120 - lecture 9
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
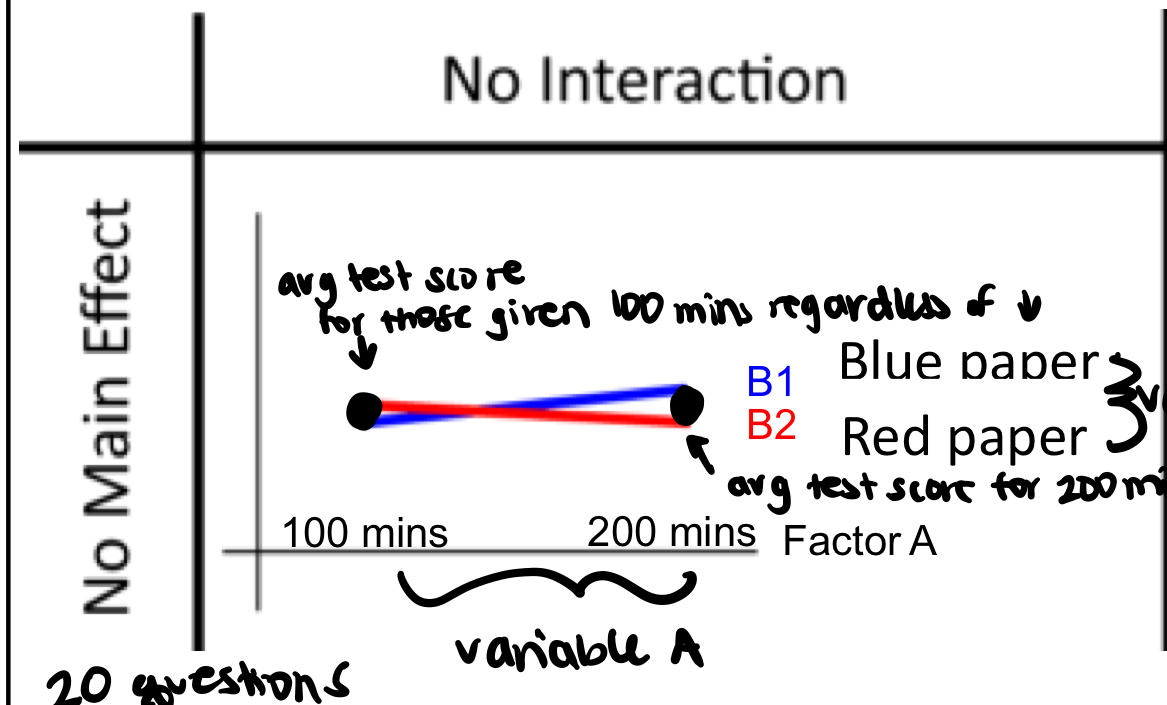
is there an interaction and main effect; why
no because slopes are same (average test score for those given 100 or 200 minutes is same regardless of the paper color); no because average for both is same
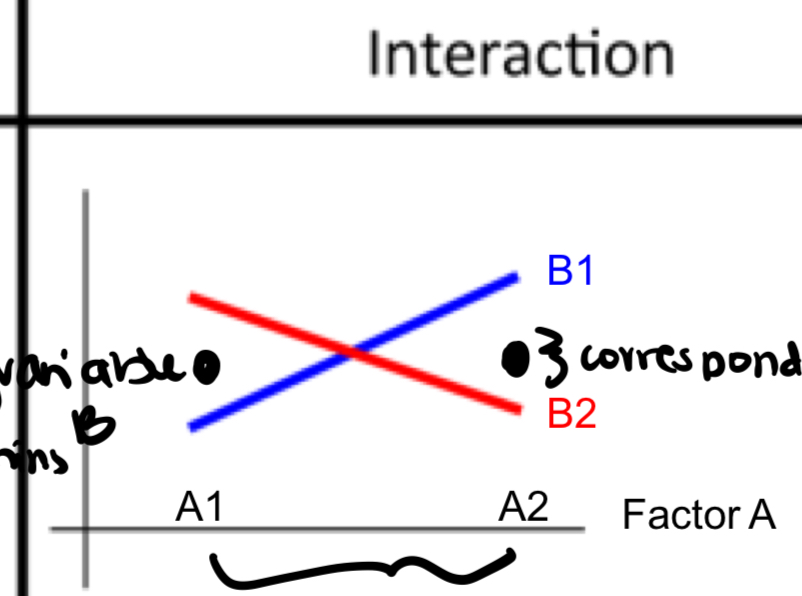
is there an interaction? is there a main effect and why
yes interaction because the slopes are different; no main effect of A or B because the average is the same
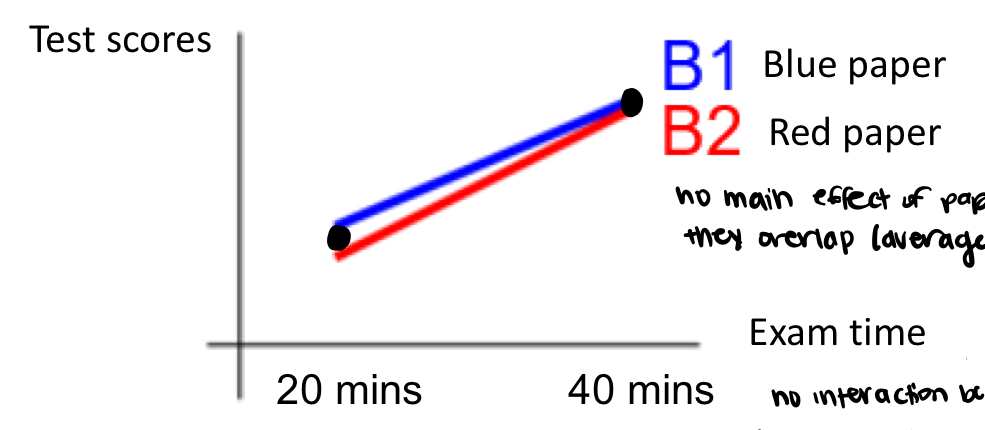
is there interaction or main effect
no interaction because both slopes are same and main of b
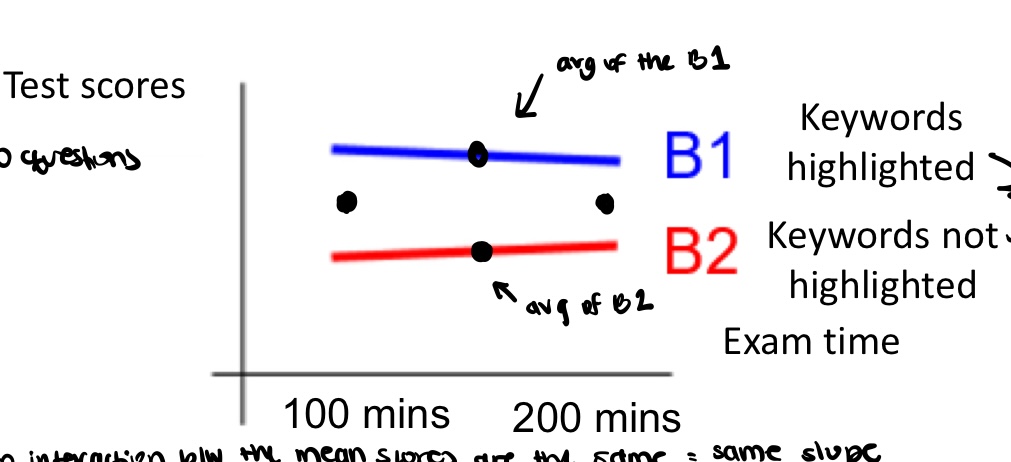
is there interaction or main effect
no interaction because slopes are same but main effect of highlighting words regardless of exam time
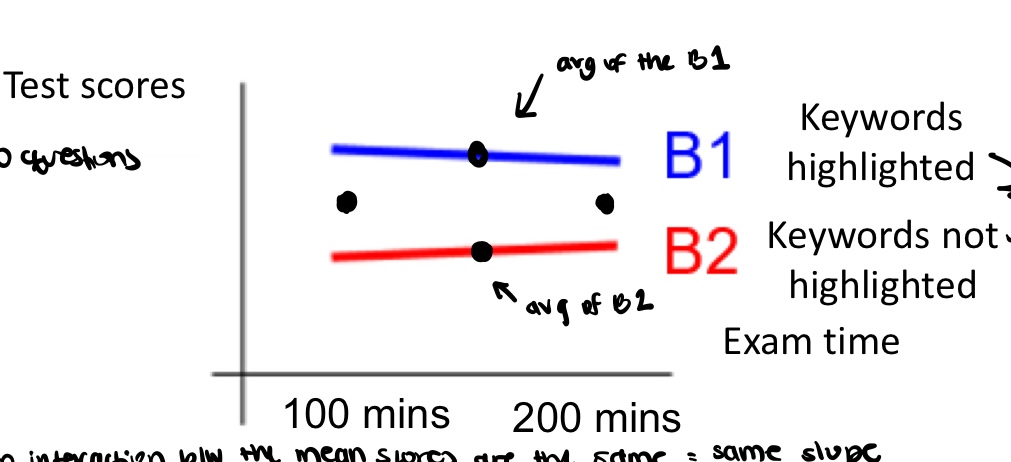
what does the no interaction mean here
regardless of whether keywords are highlighted or not, giving participants 200 minutes is not better than giving them 100 minutes
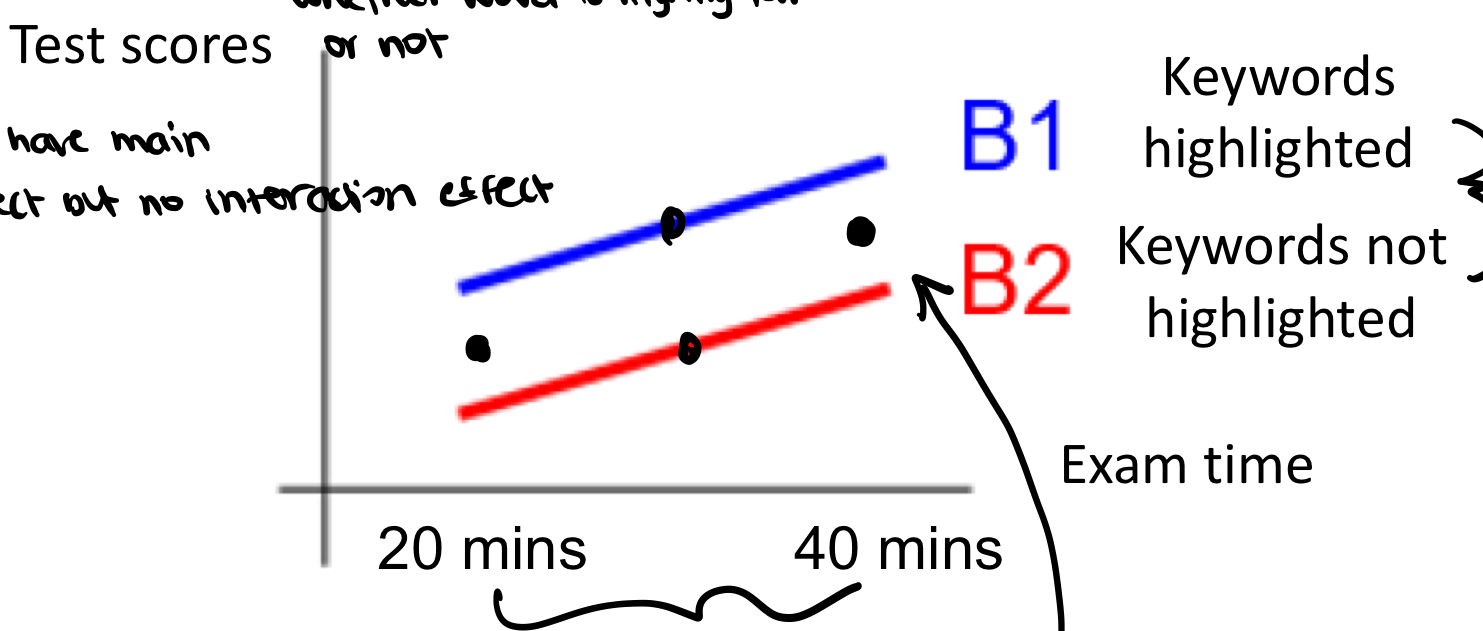
is there interaction or main effect
no interaction because slopes are same but main effect of exam time and highlighting
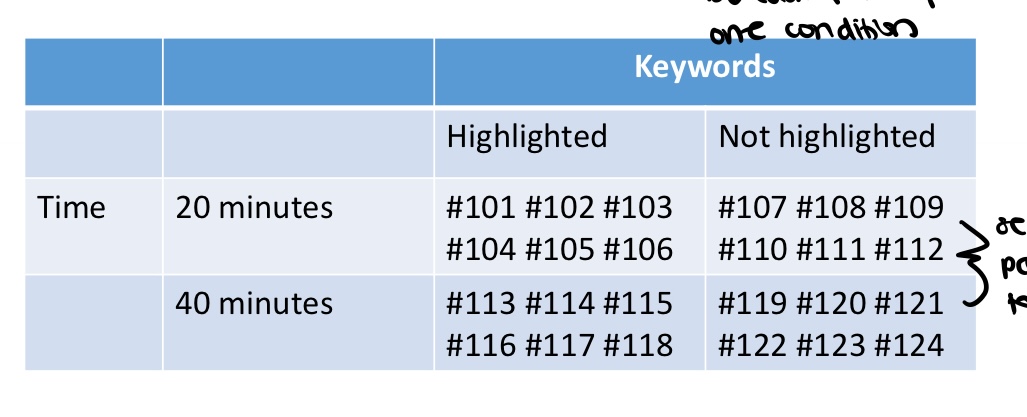
what type of design is this
between subjects
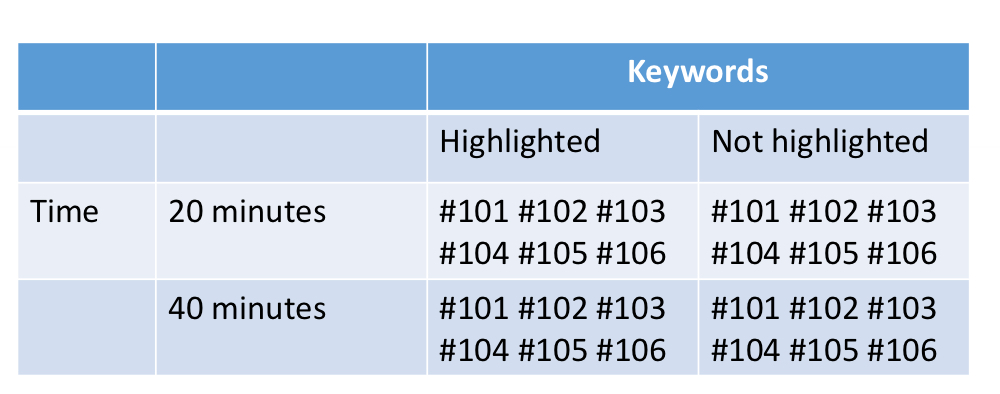
what type of design is this
within subjects
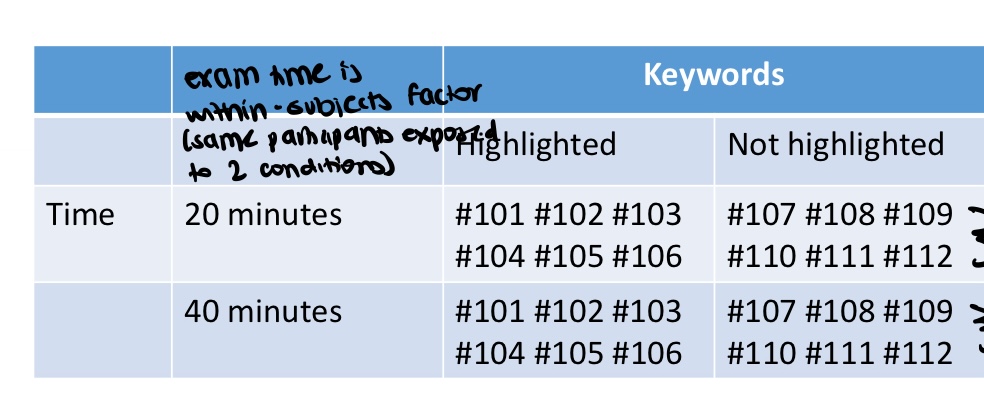
what is this an example of
mixed subjects
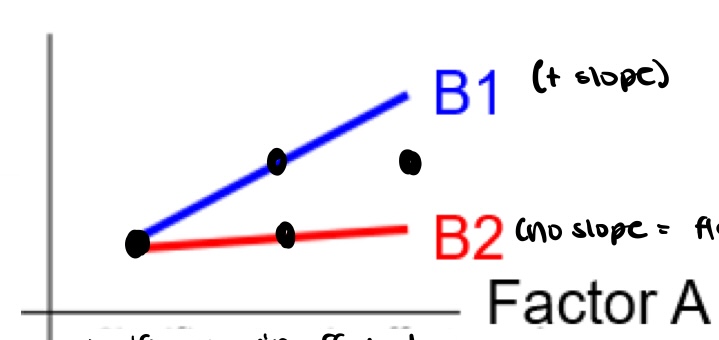
is there an interaction and main effects
yes
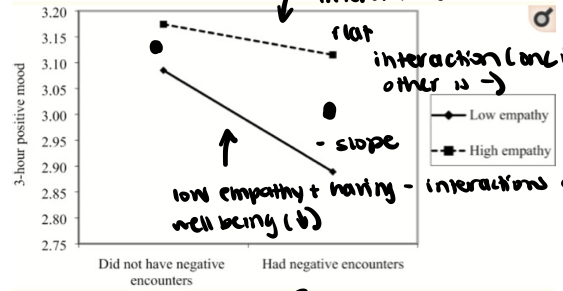
is there interaction and main effects
yes
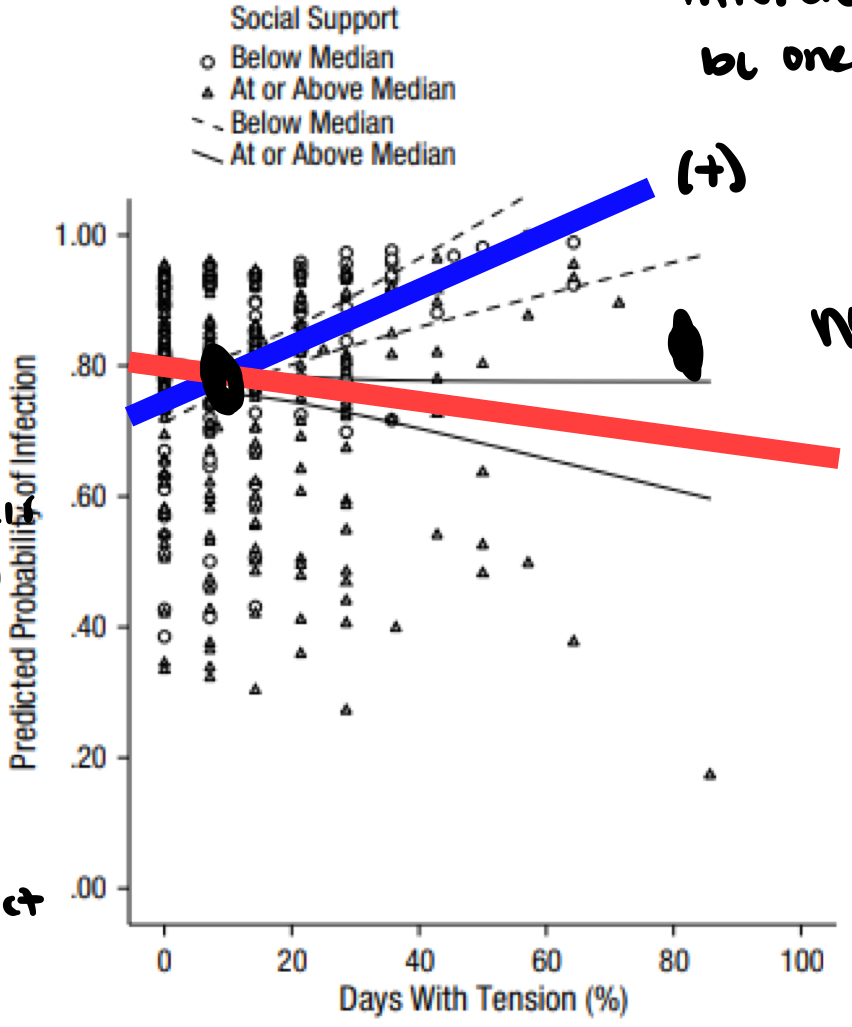
is there an interaction or main effects
yes interaction no main
A forensic psychologist was interested in the possible effects of several variables on the ability of witnesses to recall information about a crime and she recruited college students to participate in a study. Students viewed one of four 10-minute video tapes depicting a crime incident. In the videotapes, the psychologist manipulated the race of the participant) and the type of crime that was committed (violent or nonviolent). After viewing a single videotape, each student answered a series of questions about the event depicted in the video. The number of questions answered correctly determined the recall score for that student. what is the sample
students
A forensic psychologist was interested in the possible effects of several variables on the ability of witnesses to recall information about a crime and she recruited college students to participate in a study. Students viewed one of four 10-minute video tapes depicting a crime incident. In the videotapes, the psychologist manipulated the race of the participant) and the type of crime that was committed (violent or nonviolent). After viewing a single videotape, each student answered a series of questions about the event depicted in the video. The number of questions answered correctly determined the recall score for that student. how many and what is the IV
2, race and type of crime
A forensic psychologist was interested in the possible effects of several variables on the ability of witnesses to recall information about a crime and she recruited college students to participate in a study. Students viewed one of four 10-minute video tapes depicting a crime incident. In the videotapes, the psychologist manipulated the race of the participant) and the type of crime that was committed (violent or nonviolent). After viewing a single videotape, each student answered a series of questions about the event depicted in the video. The number of questions answered correctly determined the recall score for that student. what type of study design
between subjects factorial
Male and female undergraduates at a four-year university were asked to rate authors on their knowledge about topic areas. The participants were given two papers to read. One paper, Brain, discussed the roles of various brain structures in sensation and perception. The other paper, Motivation, discussed intrinsic motivation and engaging ways to enhance it in preschool children. For one-half the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as writter by John Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by David Robinson. For the other half of the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as written by Joan Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by Diana Robinson. After studying the papers, the participant rated each author's knowledge about his or her topic on a scale ranging from 1 ("Does not display a professiona level of knowledge of the topic") to 100 ("Displays a highly professional knowledge of the topic.") what is sample
male and female undergraduates
Male and female undergraduates at a four-year university were asked to rate authors on their knowledge about topic areas. The participants were given two papers to read. One paper, Brain, discussed the roles of various brain structures in sensation and perception. The other paper, Motivation, discussed intrinsic motivation and engaging ways to enhance it in preschool children. For one-half the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as writter by John Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by David Robinson. For the other half of the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as written by Joan Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by Diana Robinson. After studying the papers, the participant rated each author's knowledge about his or her topic on a scale ranging from 1 ("Does not display a professiona level of knowledge of the topic") to 100 ("Displays a highly professional knowledge of the topic."). what is IV
paper and gender
Male and female undergraduates at a four-year university were asked to rate authors on their knowledge about topic areas. The participants were given two papers to read. One paper, Brain, discussed the roles of various brain structures in sensation and perception. The other paper, Motivation, discussed intrinsic motivation and engaging ways to enhance it in preschool children. For one-half the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as writter by John Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by David Robinson. For the other half of the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as written by Joan Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by Diana Robinson. After studying the papers, the participant rated each author's knowledge about his or her topic on a scale ranging from 1 ("Does not display a professiona level of knowledge of the topic") to 100 ("Displays a highly professional knowledge of the topic."). what is DV
rating on author’s knowledge about his or her topic
Male and female undergraduates at a four-year university were asked to rate authors on their knowledge about topic areas. The participants were given two papers to read. One paper, Brain, discussed the roles of various brain structures in sensation and perception. The other paper, Motivation, discussed intrinsic motivation and engaging ways to enhance it in preschool children. For one-half the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as writter by John Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by David Robinson. For the other half of the participants, the Brain paper was labeled as written by Joan Taylor and the Motivation paper was labeled as written by Diana Robinson. After studying the papers, the participant rated each author's knowledge about his or her topic on a scale ranging from 1 ("Does not display a professiona level of knowledge of the topic") to 100 ("Displays a highly professional knowledge of the topic.") what is study design
mixed subjects
An investigator is interested how accurate children are at identifying people based on certain facial features (eyes and forehead, nose and mouth, or full face without hair showing) and whether children's accuracy also depends on target gender. To test this research question, the investigator photographs a number of men and women to create the experimental materials. The final set of materials includes 30 photographs (5 for each facial feature type and for each gender), which are counterbalanced to minimize specific item effects. Each child views 30 photos, counterbalanced to address order effects, and indicates whether the photo is of a man or woman. The investigator then records how many photos the children accurately identify in each condition. what is sample
children
An investigator is interested how accurate children are at identifying people based on certain facial features (eyes and forehead, nose and mouth, or full face without hair showing) and whether children's accuracy also depends on target gender. To test this research question, the investigator photographs a number of men and women to create the experimental materials. The final set of materials includes 30 photographs (5 for each facial feature type and for each gender), which are counterbalanced to minimize specific item effects. Each child views 30 photos, counterbalanced to address order effects, and indicates whether the photo is of a man or woman. The investigator then records how many photos the children accurately identify in each condition. what is IV
facial features and gender
An investigator is interested how accurate children are at identifying people based on certain facial features (eyes and forehead, nose and mouth, or full face without hair showing) and whether children's accuracy also depends on target gender. To test this research question, the investigator photographs a number of men and women to create the experimental materials. The final set of materials includes 30 photographs (5 for each facial feature type and for each gender), which are counterbalanced to minimize specific item effects. Each child views 30 photos, counterbalanced to address order effects, and indicates whether the photo is of a man or woman. The investigator then records how many photos the children accurately identify in each condition. what is DV
identifying people
An investigator is interested how accurate children are at identifying people based on certain facial features (eyes and forehead, nose and mouth, or full face without hair showing) and whether children's accuracy also depends on target gender. To test this research question, the investigator photographs a number of men and women to create the experimental materials. The final set of materials includes 30 photographs (5 for each facial feature type and for each gender), which are counterbalanced to minimize specific item effects. Each child views 30 photos, counterbalanced to address order effects, and indicates whether the photo is of a man or woman. The investigator then records how many photos the children accurately identify in each condition. what is study design
within-subjects; 3 × 2