3.1 Longitudinal & Transverse Waves
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
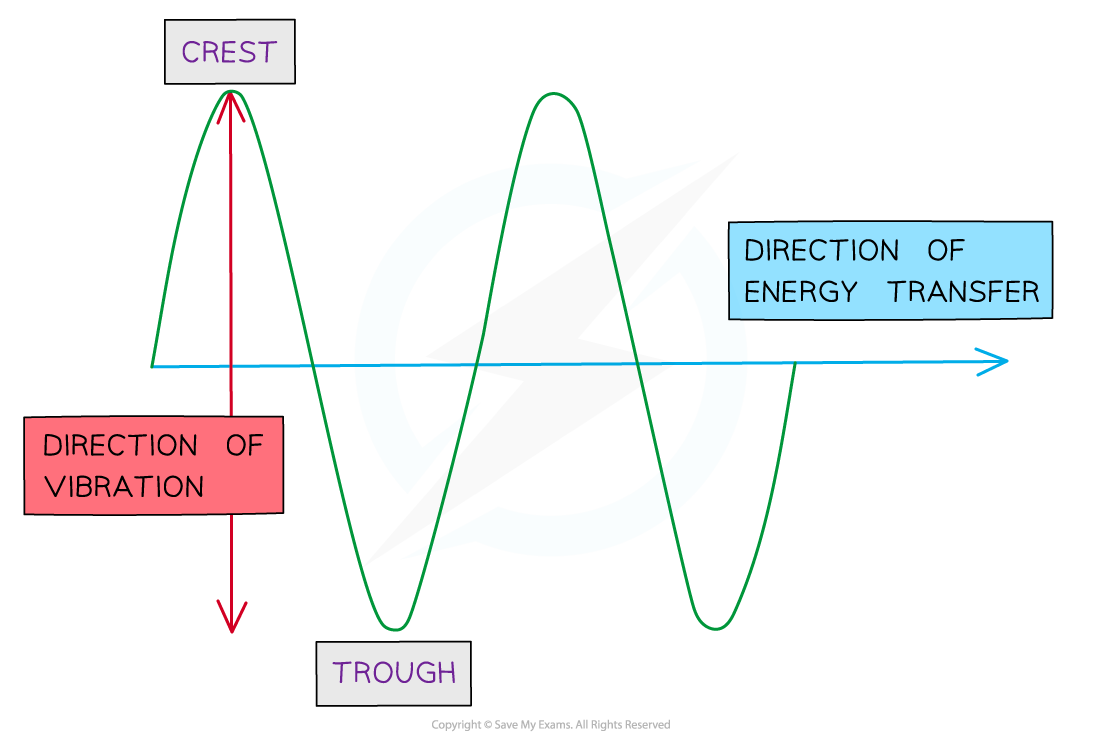
Progressive wave:
A wave that transfers energy from one point to another without transferring the medium itself
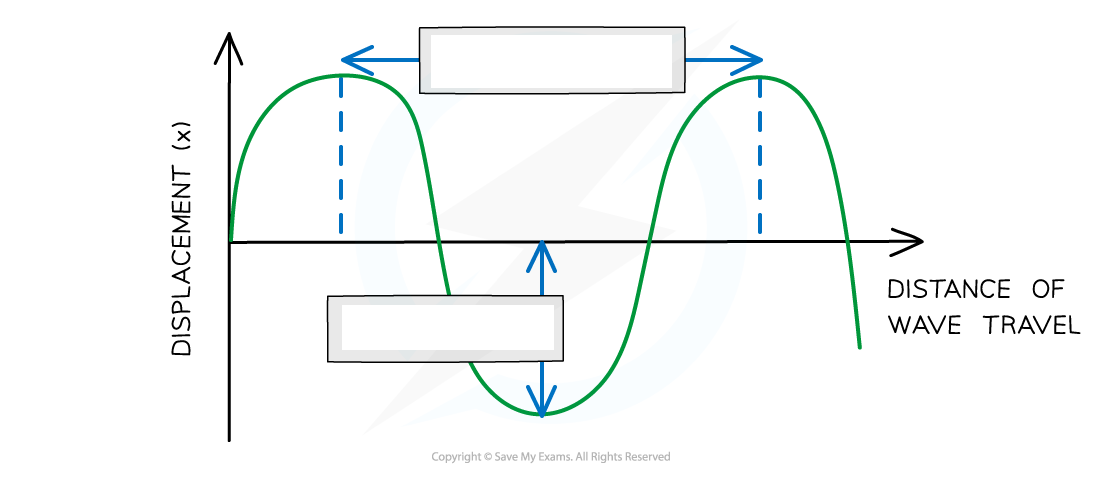
Displacement (x):
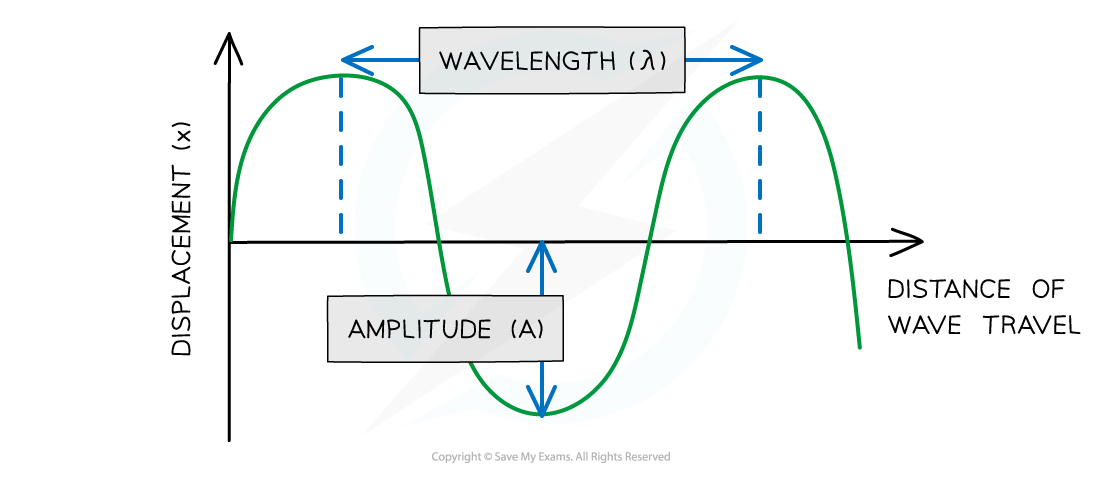
Amplitude (A):
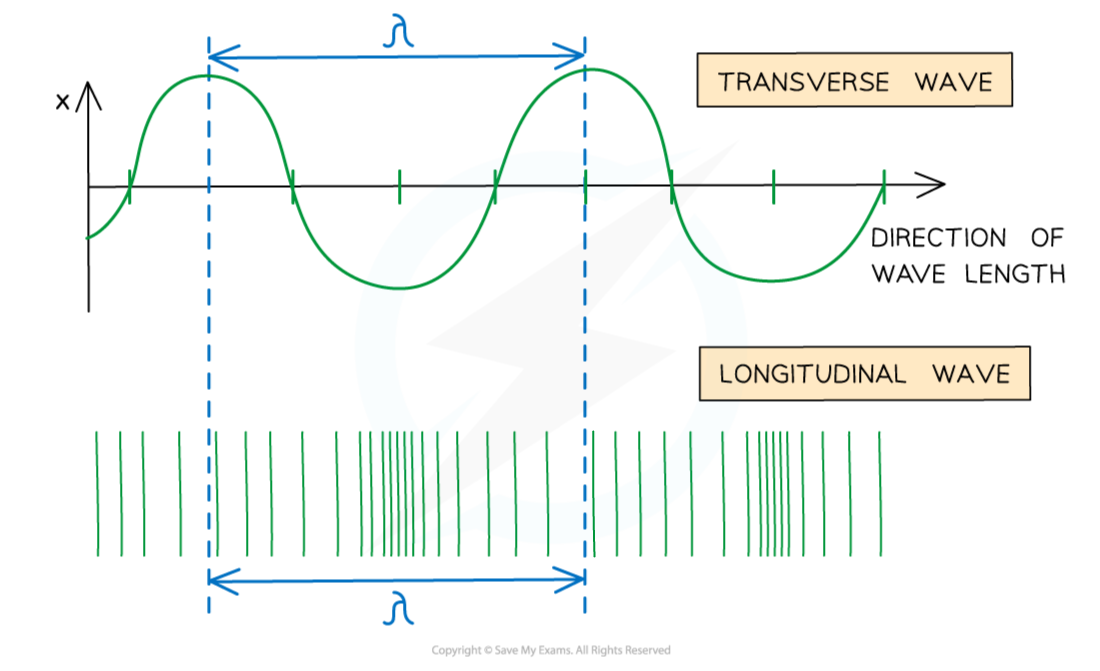
Wavelength (λ):
Measured in:
Displacement (x): distance of a point on the wave from its equilibrium position
Vector quantity; it can be positive or negative
Amplitude (A): maximum displacement of particle from its equilibrium position
Wavelength (λ): distance between points on successive oscillations of the wave that are in phase
All measured in metres (m)
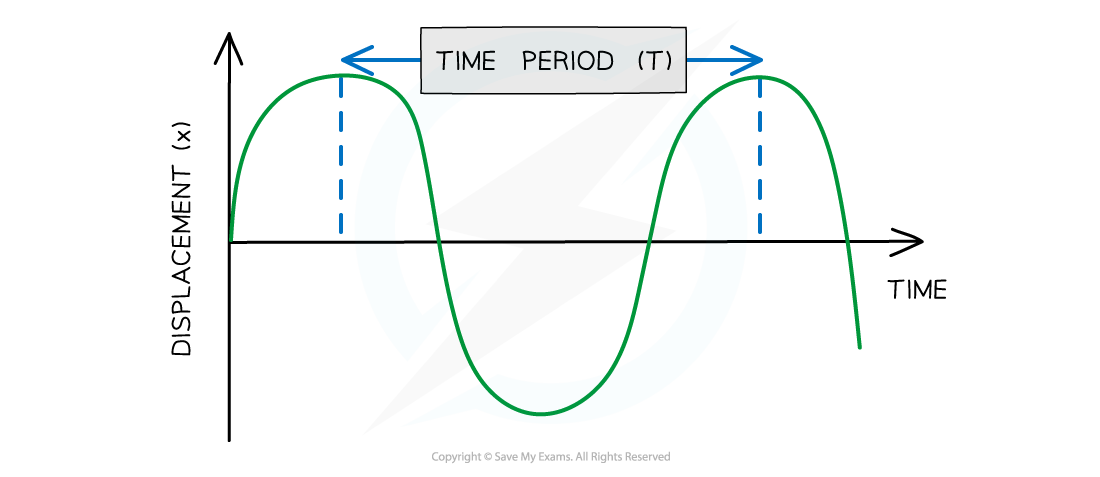
Period (T)/time period:
Measured in:
Frequency (f)
Measured in:
Speed (v)
Measured in:
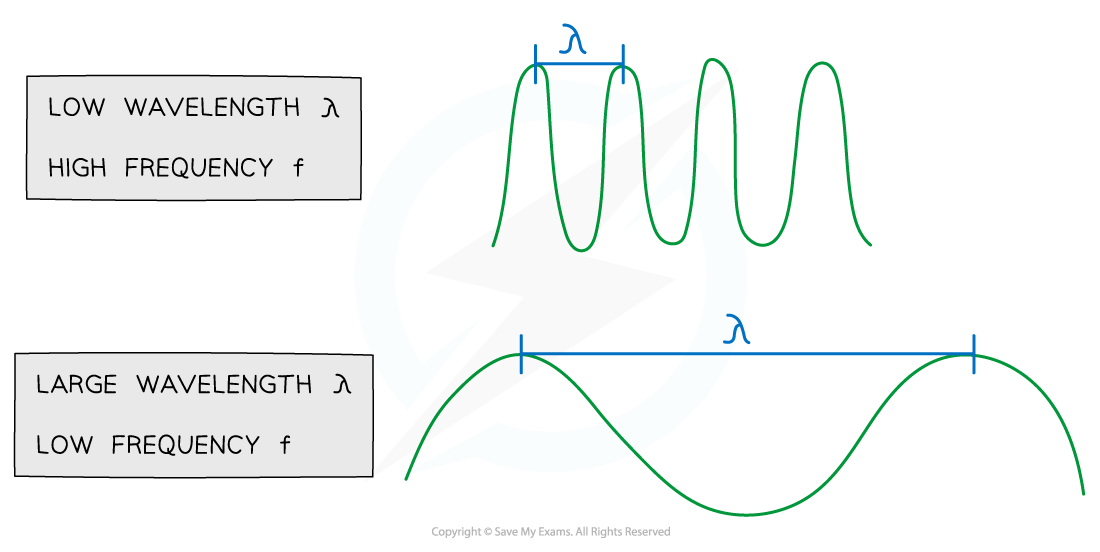
Wave equation shows for a wave of constant speed: wavelength ______, the frequency ________, wavelength ________, the frequency _______
Period (T)/time period: time taken for 1complete oscillation/cycle of the wave
Measured in seconds (s)
Frequency (f) is the number of complete oscillations per unit time. Measured in Hertz (Hz) or s1
Equation: f = 1/T
Speed (v) is distance travelled by wave per unit time
Measured in metres per second (ms^1)
Equation v = fλ
Wave equation shows for a wave of constant speed: wavelength increases, the frequency decreases, wavelength decreases, the frequency increases
Phase difference and how is it found:
In phase:
antiphase:
Phase difference between 2 waves is measure how much a point/wave is in front or behind another
Found using relative positive of crests/troughs of 2 different waves of same frequency
When crests/troughs are aligned, waves are in phase
When crest of one wave aligns with the trough of another, antiphase
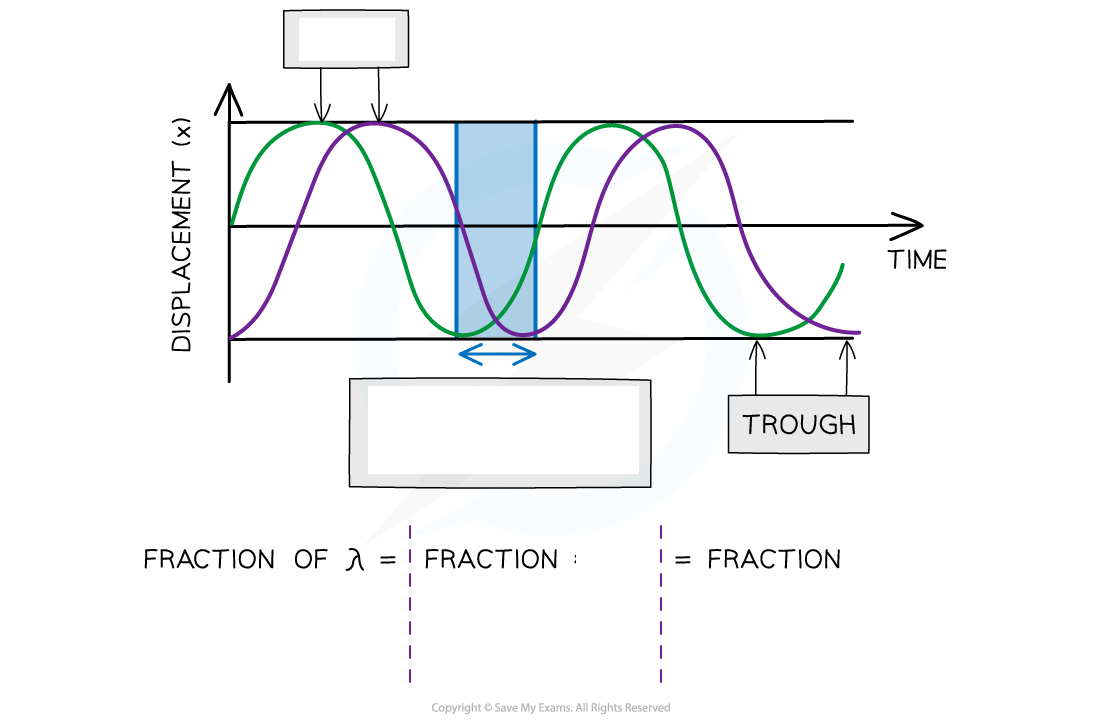
Purple wave lags behind the green wave by __
Phase difference measured in _____ of a _______, ______ or ______
Phase difference calculated from different ____ on same wave/______ point on _ different waves
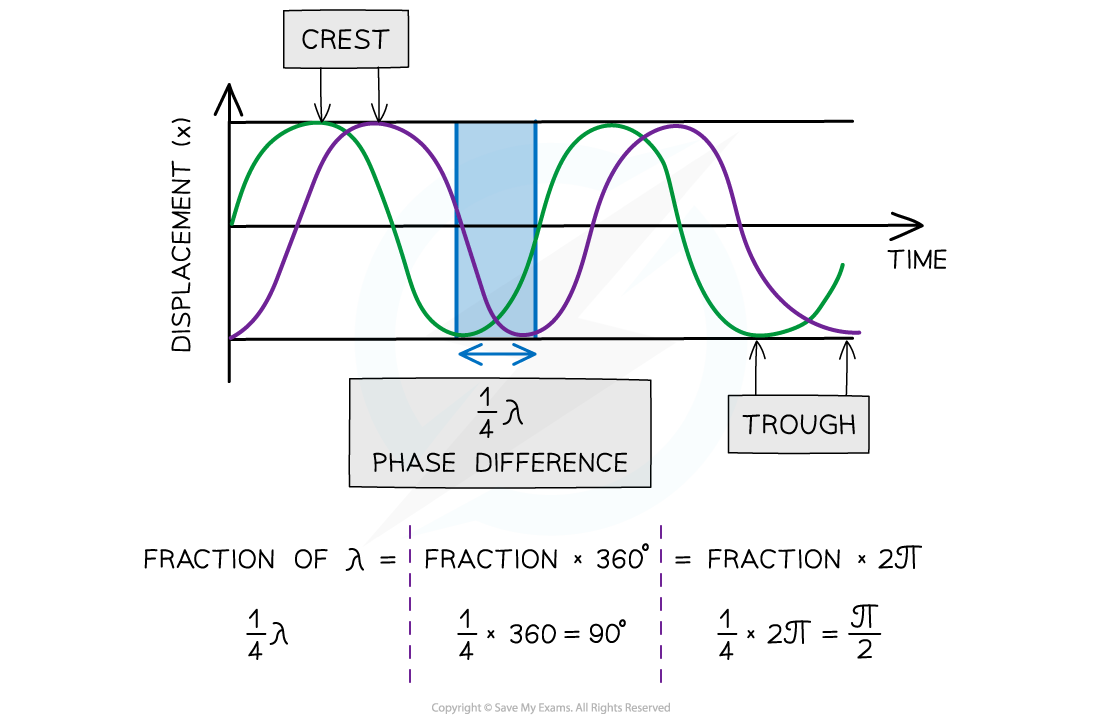
Phase difference between two points:
In phase is
In anti-phase is
Purple wave lags behind the green wave by ¼ λ
Phase difference measured in fractions of a wavelength, degrees or radians
Phase difference calculated from 2different points on same wave/same point on 2 different waves
Phase difference between two points:
In phase is 360° or 2π radians
In anti-phase is 180° or π radians
Mechanical waves particles ______ about _______ point: _______ & _______
How is type of wave determined by?
Type of wave determined by direction of oscillations in relation to direction the wave is travelling
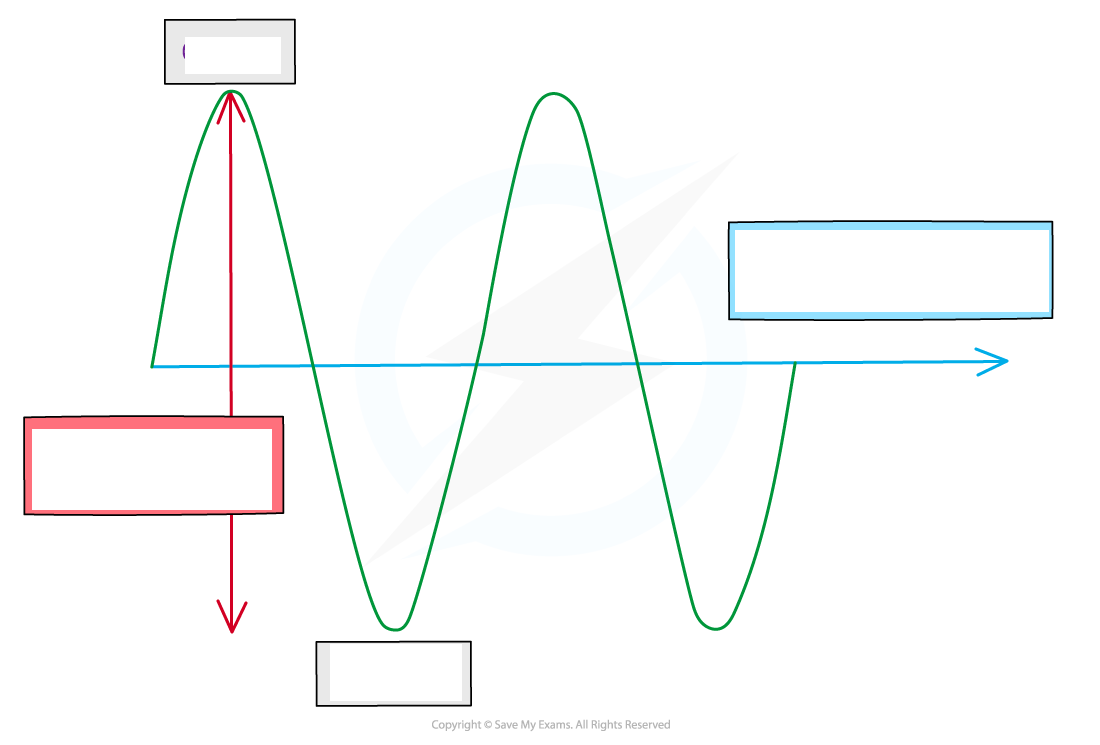
Transverse waves:
What do they show?
Examples:
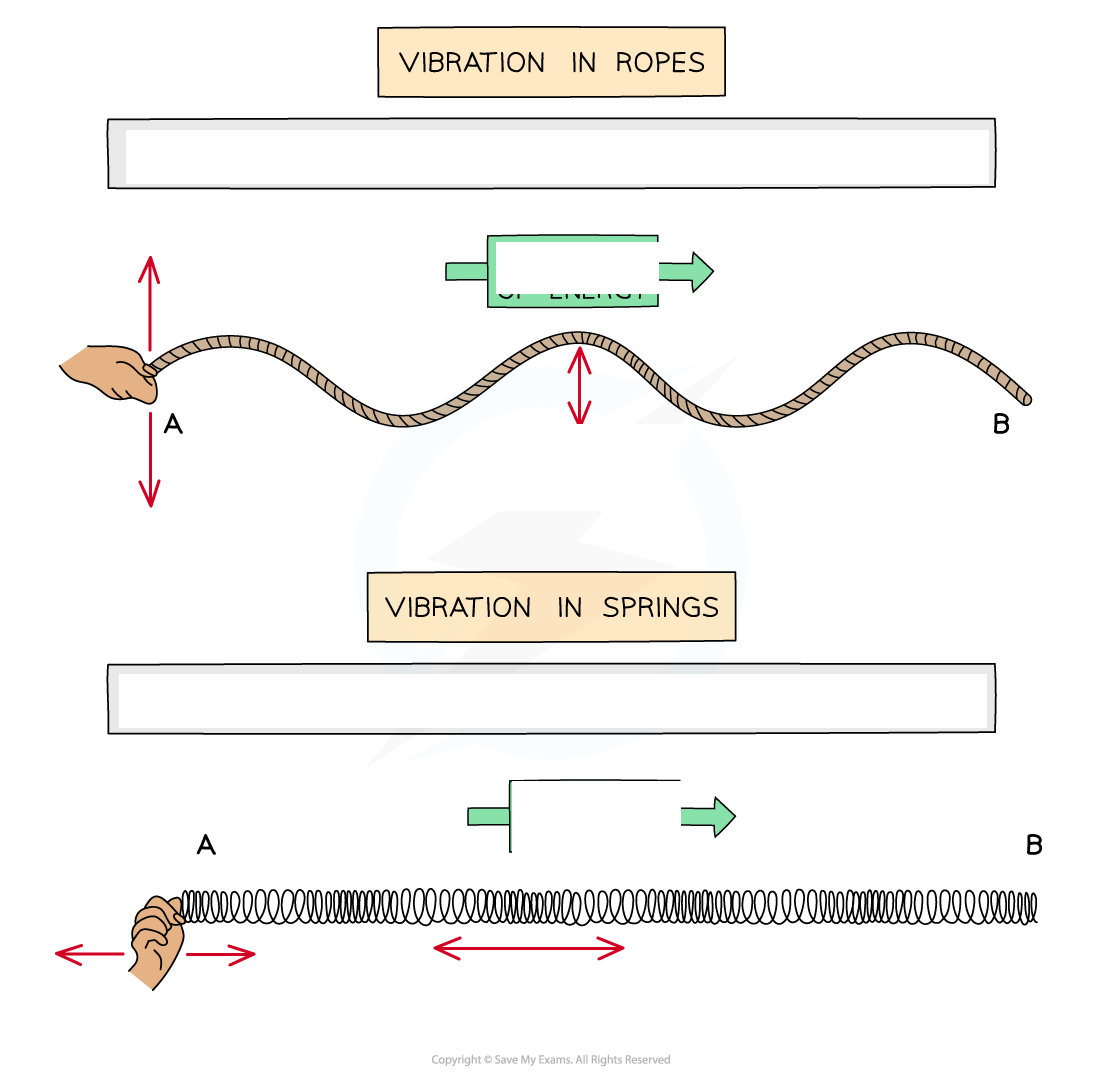
Show on a rope can be
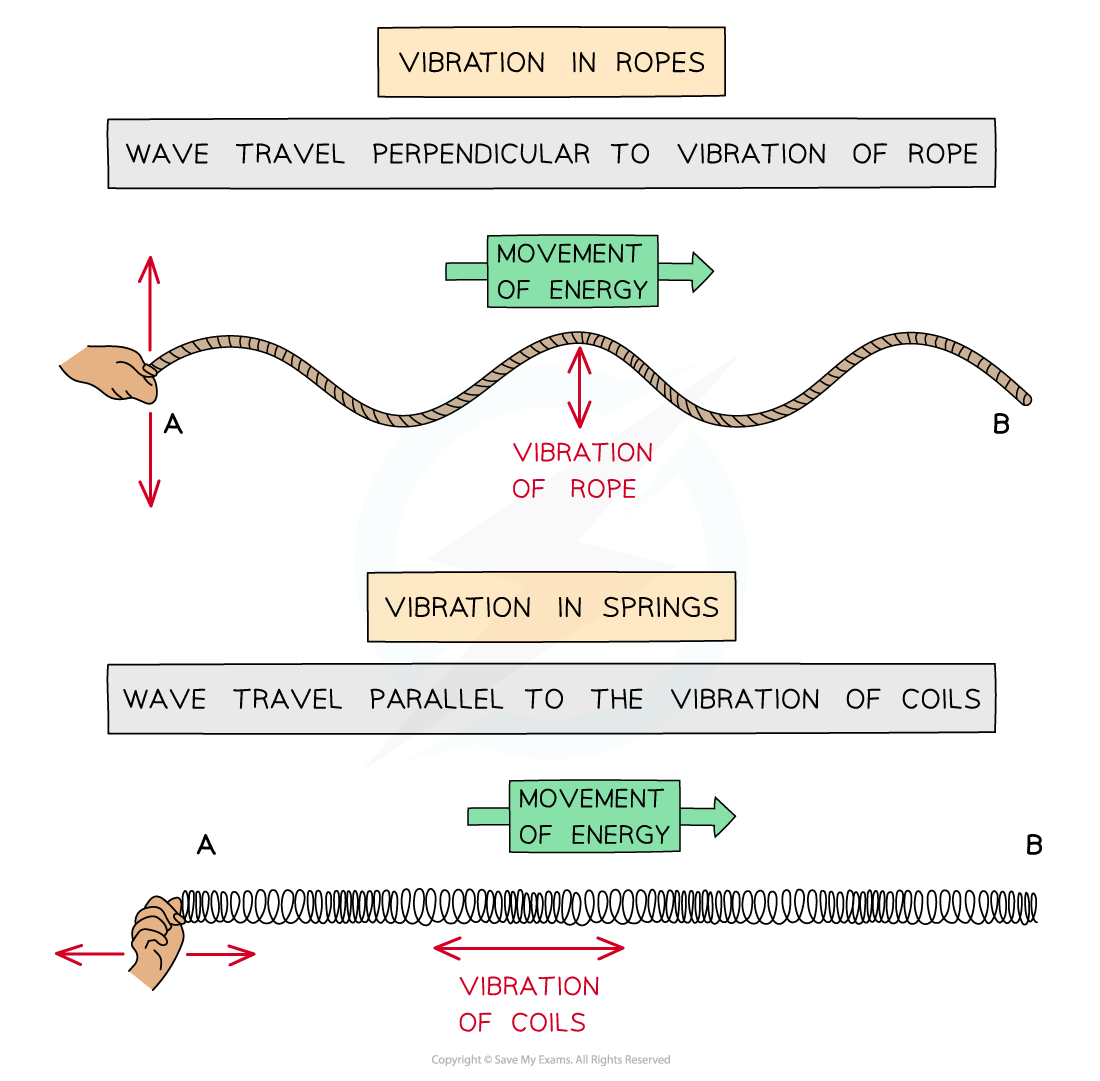
Transverse wave: A wave in which the particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the wave travel (and energy transfer)
Transverse waves show areas of crests (peaks) and troughs
Examples of transverse waves: Electromagnetic waves e.g. radio, visible light, UV, Vibrations on a guitar string
Transverse waves shown on rope, can be polarised
Longitudinal waves:
What do they show and regions of?
Examples:
Show on a slinky cannot be
Energy is transmitted through the wave by:
Longitudinal Wave; A wave in which the particles oscillate parallel to the direction of the wave travel (and energy transfer)
Longitudinal waves show areas of compressions and rarefactions
Compressions are regions of increased pressure
Rarefactions are regions of decreased pressure
Examples of longitudinal waves are: Sound waves, Ultrasound waves
Longitudinal waves shown on a slinky spring, cannot be polarised
Energy is transmitted through the wave by:
particles in medium vibrating as they are given energy
Compressions cause nearby particles to also vibrate with more energy
Produces a compression further along in the medium
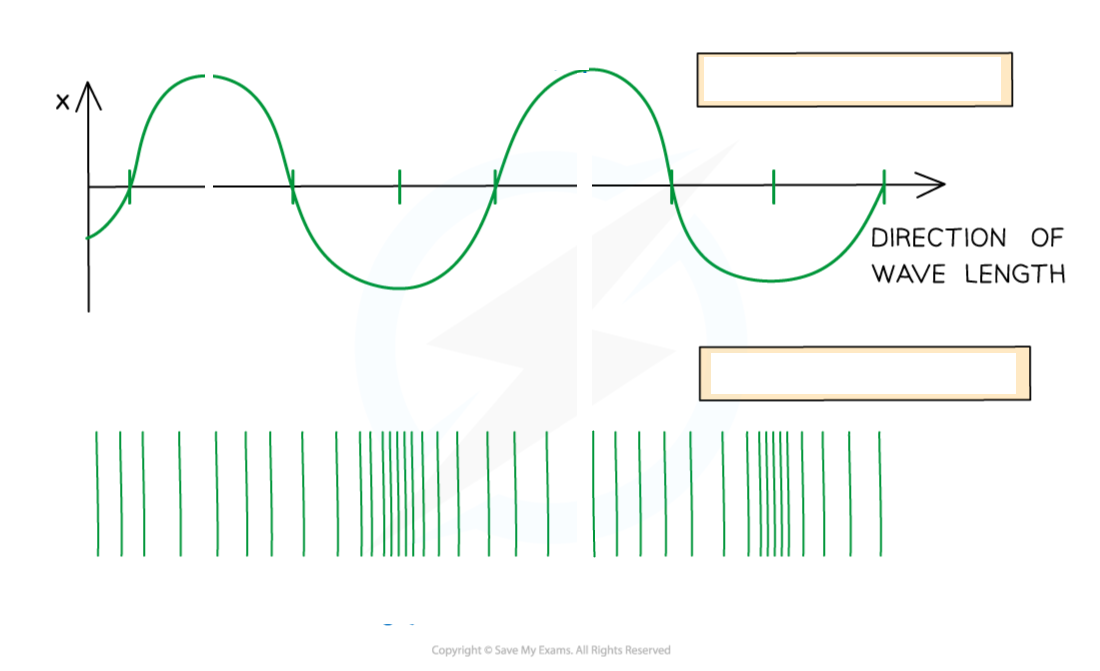
Draw wavelength and label
How is energy transferred through waves?
Waves oscillate in a __________ direction are transverse waves
Waves oscillate in a _________ direction are longitudinal waves
Examples of transverse waves are:
Examples of longitudinal waves are:
Energy transferred through moving oscillations or vibrations seen vibrations of ropes or springs
Waves oscillate in a perpendicular direction are transverse waves
Waves oscillate in a parallel direction are longitudinal waves
Examples of transverse waves are: Electromagnetic waves e.g. radio, visible light, UV - Vibrations on a guitar string - Waves on a string - Seismic (S) waves
Examples of longitudinal waves are: Sound waves - Ultrasound waves - Waves through a slinky coil - Seismic (P) waves
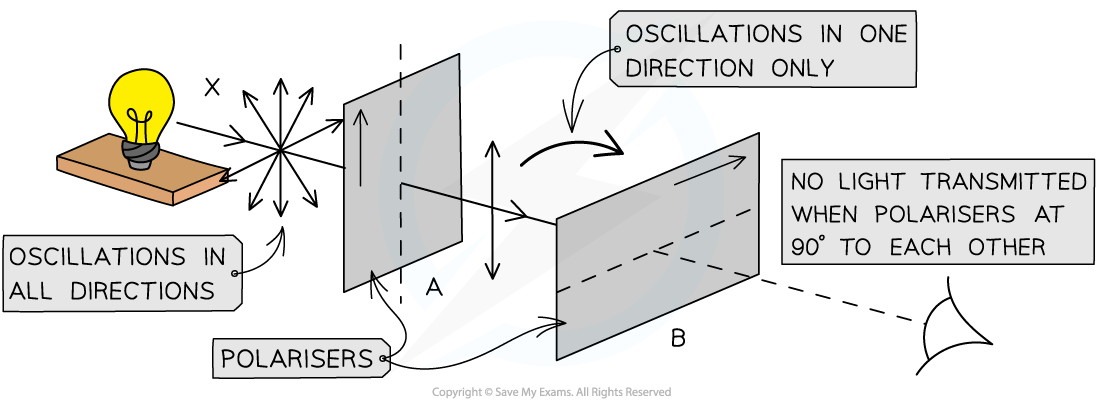
Polarisation:
When does polarisation occur?
What happens when wave is polarised and vibrations are still?
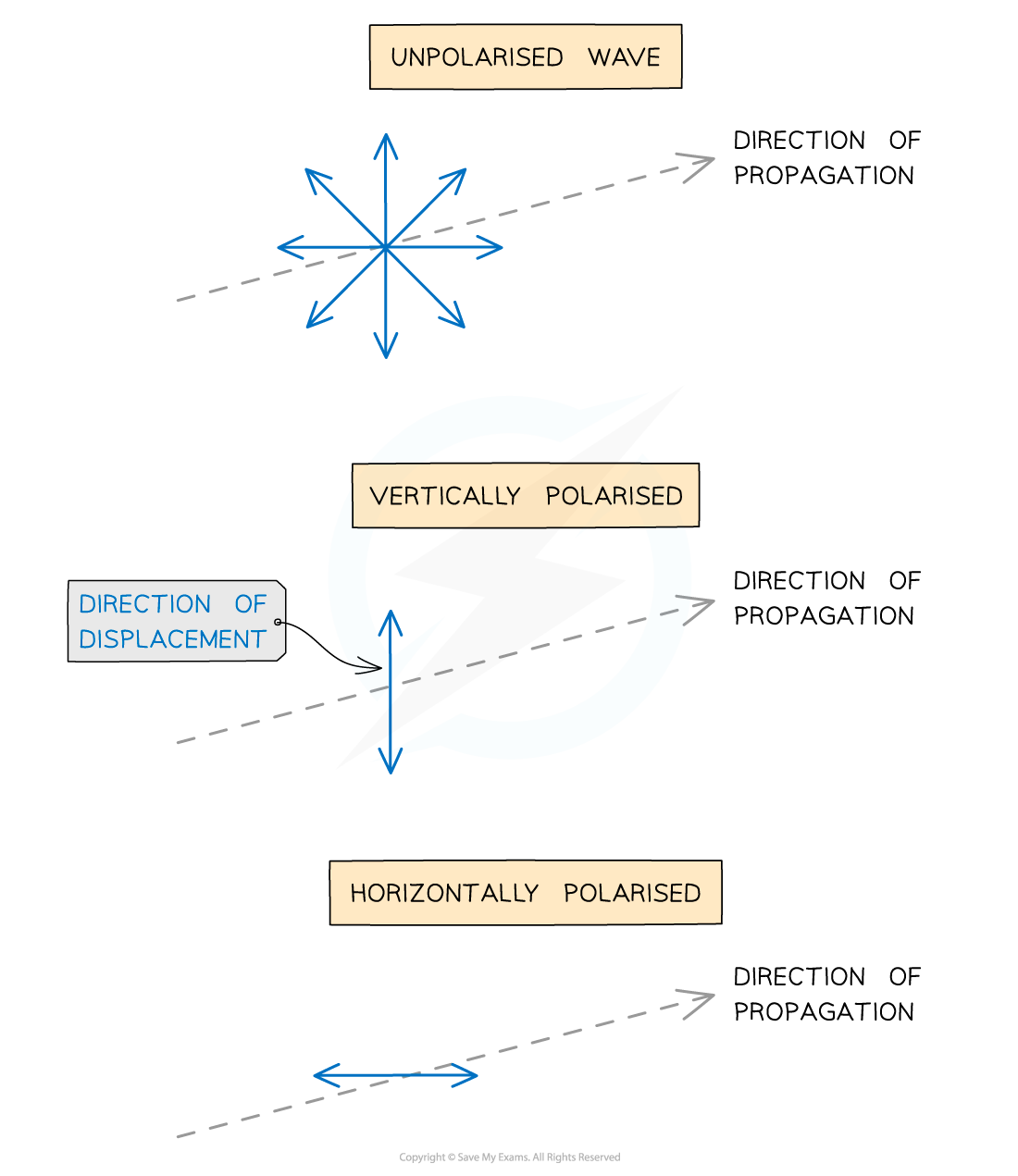
Polarisation: Particle oscillations occur in only one of the directions perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
Polarisation occur in transverse waves: transverse waves oscillate in any plane perpendicular to the propagation direction
Transverse waves polarised: Vibrations are restricted to one direction
vibrations are still perpendicular to the direction of propagation / energy transfe
Why can’t longitudinal waves be polarised?
How can waves be polarised?
Explain diagram A and B
How can light also be polarised?
Longitudinal waves (e.g. sound waves) cannot be polarised because they oscillate parallel to the direction of travel
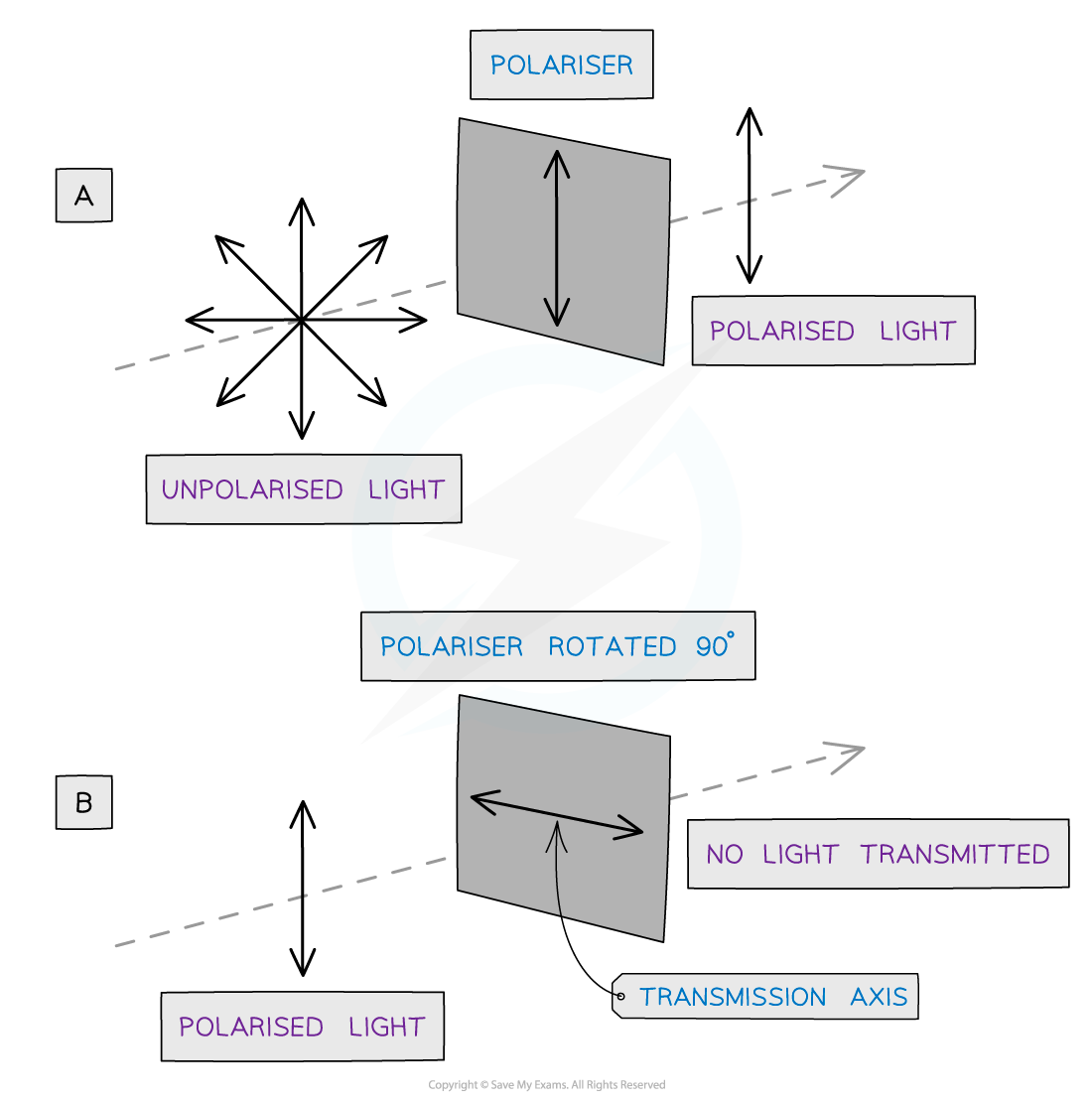
Waves can be polarised through a polariser or polarising filter, only allows oscillations in a certain plane to be transmitted
Diagram A shows: Only unpolarised waves can be polarised
Diagram B shows: polarised wave passes through a filter with a transmission axis perpendicular to the wave, none of the wave will pass through
Light can also be polarised through reflection, refraction and scattering
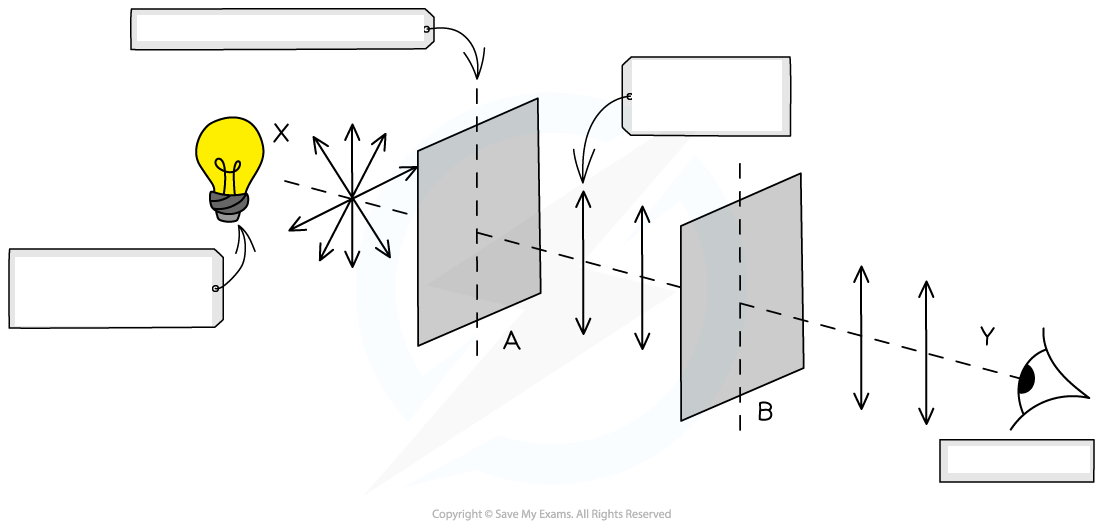
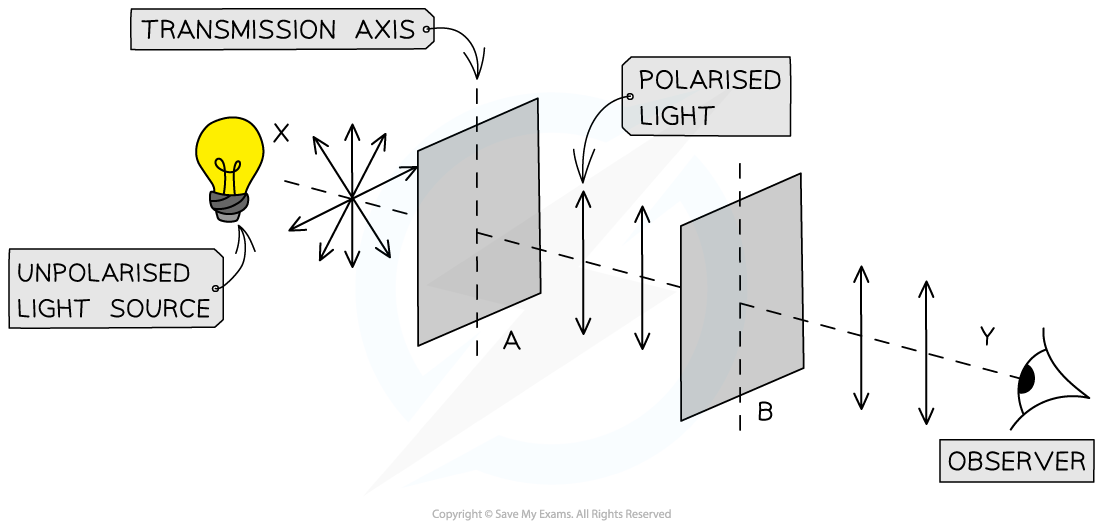
Investigating Light Intensity with Two Polarisers:
Unpolarised light source is placed in front of ______ identical polarising filters, A and B, with their transmission axes _____:
Filter A polarise the light in a _____ ____
All of ______ _____ will ______ through filter B _______
________ intensity of light is ________
Polarising filter B ________ __________, __________ of light observed changes ______ depending on the _______ B is rotated through
When both polarisers have the same transmission axis, the _______ of the transmitted light is at its _______
Unpolarised light source is placed in front of two identical polarising filters, A and B, with their transmission axes parallel:
Filter A polarise the light in a certain axis
All of polarised light will pass through filter B unaffected
Maximum intensity of light is transmitted
Polarising filter B rotated anticlockwise, intensity of light observed changes periodically depending on the angle B is rotated through
When both polarisers have the same transmission axis, the intensity of the transmitted light is at its maximum
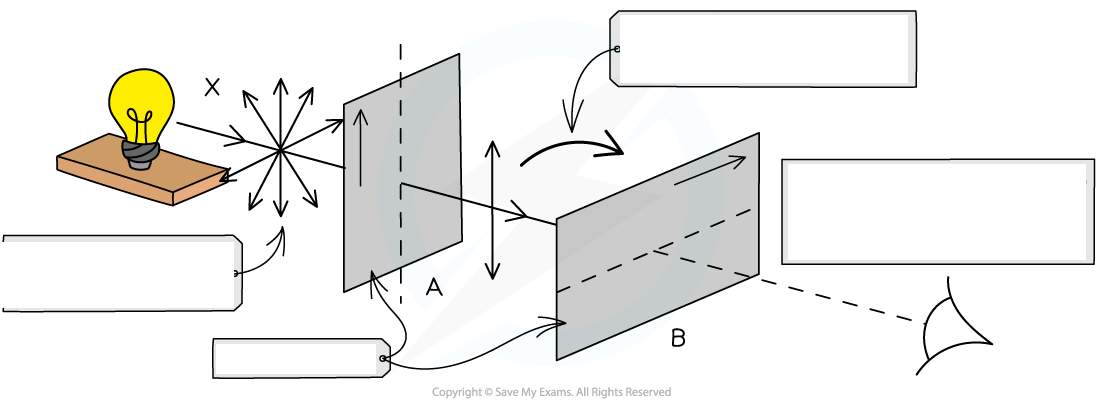
A and B have transmission axes ___________ to each other:
Filter A _______ the light in a ________ ____
________ of the polarised light will ______ through ______ __
_______ intensity of light is _____
When _____ of the polarisers is rotated through °, the __________ of the transmitted light drops to ____
A and B have transmission axes perpendicular to each other:
Filter A polarise the light in a certain axis
None of the polarised light will pass through filter B
Minimum intensity of light is transmitted
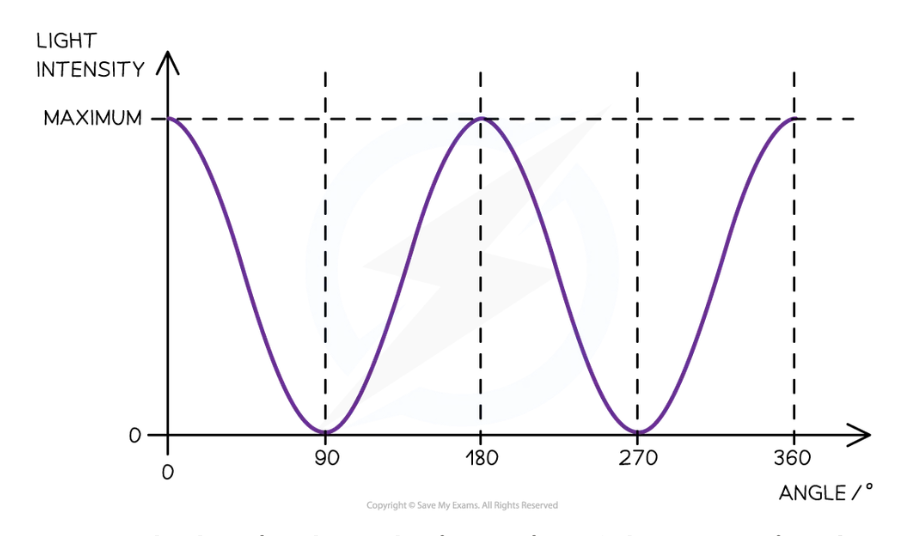
Real life, intensity of __________ electromagnetic wave _______ after it passes through a polarising filter
What does the graph show?
Real life, intensity of unpolarised electromagnetic wave reduces after it passes through a polarising filter
Graph showing how the intensity of the transmitted beam varies with the angle between the transmission axes of the two polarisers. Resulting graph of the light intensity with angle, as the second polariser is rotated through 360°:
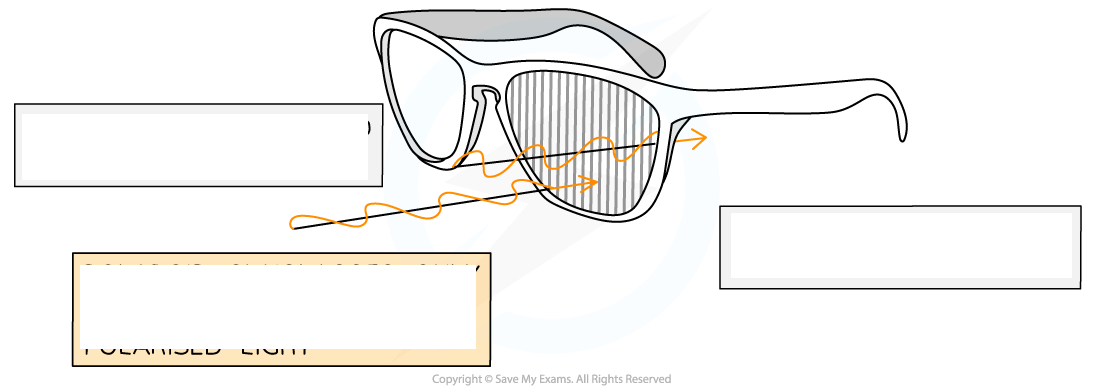
What are polaroid sunglasses?
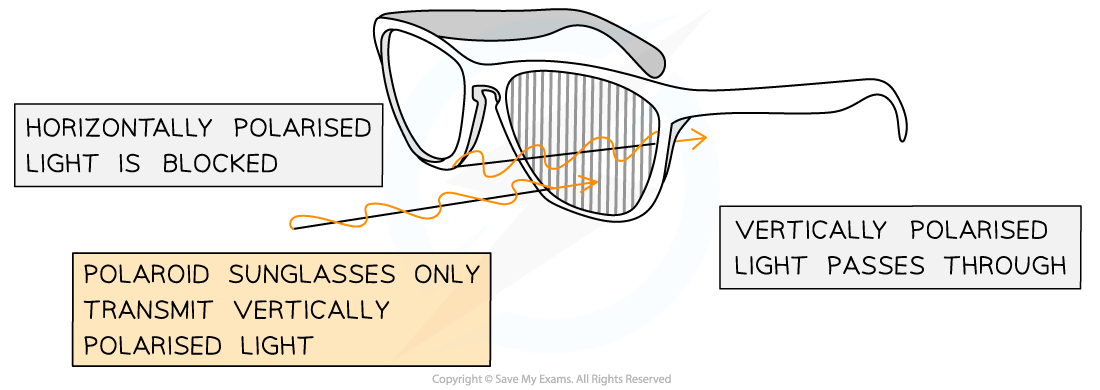
Glasses containing lens with polarising filters with transmission axes that are vertically oriented so glasses don’t allow any horizontally polarised light to pass through
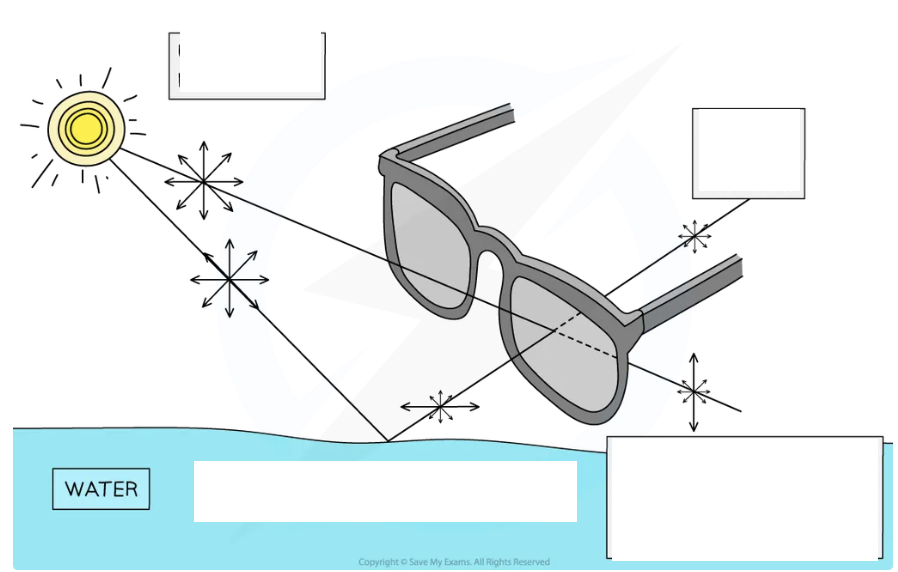
Polaroid sunglasses: light reflected from reflective surface undergo?
surface is horizontal, proportion of the reflected light will oscillate ______ in the ________ plane than the _______ plane
What is polarised sunglasses useful for and what is useful for?
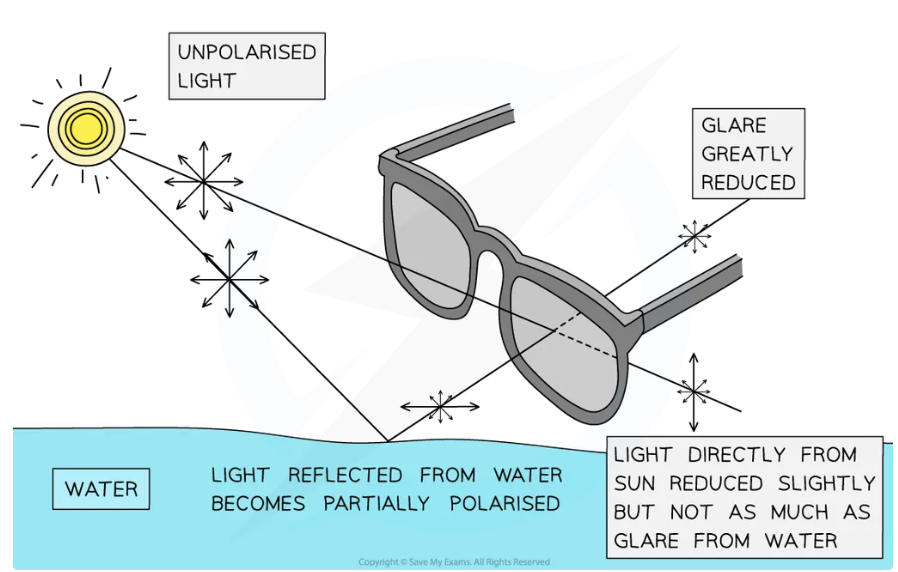
Light reflected from reflective surface e.g. the surface of water/wet road, it undergoes partial plane polarisation
surface is horizontal, proportion of the reflected light will oscillate more in the horizontal plane than the vertical plane
Polaroid sunglasses useful in reducing the glare on the surface of the water (or any reflective surface) as partially-polarised light will be eliminated by the polarising filter
Objects under the surface of the water can be viewed more clearly
What do polarising filters enable photographs do?
Light reflected on surface of water is ______ polarised in the _____ plane
Glare is _________ by the polarising lens but light from the underwater object is ____________ by the surface of the water, not reflected, so it is _______ plane-polarised
Light from the underwater object is more _________ than the glare and shows up much morE _________ in the photo
Polarising filters enable photographers to take photos of objects underwater
Light reflected on surface of water is partially polarised in the horizontal plane
Glare is eliminated by the polarising lens but light from the underwater object is refracted by the surface of the water, not reflected, so it is not plane-polarised
Light from the underwater object is more intense than the glare and shows up much more brightly in the photo
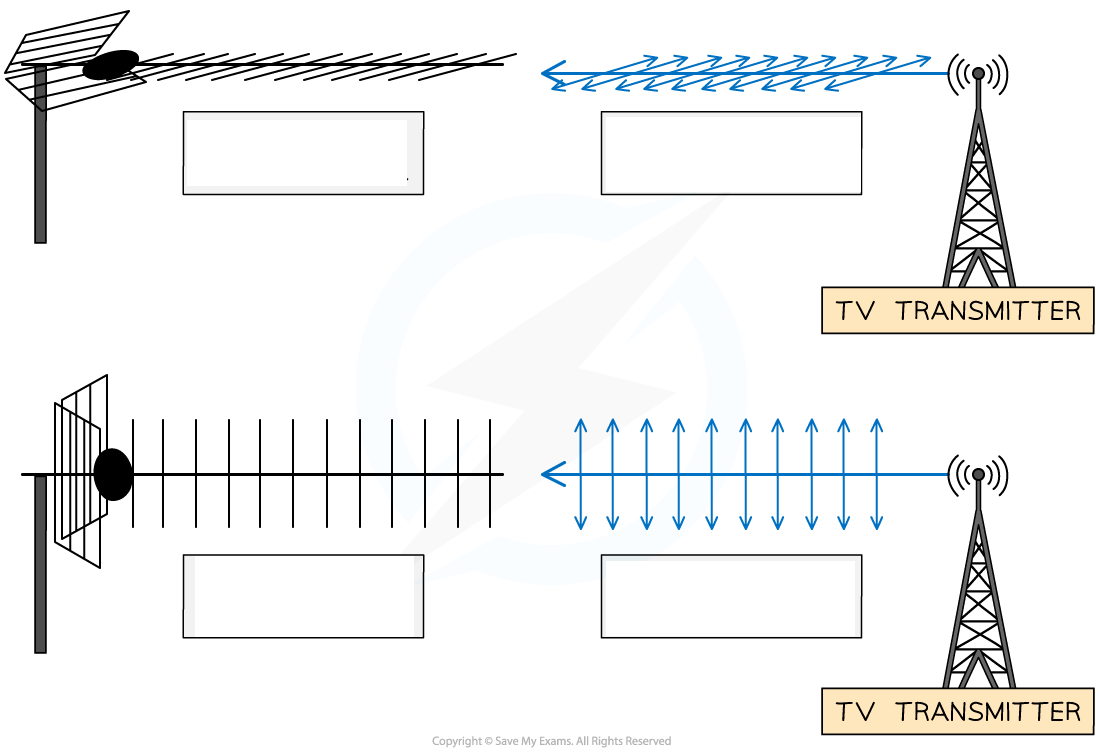
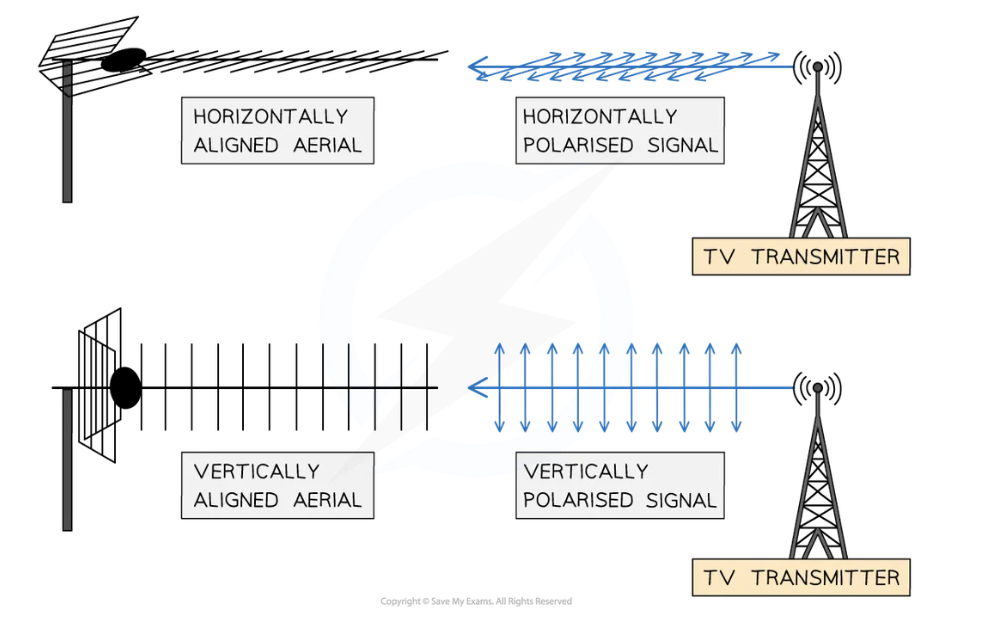
Radio and television services broadcast _______-_________/__________-__________
Reception aerial mounted ____ (horizontal)/on its _______ (vertical),
Orientation of aerial depend on _________ _________ towards and _________ of services being broadcast
Radio and television services broadcast horizontally-polarised/vertically-polarised
Reception aerial mounted flat (horizontal)/on its side (vertical),
Orientation of aerial depend on transmitter pointing towards and polarity of services being broadcast