Ultrasound and more
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
facts about ultrasound
frequency is greater than 20000 Hz
non ionising
non invasive
quick
medical imaging ultrasound has freq of 1-15MHz
can be refracted/reflected/diffracted at boundaries
can identify small features
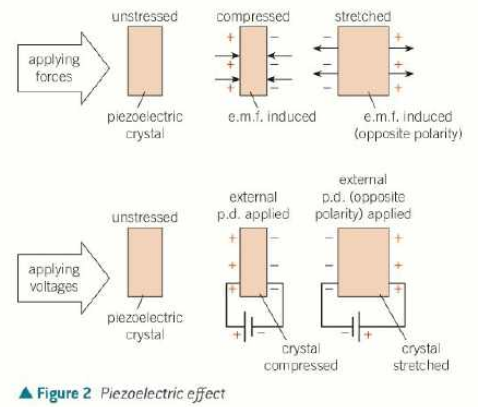
what is the piezoelectric effect?
when some crystals are compressed/stretched/twisted, they produce an emf and get a charge between opposite faces
this process is reversible so applying a pd across the crystals can compress or stretch them
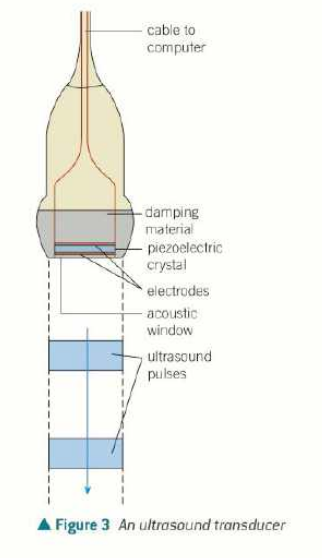
what and why are ultrasound transducers?
generates and receives ultrasound
changes electrical energy to/from sound
to generate, high frequency alternating pd is applied across opposite faces of crystal, compressing and expanding it
the frequency is the same as the frequency of oscillation of the crystal
the crystal resonates and produces an intense ultrasound signal
usually 5000 pulses of ultrasound are emitted per second
to detect ultrasound, any ultrasound incident on crystal makes it vibrate (compress/expand) so generates an alternating emf, which can be detected by circuit
the crystals are lead zirconate titanate or polyvinylidene fluoride instead of quartz nowadays
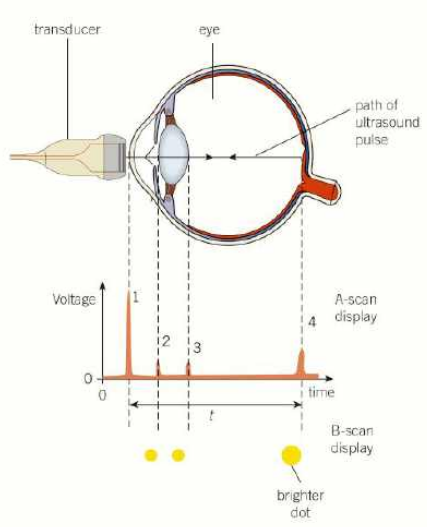
what is an a-scan?
a stands for amplitude apparently
transducer records along a straight line through the patient
can be used to determine the thickness of bone or the distance between two tissues like lens and retina
when ultrasound pulse sent into patient, it is partly reflected and partly transmitted at boundary
reflected pulse has less energy and is detected at transducer
oscilloscope displays pulses as voltage against time
distance can be calculated by multiplying time difference between initial pulse by speed of ultrasound (and dividing by 2 probably)
what is a b scan?
multiple a scans in different directions (b stands for brightness apparently)
the transducer is moved over patient’s skin so that 2D image produced
output of transducer is connected to high speed computer
for each position of transducer, dots produced on screen, showing boundary between tissues
brightness of dot is proportional to intensity of reflected ultrasound
what is acoustic impedance?
the fraction of ultrasound intensity reflected at boundary depends on it
defined as product of density of substance and speed of ultrasound in that substance
Z=pc (Z is measured in kgm-2s-1)
what is the intensity reflection coefficient?
the proportion of incident ultrasound reflected at the boundary, also known as \frac{Ir}{I0}
\frac{Ir}{I0}=\frac{\left(Z2-Z1\right)^2}{\left(Z2+Z1\right)^2} , where Z1 and Z2 are the acoustic impedances of the two substances
only works when angle of incidence is 0
the greater difference in Z, the more reflection happens
what is acoustic matching?
acoustic matching is when two substances have similar impedance values so negligible reflection occurs at their boundary
when the transducer is placed on skin, there are often air pockets between transducer and skin
the air skin boundary means 99% of ultrasound will be reflected before it enters patient
coupling gel is smeared onto skin because it has acoustic impedance similar to skin
the gel fills the air gaps and ensures that almost all ultrasound enters body
what is the Doppler effect in ultrasound?
when ultrasound is reflected off a moving object, its frequency changes
non invasive technique
range of frequencies 5-15MHz
uses reflection of ultrasound from blood cells to help doctors evaluate bloodflow through major arteries and veins
can reveal blood clots, fatty deposits
what happens during a doppler scan?
ultrasound transducer pressed lightly over skin
sends pulses of ultrasound and receives the reflected pulses from inside the patient
ultrasound reflected off tissues has same frequency, but ultrasound reflected off moving blood cells has different
when blood moving towards transducer, reflected wave has higher frequency
when blood moves away from transducer, reflected wave has lower frequency (and high wavelength)
change in f is directly proportional to v
only works for speed>1cm/s because lots of background ultrasound in tissues
computer colour codes direction and speed of blood
how to determine speed of blood with doppler effect?
\Delta f=\frac{2fv\cos\theta}{c}
f is original frequency, v is speed of blood, c is speed of ultrasound in blood
\theta is angle between skin and transducer, can’t be at right angles because cos 90=0