HSPA Chapter 10: Surgical Instrumentation
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Discuss the importance of surgical instruments and the role of the SP tech in instrument care and handling.
SP techs are responsible for ensuring instruments are safe, functional, and available when needed. This includes properly cleaning, decontaminating, packaging, and sterilizing instruments.
Review basic steps in surgical instrument manufacturing process
selecting materials, forging the material to create an outline, ground and milled, tempering, polishing, passivation layer, inspection, and etching.
What are types of stainless steel are used for instruments?
300 series and 400 series
What types of raw materials are used when manufacturing instruments?
stainless steel, titanium, copper, and silver.
What is the difference between 300 and 400 series stainless steel?
400 is hard and used when sharp cutting edges are needed. 300 is softer, more malleable and offers higher corrosion resistance.
What types of instruments are produced with 400 series steel?
scissors, osteotomes, chisels, rongeurs, forceps, hemostatic forceps, and needle holders.
What is the 400 series steel called?
martensitic stainless steel
What types of instruments are produced with 300 series steel?
retractors, cannulas, rib spreaders, and suction devices.
What is the 300 series steel called?
austenitic stainless steel
How long is a typical manufacturing cycle?
up to 6 weeks
stainless steel
an alloy of steel with chromium and sometimes another element, such as nickel or molybdenum, that is highly resistant to rusting and ordinary corrosion.
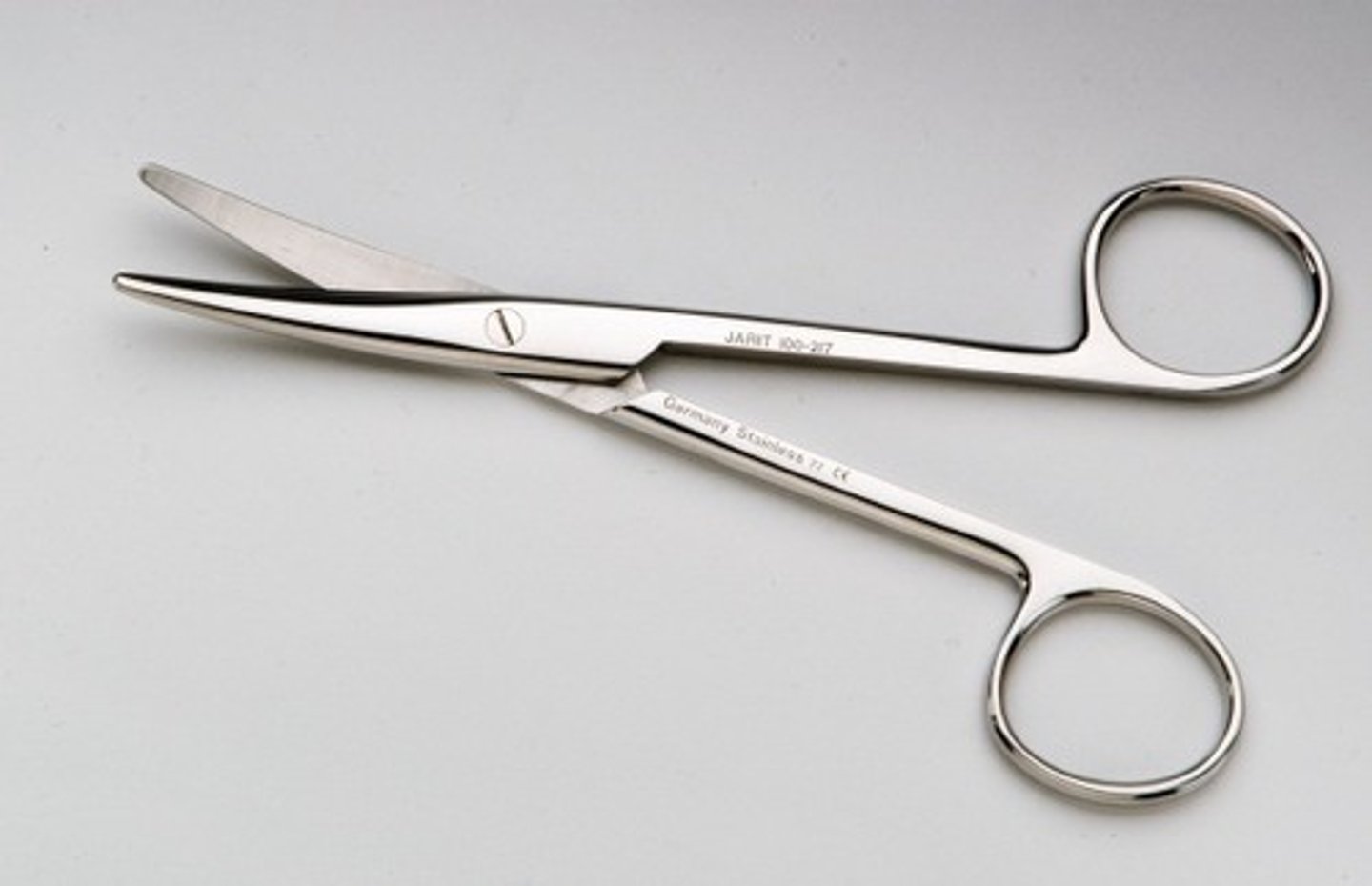
scissors
surgical instruments used to cut, incise, and/or dissect tissue
osteotomes
chisel-like instruments used to cut or shape bone
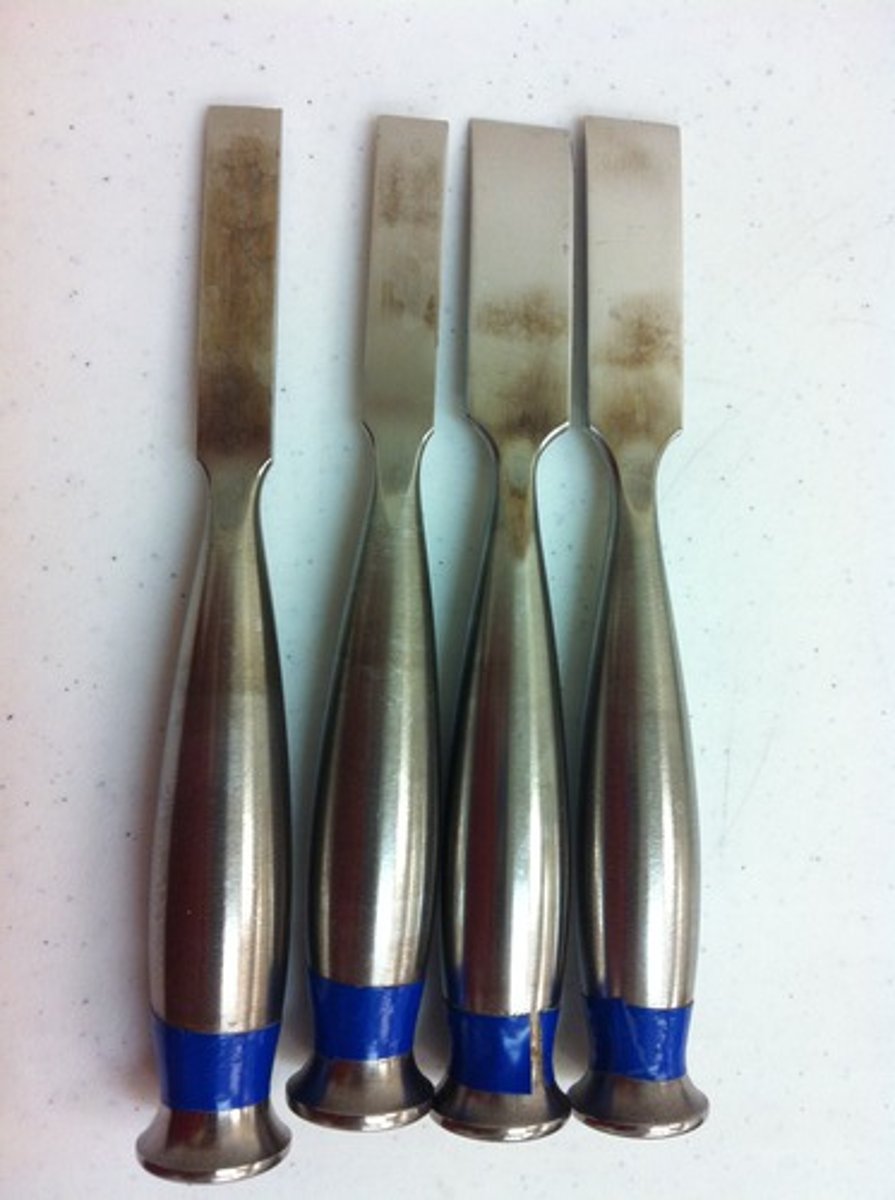

chisels
wedge-shaped instruments used to cut or shape bone
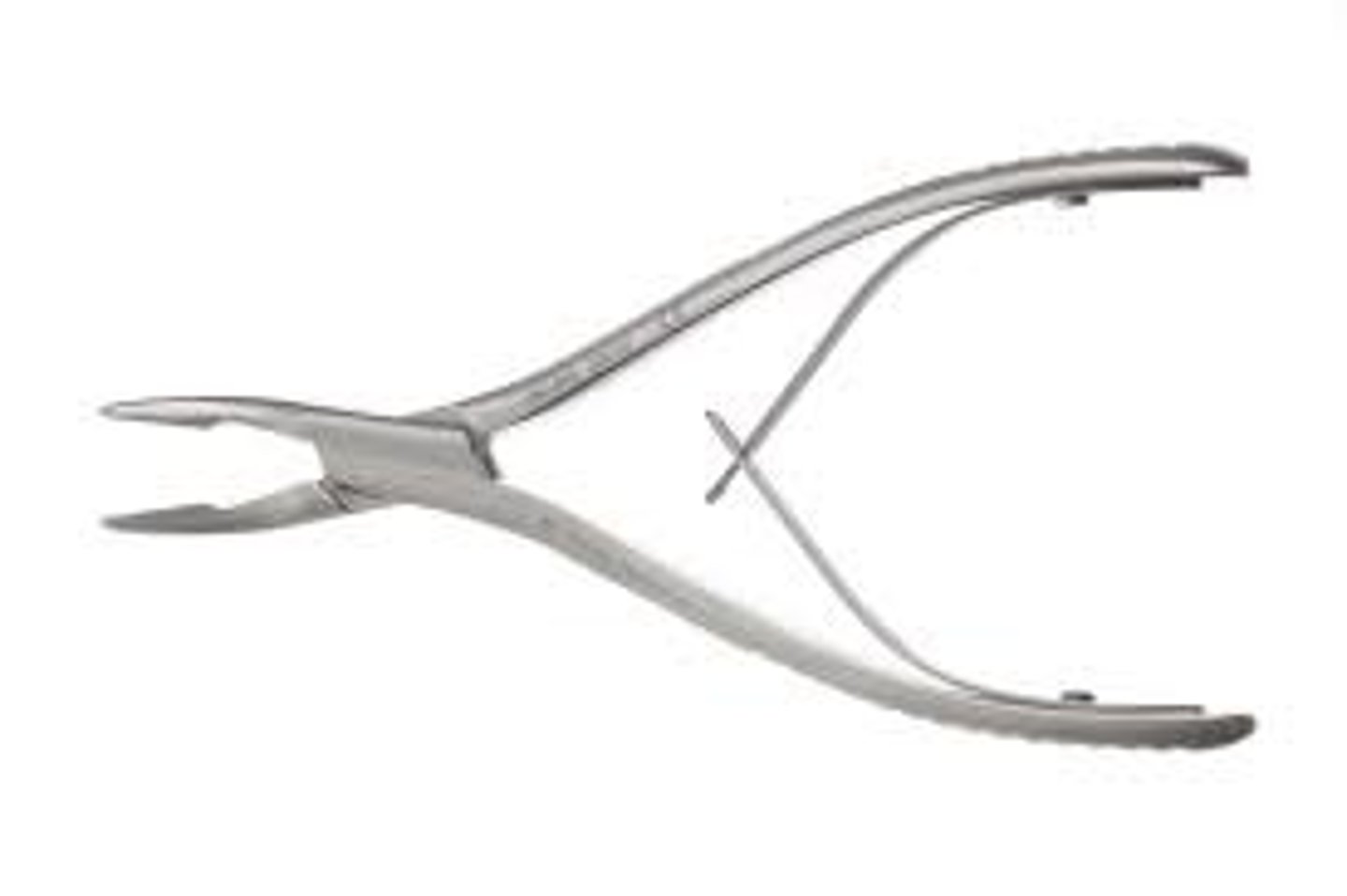
rongeurs
surgical instruments used to cut or bite away at bone and tissue

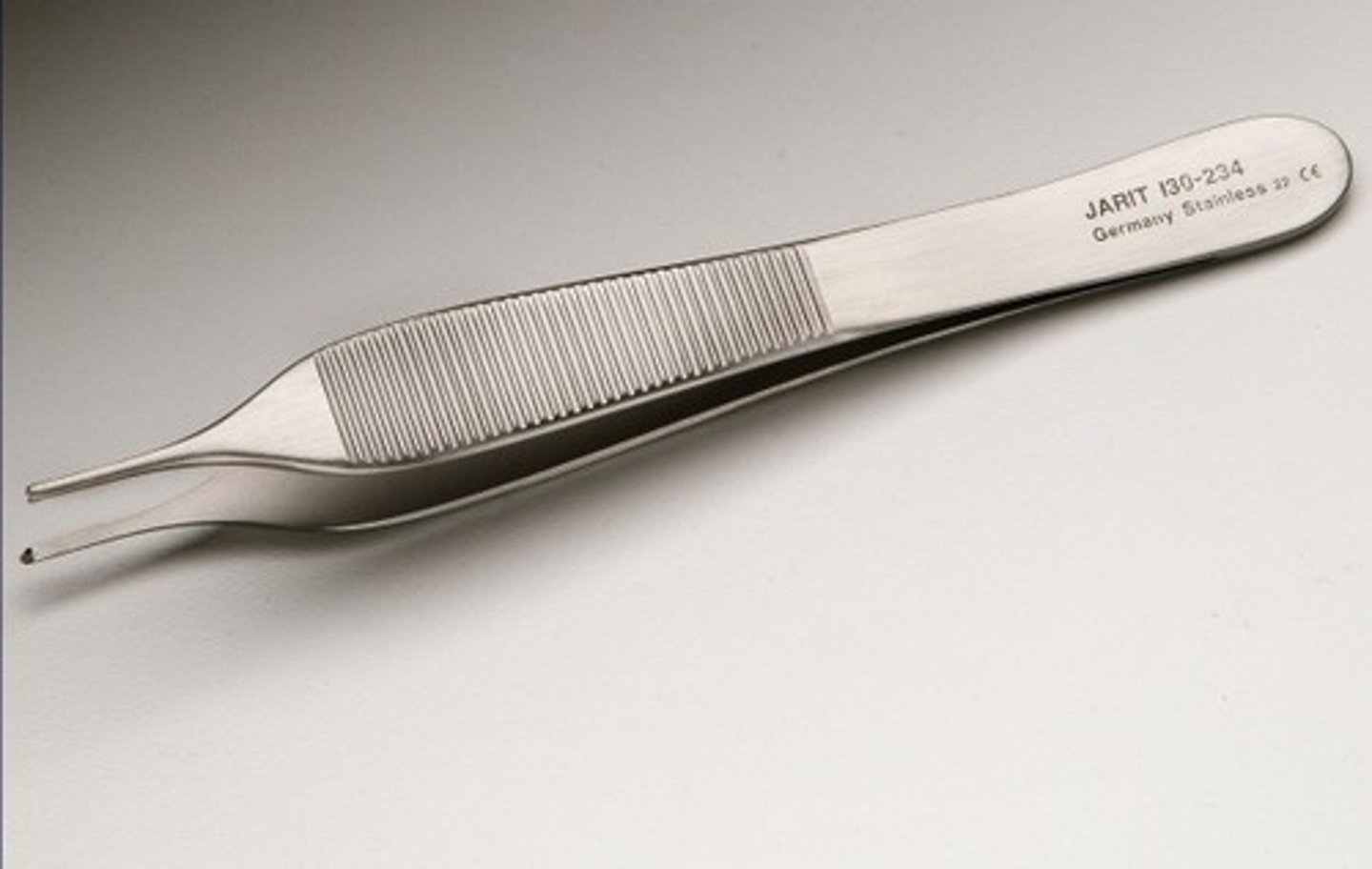
forceps
instruments used for grasping, holding firmly or exerting traction upon objects.

hemostatic forceps
surgical instruments used to control the flow of blood.
needle holders
surgical instruments designed to drive suture needles to close or rejoin a wound or surgical site.
martensitic stainless steel
aka 400-series stainless steel. It is magnetic and may be heat-hardened.
retractors
surgical instruments primarily used to move tissues and organs to keep the surgical site exposed throughout surgery.
cannulas
surgical instruments with a hollow barrel (or lumen) through their center. Cannulas are often inserted for drainage.
rib spreaders
a retractor used to expose the chest
suction devices
surgical instruments used to extract blood and other fluids from a surgical site
austenitic stainless steel
aka 300-series stainless steel. It is non-magnetic, cannot be heat-hardened and is more corrosion resistant
hemostatic forceps
primary function is to control the flow of blood
inspection points on hemostatic forceps
inspect jaw serrations for bioburden and inspect box lock for cracks and bioburden
how to measure hemostatic forceps?
from the tip to the bottom of the ring
What is the difference in serrations between a Kelly and Crile forceps?
Crile has serrations the complete length of the jaw, while Kelly only has serrations part of the way
needle holders
designed to drive suture needles to close surgical sites.
jaws
the portion that holds the needle, can be manufactured with stainless steel or tungsten carbide
What are the two patterns of jaw tread?
smooth or serrated
Stainless steel jaws
jaw treads cannot be repaired, re-jawed, or have serrations replaced after they wear out.
Tungsten carbide jaws
most popular; bright gold rings on handle; preferred because they are harder, last longer, grip the needle more firmly and can be replaced.
What are the points of inspection on a needle holder?
inspect box lock for cracks and bioburden, and inspect jaws for tread wear.
jaws
two or more opposable parts that open and close; used for holding or crushing something between them.
What are the two most common needle holder designs?
Mayo-Hegar and Crile-Wood
What is the difference between the Mayo-Hager and Crile-Wood instruments?
Crile-Wood is narrower then the Mayo-Hegar
tissue forceps
primary function is to manipulate tissue.
What are other names for tissue forceps?
rat tooth, brown forceps, and pickups
What are the inspection points for tissue forceps?
inspect tips/teeth for proper alignment
inspect handle for bioburden
inspect proximal end for cracks
dressing forceps
similar to regular forceps, except they have serrations instead of teeth at the distal end. used to manipulate tissue and pack surgical sites.
retractors
primary function is to move tissue aside for exposure and visualization of the surgical site.
What are some common self-retaining retractors?
Weitlaner, Gelpi and Beckman-Adson
What is a self-retaining retractor?
designed with a mechanical action that keeps it open to retract.
scissors
primary function is to cut tissue, suture, and other material in the surgical field. dissection requires curved scissors since their curve allows for better visualization.
What are the points of inspection for scissors?
inspect the tips/blades to be sure they meet evenly and inspect for cracks, pitting, and bioburden at screw hinge.
dissection
the process of cutting apart or separating tissue.
scissors with tungsten carbide blades
gold rings on handles. Blades have a harder and stronger cutting edge and allow scissors to remain sharper. The primary design function is tissue dissection.
scissors with serrated blades
design feature is for the prevention of tissue slippage during cutting. Some scissors have dual of these blades.
scissors with microgrind or supercut blades
black rings; design feature is to simulate a tissue/lancing/slicing action. One blade sharpened like a knife to slice tissue. Other blade causes a guillotine effect. Must be specially sharpened.
suction devices
primary function is to extract blood/fluids from the surgical site
What are the two most common suction devices?
Baron and Frazier
single-and double-action rongeurs
primary function is to cut or bite away at bone and tissue
What are the inspection points of single action rongeur?
inspect jaws for cutting edge damage and inspect box lock for cracks and bioburden. Also, inspect for cracks at hinges
kerrison/laminectomy rongeurs
primary function of this style of rongeur is to remove the disc or lamina during spine surgery.
What are the inspection points of a kerrison/laminectomy rongeur?
the distal portion must be inspected for bioburden and damage to the cutting edge. Inspection of screw hinge of handle
graves/pederson vaginal speculum
primary use is to expose the vaginal cavity.
What are the inspection points of a graves/pederson vaginal speculum?
thumb screws are present and functioning and inspecting all sides of the blades for damage.
What is the difference between a Graves and Pederson vaginal speculum?
a pederson blade is narrower
nail nippers
primary function is to cut toenails and fingernails.
What are the inspection points of nail nippers?
inspect blades for damage, along with the hinge area and springs looking for cracks.
What are the different solutions that damage stainless steel instruments?
betadine, peroxide, dish soaps, soaking in water, soaking in saline, bleach, hand soaps, porcelain cleaners, household lubricants, laundry detergents, surgeon hand scrubs
scissors longer than 4.5"
Test material: red test material (latex); orange material (latex free)
Test: must be able to cut through to the tip two to three times. Distal tip are most crucial portion. Must cut cleanly through the tips of the instrument.
scissors 4.5" and shorter
Test material: yellow test material (latex or latex free)
Test: must be able to cut through the tips two to three times. Distal tip are most crucial portion. Must cut cleanly through the tips of the instrument.
kerrison rongeur
Test material: index card
Test: punch a clean hole through the card
bone cutter
Test material: index cutter
Test: cut off a piece of the index card
laminectomy rongeur
Test material: index card
Test: should make a clean bite using half the jaw
double-action rongeur
Test material: index card
Test: should make a clean bite through the card
bone curette
Test material: plastic dowel rod
Test: shave off pieces of the dowel rod
chisels and osteotomes
Test materials: plastic dowel rod
Test: shave off pieces of the dowel rod
What are the marking methods for identifying instruments faster?
tape, acid-base etching, heat-fused nylon, powder coating, laser etching, and dot matrix system.
tape marking
a method of marking instruments using tape. Peeling/damaged tape can fall into the patient and cause infection.
acid-base etching
a method of marking instruments that uses a stencil, solutions, and electricity to mark stainless steel. It is semi-permanent and is done through instrument vendor.
heat-fused nylon
a method of marking instruments that is a liquid powder-coating process that is referred to as "dipping". Lasts years but when starts to chip, must be removed completely.
powder coating
a method of marking instruments that uses a polymer resin combined with other additives to form a powder. The powder is then sprayed onto an instrument and cured to form a high-density bond. Susceptible to cracks, nicks, and damage from harsh cleaning.
laser-etching
a method of marking instruments that is usually done by the manufacturer or an outside vendor.
dot-matrix
a method of marking instruments that is relatively easy and can be applied by SP techs. Two most popular types are: the dot marking system and the dot peen system.
dot marking system
a small barcode containing the instrument information is applied with pressure-sensitive tape.
dot peen system
laser or tungsten stylet is used to implant the information onto an instrument.
What is the possible result of using nicknames when describing or labeling instruments?
confusion, communication delays, and frustration.
How do you avoid confusion, communication delays, and frustration with the surgeon?
use proper names for all instruments
What is the possible result of failing to follow an instruments IFU?
can result in defective instruments, sterilization failure or long-term damage to the instruments.
What is the possible result of counting instruments instead of identifying each one?
relying on numeric count instead of identifying each instrument can result in incorrect instruments in the tray. Instruments that are not specifically identified are also more likely to go without inspection.
What is the possible result of failure to test instruments as directed by the IFU?
failure to test instruments correctly increases the risk that defective instruments will make their way into surgical procedures. A defective instrument can pose a risk to a patient and can cause frustration for the surgeon and OR staff.
What is the possible result of failing to assemble and then disassemble multi-part instruments.
multi-part instruments may be rendered unusable due to missing or defective parts
What is the possible result of cutting corners due to time pressures?
all instruments should receive through processing every time. Cutting corners may result in incorrect, unsafe or malfunctioning instruments being sent for use in a procedure.
What is the possible result of guessing an instruments identification or inspection protocol?
it can lead to incorrect or unsafe instruments or malfunctioning instruments being sent for use in a procedure.