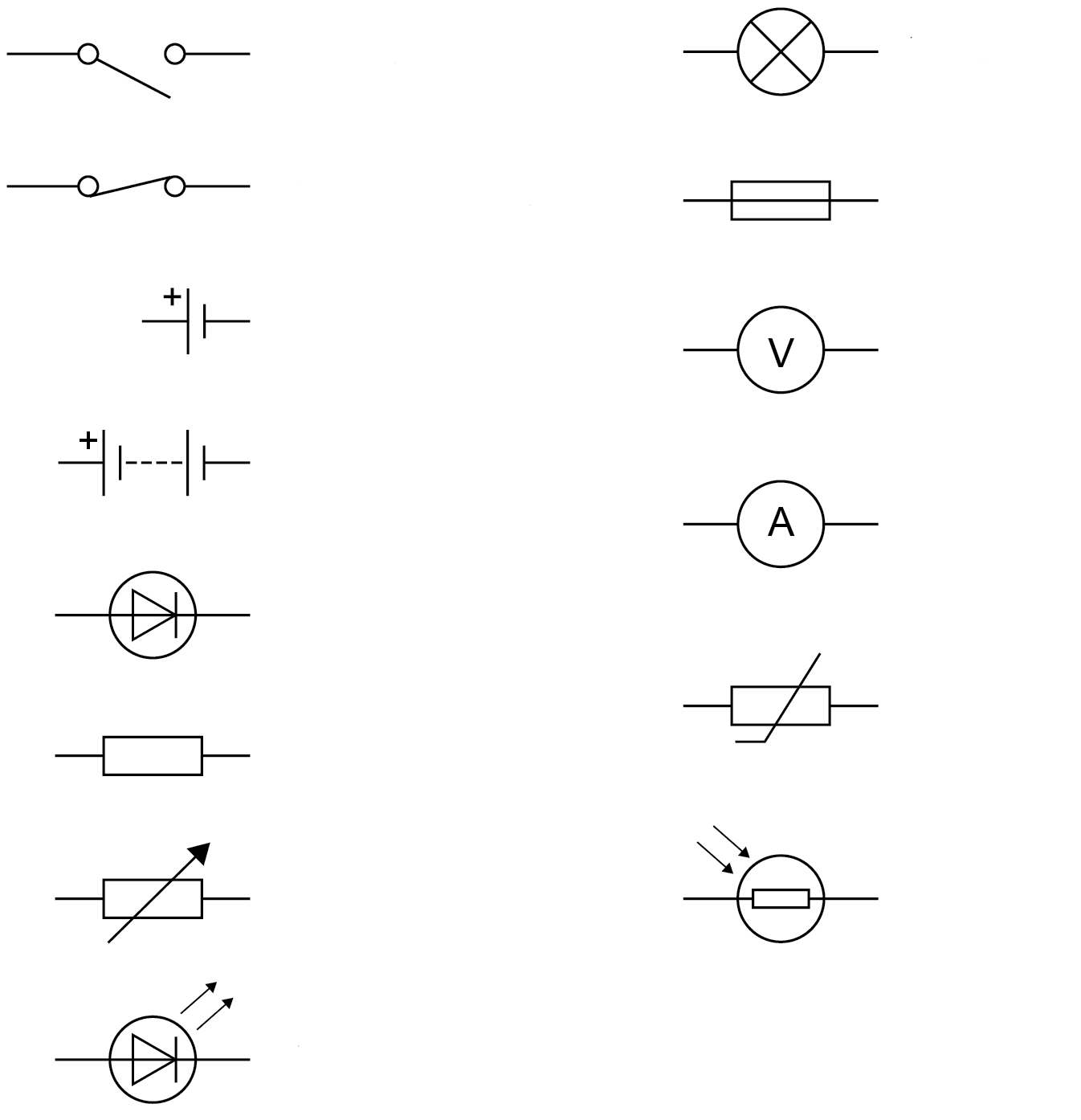
Name the circuit symbols
left to right:
open switch lamp
closed switch fuse
cell voltmeter
battery ammeter
diode thermistor
resistor LDR
variable resistor
LED