M11 Interventional Cardiology Lecture Review
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and terms related to interventional cardiology, aiding in exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the 4 primary interventions performed in interventional cardiology?
Angioplasty, stenting, atherectomy, and thrombectomy.
What does PCI stand for in the context of interventional cardiology?
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.
Compared to a diagnositc catheter a guiding catheter has a ____wall and ______lumen
Has a thinner wall and larger lumen
What is stiffer, a guiding catheter or a diagnostic catheter?
guiding catheter
stiffer to provide support for advancing the balloon-stent catheters into the coronary artery
What are the three features of guiding catheters
1. Braided wall stiffer body than diagnostic catheters
2. Larger lumen
3. Thinner wall
Coronary stenting may result in re-narrowing of the affected area within 6-months of intervention. What is the term to describe the healing process contributing to vessel restenosis?
HINT HEALING PROCESS
options
late stent thrombosis
intimal thickening
neointimal hyperplasia
atherosclerosis
NEOINtimal hyperplasia - HEALING PROCESS THAT CONTRIBUTES TO RESTENOSIS.
not thrombosis because this is a clot that usually occurs after a year
intimal thickening does describe a pathological process but rather just an observation
atherosclerosis is the process of plaque buildup in the arteries not restenosis after stenting where the answer is specific to ISR
What is the normal aortic valve area
3-4 cm²
grading of Ao stenosis
Mean gradient < 25 mmHg, AVA > 1.5 cm2
Mild
grading of Ao stenosis
Mean gradient > 40 mmHg, AVA <1.0 cm2
Severe
grading of Ao stenosis
Mean gradient 25 - 40 mmHg, AVA 1.0 - 1.5 cm2
Moderate
Mean gradient < 5 mmHg, AVA 3.0-4.0 cm²
Normal aortic valve function; indicates no significant stenosis.
When should you consider using a distal protection device? choose 2
during renal artery stenting
during SVG intervention
during carotic intervention
during rotational atherectomy
carotid intervention
SVG - SVGs are fragile and full of loose junk because they weren’t made to handle that kind of pressure, turbulence, or cholesterol rich blood flow and when theyre turned into grafts they age like milk. VG’s get rapid atherosclerosis much faster than arteries
What are the three types of angioplasty balloons?
Compliant, non-compliant, and semi-compliant.
Describe what FFR stands for.
Fractional Flow Reserve.
What is a common use for a MitraClip?
To treat mitral regurgitation.
What are some common materials used in the construction of stents?
Cobalt-chomium
stainless steel
nitinol
What is the purpose of the left atrial appendage closure?
and what patients benefit from it the most
To reduce the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation patients who are unable to take anticoagulants
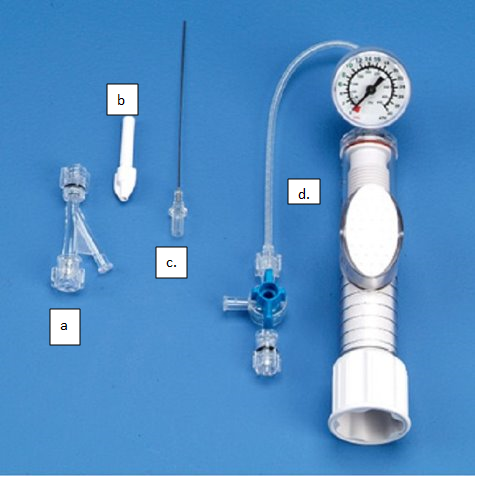
which is the hemostatic valve
A. tohouy burhst valve
a medical device, often used in interventional procedures, that helps to seal off blood vessels and minimize fluid loss during catheter insertion and manipulation
The pericardium is a fibro-serous sac surrounding the heart. This structure consiststs of how many layers and
what are the layers called
two layers: the outer fibrous layer and the inner serous layer that has parietal and visceral components.
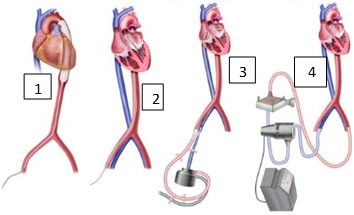
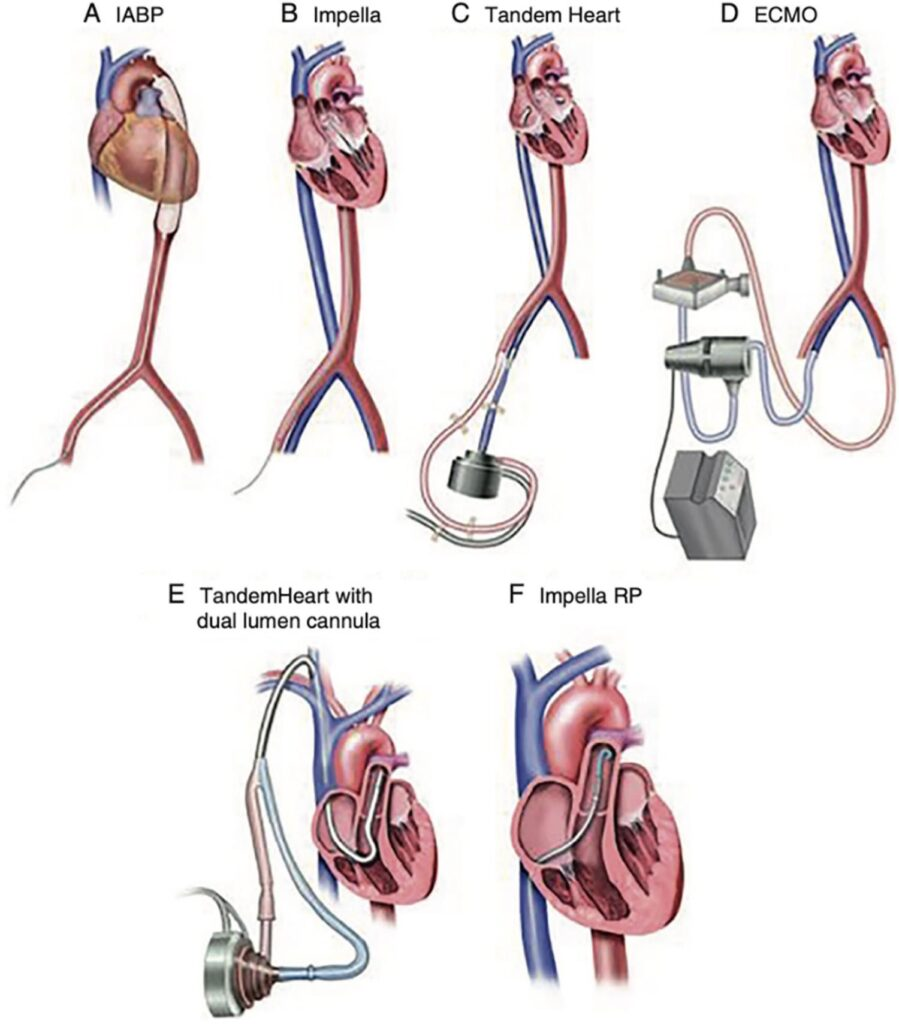
what device is 3
Tandem heart
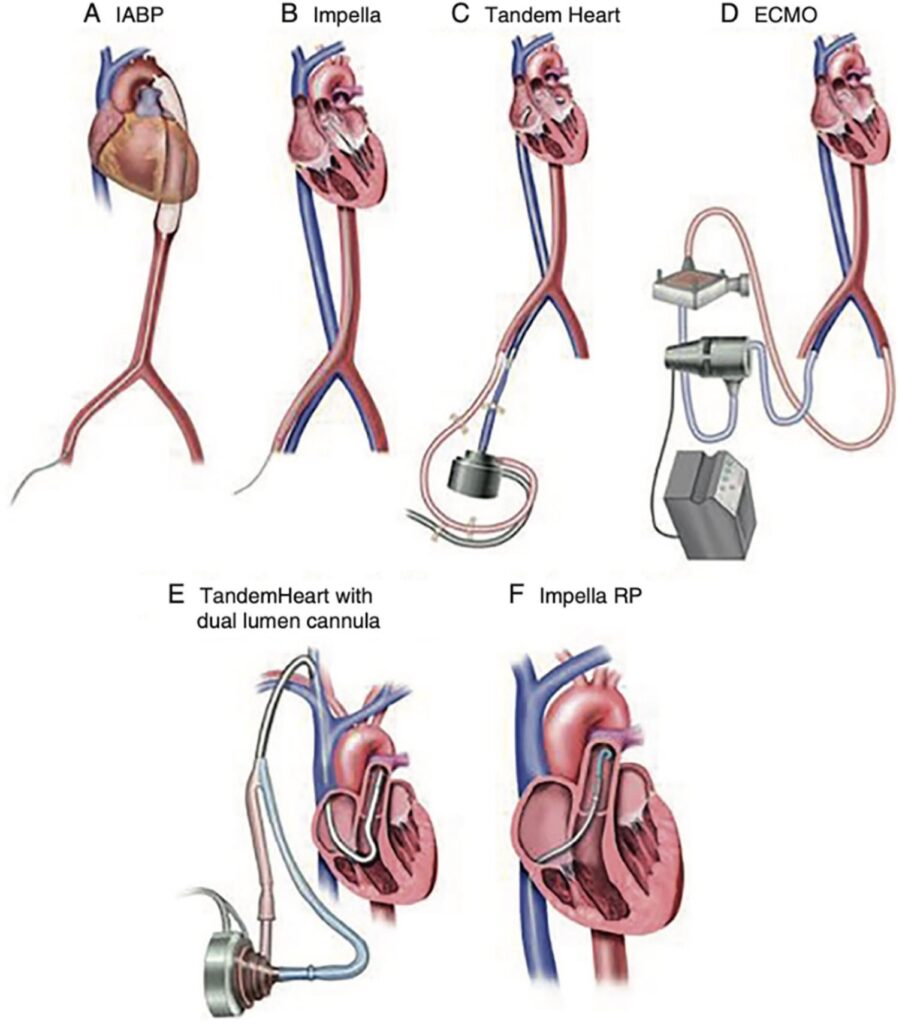
What device is number 4
ECMO
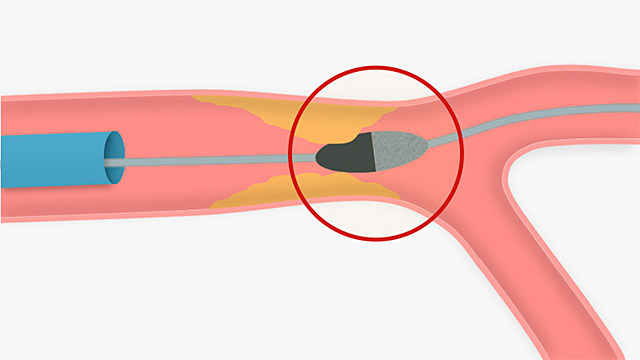
a treatment for coronary calcification that can result in burr entrapment is a complication of which device
Rotablator
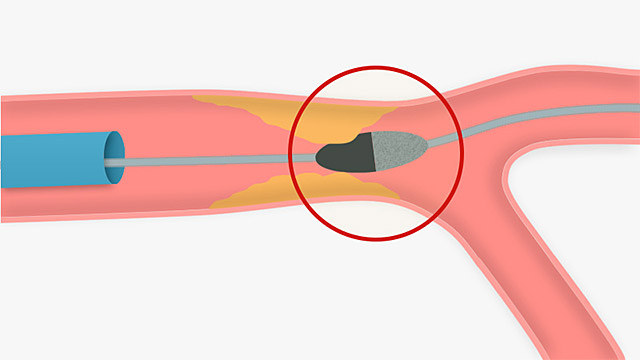
what device is this
bonus
this is a complication of this device, what is happening
rotablator, entrapment
Flextome is what kind of device
boston scientific cutting balloon

name a coronary orbital atherectomy system
CSI cardiovascular systems INC
Diamondback 360 coronary orbital atherectomy
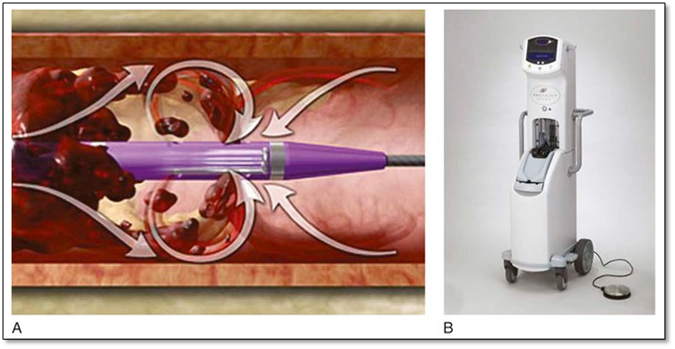
what device is this
angiojet
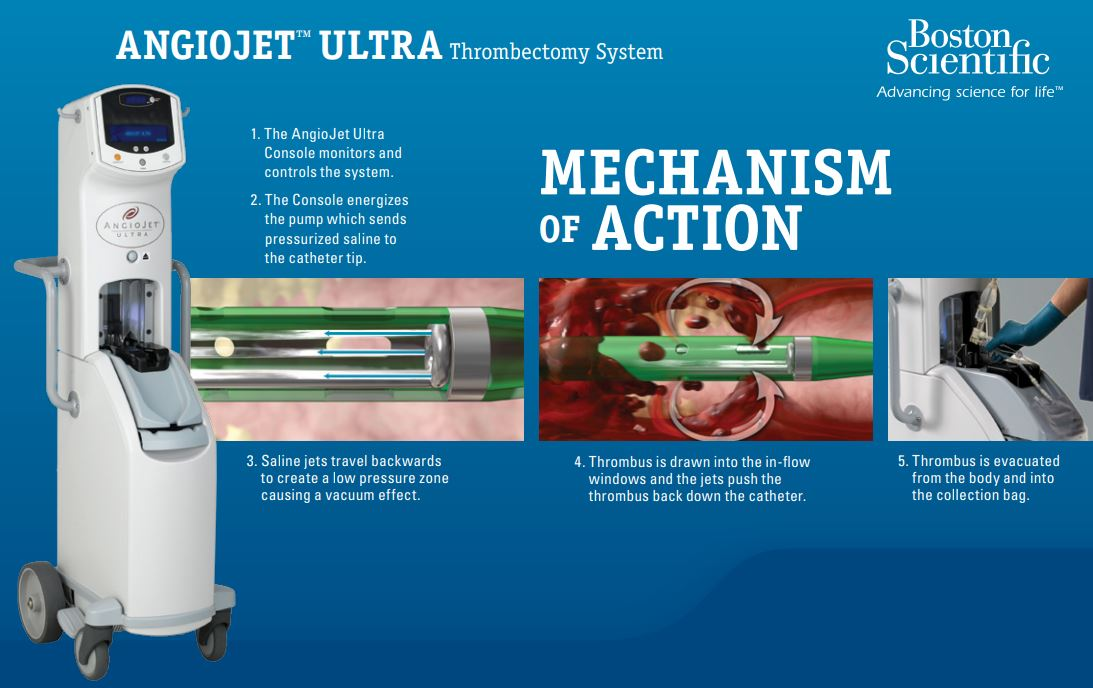
equalization of RVEDP and LVEDP is found in which of the following
constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade.
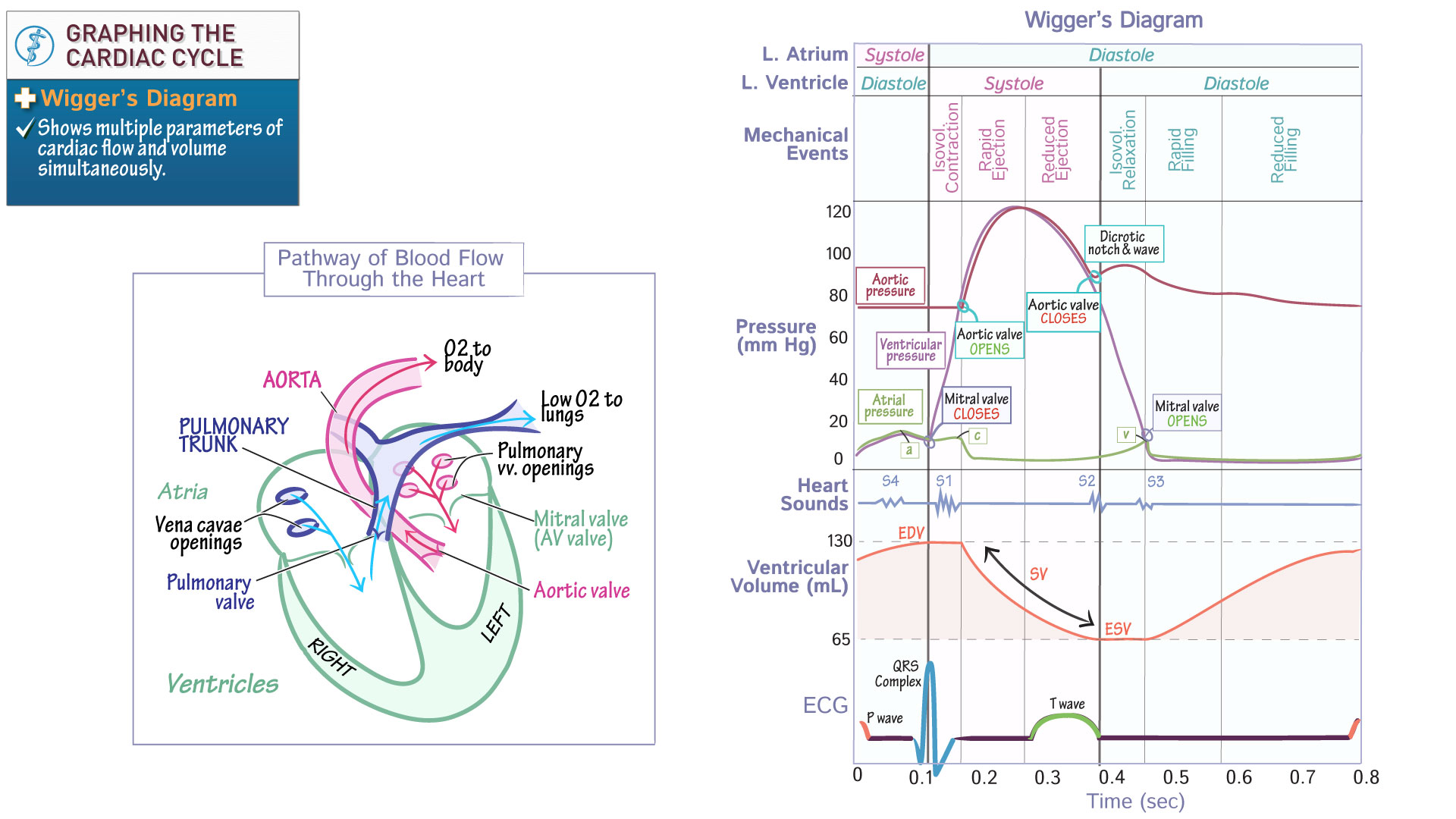
The mitral valve closes immediately after what hemodynamic waveform
a wave
The closure of the mitral valve is marked immediately following the a wave in the atrial pressure tracing, indicating atrial contraction.
Dicrotic notch on the aortic waveform represents
the closure of the aortic valve, indicating the end of systole.
In the crushing sten bifurcation technique, which stent is deployed first and which is deployed second
side branch or main branch
first is side branch with 1/3 of its length sticking out into the main branch, and second is the main branch stent, which is deployed to cover the remaining lesion.
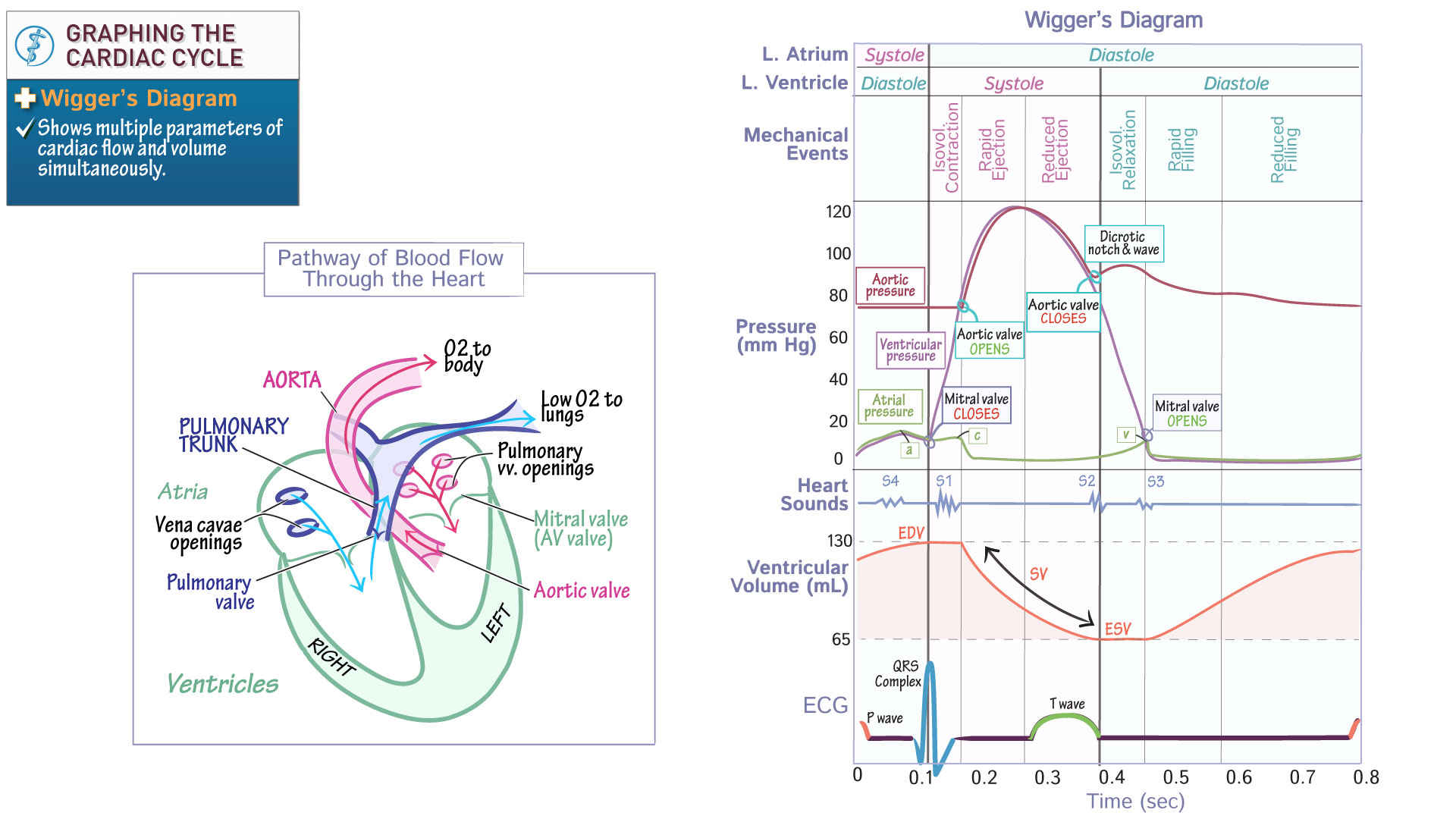
review this