Chapter 2: Special Theory of Relativity
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
What is the principle of relativity?
The laws of physics are the same in all inertial systems. There is no way to detect absolute motion, and no preferred inertial system exists.
2
New cards
What is the constancy of the speed of light?
Observers in all intertidal systems measure the same value for the speed of light in a vacuum.
3
New cards
What does Einstein’s First Postulate indicate?
That the laws of physics are the same in all coordinate systems moving with uniform relative motion to each other.
4
New cards
What is true about two simultaneous events in a single reference frame?
They are not necessarily simultaneous in another reference frame.
5
New cards
What are the Lortentz transformations?
They are equations that makes the laws of physics invariant between inertial frames of reference.
6
New cards
List the Lorentz transformations.
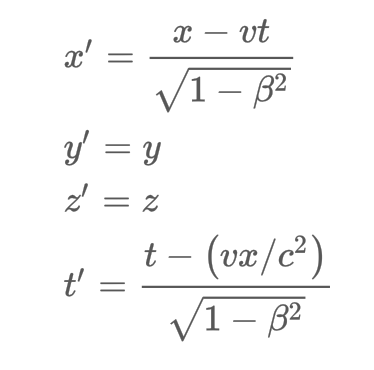
7
New cards
What are the inverse Lorentz transformation equations,.
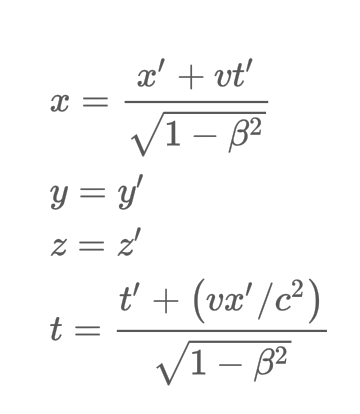
8
New cards
What is defined as the proper time?
The time interval between two events occurring at the same position in a system as measured by a clock at rest in a system.
9
New cards
Mathematically describe the formula for time dilation.
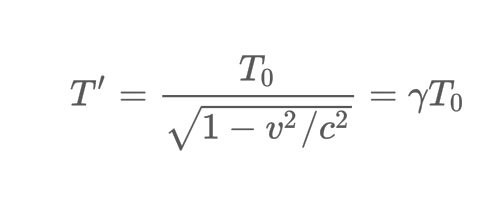
10
New cards
How is time dilation often interpreted?
By saying moving clocks run slow by the relativistic factor raised to (-1)
11
New cards
What is proper length?
The length of an object as measured by an observer at rest.
12
New cards
What is the formula for Length Contraction?
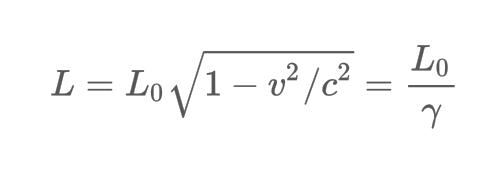
13
New cards
What is the Relativistic velocity addition formula (Lorentz velocity transformation)?
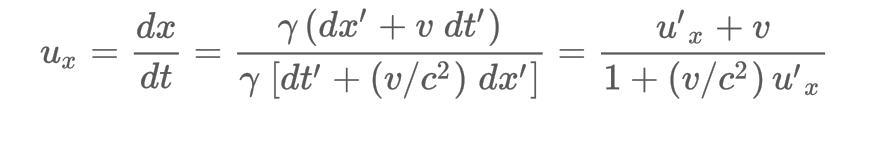
14
New cards
What is the radioactive decay law?
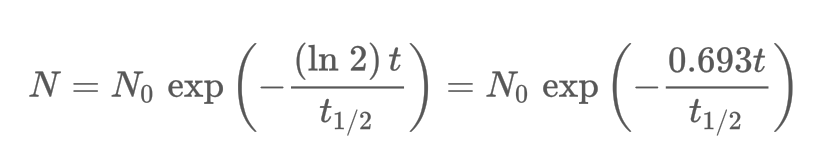
15
New cards
What is a light cone?
The path taken by a flash of light from a single event expressed geometrically by light travelling in all directions in spacetime. In such a diagram, the light cone divides spacetime into the past, future, present, and elsewhere.
16
New cards
What are invariant quantities?
Quantities that have the same value in all inertial frames.
17
New cards
What are the three possibilities for the invariant quantity Delta S squared?
1) If = 0: The two events can be connected by a light signal and have a lightlike separation
2) If > 0: No signal can travel fast enough to connect the two events. The events are not casually connected and are said to have a space like separation.
3) If < 0: Two events can be casually connected, the interval is said to be timeline.
2) If > 0: No signal can travel fast enough to connect the two events. The events are not casually connected and are said to have a space like separation.
3) If < 0: Two events can be casually connected, the interval is said to be timeline.
18
New cards
What are properties of space like separation?
There is always a findable inertial frame traveling at a velocity less than c in which the two events can occur simultaneously in time by at different places in space.
19
New cards
What are the properties of timeline separation?
There is a findable inertial frame traveling at a velocity less than c in which the two events occur at the same position in space but at different times. The two events can never occur simultaneously.
20
New cards
Mathematically define the relativistic doppler effect.
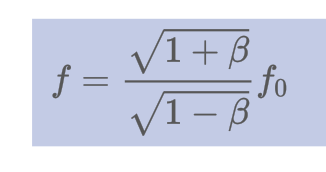
21
New cards
What are redshifts?
A change in frequency of light being emitted by an object moving at high speeds relative to us. Redshift is for a lower frequency, and blueshift is for a higher frequency than as measured by us at rest.
22
New cards
Mathematically define the the generalized Doppler shift equation.
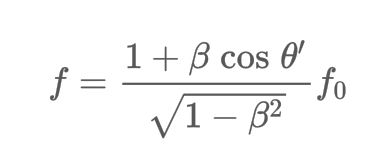
23
New cards
What is the formula for relativistic momentum?
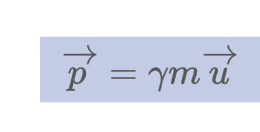
24
New cards
What is the formula for Relativistic force?
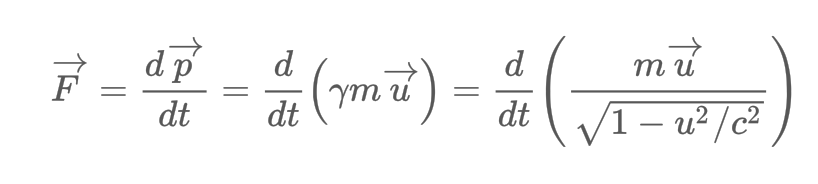
25
New cards
What is the formula for relativistic kinetic energy?
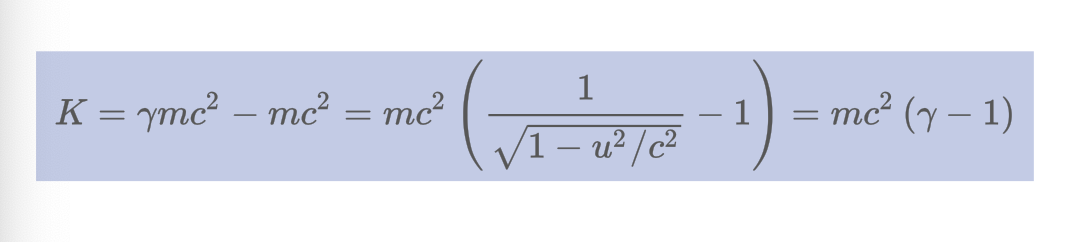
26
New cards
What is rest energy?
The energy equivalent to the mass of a particle at rest in an inertial frame of reference ,equal to the rest mass times the square of time speed of light: E naught.
27
New cards
What is total energy?
The sum of the kinetic energy and rest energy, denoted by E.
28
New cards
Mathematically describe the total energy.
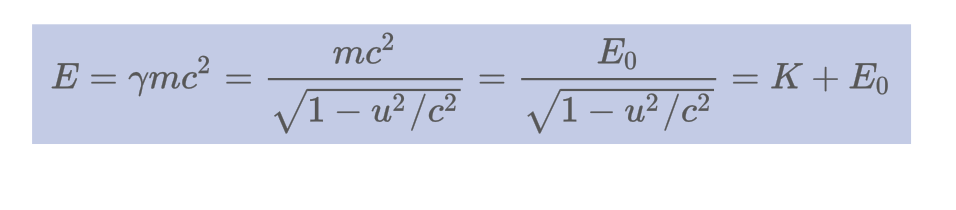
29
New cards