ESP231 - Unit 5: Foreign Exchange
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Foreign Exchange
Money or currency of a foreign country.
Foreign exchange market
The market in which currencies are bought and sold and in which currency prices are determined.
Exchange rate
The rate at which one currency is exchanged for another.

Spot rate
An exchange rate requiring delivery of the traded currency within two business days.
Forward rate
An exchange rate at which two parties agree to exchange currencies on a specified future date.
Hedging
The practice of insuring against potential losses that result from adverse changes in exchange rates.
Arbitrage
The instantaneous purchase and sale of a currency in different markets for profit.
Speculation
The purchase or sale of a currency with the expectation that its value will change and generate a profit.

Forward contract
A contract requiring the exchange of an agreed-upon amount of a currency on an agreed-upon date at a specific exchange rate.
Currency option
A right, or option, to exchange a specific amount of a currency on a specific date at a specific rate.
Currency swap
The simultaneous purchase and sale of foreign exchange for two different dates.
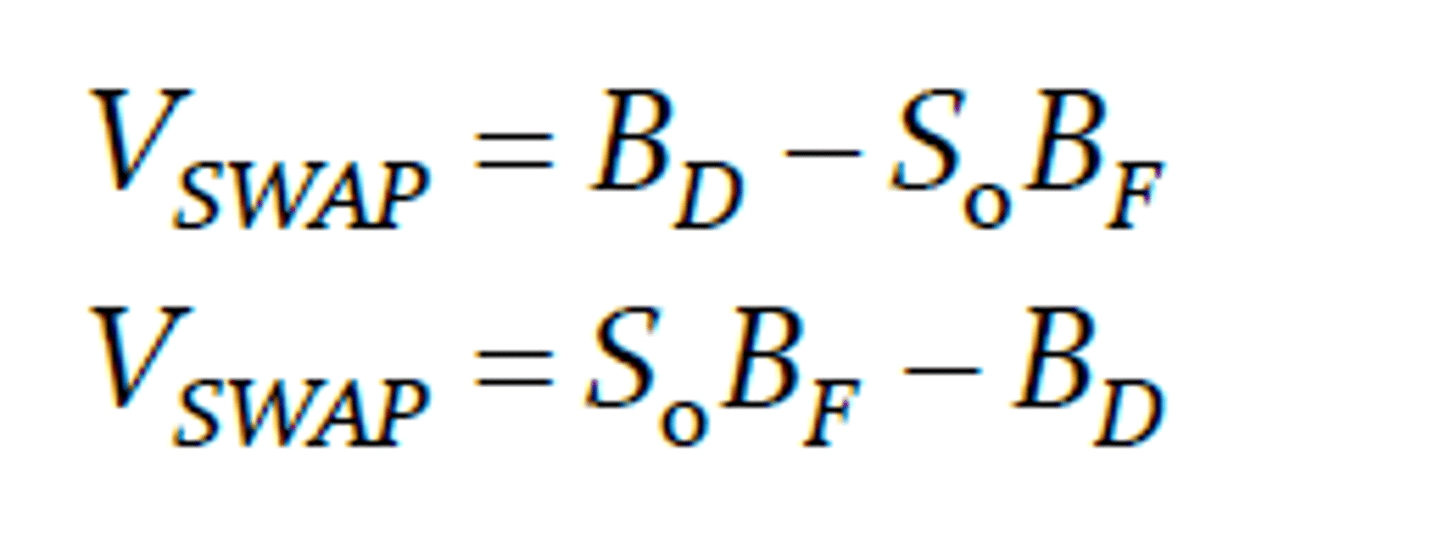
Central Bank
A country's chief bank, which is government owned, regulates commercial banks, holds foreign currency reserves, and actively intervenes in foreign exchange markets to manage currency value.

Fixed Exchange Rate
A system whereby central banks are required by international agreements to maintain their currency at a relatively fixed value.
Floating Exchange Rate
A system in which currencies have no specific par value; value is normally determined by supply and demand. Central banks are not required to intervene, but they often do to avoid wild fluctuations.
Futures
Contract to buy or sell fixed quantities of a commodity, currency, or financial asset at a future date, at a price fixed at the time of making the contract.
Commodities
Raw materials or primary products (metals, cereals, coffee, etc.) that are traded on special markets.

Derivatives
A general name for all financial instruments whose price depends on the movement of another price.
Bid quote
The price at which the bank will buy a currency.
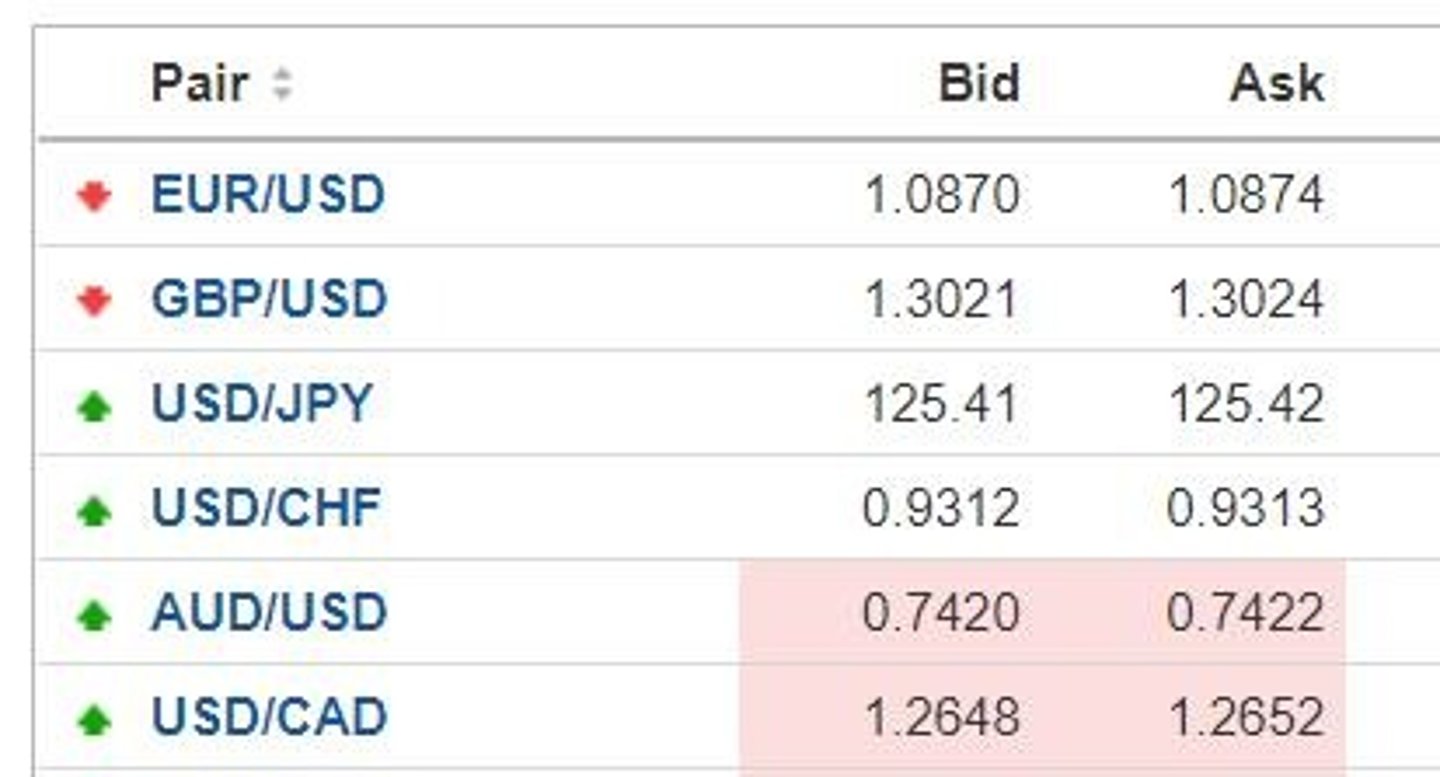
Ask quote
The price at which the bank will sell a currency.
Quoted currency
In a quoted exchange rate, the currency with which another currency is to be purchased.

Base currency
In a quoted exchange rate, the currency that is to be purchased with another currency.
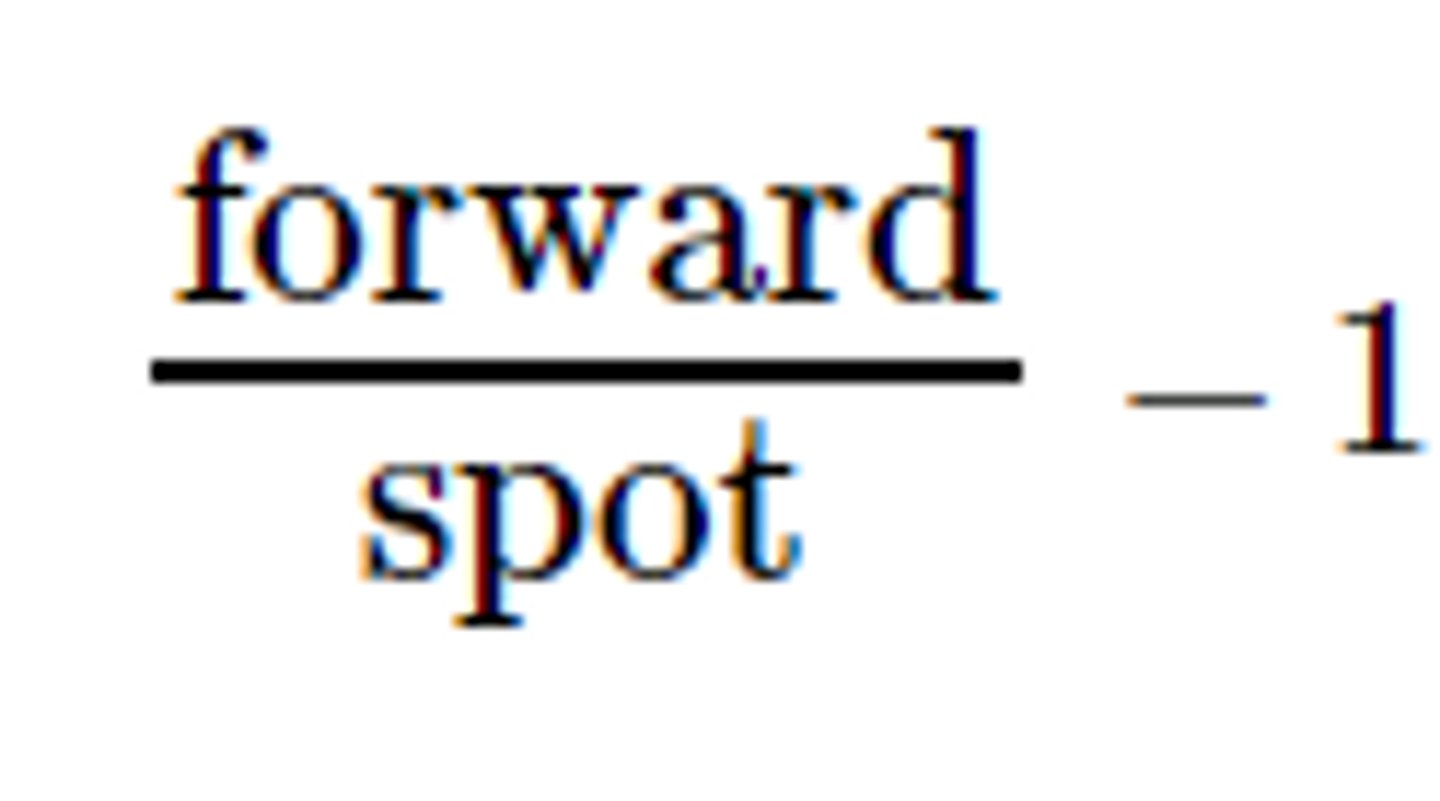
Peg (a currency)
To fix its value in relation to another currency.
Clean floating exchange rate
A system where the currency value is determined by supply and demand without government intervention.
Speculators
Individuals or organizations who buy or sell currency with the expectation that its value will change to generate profit.
Market forces
The determination of price by supply and demand (the quantity available and the quantity bought and sold).
Gold standard
A monetary system where nations link the value of their paper currencies to specific values of gold.

Bretton Woods Agreement
A 1944 agreement that established fixed exchange rates, defined in terms of gold and the US dollar, to create a new international monetary system.

IMF (International Monetary Fund)
The agency created by the Bretton Woods Agreement to regulate fixed exchange rates and enforce the rules of the international monetary system.

World Bank
The agency created by the Bretton Woods Agreement to provide funding for national economic development efforts.

Managed float system (Dirty floating exchange rates)
A system where exchange rates float but governments intervene to stabilize them at a target level.
Exchange controls
Restrictions on the flow of currency.