Exam 1: Biomechanics Concepts
1/150
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
rotary
the rolling or rotation at a joint around a center of rotation (angular motion)
y-direction, up, and to the right
translatory
the glide or translation at a joint (linear motion)
x-direction, down, and to the left
spin
a single point rotates like a top spinning
instantaneous center of rotation (ICR)
axis of a joint shifts in space as it moves
frontal plane
plane: x-y plane dividing the body into front and back
axis: z (anterior/posterior)
motion: abduction/adduction/lat flexion of the trunk
sagittal plane
plane: y-z plane dividing the body into left and right
axis: x (medial/lateral)
motion: flexion/extension + dorsiflexion/plantarflexion
transverse plane
plane: x-z plane dividing the body into top and bottom
axis: y (superior/inferior or longitudinal/vertical)
motion: rotations
degrees of freedom
number of planes a joint can move in
closed kinematic chains
distal segment is fixed to the earth or immovable surface while the proximal segment is free to move
closed kinematic chain example
stand to sit, stance phase of gait (and with a cane planted)
open kinematic chain
distal segment is free to move in space
open kinematic chain example
hand to mouth, sitting knee extension, swing phase of gait
convex-concave principle
convex moving on stable concave: roll and glide occur in opposite directions
concave moving on stable convex: roll and glide occur in the same direction
close-packed position
locked position of a joint
close-packed position conditions
1. joint surfaces are maximally congruent
2. ligaments and capsule are taut and twisted
3. usually at end range
open-packed (loose-packed) position
any unlocked position at a joint where the ligaments and capsule are lax
rotary magnitude
ROM in degrees
translatory magnitude
distance in cm
force equation
F (N) = m(kg) x a(m/s²)

what force is this?
unloaded

what force is this?
tension
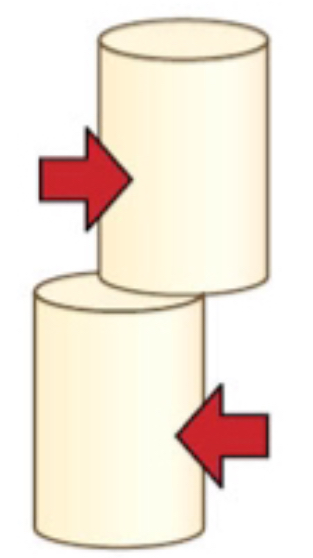
what force is this?
compressions
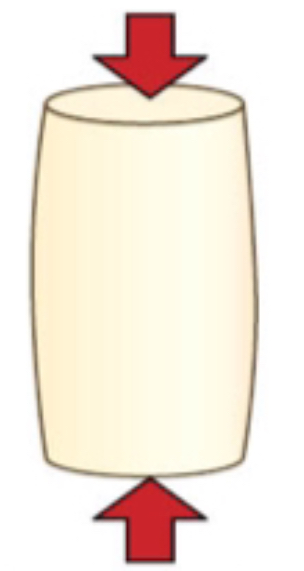
what force is this?
bending
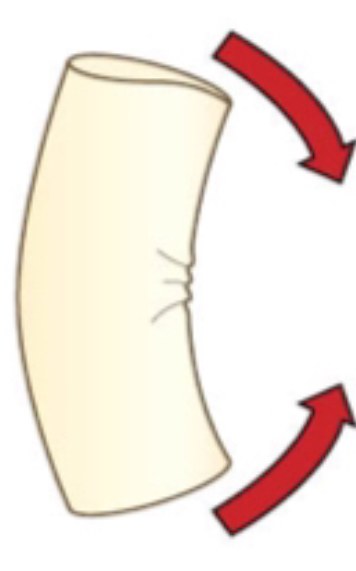
what force is this?
shear
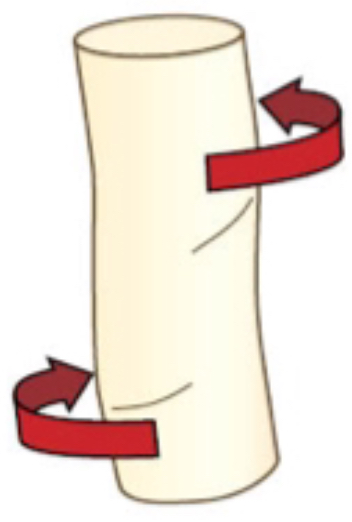
what force is this?
torsion
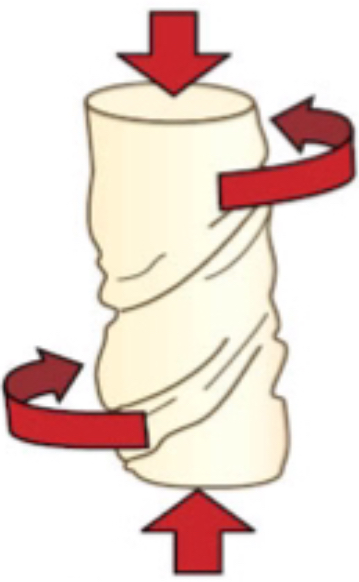
what force is this?
combined loading
what happens to muscle with strain?
change in length occurs
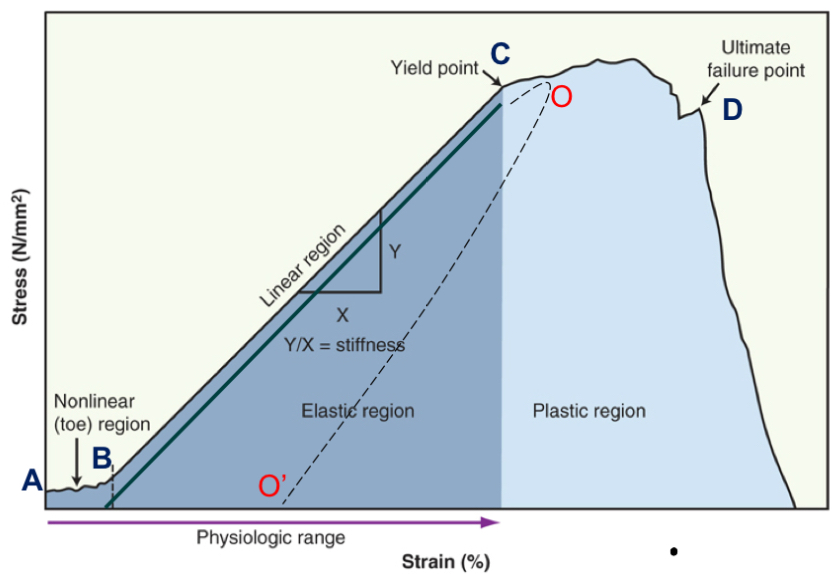
toe region
take up slack
point B
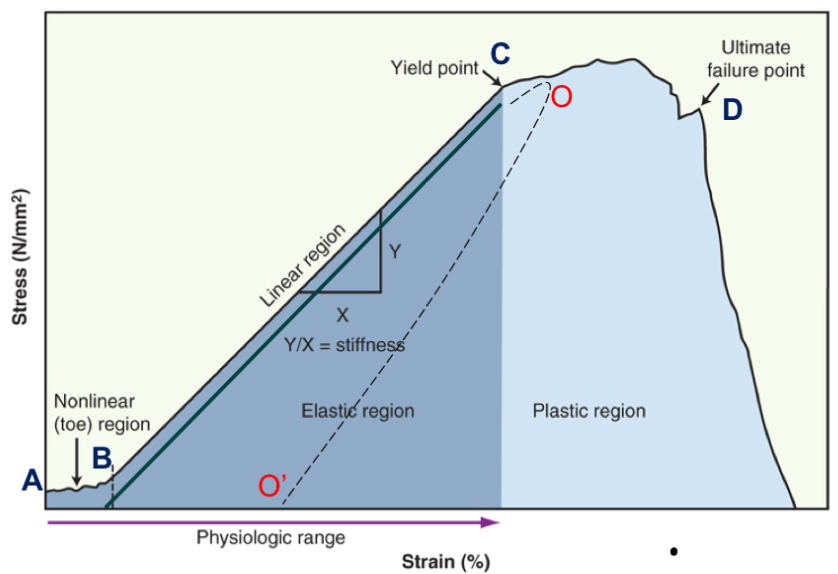
elastic region
elongation is linear, return to beginning (no change)
point B-C
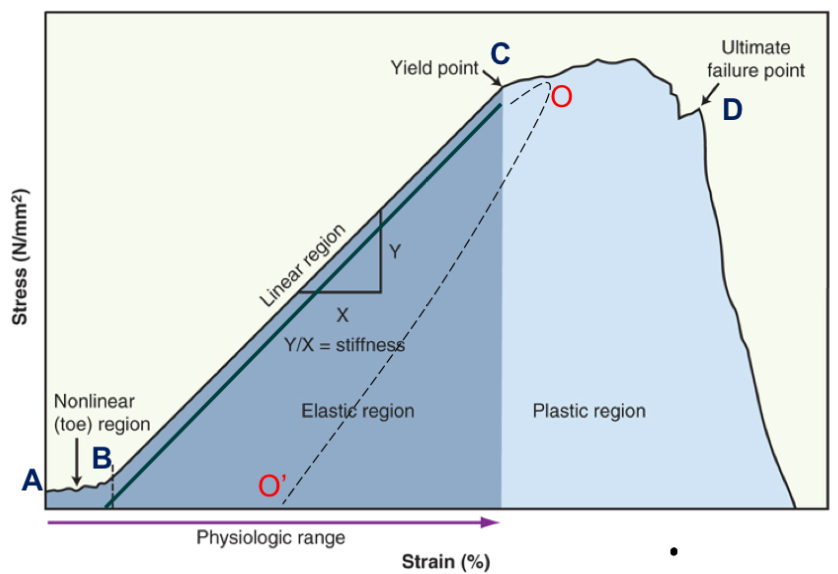
plastic region
progressive failure of tissue; permanently deformed
point C-D
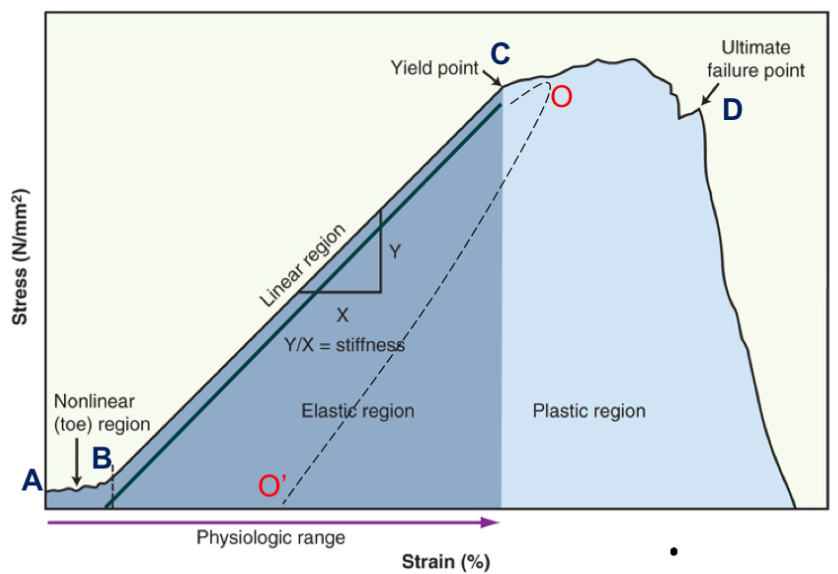
yield point
when plastic region begins
point C
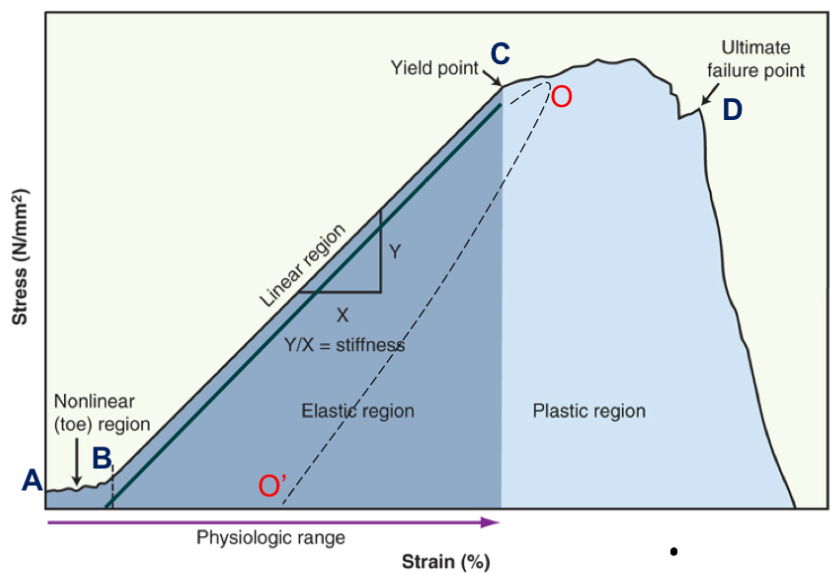
failure point
fracture, break, or tear occurs
point D
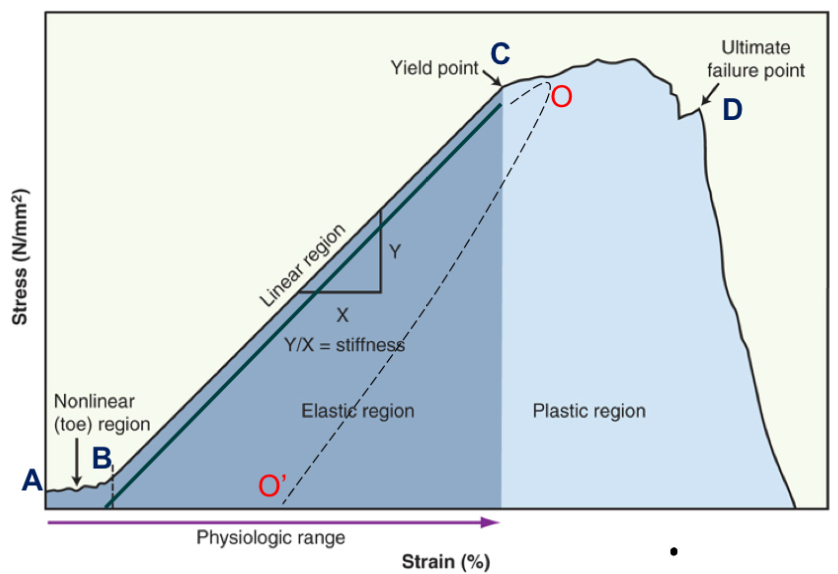
creep and hysteresis
energy is lost as heat when tissue deforms and change in length is permanent
point C-D
Poisson’s ratio
when a tissue is stretched, the tissue elongates and the diameter decreases
decreased diameter leads to increased stress
fatigue
repetitive loading weakens materials
loading rate
faster is more likely to fx so slower leads to creep
internal forces
muscles, ligaments, and bones
external force
gravity and equipment
force vectors
have a base, magnitude, and direction
all muscles are these
positive vector
up, right, or counterclockwise direction
negative vector
down, left, and clockwise direction
action line of a muscle: orientation
begins on the bone @ the point of insertion and goes in the direction of the muscle pull
rotary force orientation
starts at the insertion and is always perpendicular to the bone it inserts on
translatory force orientation
starts at the insertion and runs parallel to the bone it inserts on
center of gravity
hypothetical point at which all mass would appear to be concentrated and where the force of gravity will act → point of balance
anterior S2
line of gravity
a line drawn from COG directly down to the surface
always equal/opposite in magnitude to the gravity reaction force
base of support
feet and the space between (a box drawn around them)
assistive device and BOS
adding an assistive device will increase the BOS
factors affecting stability
height of the COG above BOS, size of BOS, location of LOG within BOS (bending over), and COG of the body
LOG and stability
squatting: LOG stays centered
bending over: LOG shifts anteriorly and decreases stability since there is extra translation
types of force systems
linear, concurrent, and parallel
types of parallel force systems
force couples and levers
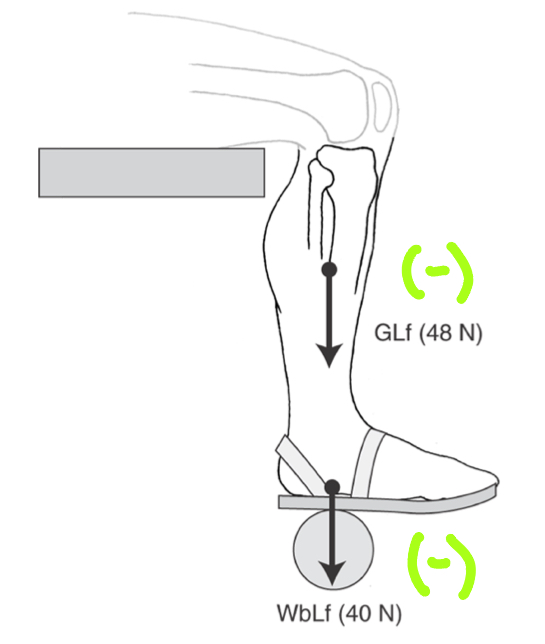
linear force system
when 2+ forced act on the same object in the same line (joint compression and distraction)
joint distraction
tensile forces (often gravity)
joint compression
joint reaction forces (often mm or surface contact)
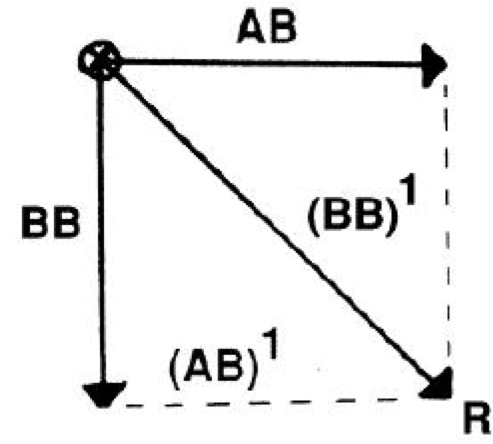
concurrent force system
2+ forces acting at a common point of application, but in divergent directions
composition is through a parallelogram
parallel force systems
2+ forces act on the same object but at some distance from each other and never converging
i.e. bones
force couples force system
2 forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction; always produces rotation
lever force system
three forces of a mechanical level and has three components: A, R, E
lever force arms
A = axis
R = resistance (loser)
E - effort (winner) and acting in the direction of rotation
mechanical advantage
= EA/RA
1st class lever
EAR or RAE
EA < = > RA
2nd class lever
ERA and ARE (most efficient)
EA always > RA
3rd class lever
AER and REA (least efficient)
EA always < RA
1st class lever example + mechanical adv
occiput on C1
it depends
2nd class lever example + mechanical adv
bicep curl
> 1.0
3rd class mechanical adv
< 1.0
torque
the ability of a force to cause rotation of a lever
T = f x d
moment arm
shortest distance between the action line and the joint axis
greatest when force is at 90 degrees to the segment
moment arm drawing
drawn perpendicular to the action line and intersects the joint axis
anatomic pulleys
change the direction of pull without changing the magnitude of the force
i.e. sesamoid (patella) bone
synarthrosis
connective tissue binds joints
synarthrosis joint types
fibrous and cartilagenous
fibrous joints
fibrous tissue connects bone to bone
i.e. skull sutures, gomphosis, and tibia+fibula
cartilaginous joints
joined by fibro or hyaline cartilage
i.e. pubis symphesis, growth plates, ribs to sternum)
diarthrosis / synovial joints
ends of bones are free to move + joint capsule
joint capsule
jt. receptors in fibrous outer layer attache to the periosteum with Sharpey’s fibers
what happens with sprains or torn ligaments in diarthrosis joints?
nerve supply is disrupted which decreases proprioception
synovial joint components
joint capsule, joint cavity, synovial membrane, synovial fluid, and hyaline cartilage
synovial fluid
provides nourishment, removes waste, and lubricates by diffusion via movement
hyaline cartilage function
decreases friction and absorbs shock
types of synovial joints
uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial
uniaxial joint
1 DOF
hinge and pivot joints
example of uniaxial joint
inter-phalangeal and atlas-axis
biaxial joint
2 DOF
condyloid and saddle joint
biaxial joint examples
metacarpal-phalangeal and carpal-metacarpal of thumb
triaxial joint
3 DOF
plane and ball-and-socket
triaxial joint examples
carpal bones and hip/shoulder
connective tissue composition
cellular matrix and extracellular matrix
cellular matrix
fibroblasts mature into fibrocytes, chondrocytes, tenocytes, or blastocytes
extracellular matrix components
ground substance and fibrous proteins
ground substance
GAGS (+) affect hydration and contribute to the strength of collagen to withstand compression
fibrous proteins
keeps extracellular matrix together with collagen and elastin
collagen
accounts for 30% of all protein in body and has tensile strength
type I or II
type I collagen
thick and stiff
type II collagen
thin
elastin
elastic and deforms under force and returns back to original state
importance of fibrous proteins
tells us the strength and stiffness of the tissue
types of connective tissue
dense, articular cartilage, and fibrocartilage
types of dense connective tissue
ligaments, joint capsule, and tendons