GCSE AQA Physics - Electricity
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Electrical current
The flow of electrical charge.
Size of current
The rate of flow of charge.
Potential difference
The energy transferred per unit of charge.
Resistance
Opposition to flow of electrical current.
The greater the resistance across a component (2)
The smaller the current that flows for a given potential difference.
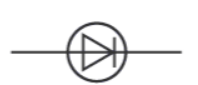
What is this component?
Diode
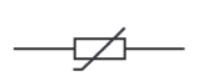
What is this component?
Thermistor
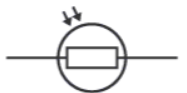
What is this component?
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
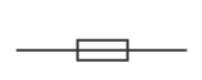
What is this component?
Fuse
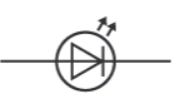
What is this component?
Light-emitting diode
Ammeter
Measures the current.
How must the ammeter be placed?
In series
Voltmeter
Measure the potential difference.
Relationship between length of wire and resistance
Resistance is directly proportional to length.
Ohm’s law
Potential difference across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, and resistance is constant.
Ohmic conductors
A conductor that follows ohm’s law, having a constant resistance.
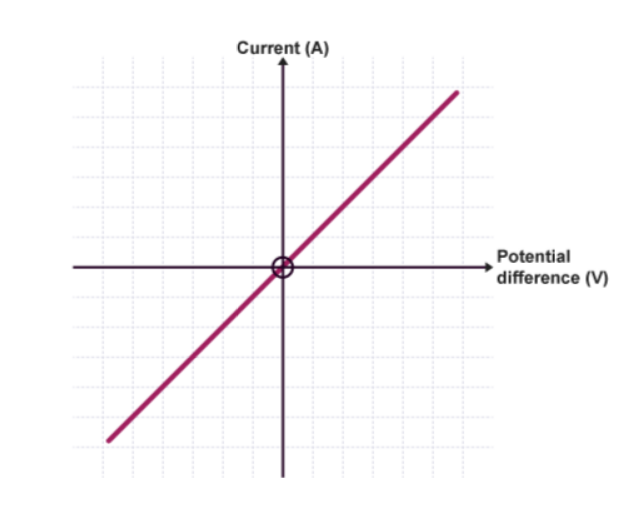
What component’s IV characteristic is this?
Ohmic conductor/variable resistor
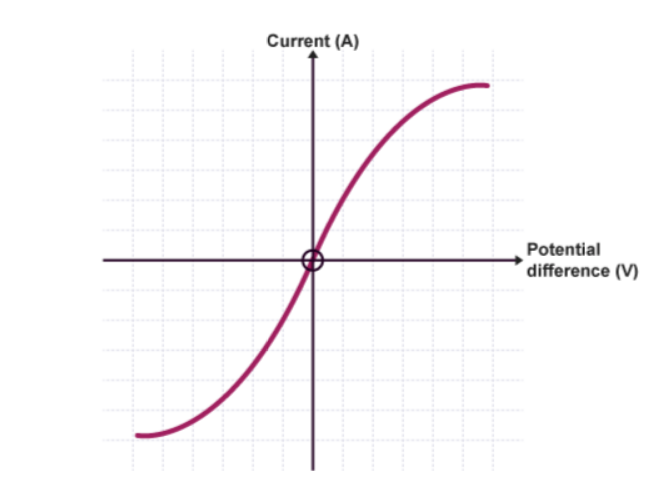
What component’s IV characteristic is this?
Filament lamp
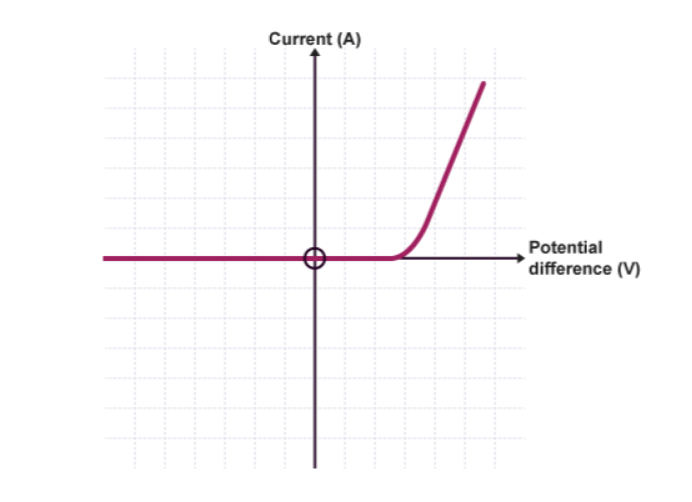
What component’s IV characteristic is this?
Diode
LDR (Light Dependent Resistor)
A resistor that is dependent on light intensity.
How is an LDR affected by light?
In bright light, resistance falls
In darkness, resistance is the highest
Thermistor
A temperature dependent resistor.
Explain why a cooling fan does not run when temperature is low in a sensing circuit
The thermistor has a high resistance
So the thermistor has high potential difference
And so potential difference across the cooling fan is low
Explain why a cooling fan runs when temperature is high in a sensing circuit
The thermistor has a low resistance
So the thermistor has a low potential difference
And so potential difference across the cooling fan is high
How come a light sensing circuit has the opposite effect to a temperature sensing circuit?
The LDR is connected in parallel to the lamp, so in the darkness resistance for the LDR and the lamp will be highest, and therefore potential difference as well.
Current in series circuits
the same flows through all components
Potential difference in series circuits
shared between components
Resistance in series circuits
adds up
Current in parallel circuits
shared between branches
Potential difference in parallel circuits
the same across each branch
resistance in parallel circuits
less than the resistance of the smallest resistor
Alternating current (AC)
Current that is constantly changing direction.
UK mains supply voltage
230V
UK mains supply frequency
50Hz
Direct current
Current that is always flowing in the same direction.
How is AC created?
By alternating voltage, in which the positive and negative ends continuously reverse.
Live wire
Brown wire that provides the alternating potential difference from the mains supply.
Neutral wire
Blue wire that completes the circuit from the appliance back to the supply. It is around 0V.
Earth Wire
green and yellow - Only carries current when there’s a fault to stop the appliance casing from becoming live.
How can the live wire give you an electric shock? (3)
Your body is at 0V
If you touch the live wire a large potential difference is produced and current flows through your body
This causes an electric shock
Why is any link between the live wire and earth dangerous?
If the link creates a low resistance path, a huge current will flow which could start a fire.
Power
The rate of energy transfer.
Power rating
The maximum safe power an appliance can operate at.
Electrical appliances
Designed to bring about energy transfers.
The national grid
A giant system of cables and transformers that distributes electrical power from the power stations to the consumers.
Why do power stations usually run below their maximum power output?
So they can spare electricity to deal with a higher demand.
How do power stations produce enough electricity for everyone when they need it?
By predicting when demand will change. For example when people wake up in the morning, or during a sporting event.
Why does the national grid use a high potential difference and a low current?
To decrease the energy lost by heating.
Transformer
A device which can change the potential difference of an ac supply.
Step-up transformer
Increases potential difference.
Step-down transformer
Decreases potential difference.
power in primary coil =
power in secondary coil
Static charge
An electrical charge which is not free to move, which usually forms on insulators.
How is a static charge created? (3)
Two insulating materials are rubbed together
Electrons will be transferred from one material to the other
This leaves a positive static charge on one and an equal negative on the other
How does a spark occur? (2)
Two objects have a high potential difference between them
This causes electrons to jump across the gap between them
Like charges
Repel
Opposite charges
Attract
Electric field
A region in which an electrically charged object will feel an electrostatic force.
Direction electric field lines
Positive to negative
Explain sparks with electric fields (4)
There is a high potential difference between two objects
This causes a strong electric field between the objects
The strong electric field causes electrons in air particles to be removed
The air is now much more conductive, allowing a current to flow through it.