tools for examining brain structure and function
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
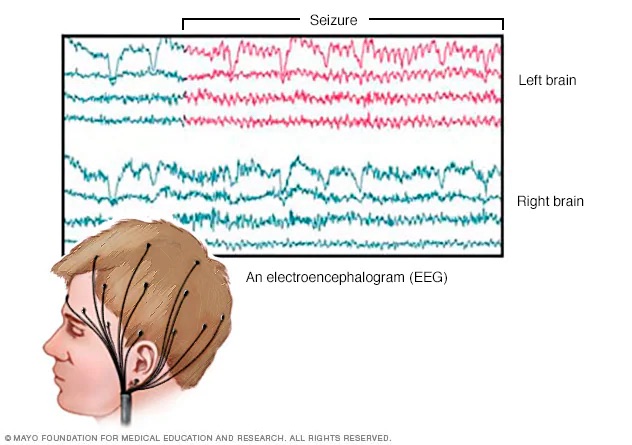
what is a electroencephalogram (EEG)?
a test that measures electrical activity in the brain
electrodes placed in specific locations around the skull detect changes in electrical activity and display them visually
strengths of EEG?
non-invasive, useful for broad based behaviours like sleeping (REM patterns)
weaknesses of EEG?
inaccurate, cannot narrow down brain activity to a specific region of the brain
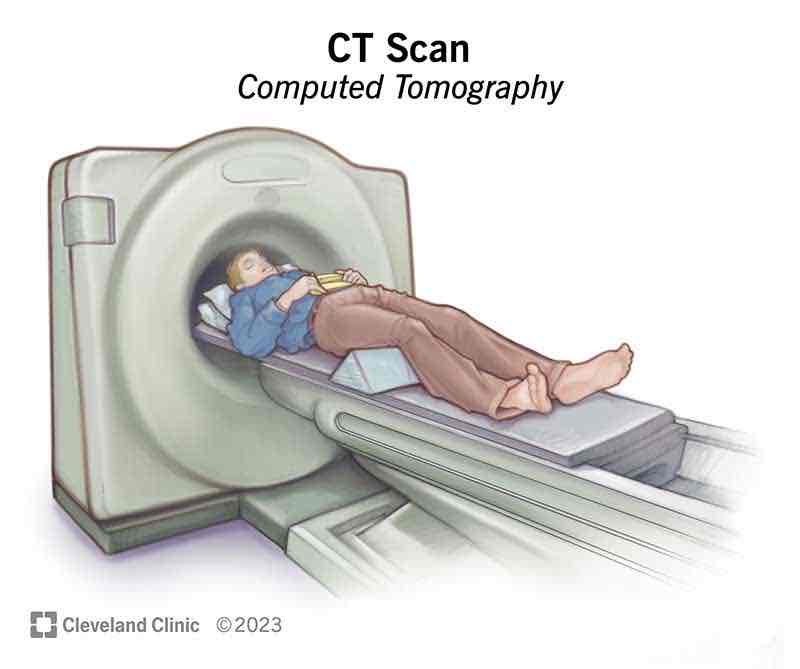
what is computed tomography (CT)?
A combined computer and X ray image showing slices of the skull from multiple angles including the soft tissues of the brain
what is a MRI?
a medical imaging technique that uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to create detailed pictures of the inside of the body
weaknesses of CT?
does not show brain activity
what is a functional MRI (fMRI)?
a noninvasive brain scan that measures brain activity by tracking changes in blood flow
the fMRI can track these changes in the brain metabolism as they occur in patients as thoughts, emotions, or actions occur
strengths of fMRI?
this enables psychologists to map the functioning regions of the brain with a high degree of accuracy
weaknesses of fMRI?
biocorrelation
strengths of MRI?
can produce a detailed three dimensional image
weaknesses of MRI?
dangerous for certain individuals – pacemakers, metal implants
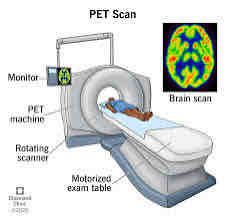
Positron Emission Tomography – PET scans
an imaging system that relies on the principle that the brain’s consumption of sugars increases in areas that are active
radioactive sugars are injected into a patient that will emit gamma rays when metabolized by the brain
these rays can be detected and an image can be produced that shows localized brain activity
strengths of PET scans?
gives a colorful and dynamic picture of brain activity; shows structural changes that indicate problems before they can show up on MRI or CT scans
weaknesses of PET scans?
not as precise as a fMRI; health problems can occur with the injection of radioactive substances
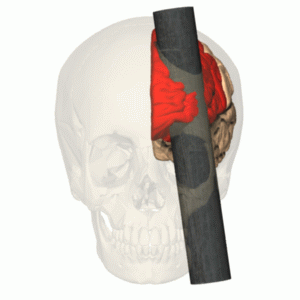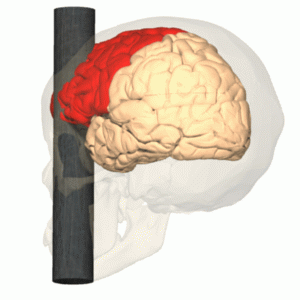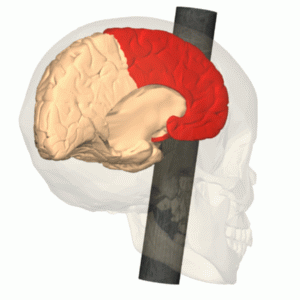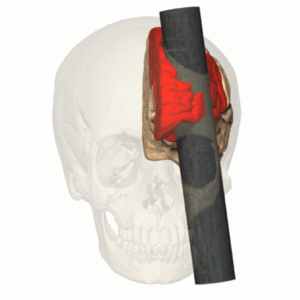
lesion studies
Removal or damage of regions of the brain and studying corresponding behaviour changes under controlled conditions
Can be done experimentally or via case study on pre-existing subjects
strengths of lesion studies?
strong correlation and clear observational variables
weaknesses of lesion studies?
ethical issues, sampling issues (humans), generalization issues (animals), biocorrelation
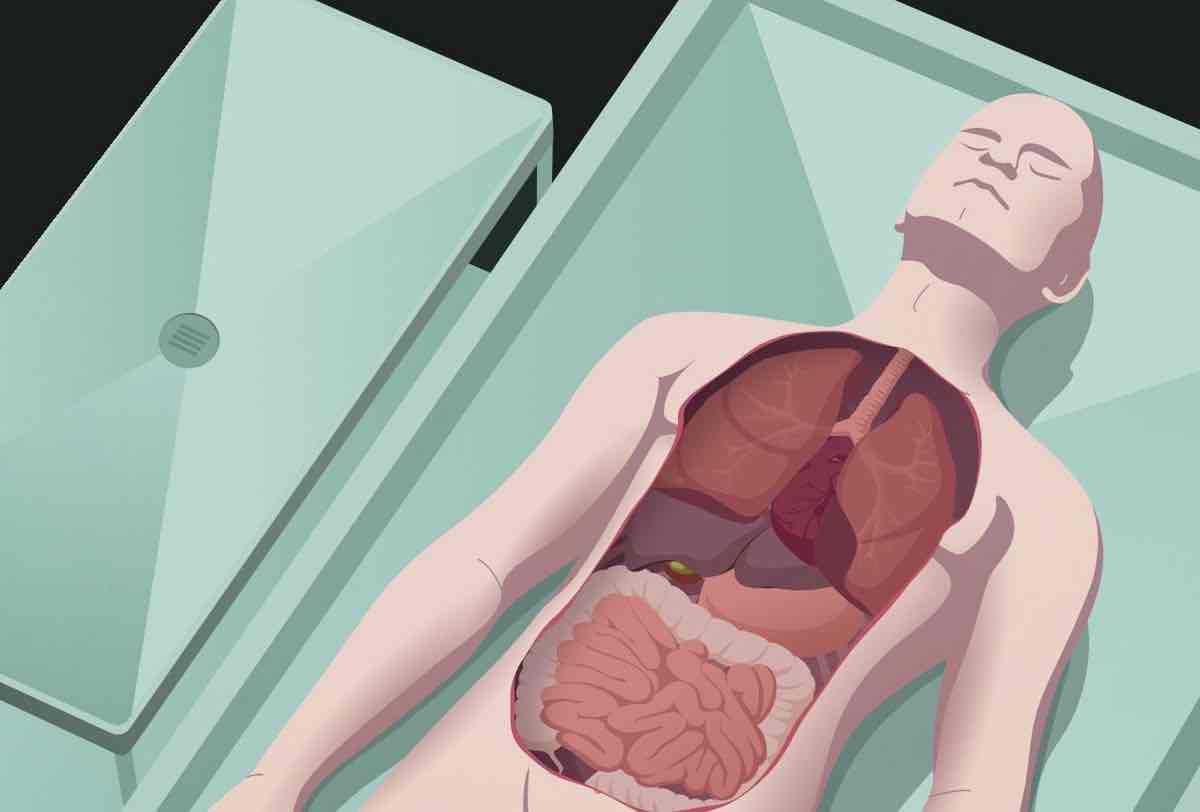
autopsy
Examination of a deceased individual’s body
strengths of autopsies?
provides valuable research data for hereditary diseases and information to next of kin
weaknesses of autopsies?
selection errors, biocorrelation, participant history