AP Environmental Science Unit 6 Energy
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Fossil fuel
A fuel derived from biological material that became fossilized millions of years ago
nonrenewable energy resource
An energy source with a finite supply, primarily the fossil fuels and nuclear fuels
subsistence energy source
An energy source gathered by individuals for their own immediate needs(straw, sticks and animal dung)
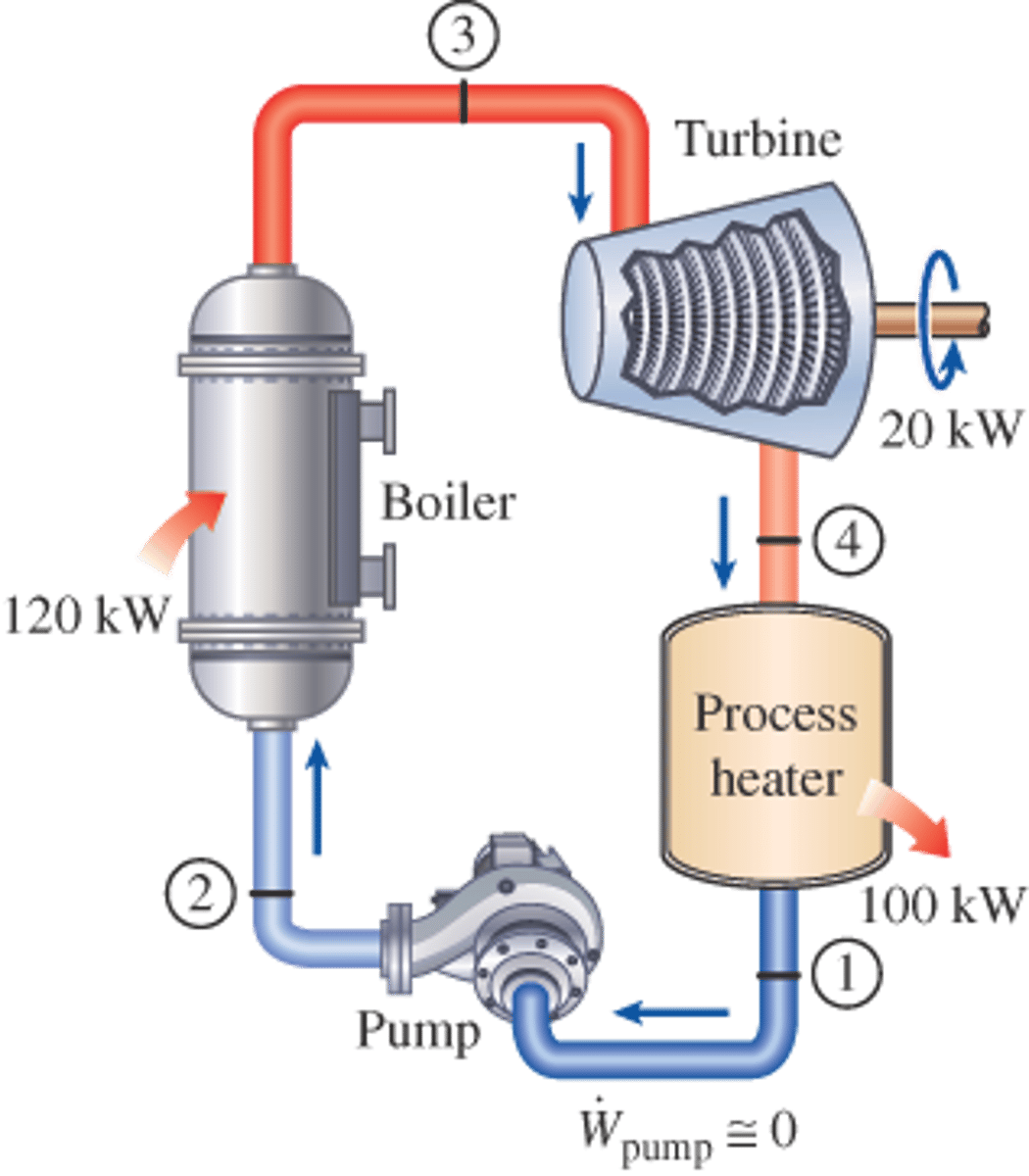
Cogeneration
Production of two useful forms of energy, such as high-temperature heat or steam and electricity, from the same fuel source.
coal
Solid fuel formed primarily from the remains of trees, ferns, and other plant materials preserved 280 million to 360 million years ago
crude oil
A fossil fuel that occurs in underground deposits, composed of a liquid mixture of hydrocarbons, water, and sulfur
Oil sands (tar sands)
Slow-flowing, viscous deposits of bitumen mixed with sand, water, and clay
Natural Gas
flammable gas, consisting largely of methane and other hydrocarbons, occurring naturally underground (often in association with petroleum) and used as fuel.
Bitumen
A degraded petroleum that forms when petroleum migrates to the surface of Earth and is modified by bacteria.
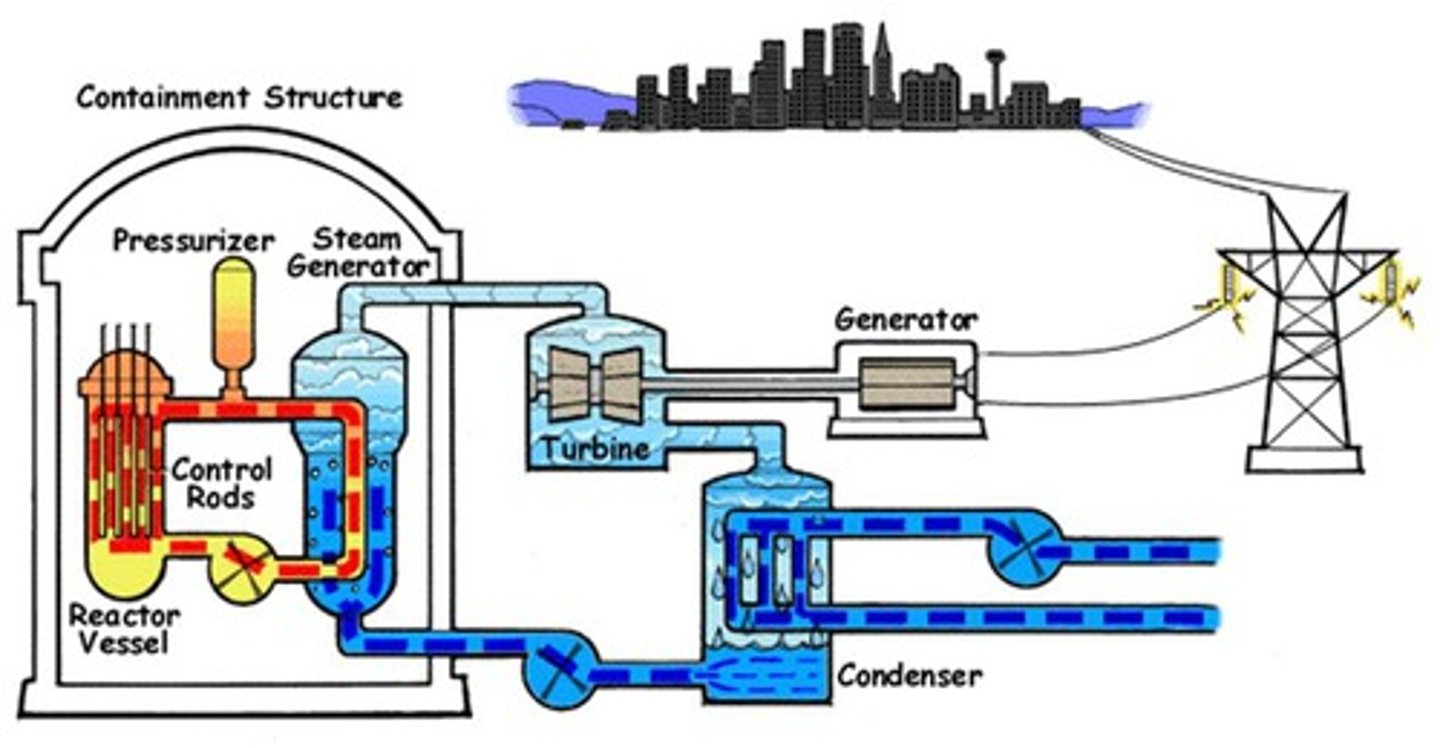
nuclear fission
A nuclear reaction in which a massive nucleus splits into smaller nuclei with the simultaneous release of energy
fuel rod
A cylindrical tube that encloses nuclear fuel within a nuclear reactor
How is electricity generated?
A fuel is burned, which produces heat, which boils water, giving off steam. The steam then drives a turbine, which powers the generators. This produces the electricity, which is sent to the National Grid, via a step-up transformer.
radioactive waste
Nuclear fuel that can no longer produce enough heat to be useful in a power plant but continues to emit radioactivity
Energy conservation
the practice of finding ways to use less energy or to use energy more efficiently
renewable energy
In energy management, an energy source that is either potentially renewable or nondepletable
Biomass
Fuel for energy that includes wood, charcoal, animal waste, plant remains, municipal solid waste, ethanol (from corn or sugar) and bio diesel. Accounts for 10% of world energy consumption
tidal energy
Energy that comes from the movement of water driven by the gravitational pull of the Moon.
active solar energy
energy captured from sunlight with advanced technologies
photovoltaic solar cell
A system of capturing energy from sunlight and converting it directly into electricity
wind energy
Energy generated from the kinetic energy of moving air
geothermal energy
Energy from steam or hot water produced from hot or molten underground rocks.
wind turbine
A turbine that converts wind energy into electricity
fuel cell
converts fuel (usually hydrogen) directly into electrical current.
Control rod
A rod inserted between the fuel rods in a nuclear reactor to absorb excess neutrons and slow or stop the fission reaction
thermal pollution
harm to lakes and rivers resulting from the release of excessive waste heat into them
half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
Ethanol
Biofuel derived from crops such as corn (US) or sugar (Brazil)
Three Mile Island
Nuclear Power Plant in Pennsylvania which failed, causing radiation to be admitted in the air
Chernobyl
nuclear power plant in Russia that had a meltdown in 1986 & released radioactive materials into the air
Fukushima
Nuclear power plant in japan, largest disaster since Chernobyl. Series of equipment failures, nuclear meltdown (core was damaged due to overheating) resulting from earthquake and tsunami impact
anthracite
coal of a hard variety that contains relatively pure carbon and burns with little flame and smoke.
Lignite
the least pure coal, releases the most pollution when burned for energy
Hybrid electric vehicle (HEV)
A car that combines the engine of a conventional vehicle with the battery and electric motor of an electric vehicle, allowing it to achieve twice the fuel economy of a conventional car
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
A car that does not burn any fuel. It uses a battery and an electric motor and needs to be charged regularly. These cars have a range of 150-250 miles (2019) depending on the make and model.
Advantages of coal use
1. generates electricity
2. steel production
3. easy to obtain (surface mining)
4. low economic costs
Fractional distillation of crude oil
the separation of crude oil into individual hydrocarbons
kWh (kilowatt hour)
the unit used to measure the amount of electrical energy used in an hour. Also the unit that power companies track to charge for the electricity used.
Uranium-235
an isotope used to fuel most nuclear fission reactors
Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels
- combustion products can produce pollution
- environmental effects of wastes and extraction
- extraction can damage the environment
- coal-fired stations need large amounts of fuel
Fracking (hydraulic fracturing)
The pumping of water at high pressure to break apart rocks in order to release natural gas
Combustion
A rapid reaction between oxygen and fuel that results in fire
Methods for Conserving Energy
include improving fuel economy for vehicles, using BEVs (battery electric vehicles) and hybrid vehicles, using public transportation, and implementing green building design features
Peat
partially decayed plant matter found in bogs that can be used for fuel.
smart grid
an efficient, self-regulating electricity distribution network that accepts any source of electricity and distributes it automatically to end users
wind energy pros
Clean emissions
Free energy source
Affordable power
wind energy cons
Fluctuating (intermittent) source of energy and is not suited to meet the base load energy demand unless some form of energy storage is utilized (e.g. batteries, pumped hydro).
The manufacturing and installation of wind turbines requires heavy upfront investments - both in commercial and residential applications.
Wind turbines can be a threat to wildlife (e.g. birds, bats).
Noise is regularly reported as a problem by neighboring homes.
How wind turbines look (aesthetics) is a legitimate concern for some people.
water impoundment (dams)
dam built in a river creates a large artificial lake behind the dam (reservoir)
hydroelectric power pros
no emissions, reliable, capable of generating large amounts of power, output can be regulated to meet demand
hydroelectric cons
kills/hurts wildlife, expensive to build, all good sites already built, leads to flooding, habitat destruction, only useful near water
tidal power
Electricity generated by the movement of sea water caused by the tides
hydrogen fuel cells
creates electricity chemically by combining hydrogen fuel with oxygen from the air
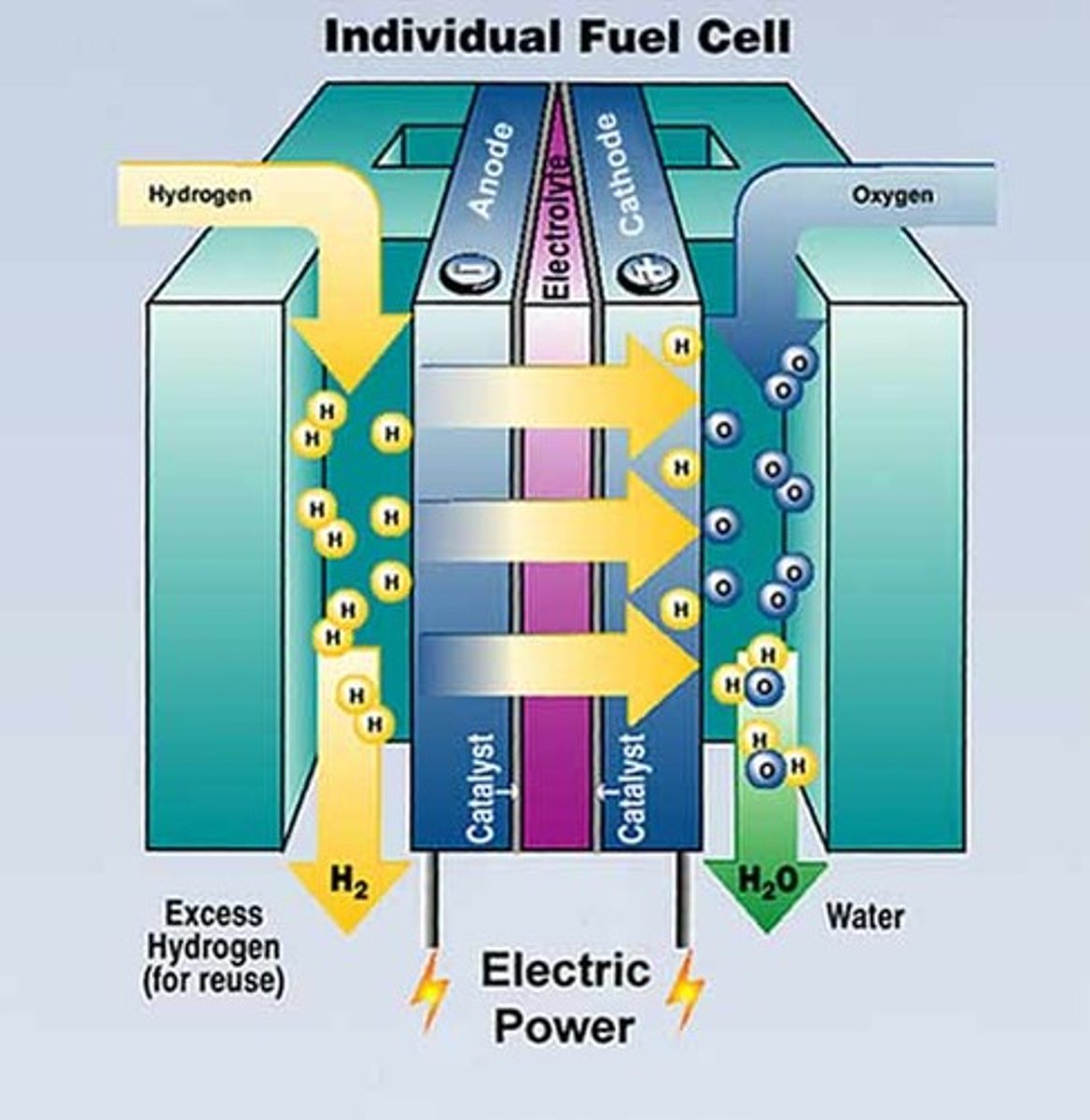
Electrolysis
the process in which an electric current is used to produce a chemical reaction, such as the decomposition of water
Steam Reforming
Process in which steam is used to separate molecules of methane (CH4) into their component carbon and hydrogen atoms
Separates hydrogen from carbon in methane
CH4(g) + H2O → CO +3H2(g) + energy
hydrogen fuel cell pros
(A) Can be produced
from water
(B) Low environmental
impact-No CO2 emissions
(C) Good substitute for oil
(D) Competitive price if environmental and social costs are included in cost comparisons
(E) Easier to store than electricity
(F) Safer than gasoline and natural gas
(G) High efficiency (65-95%) in fuel cells
hydrogen fuel cell cons
(A) Not found in nature
(B) Energy is needed to produce fuel
(C) Nonrenewable if generated by fossil fuels or nuclear power
(D) High costs (but expected to come down)
(E) Short driving range for current fuel cell cars
(G) No distribution system in place
photovolatic cells
are devices that convert sunlight to electricity

Concentrated solar power (CSP)
a means of generating electricity at a large scale by focusing sunlight from a large area onto a smaller area
heliostats
large stationary tracking mirrors concentrating sunlight to a central point
Solar Heating Systems
converts radiant energy from the sun to thermal energy
Active Solar Energy
energy captured from sunlight with advanced technologies
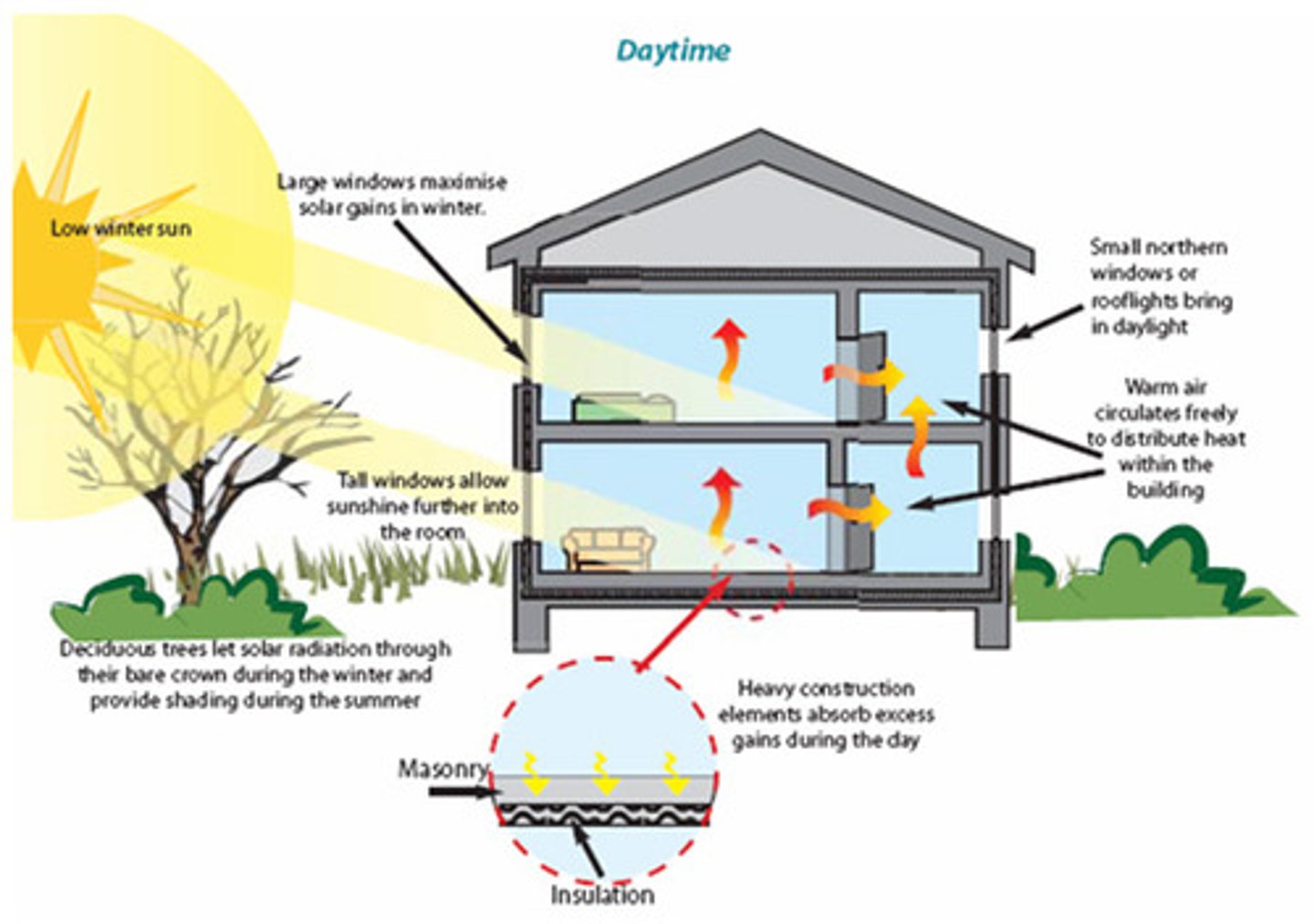
passive solar energy
uses the solar energy that naturally falls on a building to heat it directly
solar energy pros
Renewable
Abundant
Sustainable
Environmentally Friendly
Good Availability
Reduces Electricity Costs
Many Applications
Shared Solar
Silent
Financial Support from Government/State
Low Maintenance
Technology is Improving
solar energy cons
-Semiconductor metals (silicon) still need to be mined to produce PV cells (solar panels)
-This can disrupt habitats & pollute water with mine tailings, air with PM
-Silicon is a limited resource
-Solar panel farms can displace habitats
Disadvantages of Dams
Human displacement, alter the dynamics of the river ecosystem downstream, contain less oxygen than do free-flowing rivers, affecting which species can survive in the waters, release of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere during construction
advantages of dams
provide electricity, reduces dependency on fossil fuels, protect people from flooding, generates jobs
Biodiesel
A diesel substitute produced by extracting and chemically altering oil from plants
Chernobyl, Ukraine
April 26, 1986, unauthorized safety test, leads to fire and explosion at nuclear power plant—millions exposed to unsafe levels of radiation.
Commercial Energy Source
energy source which is bought and sold (ex., coal, oil, natural gas; sometimes wood, charcoal, animal waste)
Bitumous Coal
soft; black coal; major coal used in power generation and industry; high energy
Consequences of Coal
landscape degradation, groundwater pollution, air pollution, increase in greenhouse gasses
What are the disadvantages of using crude oil?
It pollutes the environment, it is a finite resource and increases risks of oil spills
What are the consequences of using hydraulic fracturing (fracking)?
A. Possibility of well leaking & contaminating groundwater with fracking fluid (salt, detergents, acids) or hydrocarbons
B. Ponds can overflow or leach into ground & contaminate surface or ground waters with fracking fluid (salt, detergents, acids)
C.Hab. loss/fragment
D. Release of GG such as Methane (CH4)
E. Depletion of ground or surface waters nearby (as they're drawn from for fracking fluid)
F. Increased seismic activity (earthquakes) linked with wastewater injection wells (storing fracking fluid deep underground)
advantages of nuclear power
-Doesn't emit CO2
-Produces a lot of energy
-Reliable
disadvantages of nuclear power
- non-renewable
- need to store carefully (if escapes into water sources underground, you can contaminate water sources, leading to cell mutation and cancer)
- high decommissioning costs (need to be taken apart - expensive)
flex-fuel vehicles
Can run on either gas or E-85 (85% ethanol, 15% gas) fuel.
Disadvantages of Biomass
- Requires land, water and energy
- Can lead to
• Deforestation
• Desertification
• Soil erosion
How do photovoltaic cells generate electricity?
Their semiconducting surface converts solar energy directly into electricity

Siltation
The accumulation of sediments, primarily silt, on the bottom of a reservoir.
ground source heat pumps (GSHPs)
geothermal pumps heat buildings in the winter by transferring heat from the ground to the building
geothermal energy advantages
-medium net energy yield and high efficiency at accessible sites
-lower CO2 emissions than fossil fuels
-low cost at favorable sites
geothermal energy disadvantages
Not everywhere on earth has access to geothermal energy reaching close enough to surface to access it
Hydrogen sulfide can be released, which is toxic and can be lethal to humans & animals
Cost of drilling that deep in the earth can be very high initially
Sometimes so high that it's not even worth it
CAFE Standards (Corporate Average Fuel Economy)
these standards set mile per gallon standards for a fleet of cars; increased fuel economy = lower energy usage
hybrid vehicles
Vehicles that use a gas engine to drive an electric generator and use the generator and/or storage batteries to power electric motors.