CP1 Quiz 1 Lecture (copy)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Who was the founder of Chiropractic?
Daniel David (D.D) Palmer
What type concepts did D.D. Palmer blend?
Spiritual and Metaphysical
D.D. Palmer applied force to which vertebra on Havrey Lillard to restore his hearing?
T4
Who was known as the developer?
B.J. Palmer
What is Prop 16?
California Chiropractic Initiative Act of 1922
Legal framework for the practice of chiropractic in California. It also outlines the requirements for licensure.
The U.S. Department of Education recognized the ______ as the accrediting agency of the Chiropractic profession.
Council on Chiropractic Education (CCE)
Broad-scope Chiropractic Care is committed to _______ and working with patients to optimize their health.
Holistic health care
How many national board exams do you need to pass to become a licensed chiropractic?
4 (PART I-IV), plus physiotherapy
Chiropractic is the largest _____ profession!
CAM (Complimentary and Alternative Medicine)
What are the biomechanics of the SI Joint?
Nutation
Counternutation
Internal Rotation
External Rotation
Nutation and Counternutation ONLY occur with?
Trunk Flexion and Extension when changing from upright, seated and recumbent positions
Define: Static Listings
Describe a "fixed" malposition or restriction in the sacroiliac (SI) joint when the body is in a non-moving state
Define: Dynamic Listings
Refer to problems that manifest or are triggered during motion, such as when the patient stands, sits, walks, or performs other functional movements.
Axes of Motion: Sagittal Plane
Divides the body from left and right
Axes of Motion: Frontal/Coronal Plane
Divides the body from anterior and posterior
Axes of Motion: Horizontal/Transverse Plane
Divides the body from superior and inferior
Types of Sagittal plane movement?
Flexion and Extension
Types of Frontal/Coronal plane movement?
Lateral flexion, adduction and abduction
Types of Horizontal/Transverse plane movement?
Rotation
What are the six degrees of freedom?
Flexion
Extension
Right Rotation
Left Rotation
Right Lateral Flexion
Left Lateral Flexion
What are the doctor positions?
Fencer Stance
Square Stance
Contact Hand/Point (CH/CP):
Doctor’s hand
Focus of force
Line of drive
Endfeel assessment
Indifferent / Support Hand (IH /SH):
Doctor’s hand
Stabilize
Fixate
Support
Segmental Contact Point (SCP):
Patient’s body
Usually bony landmark (PSIS, Sacral Ala, Ischial Tuberosity, etc)
Tissue Slack (TS):
Removes slack from superficial soft tissues
Estabilishes positive contact CH and SCP
Don’t know how much till you do it!
Line of Drive (LOD):
The direction in which force is applied
Joint Motion consists of FIVE qualities of movement for normal joint function:
Joint Play
Active ROM
Passive ROM
Endfeel
Paraphysiologic Movement
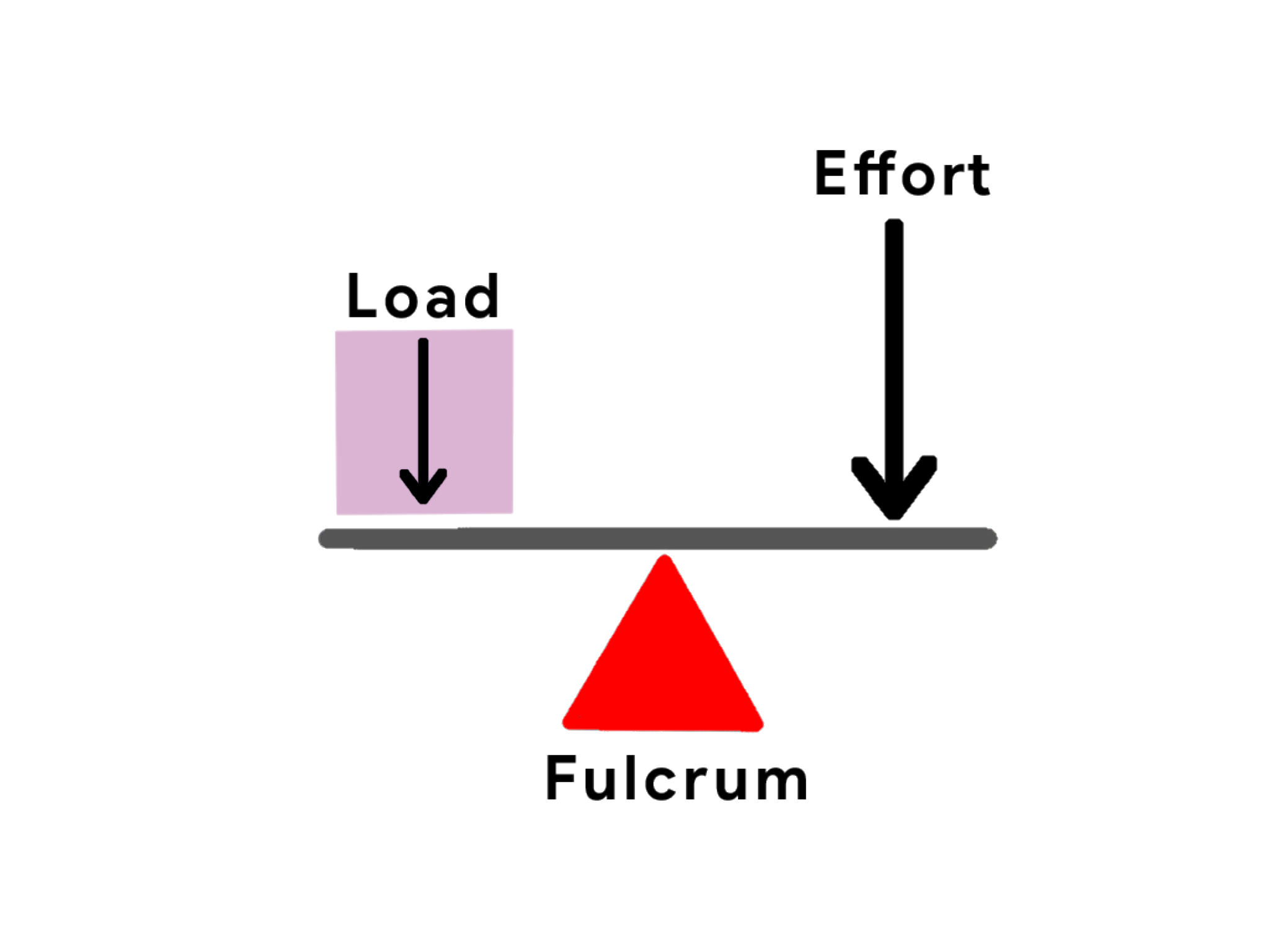
1st Class Levers:
The axis is between the force and resistence
Ex: Seasaw, biscep curl
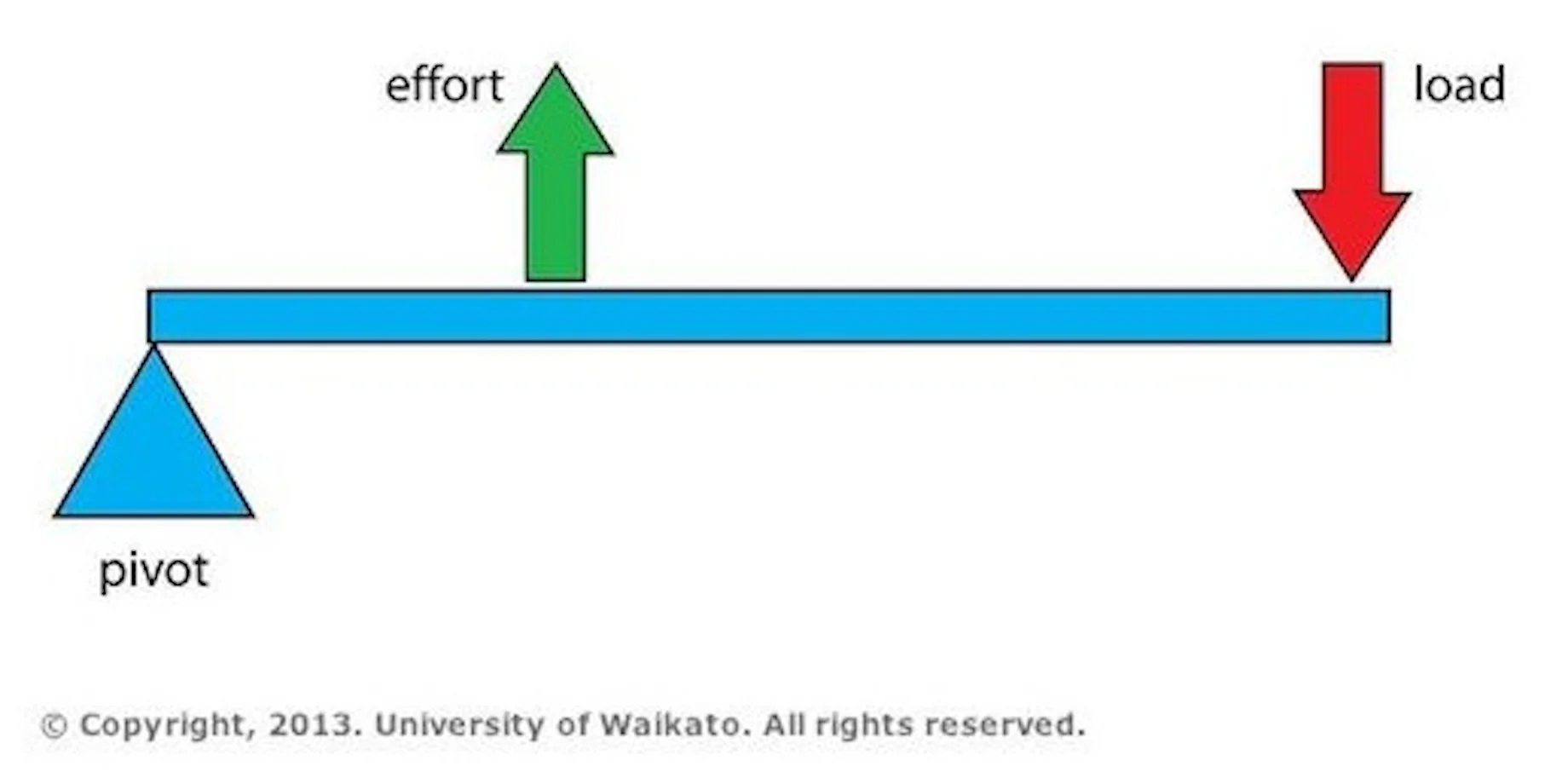
2nd Class Levers:
The resistance is between the axis and the force
Ex: Barrel
3rd Class Levers:
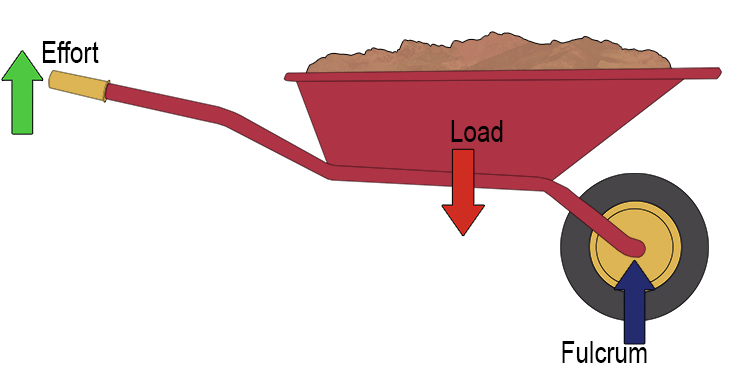
The force is between the axis and resistance
Ex: Shovel
Define: Joint Subluxation/Dysfunction Syndrome (JSDS)
Clinical diagnosis defined by an aggregate of signs and symptoms that are assumed to identity dysfunction of spinal, pelvic, or peripheral joints.
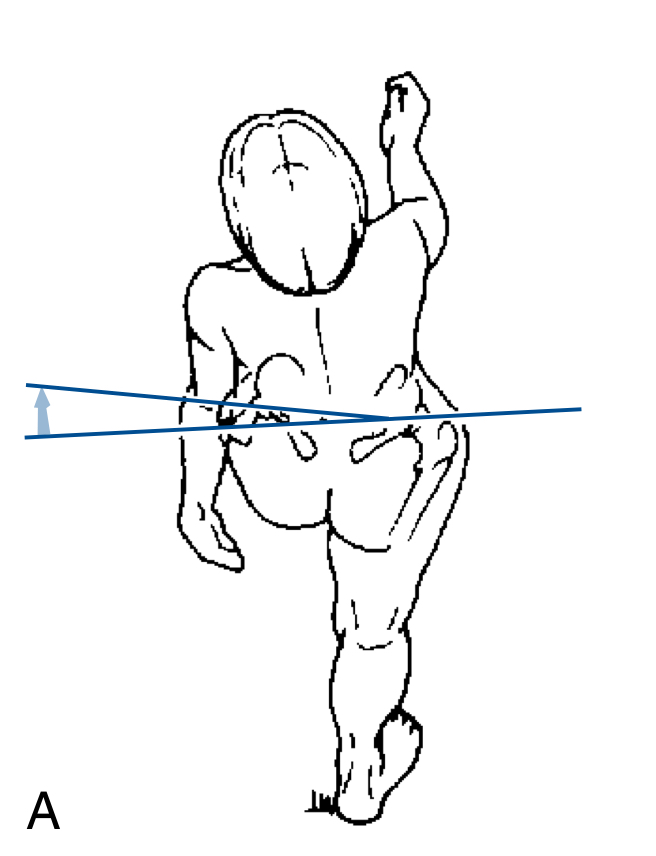
Describe the posterior movement of the pelvic joint:
Left hip and sacroiliac joint flexion and right hip and SI joint extension.