Unit 1 biochemistry Test (Part 2)
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
elements
a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reaction
92
how many elements occur on nature
compound
a substance consisting of two or more elements is a fixed ration
Essential elements
elements essential to survive and reproduce
CHOPN
CHOPN
make up 96% of living matter
Atomic #, # of protons
# above element

Atomic mass #, proton + neutrons average over all isotopes
# below element

elements in same vertical column (group)
have same # of valence
elements in same horizontal row (period)
have same # of electron shell
1st, 2nd, 3rd Shells can hold
2,8,18 electrons
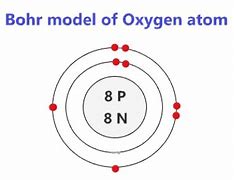
bohr model
model with a electron shell
Lewis dot model
model with a dot of valence electrons

Octet rule
Elements wants to get all 8 electron to be stable so they gain, lose, share their valence shell electron. (like noble gases)
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself
increase - left to right of period
decrease - top to bottom of group
covalent bond
two or more atom share electrons (nonmetals)
polar covalent bond
Electron is unequally shared
Ionic bonds
attraction between oppositely charged atoms (Ion)
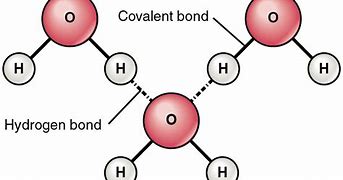
hydrogen bond
the partially positive hydrogen atom is one polar covalent molecule will be attracted to an electronegative (-) atom in another polar covalent molecule
Intermolecular bond (hydrogen bond in water)
bond formed between molecules (exist among particles)
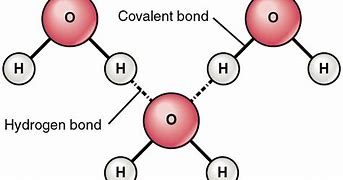
Intramolecular bond (covalent bond in water)
bond formed exhibited inside a particle
8 properties of water
polarity, cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, high specific heat, evaporative cooling, floating ice/ density, universal solvent (also surface tension)
polarity
unequal sharing of the electrons make water a polar molecule
Cohesion
Attraction of molecules for other molecules of the same kind
responsible for surface tension
living system of cohesion
Increase Hydrogen bond makes a surface tension
- Leaf floating: plants often time rest in surface of water and allowing them to have more access to sunlight for process of light photosynthesis
Ice float: Water's cohesive properties allows for unique hydrogen bond intercalations in water's solid state. And this makes water as a solid less dense than water as a liquid.
- Aquatic organism able to live in water in freezing climates because the water will freeze on the surface leaving liquid water underneath for those organism
High heat capacity: water's cohesive property allows it to absorb a lot of thermal energy before changing chemical states resisting sudden changes in temperature
- Many aquatic organism like the fish will depend upon this property of water, so that they can maintain appropriate temperature regulations of their bodies
Adhesion
The clinging if one molecule to a different molecule
living system of adhesion
Water's adhesive property gives water a high solvency ability in liquid state
- Organism must obtain key nutrients from their environment. Considering that living things are made up of 70% water. Dissolved materials in the water allow for easy access by cells
living system of cohesion and adhesion
Capillary action is a result of both the adhesive and cohesive properties of water
- Plants can access water from the soil through this capillary action ability into their roots (xylem of leaf)
Evaporative cooling
Water has a high heat of vaporization (meaning it takes a lot of energy to convert liquid to gas)
importance of evaporative cooling
moderates Earth's climate
Stabilizes temp in lakes and ponds
Prevents terrestrial organisms from overheating (sweat)
Prevents leaves from overheating
solution
Homogenous mix of 2+ substances
solvent
Dissolving agent in a solution
solute
Substance that is dissolved
“like dissolves like”
Water will form hydrogen bonds with the sugar or protein to dissolve it
pH
depends on the hydrogen ion concentration in that solution
high concentration low pH
low concentration high pH
pH levels
pH 7 being neutral, pH less than 7 being acidic, and pH greater than 7 being basic
organic compounds
compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen
organic chemistry
the study of compounds with covalently bonded carbon
H, O, N
carbon most commonly forms bonds with
Hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
skeleton
carbon chains form the ______ of most organic molecules
functional groups
Chemical groups attached to the carbon skeleton that participate in chemical reactions
Molecular diversity
variations in carbon skeletons allows for
Macromolecule
carbon can form large molecules known as
4 macromolecules
Carbonate
Protein
Nucletic acid
lipids
polymers
Chain like macromolecules of similar or identical repeating unit that are covalently bonded together
monomers
the repeating units that makes up polymers
dehydration reaction
bonds two monomers with the loss of H2O
monomer + monomer = polymer +H2O
hydrolysis reaction
breaks the bonds in a polymer by adding H2O
Polymer +H2O = monomer + monomer
Carbohydrates
C,H,O
carbonyl group and hydroxyl group
what functional group does carbohydrate have?
monosaccharides
simple sugar
monomer of carbohydrates
*most common is Glucose - form a ring in aqueous solutions
Alpha Glucose
(OH bottom) makes starch (covalent bond \ o/) Branch
Beta Glucose
(OH top) makes cellulose (covalent bond / o\) linear
Diaccharides
two monosaccharides joined together by covalent bonds
*most common Sucrose = Glucose + fructose
Polysaccharides
polymer of carbonates
many sugar joined via dehydration reaction
storage polysaccharides
Plants - STARTCH: allows plants to store excess glucose
animals - GLYCOGEN: stored in liver and muscle cells
structural polysaccharides
Cellulose: tough substance that forms plant cell walls
Chitin: forms exoskeleton of arthropods.
Proteins
C,H,O,N,S
molecule consisting of poly peptides folded into a 3D shape
shape determine the function
protein order
Amino acid small → peptide → polypeptide → protein large
Amino Acids
monomer of protein
structure of amino acid
R (variable side chain) CH3 hydrophobic, H - polar
amino group — C — carboxyl group
N terminus H C- terminus
(Base) (Acid)
Polypeptides
polymer of protein
many amino acid liked by peptide bonds
*unique sequence of polypeptide = Gene
Function of protein
Antibody: help protect the body from disease
Enzyme: Carry out chemical reactions or assist in creating new molecules
Messenger: Transmit signals (ex. hormones)
Structural: Provide structure and support
Transport/storage: Bind to and carry small atoms and molecules through the body
Level of protein structure
Primary, Secondary, tertiary, Quaternary
Primary protein structure
Linear chain of Amino Acids
determined via Gene
Secondary protein structure
Coils and folds due to HYDROGEN BONDING within the polypeptide backbone
Beta Pleated sheet - hydrogen bonds between polypeptide chains lying side by side
Alpha - hydrogen bonding between every 4th amino acid
Tertiary protein structure
3D folding due to interactions between the side chains of the Amino Acids
- Reinforced by hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bridges of the side chains
Quaternary protein structure
Association of two or more polypeptides
Found in only some proteins
Nucleic acid
Polymers made of Nucleotide monomers - DNA, RNA
Function of nucleic acid
Store, transmit, and express hereditary information
components of nucleic acids
nucleotide(monomers) → polynucleotides → nucleic acid (polymers: DNA, RNA)
3 parts of nucleic acid
Nitrogenous base
Five carbon Sugar (pentose)
Phosphate groups (in polynucleotides each monomer only has one phosphate group
Nitrogenous base (nucleic acid)
Pyrimidines and purines
Pyrimidines
One ring with 6 atoms
- Cytosine; C
- Thymine; only found in DNA
- Uracil; only found in RNA
Purines
One ring with 6 atoms bonded to one ring with 5 atoms
- Adenine
- Guanine
A, T
has 2 hydrogen bond
C, G
has 3 hydrogen bond
Five carbon Sugar
A sugar is bonded to the base
- In DNA the sugar is deoxyribose (H)
- In RNA the sugar is ribose (OH)
Phosphate Group
Functional group in Nucleic Acid
Polynucleotides
Phosphate groups like adjacent nucleotide
- Phosphodiester linkage
- Directionality (5' phosphate end to 3' hydroxyl end)
The sequence of bases along the DNA or mRNA is unique for each Gene
- Dictates AA sequence
○ Dictates the primary structure of a protein
(Dictated 3D structure of a protein)
DNA
Consist of TWO polynucleotides (Deoxyribose)
- Forms a double helix
○ Strand are antiparallel
Held together by hydrogen bonds between bases
Cytosine binds to guanine
Adenine binds to thymine
antiparallel
5’ to 3’ + 3’ to 5’
RNA
single helix
Ribose
Adenine binds to Uracil
Lipids
Class of molecules that do not include true polymers
- Generally small in size
○ Often not considered to be a macromolecule
Lipids are nonpolar-hydrophobic
Types of lipids
Fats, Phospholipids, Steroids
Fat
composed of Glycerol and Fatty Acid (monomer of lipids)
Glycerol
classified as an alcohol (hydroxyl group)
Fatty Acids
long carbon chains (carboxyl group at one end)
3 fatty acids join to a glycerol via Ester linkage
Saturated and unsaturated
hydroxyl groups, carboxyl group
Functional groups of lipid
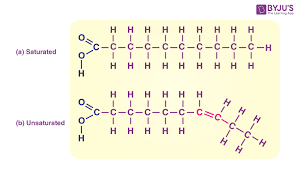
Saturated fatty acid
NO double bonds between carbons in the carbon chain = more hydrogen (think: saturated with hydrogen)
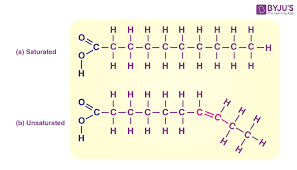
Unsaturated fatty acid
Contains one or more double bonds
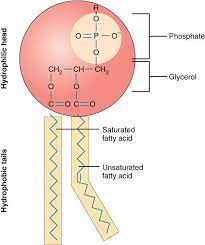
Phospholipids
major component of cell membranes
- Two fatty acids attached to a glycerol and a phosphate
Assemble as a bilayer in H2O
- Tails are hydrophobic
- Head is hydrophilic
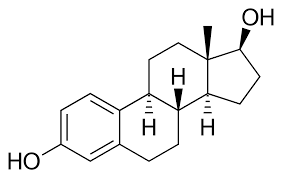
Steroids
Lipids that have four fused rings
- Unique groups attached to the ring determine the type of steroid
Ex. testosterone
Hydroxyl group
—OH
Carbonyl Group
\
C = O
/
Carboxyl group
—COOH
Amino Group
—NH2
Sulfhydrl group
—SH
Methyl Group
H
|
— C — H
|
H