Human Physio Renal function and fluid balance
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
extracellular, blood pressure
Regulation of ______ fluid volume & ______
2
New cards
plasma osmolarity, ion balance
Regulation of ______
Maintenance of ________
Maintenance of ________
3
New cards
pH, H+, HCO3-
Homeostatic regulation of ____
remove or conserve either ____ or ______ (bicarbonate ions) as needed
remove or conserve either ____ or ______ (bicarbonate ions) as needed
4
New cards
Excretion of waste
removes metabolic wastes dissolved in plasma e.g. uric acid and creatine
5
New cards
Secretion of hormones and enzymes
erythropoietin (RBC production), renin (sodium balance and BP homeostasis) & vit D conversion to control Ca2+ balance
6
New cards
Renal corpuscle
________ filters blood plasma
Glomerulus capillary network
Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule double walled up surrounding glomerulus
Glomerulus capillary network
Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule double walled up surrounding glomerulus
7
New cards
Proximal, loop of henle, Distal
Renal tubule filtered fluid passes into:
_____ convoluted tubule
descending, ________ (nephron loop) and ascending
______ convoluted tubule
_____ convoluted tubule
descending, ________ (nephron loop) and ascending
______ convoluted tubule
8
New cards
Urinary excretion
_______ of substance depends on its filtration, reabsorption and secretion.
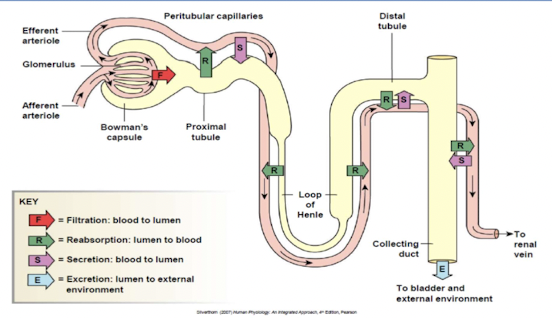
9
New cards
Glomerular, Basal, Epithelium
Filtration barriers:
_______ capillary endothelium
________ lamina
________ of Bowman’s capsule- podocytes
_______ capillary endothelium
________ lamina
________ of Bowman’s capsule- podocytes
10
New cards
Hydrostatic/blood pressure
pressure of flowing blood in glomerular capillaries
favors movement of filtrate into Bowman’s capsule
favors movement of filtrate into Bowman’s capsule
11
New cards
Colloid osmotiv pressure
plasma proteins entering capsule create a gradient that favors movement back into capillaries
12
New cards
Hydrostatic fluid pressure
in fluid up in enclosed Bowman’s capsule
creates a gradient that favors movement back into capillaries
creates a gradient that favors movement back into capillaries
13
New cards
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
volume of fluid that filters into Bowman’s capsule per unit time
14
New cards
pressure, surface area, permeability
Factors influencing GFP:
Net filtration ______
_______ of glomerular capillaries
________ between capillary & Bowman’s capsule
Net filtration ______
_______ of glomerular capillaries
________ between capillary & Bowman’s capsule
15
New cards
Myogenic response
Intrinsic ability of vascular smooth muscle to respond to pressure changes
↑afferent arteriole resistance →↓GFR
↑efferent arteriole resistance → ↑GFR
↑afferent arteriole resistance →↓GFR
↑efferent arteriole resistance → ↑GFR
16
New cards
Tubuloglomerular feedback
Paracrine control through loop of Henle
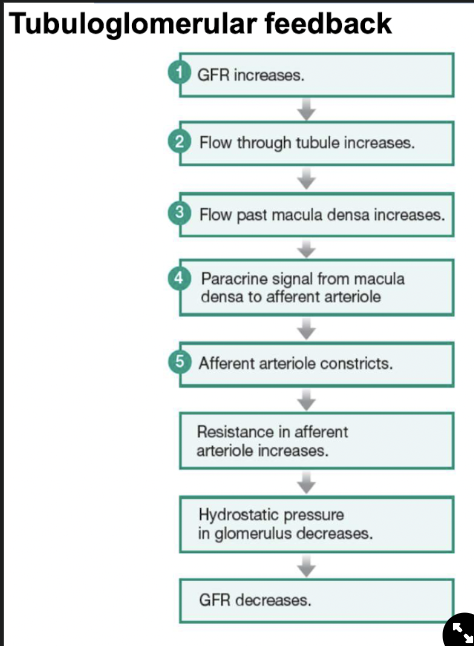
17
New cards
resistance, filtration coefficient
Hormones and autonomic neurons:
By changing _____ in arterioles
By altering the ______
Angiotensin II - vasoconstrictor
Prostaglandins - vasodilators
By changing _____ in arterioles
By altering the ______
Angiotensin II - vasoconstrictor
Prostaglandins - vasodilators
18
New cards
Reabsorption
movement of filtered solutes and water from lumen of tubule back into plasma
takes places in proximal tubule and distal segment of nephrons
takes places in proximal tubule and distal segment of nephrons
19
New cards
active, electrochemical, osmotically
Principles governing tubular reabsorption of solutes & water:
_____ transport to create concentration of ______ gradient
water ______ follow solutes
_____ transport to create concentration of ______ gradient
water ______ follow solutes
20
New cards
Transepithelial transport (passing through cells)
substances cross both apical and basolateral membrane
21
New cards
Paracellular pathway (passing around cells)
substances pass through junction between two adjacent cells
22
New cards
Secretion
Transfer of molecules from extracellular fluid into lumen of nephron
dependent on membrane transport proteins to move organic compounds
dependent on membrane transport proteins to move organic compounds
23
New cards
against, K+, H+, homeostatic regulation
active process move substrates ____ concentration gradient & use secondary active transport to move into lumen
secretion of ___ and ___ is important in ___________
secretion of ___ and ___ is important in ___________
24
New cards
excretion
enables nephron to enhance excretion of substance:
adds to substances collected during filtration, making _______ more effective
adds to substances collected during filtration, making _______ more effective
25
New cards
Plasma proteins
________ entering capsule create a gradient that favors movement back into capillaries.
26
New cards
urinary loss
In response to diet intake, ________ helps to maintain proper levels of Na+, K+, Ca2+ ions.
27
New cards
Kidneys
________ can not replenish lost water; only preserve or get rid of excess amounts.
28
New cards
Urinary excretion of substance
________ depends on its filtration, reabsorption and secretion.
29
New cards
aldosterone release
Angiotensis II (ANG II) is the usual signal controlling ________ from the adrenal cortex
30
New cards
RAS pathway
The ________ begins when afferent arterioles secrete renin.
31
New cards
angiotensinogen, ANG II
Renin converts inactive ______, into angiotensis I (ANG I)
ANG I converted into ____ by angiotensis-converting enzyme (ACE)
ANG I converted into ____ by angiotensis-converting enzyme (ACE)
32
New cards
adrenal gland, Na+
ANG II → _______ → synthesis and release of aldosterone
Aldosterone reabsorb ____ at collecting duct
Aldosterone reabsorb ____ at collecting duct
33
New cards
Renal filtration
________ will stop if there is a major loss causing extremely low blood pressure and blood volume.
34
New cards
ANG II
________ increases blood pressure and inflammation, death of cells in alveoli.
35
New cards
Homeostasis
________ maintains water balance unless there is pathology or an abnormal ingestion of water.
36
New cards
nephron
The ________ is the functional unit of the kidney.
37
New cards
ACE2
When the SARS- CoV- 2 virus binds to ________, it prevents ________ from performing its normal function to regulate ANG II signalling.
38
New cards
Diuretics
________: drugs that promote urine excretion.
39
New cards
Osmolarity
________ of urine measure of how much water is excreted by kidneys.
40
New cards
Osmolarity changes
________ as filtrate flows through nephron.
41
New cards
Angiotensis II
________ (ANG II) is the usual signal controlling aldosterone release from the adrenal cortex.
42
New cards
Autoregulation of glomerular filtration rate
________ takes place over a wide range of blood pressures.
43
New cards
ACE2
________ is present in many cell types and tissues including the lungs, heart, blood vessels, kidneys, liver and gastrointestinal tract.
44
New cards
ACE2
________ is highly abundant on type 2 penumocytes in alveoli.
45
New cards
Epithelium of Bowmans capsule
podocytes
46
New cards
Angiotensin II
vasoconstrictor
47
New cards
Prostaglandins
vasodilators
48
New cards
Diuresis
removal of excess water in urine
49
New cards
diuretics
drugs that promote urine excretion
50
New cards
aquaporins, vasopressin/antidiuretic hormone
water reabsorption process involves adding or removing ______ in apical membrane
depends on secretion of ______ (ADH)
depends on secretion of ______ (ADH)
51
New cards
hypothalamus
Vasopressin is secreted by _______
52
New cards
osmolarity, osmoreceptors, pressure, volume
3 stimuli controlling vasopressin secretion:
Plasma osmolarity > 280mOsM
higher the _______, more vasopressin released by posterior pituitary
_______ in hypothalamus detect changes in osmolarity
Blood p_____
Blood v______
Plasma osmolarity > 280mOsM
higher the _______, more vasopressin released by posterior pituitary
_______ in hypothalamus detect changes in osmolarity
Blood p_____
Blood v______