Unit 5- removal of permanent teeth in normoposition
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is syndesmotomy?
Initial cut of periodontium circular fibres- separates gingival margin tissues
Why is it easier to extract in maxilla than mandible
Has spongy bone
No articulation
Less saliva/blood and no tongue- better visibility and access
How does the root anatomy, anatomical relationships of upper central incisor effect exodontia? What materials should be used?
Powerful root, elliptical cross section, apex towards distal
Close to nasal floor and nasopalatine foramen- risk of perforation
Straight elevator, upper incisor forceps
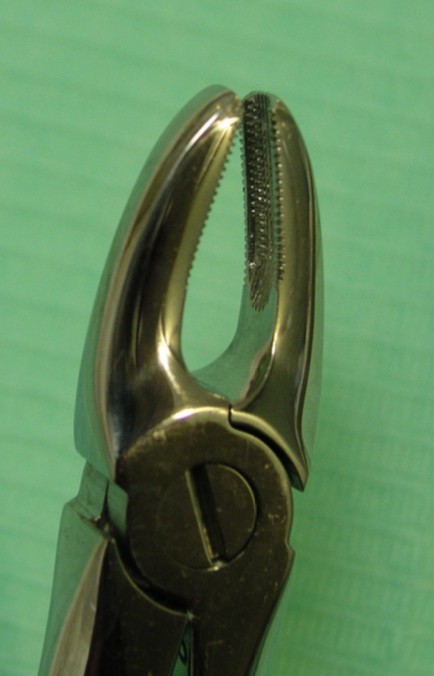
How does the root anatomy, anatomical relationships of lower incisors effect exodontia? What materials should be used?
Conical root, flat MD
Buccal cortical plate- thick solid, lingual- thinner, but increased resistance in lingual cortical
Lower incisor forceps, 90 degrees and narrow valves, elevators
Avoid rotation

What is the exodontia technique for upper lateral incisors?(5)
Syndesmotomy- with straight elevator
Prehension with narrow valves forceps
Luxation with movements Bc (low amplitude) –Pt (greater amplitude)
Rotation carefully due to root curvatures
Traction downwards and forward
Why is extracting the upper canine difficult?
Very long root
Buccal cortical plate- thin vs thick palatally
Syndesmotomy and luxation with straight elevator
Careful luxation towards Bc and wider towards Pt
Short rotational movements
Traction downwards and forward
What’s the difference in extracting as a 1st upper premolar?
Syndesmotomy and location with straight elevator
Luxation
Never rotational movements
Traction
Two thin fragile roots, very close to maxillary sinus, danger of root fracture
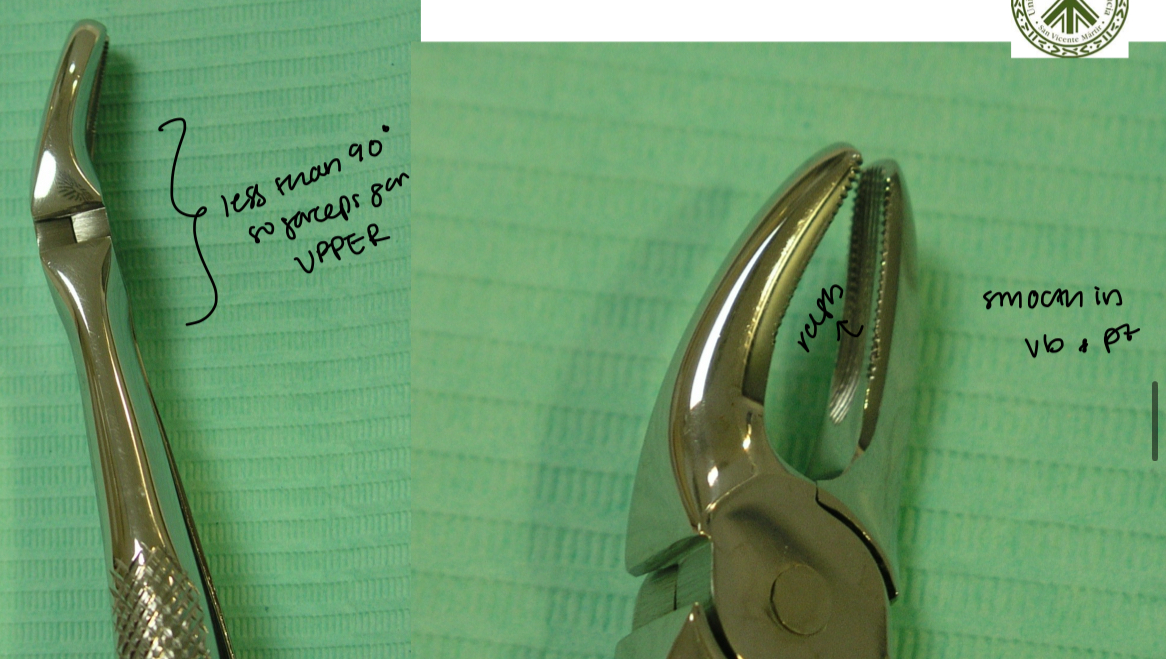
What’s the difference between extracting upper 1st vs 2nd premolar?
Only 1 root
Can have some rotational movements
What anatomical features should you consider when extracting a first upper molar?
3 divergent roots towards apical-
Pt- powerful, long and thick cone towards pt
MB- fine root, short and flattened MD
DB- thinner and flattened upwards
Direct relationship with the maxillary sinus (NO ROTATION)
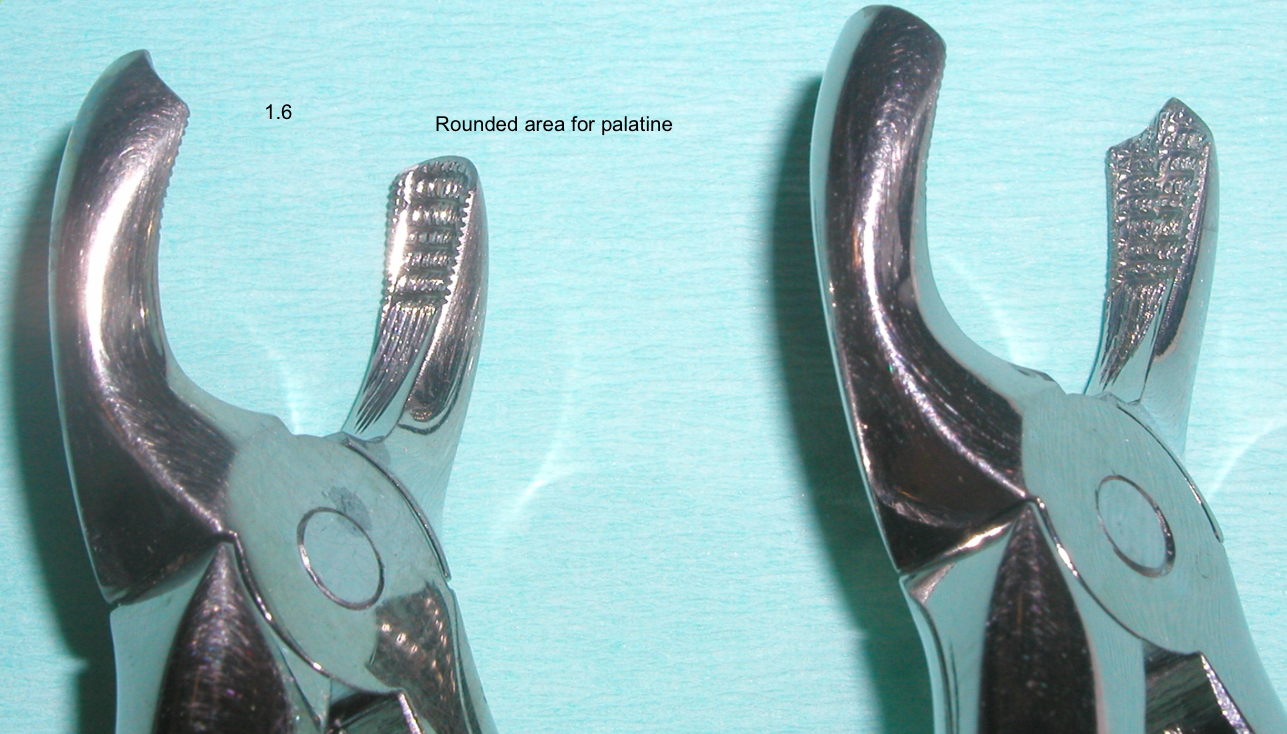
What is the technique to extract an upper 1st molar?
Syndesmotomy and luxate (bc-pt) with straight elevator
Grip- Palatal side- grip with a ribbed, straight valve
Buccal side- forceps beak positioned into the interradicular furcation
Circumduction- rotate
Traction
Odontosection if roots too divergent or fractured
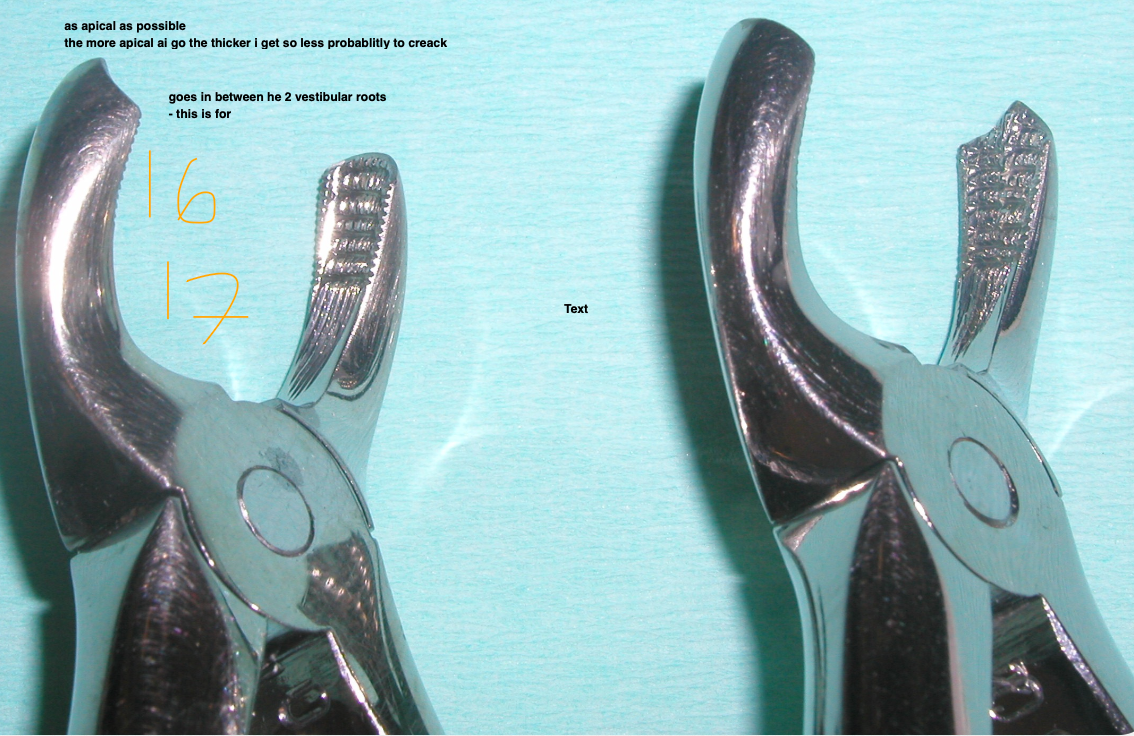
How does the root anatomy and anatomical features effect extraction of 2nd upper molar?
3 roots- can be divergent or fused or separated or convergent
Outer buccal cortical plate thicker due to zygomatic process
Close to maxillary sinus, palatine root close to posterior palatine foramen
X ray to see relationship with 3rd molar
How does the root anatomy and anatomical features effect extraction of 3rd upper molar and its technique?
Number of roots vary, fused
Distal- maxillary tuberosity- fragile, can fracture
1st luxation with elevator- rotational, force down and backwards
2nd luxation + traction with forceps- not fully open mouth
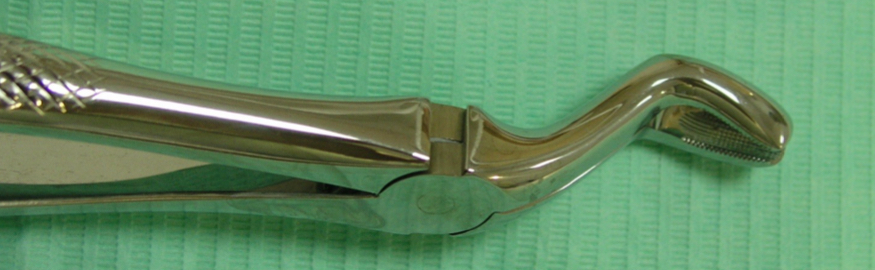
How does the root anatomy and anatomical features effect extraction of lower canine?
Same as upper
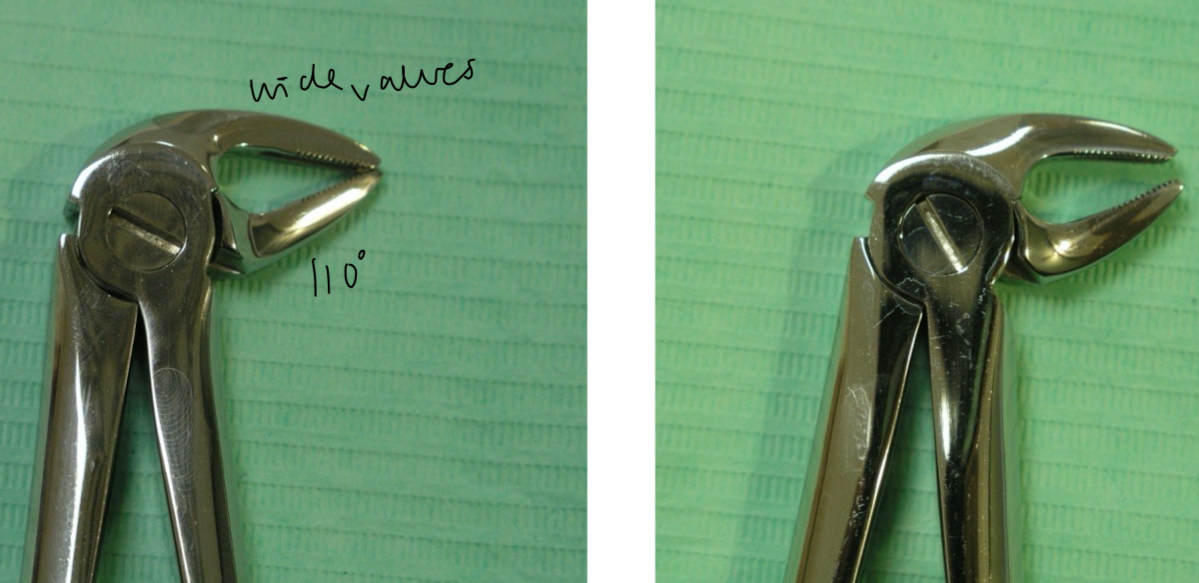
How does the root anatomy and anatomical features effect extraction of lower premolars?
Single strong conical root, weak narrow neck, compact corticals
Careful of mental foramen
Same forceps as lower canines (110 degrees and large valves)
How does the root anatomy and anatomical features effect extraction of 1st lower molar?
2 roots=no rotation
Mesial- large, tapered, flat md
Distal- longer, straight-ish
Compact cortical and strong interradicular septum
Luxate, prehension, laterality, traction towards bc
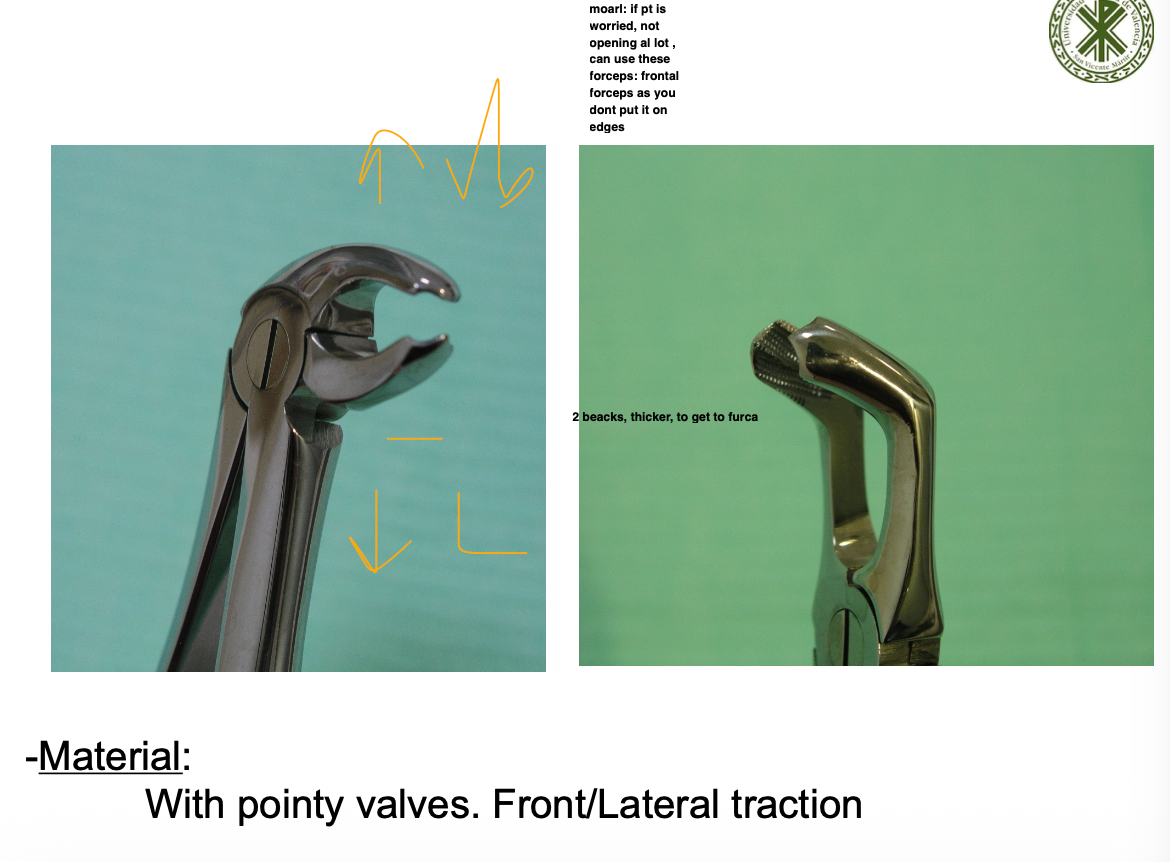
How does the root anatomy and anatomical features effect extraction of 2nd lower molar, how so you extract if fused bs separated?
2 smaller straight conical
Compact thick cortical
If fused roots- luxate distal with elevator or physick
Separated- lateral traction
How does the root anatomy and anatomical features effect extraction of 3rd lower molar?
Thick buccal cortical
Do x ray
Technique same as 1st and 2nd molar
When is extraction of temporary teeth is indicated and what should you be cautious of?
Destructive caries or delay in replacement
X ray to assess relationship with definitive germs
Permanent pm germ between temp molar roots