Carbonyls
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Identify the geometry around the carbon atom in the C=O bond of the aldehyde and ketone functional group
Trigonal planar
Explain the solubility of carbonyl compounds with water
They can form hydrogen bonds with water. The y are very soluble in water, especially with shorter chains
How can aldehydes and ketones be formed from alcohols
(Partially) oxidise a primary alcohol to form an aldehyde - fractional distillation
Oxidise a secondary alcohol to form a ketone
Identify the oxidising agent used to obtain an aldehyde or ketone
Potassium or sodium dichromate (VI) in sulphuric acid
State the observation made and the species responsible when the oxidising agent is used to oxidise an alcohol
Orange solution (Cr2O72-) to green solution (Cr3+)
What is formed in the oxidation of alcohols
A carbonyl and a water molecule
Why can’t ketones be oxidised further
The carbon in the C=O functional group have no other hydrogen atoms bonded
What is Tollen’s Reagent
Ammonical silver nitrate [Ag(NH3)2]+
What happens when aldehydes are heated with Tollens’ Reagent
The aldehyde is oxidised to a salt of carboxylic acid and the silver ions are reduced to form a silver mirror
Explain why salts of carboxylic acids form in the reaction with Tollens’ reagent instead of protonated carboxylic acids
Tollens’ reagent solution is basic due to ammonia so a deprotonated form of the carboxylic acid will form
What happens when aldehydes are heated with Fehling’s solution
Aldehydes reduce blue solution containing Cu2+ to Cu+ to form red precipitate of copper (I) oxide (Cu2O)
What is formed in the reduction of carbonyls
Alcohols
What is the reducing agent used to reduce carbonyls
Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate (III) (LiAlH4) in a dry ether solvent [H]
Give the general, displayed formula equation for the reduction of aldehydes
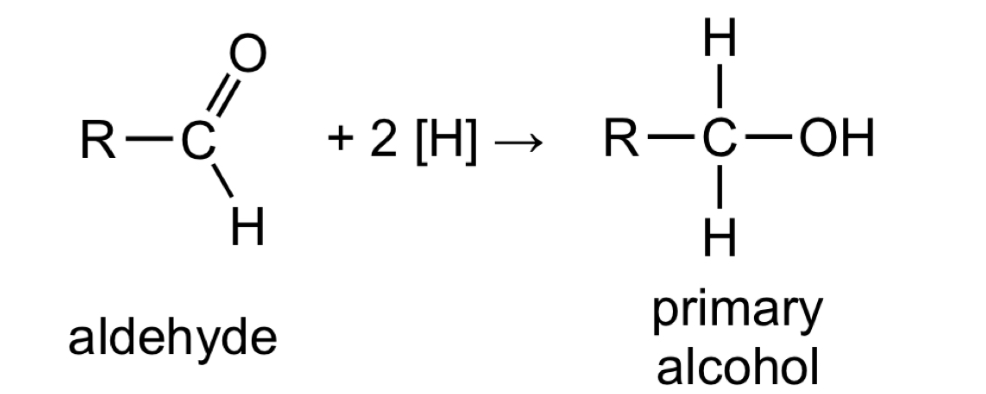
Give the general, displayed formula equation for the reduction of Ketones
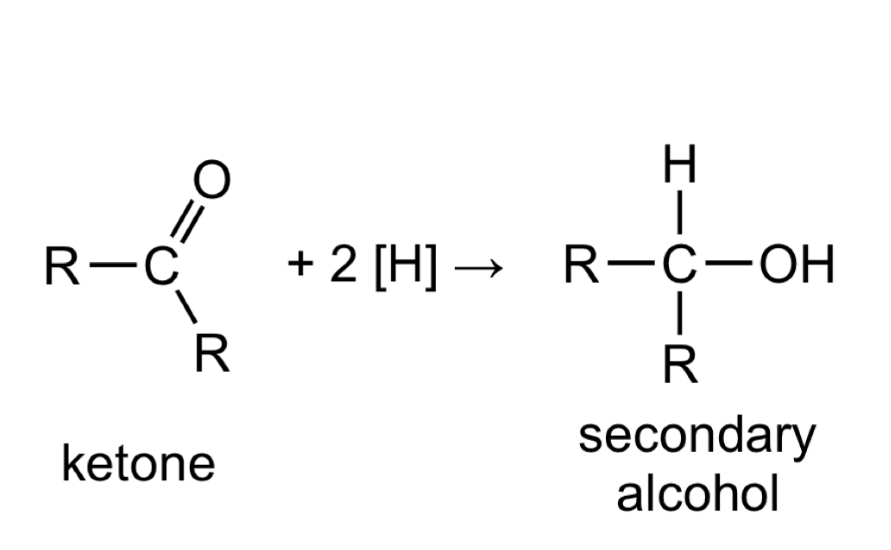
How many [H] is needed in the reduction equation forming alcohols from carbonyls
2[H]
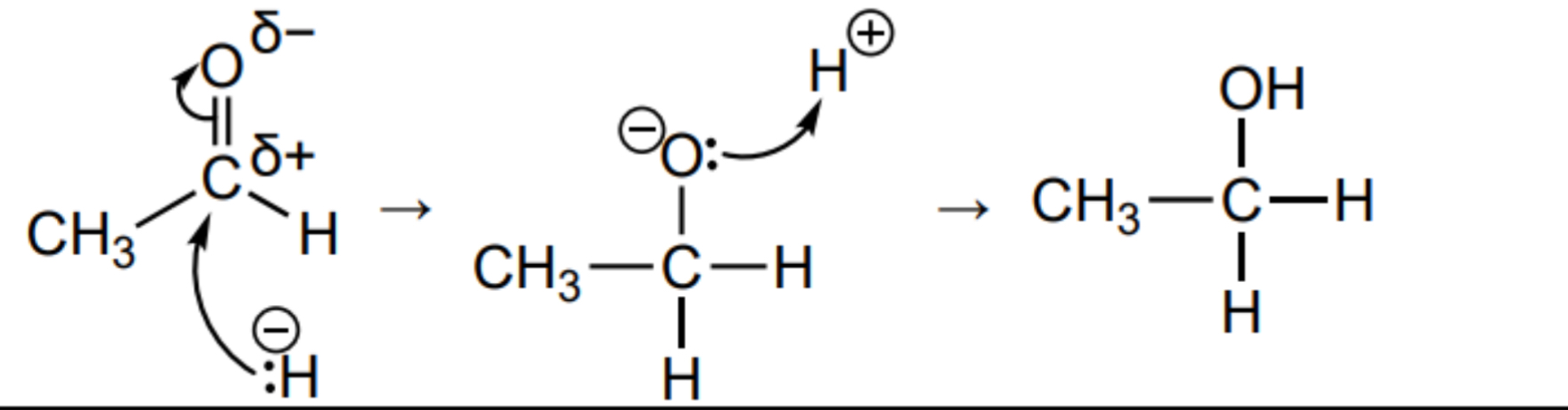
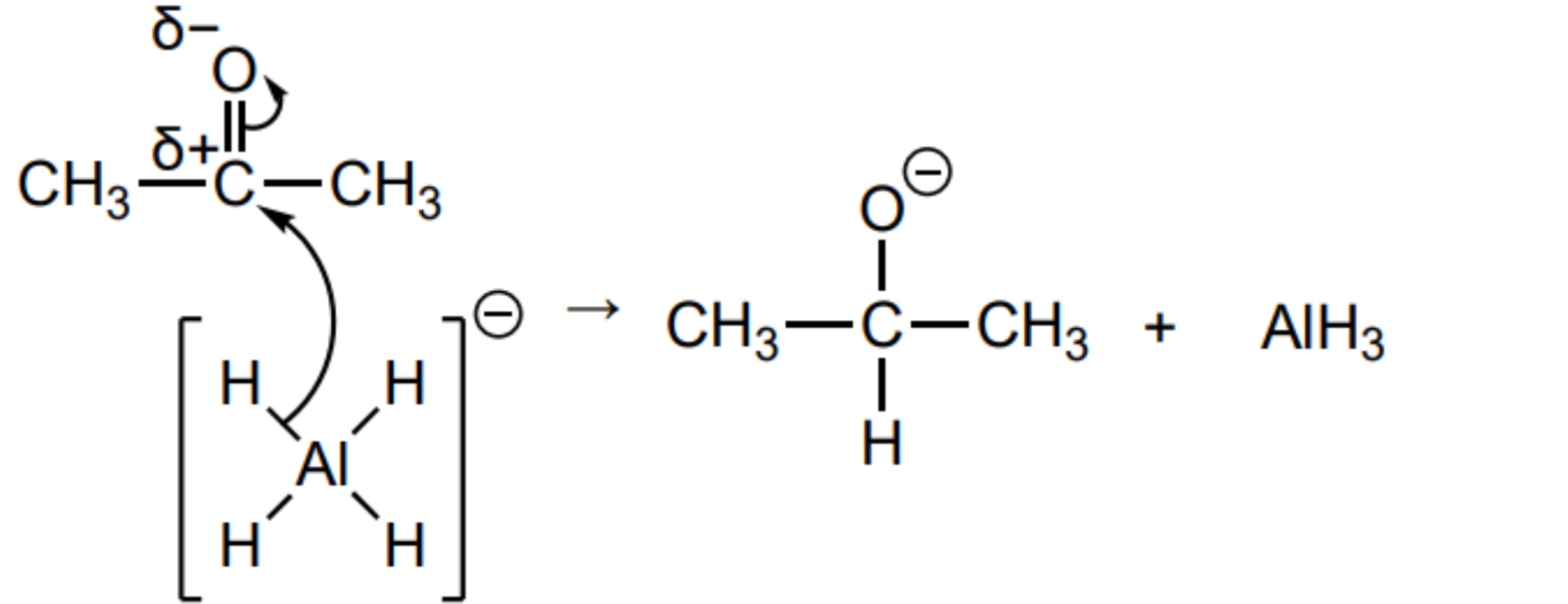
By what mechanism are carbonyls reduced
Nucleophilic addition - a nucleophile attacks the partial positive charge on the carbon caused by the electronegative oxygen
What is the nucleophile in a nucleophilic addition reaction
The H- from the LiAlH4
What is the purpose of the H+ ions in nucleophilic addition
In the protonation step, it gets attacked by the lone pairs on the oxygen atom which is acting as a nucleophile
They come from an acid during the work-up of the product
Outline the mechanism for the nucleophilic addition for the reduction of ethanal
Outline the mechanism for the reduction of propanone using the full structure of the AlH4- ion
State one alternative that can be used in the protonation step of the reduction of carbonyls and why
A water molecule due to the δ+ charge on the hydrogen from its dipole
Outline the mechanism for the reaction between ethanal and KCN in the presence of HCN
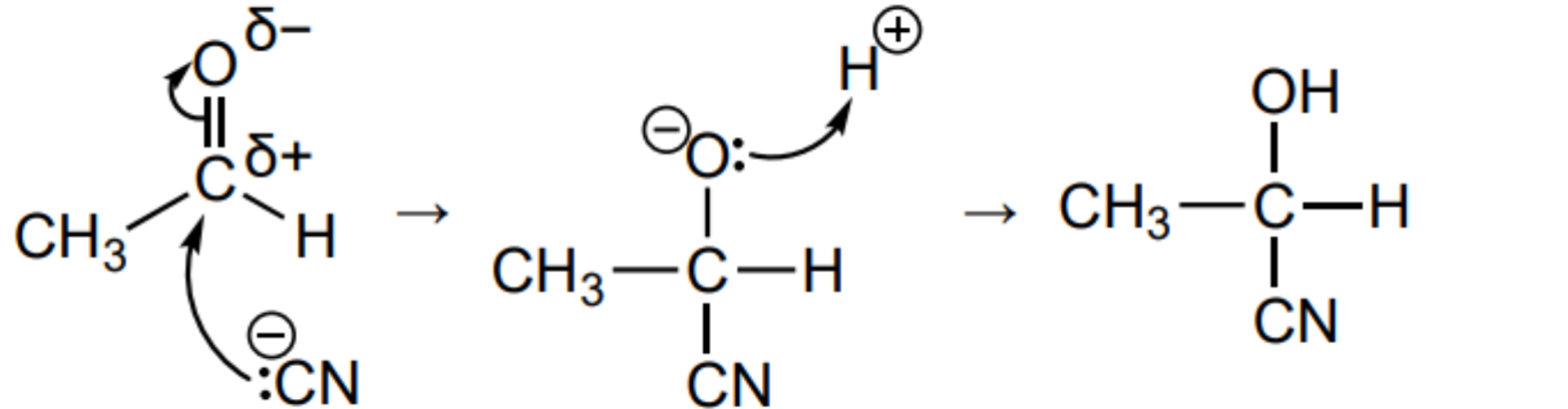
Explain why the product of the reaction between ethanal and KCN in HCN is optically inactive
The CN- nucleophile can attack the carbon atom in the C=O bond from either face with equal probability.
Forms a racemic mixture with both enantiomers forming in 1:1
Equal rotation of plane polarised light clockwise and anticlockwise so cancel each other out
Why is KCN in HCN or KCN in acid a more preferable reaction mixture to pure HCN
Pure HCN is an extremely toxic gas - KCN is a toxic solid so is easier to handle
What can be used to test for an aldehyde or ketone containing a CH3COR group
An iodoform reaction
How do you carry out the iodoform reaction
Iodine solution is added to a small amount of aldehyde or ketone, followed by just enough sodium hydroxide solution to remove the colour of the iodine
Explain why the product of the reaction between propanone and KCN in HCN is optically inactive
There is no chiral carbon so not optically active
State the observation made and the species responsible when aldehydes and ketones containing a CH3COR group are reacted with iodine in presence of sodium hydroxide
Straw yellow precipitate of CHI3 (s)
What does the first stage of the iodoform reaction involve
the substitution of all three hydrogens in the methyl group by iodine atoms
The presence of hydroxide ions is important for the reaction to happen
Write an equation for the first step of the reaction of the reaction of iodine with propanone in the presence of hydroxide ions
CH3COCH3 +3I2 + 3OH- → CI3COCH3 + 3I- + 3H2O
What is involved in the second stage of the iodoform reaction
The bond between the Cl3 and the rest of the molecule is broken to produce triiodomethane (iodoform) and the salt carboxylic acid
Write an equation for the second stage of the reaction between iodine with propanone in the presence of hydroxide ions
CI3COCH3 +OH- → CHI3 + CHCOO-
Write the overall equation for the reaction of iodine with propanone in the presence of hydroxide ions
CH3COCH3 + 3I2 + 4OH- → CHI3 + CH3COO- + 3I- +3H2O
What is compound is used to test for the carbonyl function
Brady’s Reagent
2,4 - DNPH
2,4 - dinitrophenylhydrazine
State the observation made when aldehydes and ketones are reacted with 2,4-DNPH
Orange solution forms yellow precipitate
Which is more reactive between aldehydes and ketones and why
The more polar the C=O bond, the more susceptible the carbon atom in the C=O bond in a carbonyl compound is to attack from a nucleophile.
Ketones contain two alkyl groups with positive inductive effects (electron pushing)
Aldehydes contain only one only one alkyl group
More positive inductive effect means less δ+ the carbon atom so less polar the C=O and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack
What effect do chlorines have on the reactivity of aldehydes
As the number of adjacent chlorine atoms increases, the magnitude of the negative inductive effect (electron pulling) increases caused by the electronegative chlorines
Electron density pulled away from the C=O bond making it more polar so more susceptible for nucleophilic attack so more reactive
How can a carbonyl tested with 2,4 - DNPH be identified
separate the yellow/orange ppt using filtration
Purify the residue using recrystallisation
The melting point of the solid can be determined and compared to a data book value