4.5.1.4 Resultant forces + 4.5.2 Work done and energy transfer
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:33 AM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
1
New cards
what is a resultant force
the overall force on a point or object
if you have a number of forces acting on a single point, you can replace them with a single force
this single force is called a resultant force
if you have a number of forces acting on a single point, you can replace them with a single force
this single force is called a resultant force
2
New cards
what does a free body diagram show
all the forces acting on an object
3
New cards
what happened to work if a resultant force moves an object
work is done
4
New cards
equation for work done, force and distance
W= Fs
\
work done (j)
Force (N)
distance (moved along the line of action of force(m))
\
work done (j)
Force (N)
distance (moved along the line of action of force(m))
5
New cards
joules and newton-metre
1 joule = 1 newton-metre
6
New cards
frictional forces
Work done against the frictional forces acting on an object causes a rise in the temperature of the object.
when you push something along a rough surface you are doing work against frictional forces. Energy is being transferred to the kinetic energy store of the object because it starts moving, but some is also being transferred to thermal energy stores due to the friction. Causes the overall temperature of the object to increases
when you push something along a rough surface you are doing work against frictional forces. Energy is being transferred to the kinetic energy store of the object because it starts moving, but some is also being transferred to thermal energy stores due to the friction. Causes the overall temperature of the object to increases
7
New cards
using sale drawings to find resultant forces
1. draw all the forces acting Onan object, to scale
2. draw a straight line from the start of the first force to the end of the last force- this is the resultant force
3. measure the length of the resultant force on the diagram to find the magnitude and the angle to end the direction of the force
8
New cards
Pythagorus rule
a + b = c²
F²= (Fcos∅)² + (Fsin∅)²
F²= (Fcos∅)² + (Fsin∅)²
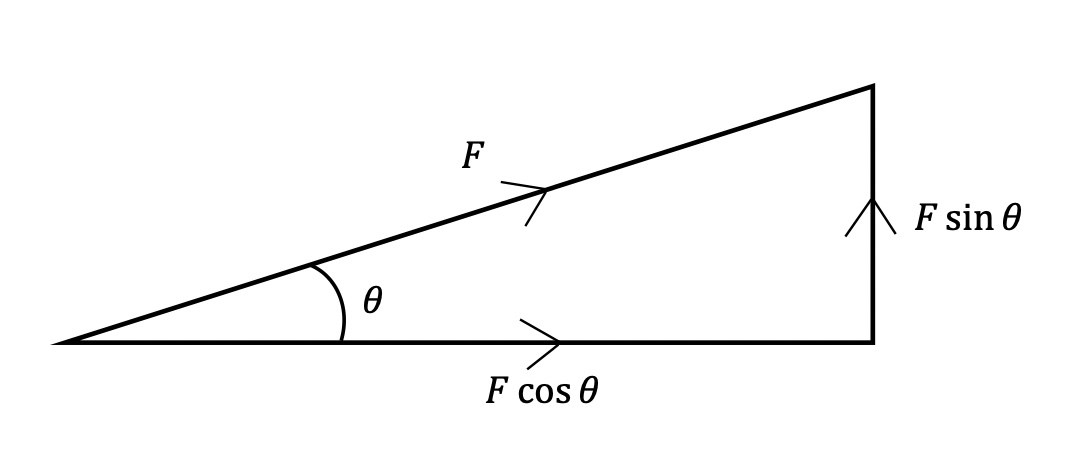
9
New cards
what do balanced forces mean
that an object has an equilibrium
if all of the forces acting on an object combine to give a resultant force of 0
if all of the forces acting on an object combine to give a resultant force of 0