RNA and Protein Synthesis
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
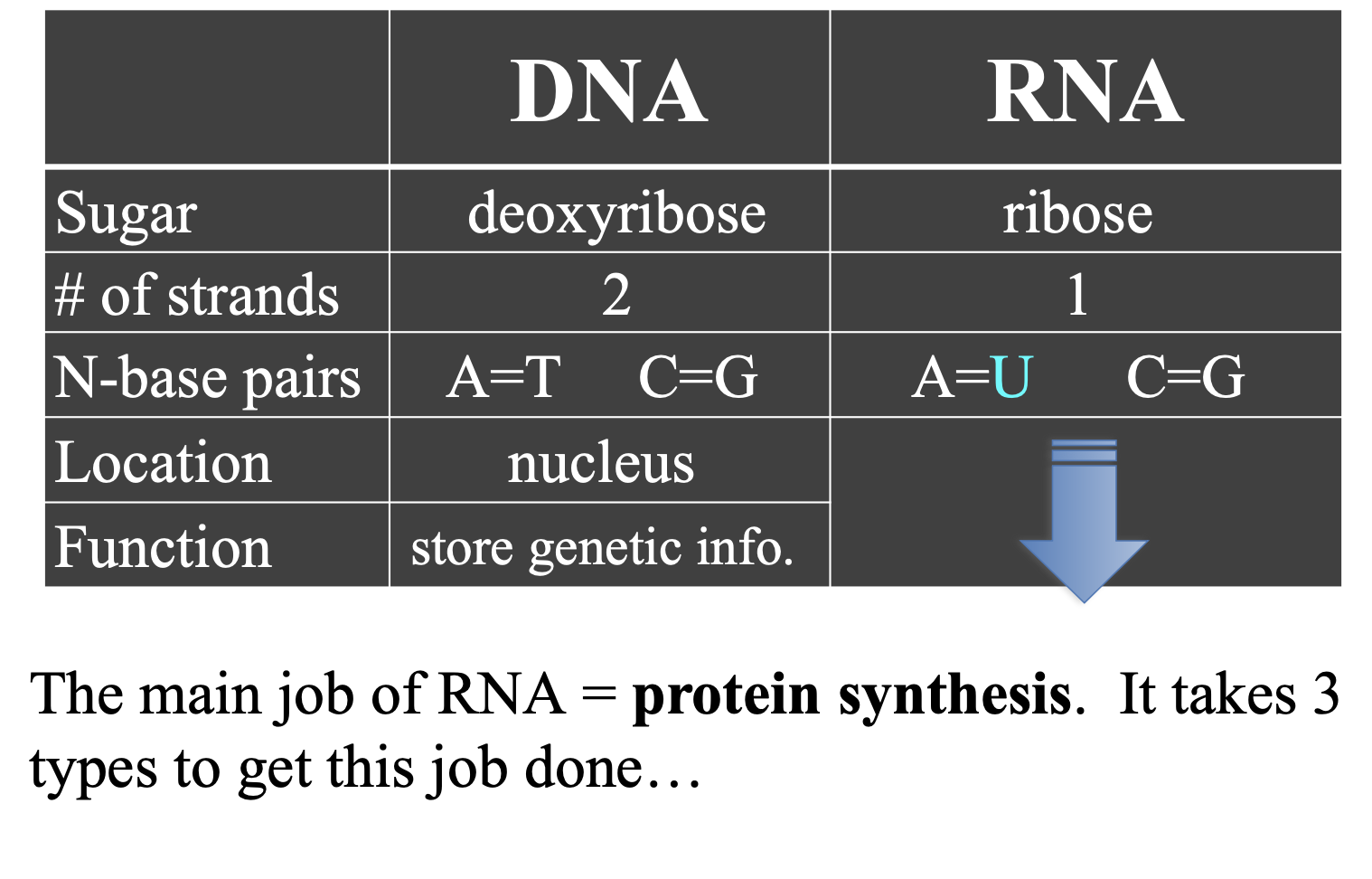
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
single strand of nucleotides
5 C sugar is ribose
uracil instead of thymine, adenine in RNA binds to uracil (U)
Similarities between RNA and DNA
are both nucleic acids made up of nucleotides (sugar attached to a phosphate and N-base)
Table for DNA and RNA
What are the 3 types of RNA called?
mRNA - messenger RNA
rRNA - ribosomal RNA
tRNA - transfer RNA
What are the three consecutive bases on mRNA called?
Codon
mRNA
Location: 1. nucleus, 2. cytoplasm
Function:
transcription
carry code (message) to ribosomes
rRNA
chemical that makes up the ribosomes
tRNA
Location: travels to ribosomes
Function:
translation = transfers amino acids to build the protein
Protein Synthesis
Transcription = making RNA
Translation = making protein
Transcription
mRNA is made by copying the code from DNA in the nucleus.
mRNA leaves the nucleus to the cytoplasm where ribosomes will attach to it
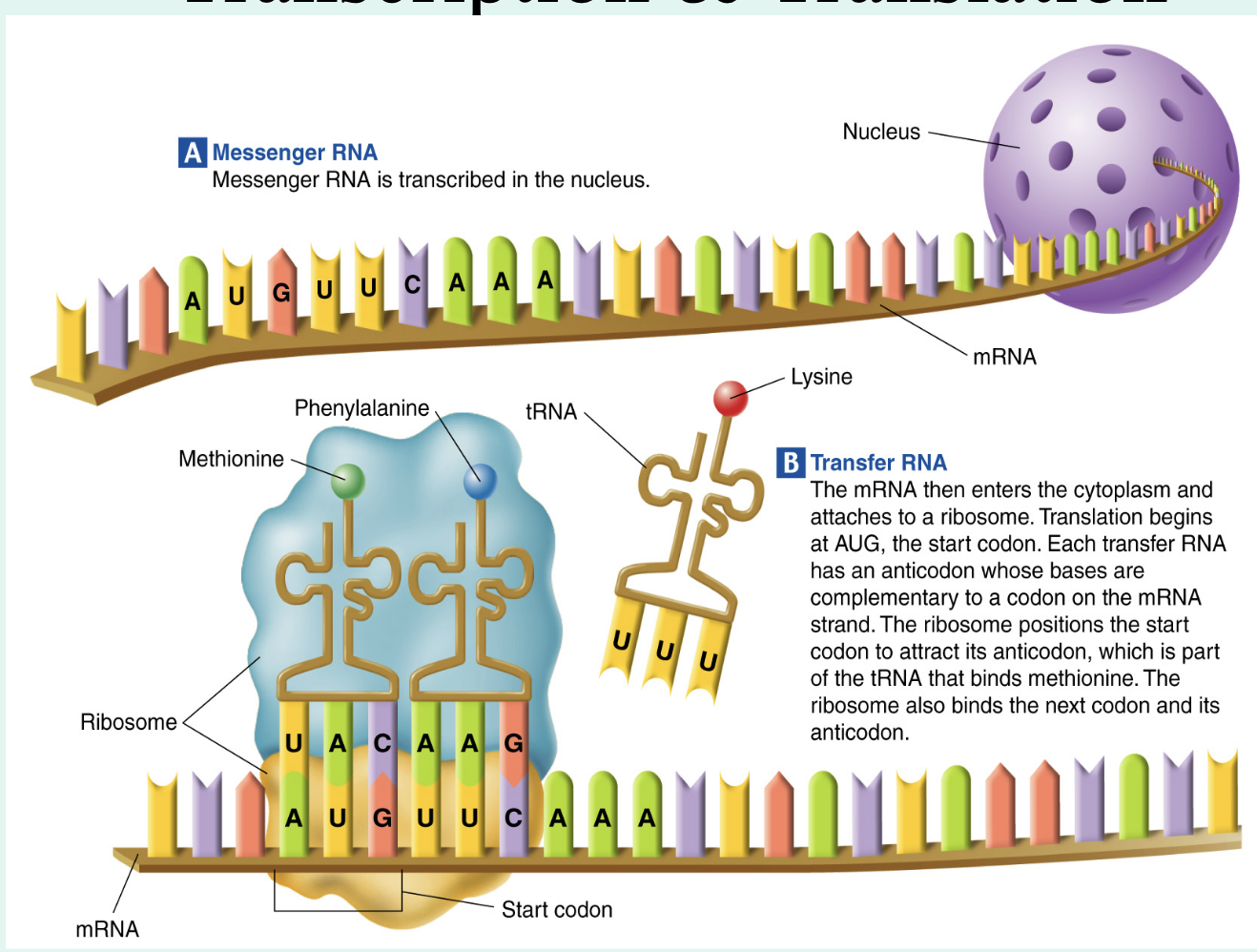
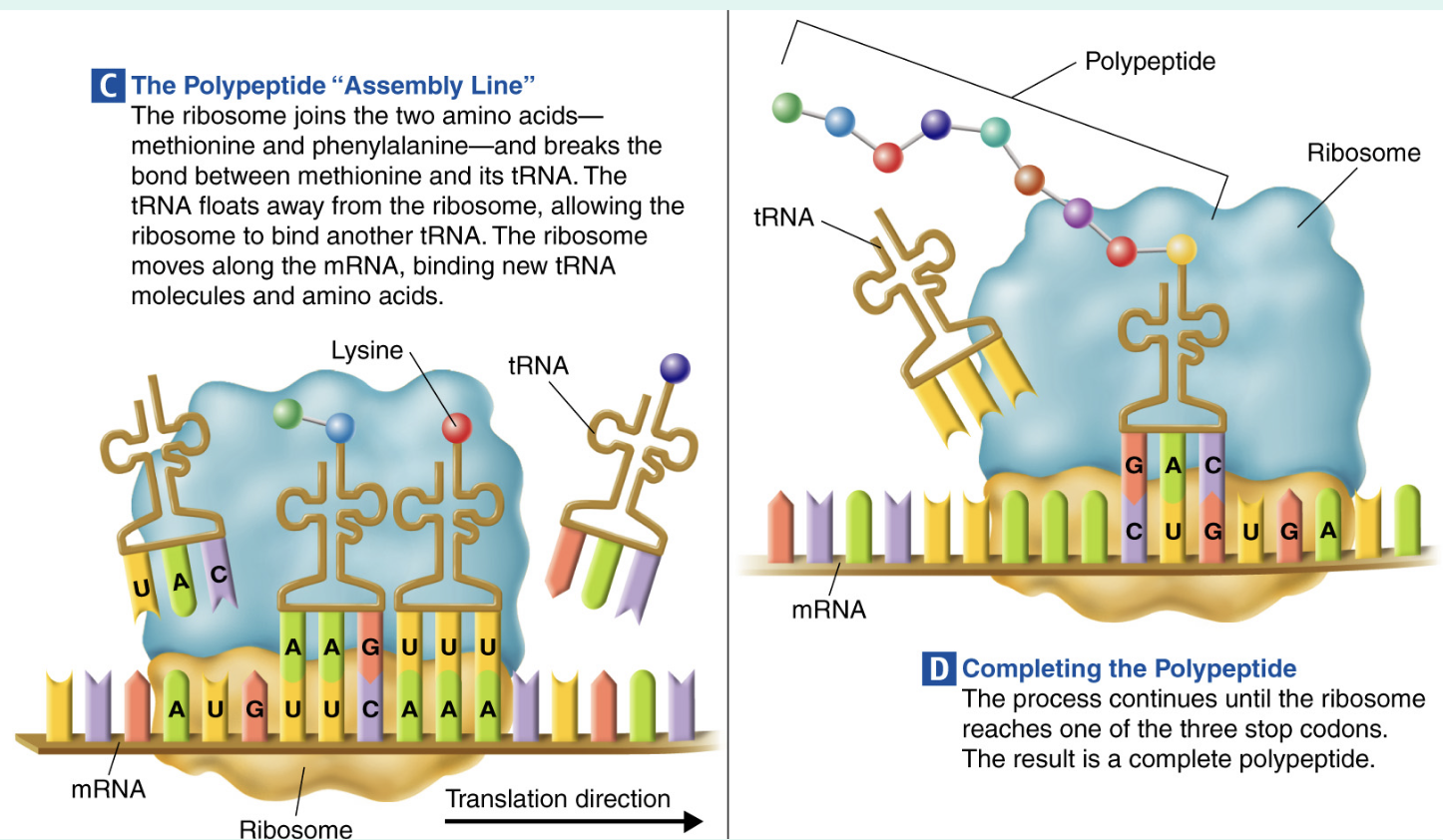
Translation
Matching codons with anticodons, tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes where they are assembled into proteins.
Proteins
buildings blocks are amino acids