5 - vector borne diseases
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is a vector borne disease?
a disease that requires a vector for transmission
What phylum are most vectors?
arthropods
List 4 generalised methods of treating the infected person
vaccines
medicines
hygiene
public health information
List 3 generalised levels that vectors can be treated
ecological
organismal
molecular
What are a combination of treatments on multiple levels called?
IVM - integrated vector management
List 8 vectors
mosquitoes
aquatic snails
culicoides flies
blackflies
fleas
sandflies
ticks
List 3 genus of mosquitoes
Ades
Anopheles
Culex
List 3 diseases transmitted by Ades mosquitoes and what kind of pathogen each are
lymphatic filariasis - nematode
rift valley fever - virus
zika - virus
List 3 diseases transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes and what kind of pathogen each are
lymphatic filariasis - nematode
malaria - protozoa
O’nyong’nyong virus
List 3 diseases transmitted by Culex mosquitoes and what kind of pathogen each are
japanese encephalitis - virus
lymphatic filariasis - nematode
west nile fever - virus
List a disease transmitted by aquatic snails and what kind of pathogen causes it
schistosomiasis - trematode
List a disease transmitted by culicoides flies and what kind of pathogen causes it
oropouche fever - virus
List a disease transmitted by blackflies and what kind of pathogen causes it
onochocerciasis (river blindness) - nematode
List a disease transmitted by fleas and what kind of pathogen causes it
plague - bacteria
List 2 diseases transmitted by lice and what kind of pathogen causes them
typhus - bacteria
louse-borne relapsing fever - bacteria
List 2 diseases transmitted by sandflies and what kind of pathogen causes them
leishmaniasis - protozoa
sand fly fever - virus
List 3 diseases transmitted by ticks and what kind of pathogen causes them
crimean-congo haemorrhagic fever - virus
lyme disease - bacteria
relapsing fever - bacteria
Define an arbovirus
any group of RNA virus developed in arthropods
List the 5 main steps of a mosquito life cycle
females lay eggs on raft in water, often in domestic areas
eggs hatch → larvae → pupa
eggs can be dormant indefinitely / larvae mature to adults in ~7 days
adults mate, females seek blood to nourish eggs
bites - Ades bite during the day, Anopheles bite at night
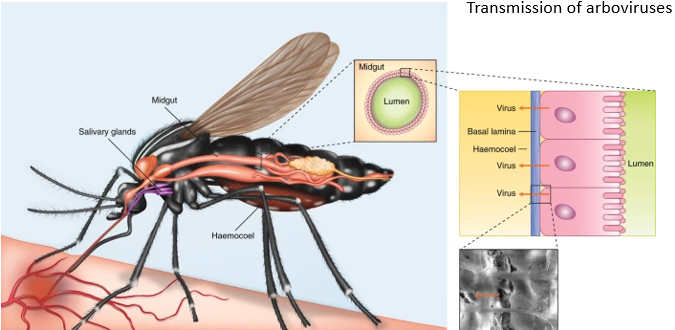
List the 3 main steps of transmission of arboviruses
once a mosquito is infected, the pathogen spreads around the whole body via an open haemolymph circulatory system
pathogen travels to salivary gland
when the mosquito collects a blood meal, there’s an exchange of fluid, both blood into it and infected haemolymph into the host
Is zika mostly symptomatic?
no its mostly asymptomatic
List 5 symptoms of the zika virus
fever
rash
headachs
joint pain in 2-7 days
microcephaly in infants
Define a PHEIC
an extraordinary event which is determined to constitute a public health risk to other countries
List 3 contributions to a fall in cases of the Zika pandemic
infection conferred immunity
ministry of health expanded mosquito control programs
increased access to care and quicker identification and isolation of access prevented re-emergence
List the 4 steps in Dengue infection
extrinsic incubation - virus infects the midgut of Aedes, eventually travelling to the salivary glands (8-10 days)
human infection - one mosquito infects several humans
intrinsic incubation - the onset of symptoms usually takes 4-7 days
mosquito infection - mosquito takes a blood meal from a person with acute dengue
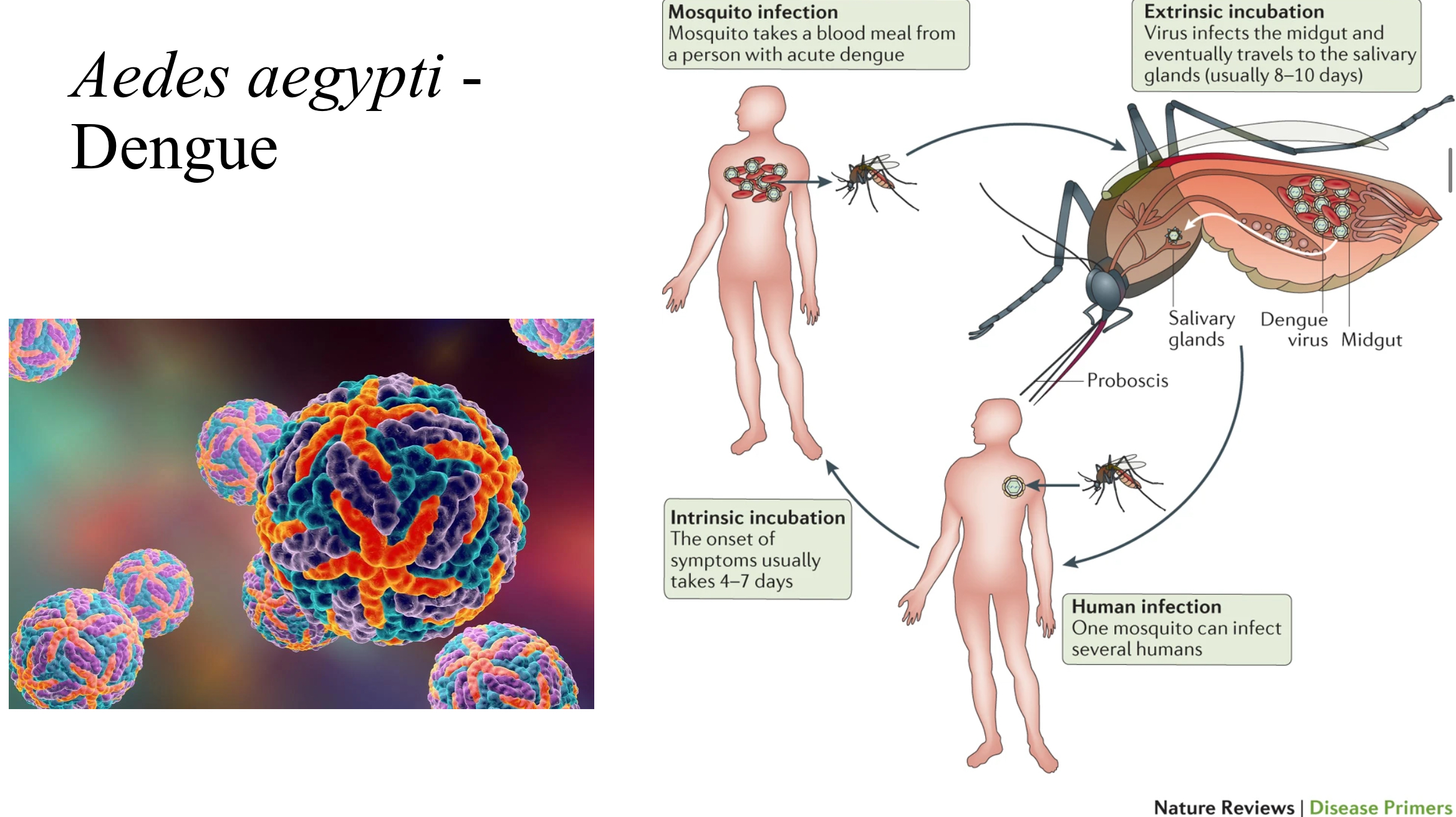
State 2 organisms that transmit dengue
Aedes aegypti
Aedes albopictus
How many serotypes of dengue are there?
4
List 4 factors to consider during ecological vector management
where to treat
resistance
community engagemennt
environmental risk
Aedes aegypti: location
lives near people and homes
Aedes aegypti: organismal preference
anthropophilic
Aedes aegypti: resistance
3% resistance to malthion
68% resistance to permethrin
27% resistance to deltamethrin
Aedes aegypti: eggs
lays multiple batches of eggs
Aedes aegypti: activity
crepuscular, occasionally nocturnal
Aedes albopictus: location
outdoors in more rural areas
Aedes albopictus: organismal preference
anthropophilic and zoophilic
Aedes albopictus: resistance
21% resistance to malathion
64% resistance to DDT
2% resistance to deltamethrin
Aedes albopictus: eggs
lays one egg batch per bloodmeal
Aedes albopictus: activity
crepuscular
Give an example of fungi being used for biocontrol against dengue
entomapathogenic fungi are non specific parasitic fungi that target mosquitos
Give an example of fish being used for biocontrol against dengue
Gambusia affinis are non specific and cause potential damage to ecosystems
Give an example of mosquito being used for biocontrol against denguee
larvae are voracious predators of other species of other mosquito larvae, including Ades aegypti
List 4 technologies for vector control
SIT - sterile insect techniques
IIT - incompatible insect techniques
RIDL - release of insects carrying dominant lethal genes
gene drives
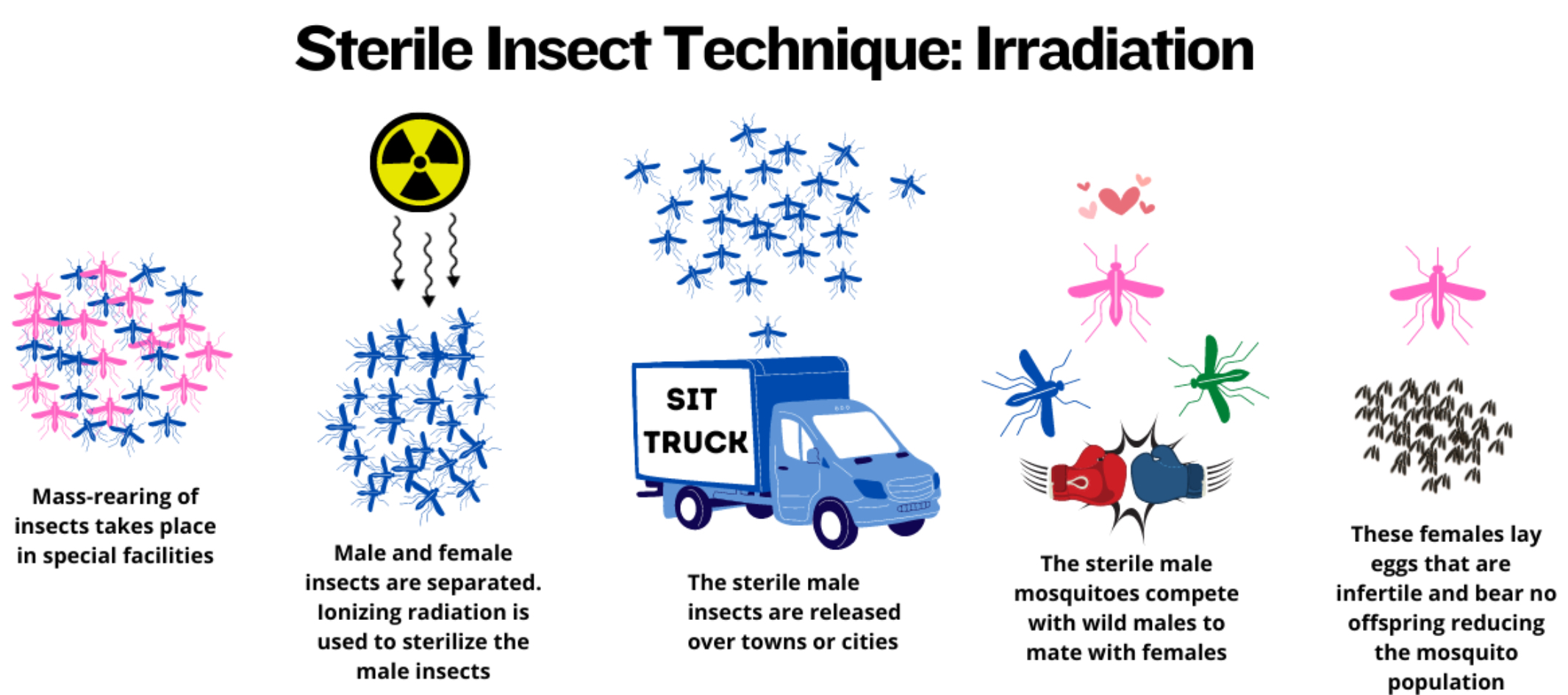
Sterile insect technique: irradiation (5 steps)
mass rearing of insects takes place in special facilities
male and female insects are separated, ionising radiation is used to sterilise the male insects
male insects are released over towns or cities
sterile male mosquitos compete with wild males to mate with females
females mated with the sterile eggs lay infertile eggs, reducing the population
What is Wolbachia?
common entomopathogenic bacteria that reduces mosquitos ability to transmit viruses
How are incompatible insect techniques performed?
male mosquitos artificially infected with Wolbachia mate with females causing their eggs to die due to cytoplasmic incompatibility
How does Wolbachia cause eggs to die due to cytoplasmic incompatibility?
male gametes infected with Wolbachia have a different orientation of chromosomes during metaphase which is then unable to line up correctly with female gamete chromosomes
List 2 dominant lethal genes Oxitec has created in order to promote vector control
OX513A
OX5034
What is the effect of the OX513A strain?
all offspring die
What is the effect of the OX5034 strain?
female offspring die, males pass on genes
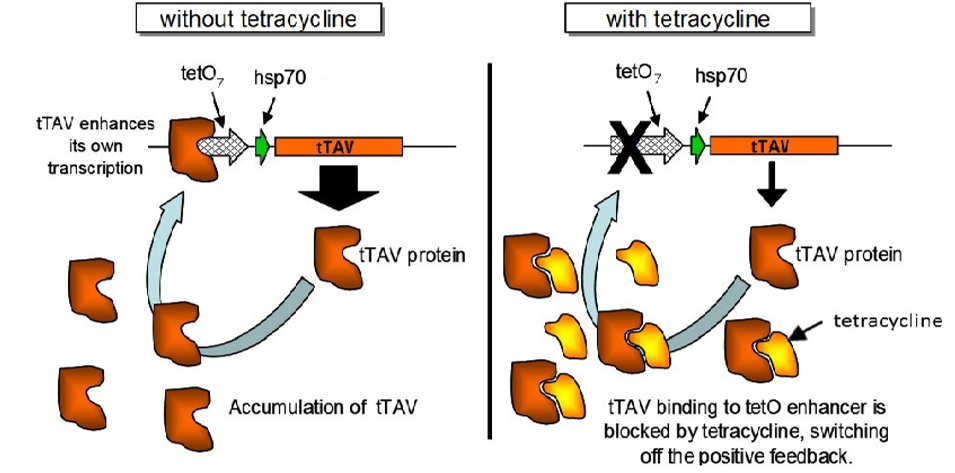
How do the created oxitec gene strains cause mortality (2 points)
Tetracycline-repressible transcriptional activator (tTAV) controls yhe binding site of tetracycline operator (TetO) creating positive feedback loop, allowing downstream creation of the gene causing late larval lethality
the introduction of tetracycline prevents mortality
How can the OX513A be visually identified?
possesses a heritable fluorescent marker gene
How does CRISPR contribute to gene drives?
genetic modification alters gene drives to ensure phenotypic expression, in this case death of larvae
What pathogen causes Trypanosomiasis brucei?
protozoa kinoplastid
Where does Trypanosomiasis brucei operate?
extracellularly, inhibits blood plasma and bodily fluids
List 3 subspecies of Trypanosomiasis brucei
T. b. brucie
T. b. gambiense
T. b. rhodesiense
What organisms do T. b. brucie target?
non human mammals
What organisms do T. b. gambiense and T. b. rhodesiense target and what does they cause?
humans, causing Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT) - African sleeping sickness
What is the primary vector of Trypanosomiasis?
Tsetse flies
List 3 methods of diagnosis of Trypanosomiasis
direct observation of parasite in peripheral blood, lymph, or CSF
a CATT (card agglutination test for Trypanosomiasis) assay can be used for detection of T. b. gambiense antibodies, however there are high false positive rates
LFIAs (lateral flow immunochromatographic assays) detect antibodies with high sensitivity and specificity
World Health Organisation - 2020
WHO eliminated gHAT as a global health problem
List 2 current targets of the WHO
eliminating rHAT as a global health problem by 2030
eliminate all transmission of gHAT
List 3 methods that WHO is using to eliminate transmission of HAT
active screening
passive screening
vector control