Exam 3, PSYCH 111, UMICH,Shelly Schreier
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
300 Terms
attachment deprivation - Harlow Monkey Studies
- reared monkeys in isolation or with a surrogate mother
- after 6 months sent back to colony
- isolated monkeys showed indifference, were terrified or were aggressive with other monkeys, failed to form relationships with opposite sex, were abusive to their offspring
Attachment and Contact Comfort
hypothesized that animals/humans need warmth, comfort as a primary need
DevelopmentalTheories as Stage Theories
- individuals must progress through stages in a particular order, stages build on each other
- progress is strongly related to age
- development is marked by discontinuities that result in dramatic transitions
Jean Piaget and Cognitive Development
Studied how child thinks, including reasoning, remembering, and problem solving
What are Schemas?
models about how the world works
What two development processes did Jean Piaget talk about?
Assimilation - how to fit new info into the present system of knowledge
Accommodation - existing structure don't fit so a child must develop new schemas
What are Piaget's stages of Cognitive Development?
1. Sensorimotor (birth-2 years)
2. Preoperational (2-7 years)
3. Concrete Operations (7-11 years)
4.Formal Operations (12-up)
Explain Piaget's Sensorimotor stage of Cognitive Development
- birth-2 years
- infants learn through concrete motor actions; by touching, tasting, and smelling
- Accomplish object permanence (6 months)
- Develop capacity for mental imagery
- Organize information into categories
- Increasingly able to use purposeful activity
Explain Piaget's Preoperational stage of development?
- 2-7 years
- Gradually improve in mental images
- Can pretend
- Action Oriented
- Develop representational thought
- Have NOT mastered conservation: basic properties of an object remain stable even if superficial properties change
What are the flaws of thinking in Preoperational Children?
- Centration: focus on one aspect of a problem and neglect other aspects
- Irreversibility: inability to envision reversing an action
- Egocentrism: thinking characterized by a limited ability to share another person's point of view
Explain Piaget's stage of Concrete Operations?
- 7-11 years
- the child performs operations on tangible objects and events
- show increased flexibility in thinking
- Can begin to see cause and effect
- Masters reversibility and decentration
- Can retrace thoughts
- More successful with hierarchical constructs
Explain Paiget's Formal Operations
- 12 years and up
- begin to see abstract reasoning
- understand metaphor and deductive reasoning
- become more systematic in thinking
- can discuss moral values
What is Piaget criticized for in his studies?
Criticized for underestimating children's abilities, not focusing enough on individual differences; much research still supports his feelings and beliefs
Adolescent growth spurt
rapid growth in height and weight as the body is preparing for hormonal shifts/maturation
Asynchrony
certain body parts grow at different speeds leading to a lack of proportion
Prefrontal Cortex
final maturation of the prefrontal cortex takes place in late adolescence and young adulthood.
This area is responsible for organization, planning, emotional regulation and impulse control
Puberty
sexual functions reach maturity; impacts social and emotional development
Menarche
first occurrence of menstruation
Spermarche
first occurrence of ejaculation
How do early maturing males feel about themselves?
they have positive self-concepts
How do early maturing females feel about themselves?
There is a greater chance of depression, anxiety, and eating disorders
What is the impact of early puberty usually?
associated with obesity, higher BMI
What did Elkind say about Adolescent Egocentrism?
Way of thinking the world is focused on themselves
What did Elkind describe as Imaginary Audience?
the belief that everyone in the environment is concerned with the behavior/ appearance of him/herself
What did Elkind describe as a Personal Fable?
View him/herself as somehow unique or heroic
What did Elkind describe as Invincibility Fable?
false sense that he/she can't be harmed
Elkind with "Storm and stress"
Storm and Stress: more modulated (not as intense) as not as frequent as once thought
TRUE OR FALSE:
Adolescents are more similar to their parents for issues related to finances, education and career, religion and politics
TRUE
Elkind and Peer Relationships
Provide a source of social support, a framework for negotiating conflict and compromise, allow for social comparison, define code/culture
What did Erik Erikson (really thats his name?) say about the Theory of Lifespan Development?
Believes each stage involves a psychosocial crisis: a transition which is organized around social relationships and that personality is determined by these stages
Erikson's Lifespan Development
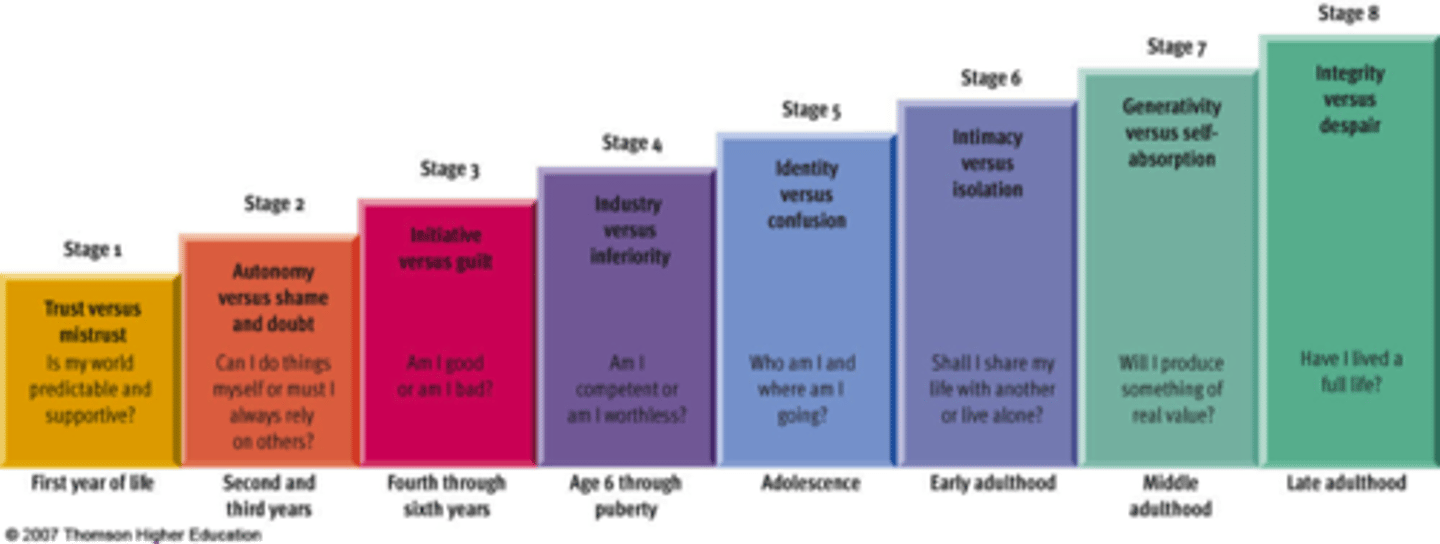
Lifespan Issues in Development
- Our country is getting OLDER
- Living more productive lives for more years
- More career shifts seen in the population
Intellectual Functioning and Age:
Fluid Intelligence: (basic information processing skills) is more likely to decline with age
Crystallized Intelligence: application of accumulated knowledge remains more stable
Langer and Rodin Study
Maintaining a sense of control over one's life leads to greater psychological well-being in the elderly
What are the ways to promote healthy aging?
- increase healthy behaviors
- promote companionship
- take vitamin supplements
- stay active physically and intellectually
- volunteer or work
- maintain positive relationships with family/friends
- have a positive attitude
- decrease sun exposure
- decrease smoking, drinking
- be a health care consumer; ask questions
- explore medication interactions
- find faith
Developmental Psychology
Universal aspects of lifespan development from conception through death; identifies cultural variations
- explores physical, cognitive, social, and emotional development
- Looks at elements of continuity and change over time
Germinal phase of Prenatal Development
- conception to 2 weeks
- Zygote: fertilized egg; divides and implants itself in the wall of the uterus
- Placenta: structure that allows oxygen and nutrients to pass into fetus from mother's bloodstream; allows waste to pass out
Embryonic Stage of Prenatal Development
- head, face, and neck develop
- buds for limbs form and grow
- Major organs/digestive system differentiating
- heartbeat begins
3rd month of Fetal stage of prenatal development
- digestive organs to begin function
- buds for teeth form
- sex organs develop rapidly
- arms/fingers move
4th month of fetal stage of prenatal development
- face looks human
- lower body outgrows head
- bones are defined
5th month of fetal stage of prenatal development
- fingernails and toenails appear
- Lanugo: fine, woodly hair over body
- vernix: waxy coating collects
6th month of fetal stage
- eyebrows/lashes well defined
- eyes completely formed
7th month of fetal stage
- fetus capable of life outside uterus, age of viability has changed and now considered to be 24 (used to be 27-28)
8th/9th month of fetal stage
- fat is deposited for later use
- fingernails beyond fingertips
- lanugo is shed
- myelination of brain takes place in the fetal stage
- chief organs increase functioning
- vernix covers body
Physical and Motor Development
- Cephalocaudal:"top to bottom" motor skills emerge from the head to feet
- Proximodistal: "inside-to-outside rule" motor skills emerge in a sequence of center moving outward
Teratogens
harmful toxins that affect development resulting in defect, damage or anomaly
Important concepts with teratogens
- dose
- genetics/heredity: stability
- interaction with environmental influences: stress, nutrition, lack of medical care
- Age of organism at exposure
Drugs or chemicals
increased understanding of the role of prenatal exposure to drugs on the developing child: Thalidomide: helped identify how certain drugs could alter development
Stress impact on prenatal development
prolonged stress linked with prematurity and low birth weight
Smoking on prenatal development
mild stimulant; increases fetal activity; low birth weight, perceptual and attentional problems, increased SIDS
Marijuana impact on prenatal development
low birthweight, disturbed sleep in newborns, reduced attention to environment
Heroin impact on prenatal development
premature birthweight, tremulous behavior, poor sleep, poor sucking and feeding, risk of SIDS
Cocaine impact prenatal development
"crack babies"
- premature size/weight, tremulous, high pitched crying, respiratory and regurgitation problems, rigidity, withdrawal symptoms, deformities
Comorbidity
abuse of multiple substances likely
Alcohol impact on babies
leading teratogen in the U.S. causing mental retardation
- physical symptoms: growth retardation, head and facial abnormalities, microcephaly, skeletal, brain and heart damage
- Behavioral symptoms: Poor impulse control, poor attention, hyperactivity, and cognitive defects
- Fetal Alcohol Effects: some symptoms of FAS, but less physical symptoms (ARND)
TRUE OR FALSE: paternal age may be a non factor in birth defects and/ or certain developmental disabilities
FALSE - paternal age may be A FACTOR in birth defects
ex. men at the age of 65 having children they have a greater risk of autism
Vision as Reflexes and sensory abilities of newborns/infants
- poor fixation ability
- limited ability to discriminate color
- estimated visual acuity of between 20/200 and 20/400
- preference for human faces
Hearing abilities in newborn/infant
fetus can hear sounds around 6 months in utero
recognized mother's voice
taste and smelling abilities in newborn
both present at birth
preference for sweet stuff
touch abilities of newborn/infants
heat, cold, pressure and pain all present at birth
reflexes of newborns
inborn, automatic responses to a particular form of stimulation
rooting reflex of newborn
survival value, stroke baby's cheek and the baby will turn head toward the stimulation
stepping reflex in newborns
basis for complex motor skills,
with bare feet touching floor, infant will mimic stepping response
THIS DISAPPEARS AROUND 2 MONTHS
Sucking reflex in newborns
place a finger in mouth and baby will suck; permits feeding
eyeblink reflex in newborn
shine a bright light or clap, baby will close eyelids
protects form strong stimulation
Babinski reflex
stroke the heel to see reactions of the toes which flex/fan out; normal in infants, if persists as baby gets older, can indicate neurological problems
Gross and Fine Motor Development
Individual differences exist!!!
normative expectations for these skills and abilities often called MILESTONES
Gross Motor and Fine Motor in Ages 2-3
Gross motor: walk rhythmically, jump, hop, push a riding toy with feet
Fine motor: remove simple clothing items, start to use a spoon
Gross motor and Fine motor in ages 3-4
Gross motor: walks upstairs alternating feet, catches ball by trapping in chest, rides a tricycle
Fine motor: fasten/unfasten large buttons, uses scissors, copies lines, circles, draws tadpole person
Gross motor and Fine motor in ages 4-5
Gross motor: walks downstairs alternating feet, runs smoothly, catches ball with hands, rapid/smooth steering
Fine Motor: uses a fork, cuts with scissors on lines, copies triangles and some letters
Gross motor and Fine motor in ages 5-6
Gross motor: increases running speed, true skipping, ride bicycle
Fine motor: uses knife to cut food, tie shoes, draw 6 part person, copies words and numbers
TRUE OR FALSE:
There are universal elements of gross and fine motor development
TRUE
Gender Differences
boys ahead of girls in force and power
girls ahead in fine motor and gross motor skills which involve good balance
Temperament
relatively constant basic disposition which is inherent in a person that underlies and modulates his/her behavior
What did Thomas and Chess do?
Identified three basic temperaments for infants; difficult, slow to warm and easy
Thomas and Chess's Difficult temperament
10%
often wail, cry, and are negative in new situations, eat and sleep irregularly
Thomas and Chess's Slow-To-Warm-Up temperament
15%
often inactive, adapt slowly and can be withdrawn and show a negative mood
Thomas and Chess's Easy Temperament
40%
Cheerful, adaptable, easily establish routines
Thomas and Chess's mixture temperament
35% have a mixture of the 3 temperaments
Goodness of Fit
the match between the characteristics of the infant and his/her family is critical to development
Some are better matches than others
Kagan found that infants who react fearfully to novel stimuli tend to be more subdued, less social and less positive at what age?
4 years of age
Attachment
the affectional bond between an infant and its caretaker
Who studied attachment in her attachment paradigm that is still being used today?
Ainsworth
What allows researchers to assess attachment relationships?
the "Strange situation"
Separation anxiety
infants express their wish to be attached by wishing to be close to their caretaker and showing signs of distress when their caretaker departs (an emotional upset)
Stranger anxiety
develops when infants are around 6-7 months ending around 18 months
If a stranger approaches, the infant becomes afraid and reaches for the caregiver for comfort and reassurance
What are the 4 types of attachment patterns based on Ainsworth's research?
1. securely attached
2. avoidant attachment
3. ambivalent/resistant attachment
4. Disorganized/Disoriented Attachment
Securely attached
child uses the parent as a safe base to explore, when separated the child may not cry during absence, seek contact when parent returns, decrease crying if present (60% of U.S. infants)
Avoidant attachment
unresponsive to parent when present, no distress when she leaves, react to stranger similar as to parent, slow to greet parent when she returns, 20% show this pattern in the U.S.
Ambivalent/Resistant attachment
seek closeness with their parents, fail to explore, upon return display angry, resistant behavior, cannot be comforted, 15% of U.S.
Disorganized/Disoriented Attachment
greatest amount of insecurity, in reunion show disorganized, confused behaviors
seem confused, glazed and spacey
mothers are more avoidant and inconsistent with lack of sensitivity to infants needs
5% of infants in the U.S.
4 Parenting Styles and Child outcome research by Baumrind
1.authoritarian
2. authoritative
3. permissive
4. uninvolved
authoritarian parenting style
restrictive parenting; insist on obedience, rigid rules; no explanations and insensitivity.
Preschoolers were moody; easily annoyed, unfriendly, less motivated
authoritative parenting style
assume control with flexibility; reasonable demands; provide reasons for rules/decisions
Preschoolers were cheerful, socially responsible, achievement oriented and cooperative
Permissive parenting style
accepting and lax with few demands; little monitoring; few controls
Preschoolers were impulsive, aggressive, bossy, self-centered, low in independence and achievement
Uninvolved (Maccoby) parenting style
removed or hostile parenting; overwhelmed with own stressors, have little time or energy to parent
Children high in aggression, temper tantrums, perform poorly in classroom
Personality
a distinctive pattern of behavior, thoughts, motives, and emotions that are CONSISTENT in an individual over time
Personality Traits
long-term disposition to behave in particular ways in a variety of situations
Cattel's Theory of Personality
Studied traits using factor analysis
Developed the 16 personality factors Questionnaire
Examples: reserved-outgoing; relaxed-tense; trusting-suspicious
McRae and Costa Theory of personality traits
developed the "Big Five" personality traits
believe most personality traits fall under these categories:
CANOE: Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, Neuroticism, Openness, Extraversion