bio unit 3
1/43
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
metabolism
the entire set of chemical reactions that sustain life is called
catabolism
large molecules are broken down and ATP is produced in the process of
ribose
the atp molecule contains
the use of ATP by cells began long ago and has been conserved over time
nearly all cells use ATP as their primary energy source. This is evidence that ______
heat
in chemical reactions, most of the entropy increase occurs as
entropy
the lid of a container containing gas is removed. As a consequence, the molecule of the gas has more space available to them to spread out. For the gas released from the container, which increases?
the difference in energy between the transition state and the product
the energy of activation of a reaction is:
activation energy
in a reaction, enzymes change the ___
highly specific
enzymes are typically
a site on the enzyme that is not the active site
allosteric inhibitors of an enzyme bind to ____
enzymes catalyze chemical reactions
which statement is true regarding enzymes?
the transition state when the reaction is not catalyzed by an enzyme
in a given reaction, which has the highest amount of free energy?
a narrow range of pH
most enzymes work best at _____
plants use chlorophyll and chloroplasts to convert light energy into chemical energy
which of the following is the best biological example/application of the first law of thermodynamics?
exergonic
-delta G, spontaneous, catabolic
endergonic
+delta G, non-spontaneous, anabolic
hydrolysis; exergonic, phsophorylation; endergonic
the ___ of ATP is ____
non covalent; reversible
the bonds between enzyme and substrate at the active site tend to be ___ and therefore, ___
sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water
photosynthesis is the pathway used to synthesize carbohydrates from
H2O
in plants and algae, what is the source of the electrons needed for photosynthesis?
O2
in plants an algae, which is a by-product of photosynthesis?
water, H2O
during photosynthesis in plants and algae, what molecule is (as in “becomes”) oxidized?
CO2
during photosynthesis in plants and algae, what molecule is reduced?
in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast
where is the photosynthetic electron transport chain located in plant cells?
stroma of the chloroplast
in the chloroplasts of plant cells, the synthesis of carbohydrates takes place in the
the changes in the energy level of electron donors along the photosynthetic electron transport chain
the z scheme refers to
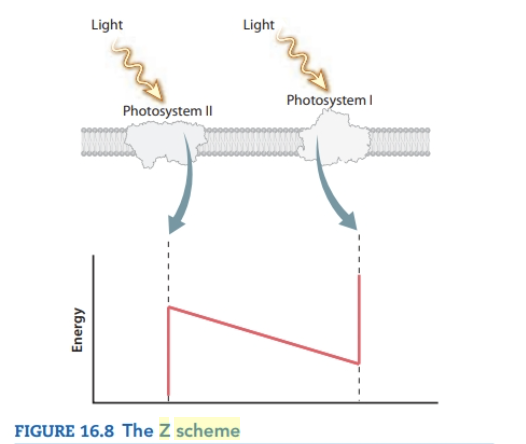
reduced - gain of electrons, charge goes down, WITH H
in the light reactions of photosynthesis, NADP+ is
ATP and NADPH
which products of the light reactions of photosynthesis are required as reactions of the calvin cycle?
thylakoid space to the stroma
chloroplast ATP synthases are powered by the flow of protons from the
it is one of the most abundant enzymes on earth
which is a characteristic of rubisco?
a small amount of ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation; most is produced by oxidative phosphorylation
which best describes ATP production during cellular respiration?
two pyruvate molecules (each having 3 C’s)
at the end of glycolysis, the carbon molecules originally found in the starting glucose molecule are in the form of
oxidized
in cellular respiration, glucose is ___ through the process of cellular respiration
oxygen
the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain is
mitochondrial matrix
in eukaryotes, pyruvate oxidation takes place in
oxygen gas
which is not a product of cellular respiration?
gains electrons and is reduced
in cellular respiration, oxygen
ATP is synthesized by substrate-level phosphorylation
during the krebs cycle
cytoplasm
fermentation takes place
catabolic reactions
cellular respiration is a series of
reduced
during lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is
it loses electrons
which statement is true regarding a molecule that is oxidized?
glycogen in animals
excess glucose is stored in large branched molecules of
ATP synthase
for the potential energy of a proton gradient to be converted to the chemical energy of ATP, the movement of protons down their electrochemical gradient must be coupled with ATP synthesis. This coupling is made possible by