305 pt 1: Posterior Abdominal Wall and Kidneys (Imported)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
T7
the abdomen "technically" begins at what vertebral level?
psoas major m.
iliacus m.
quadratus lumborum m.
transversus abdominis m.
name the 4 muscles of the posterior abdominal wall:
latissimus dorsi m.
external oblique m.
iliac crest
what structures make up the lumbar triangle (of Petit)?
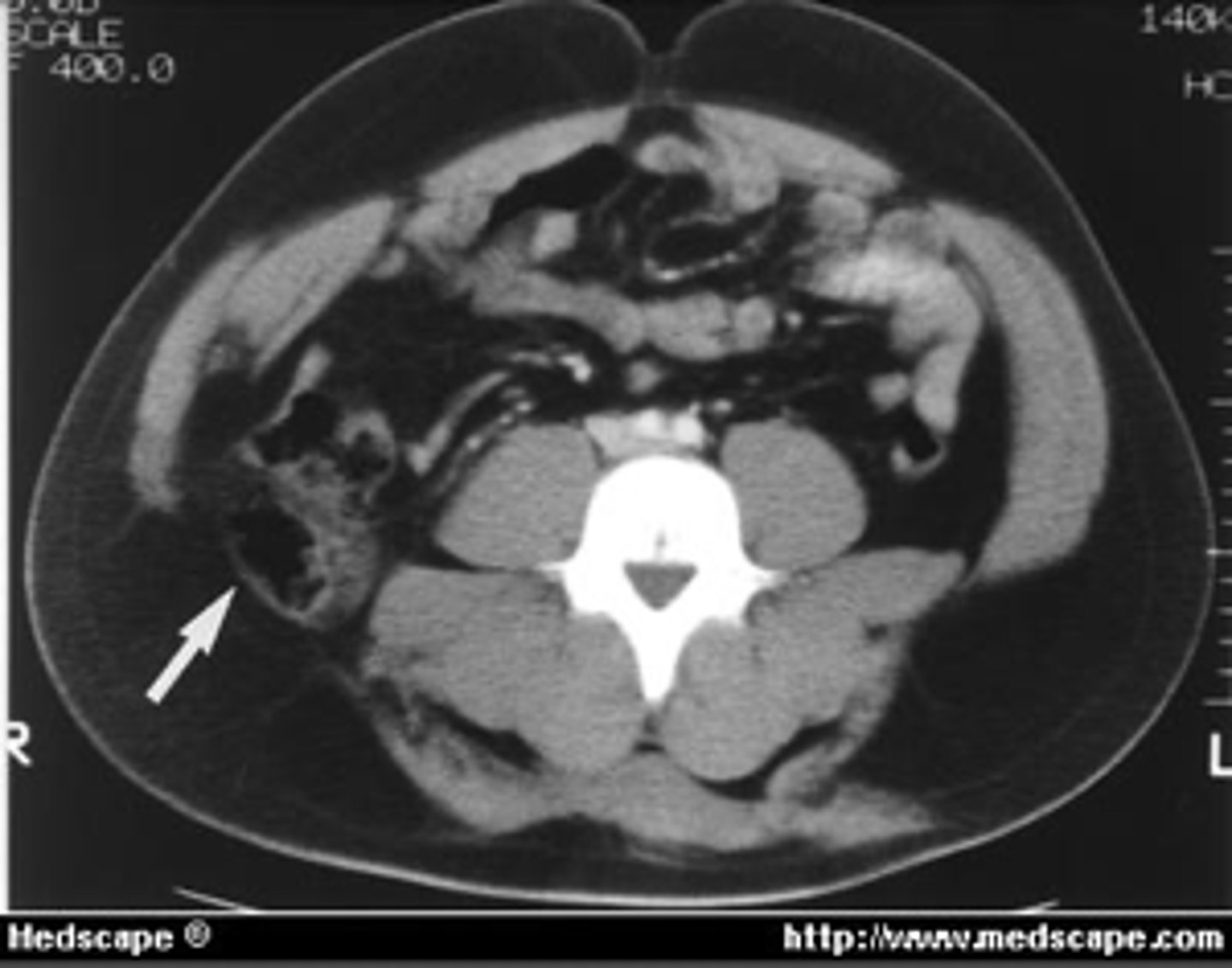
lumbar hernia
identify the pathology
quadratus lumborum m.
identify the structure
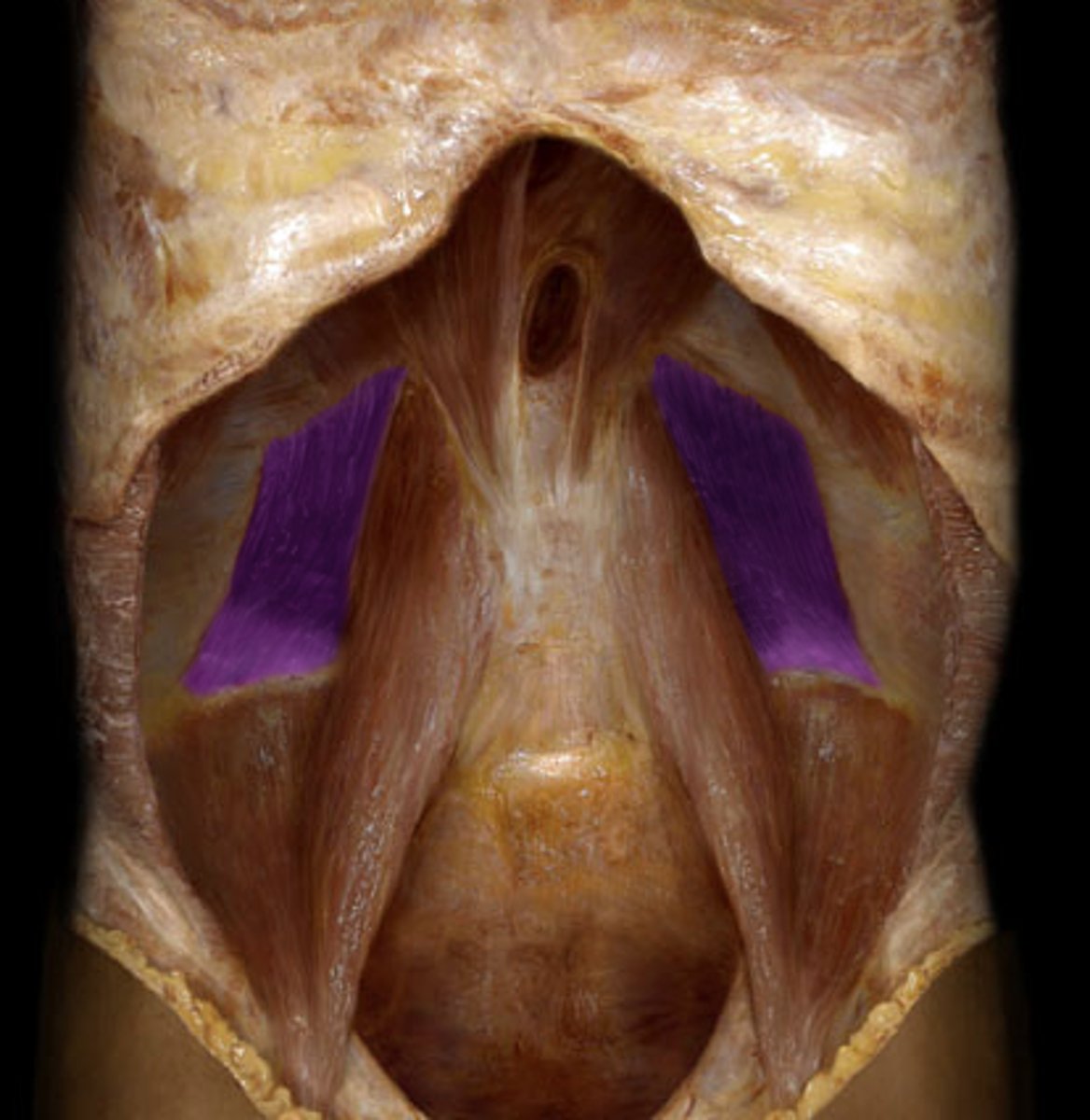
Iliopsoas m.
what muscle of the posterior abdominal wall allows for hip flexion?
Iliopsoas m.
identify the structure
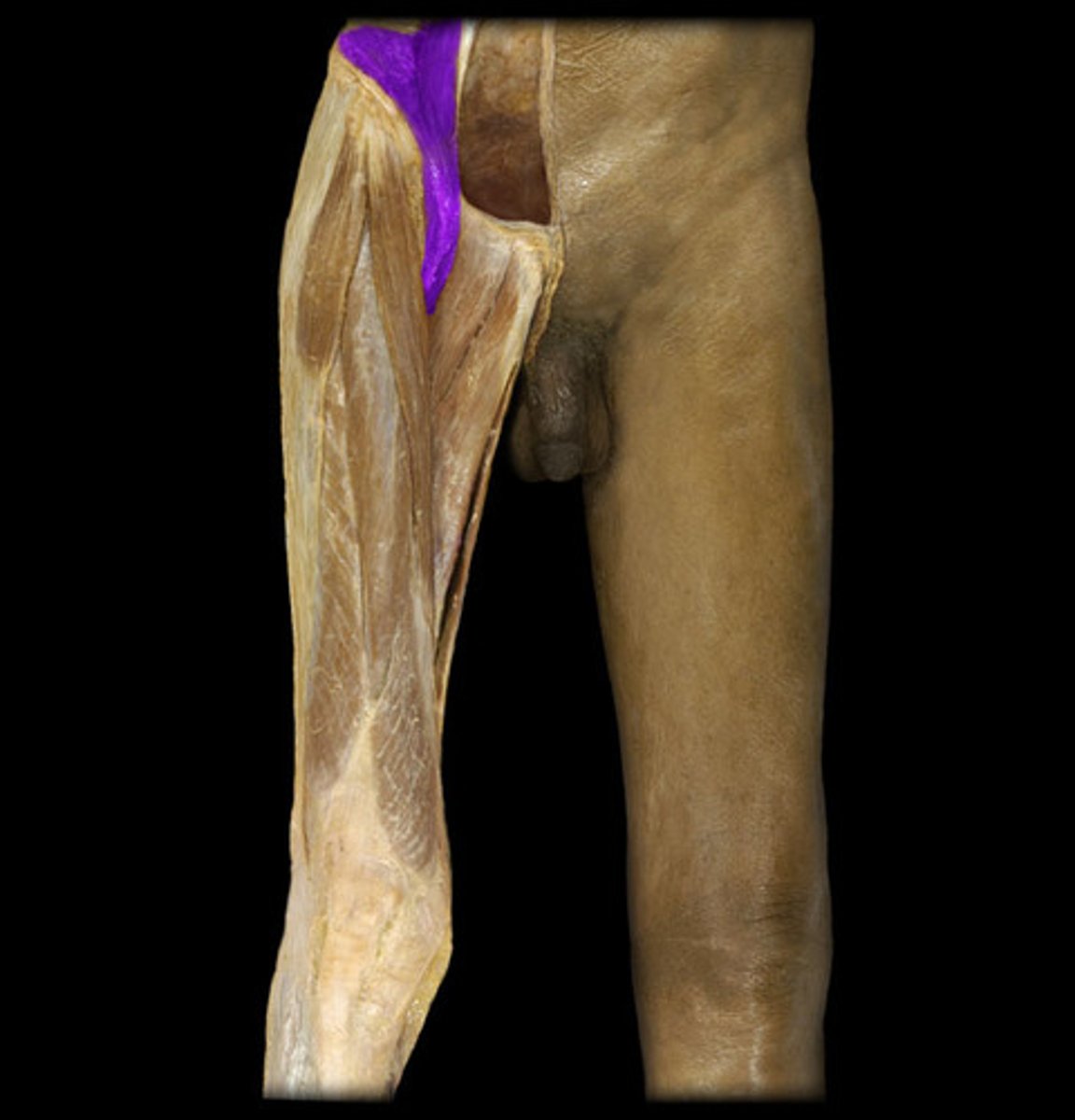
psoas major m.
identify the structure
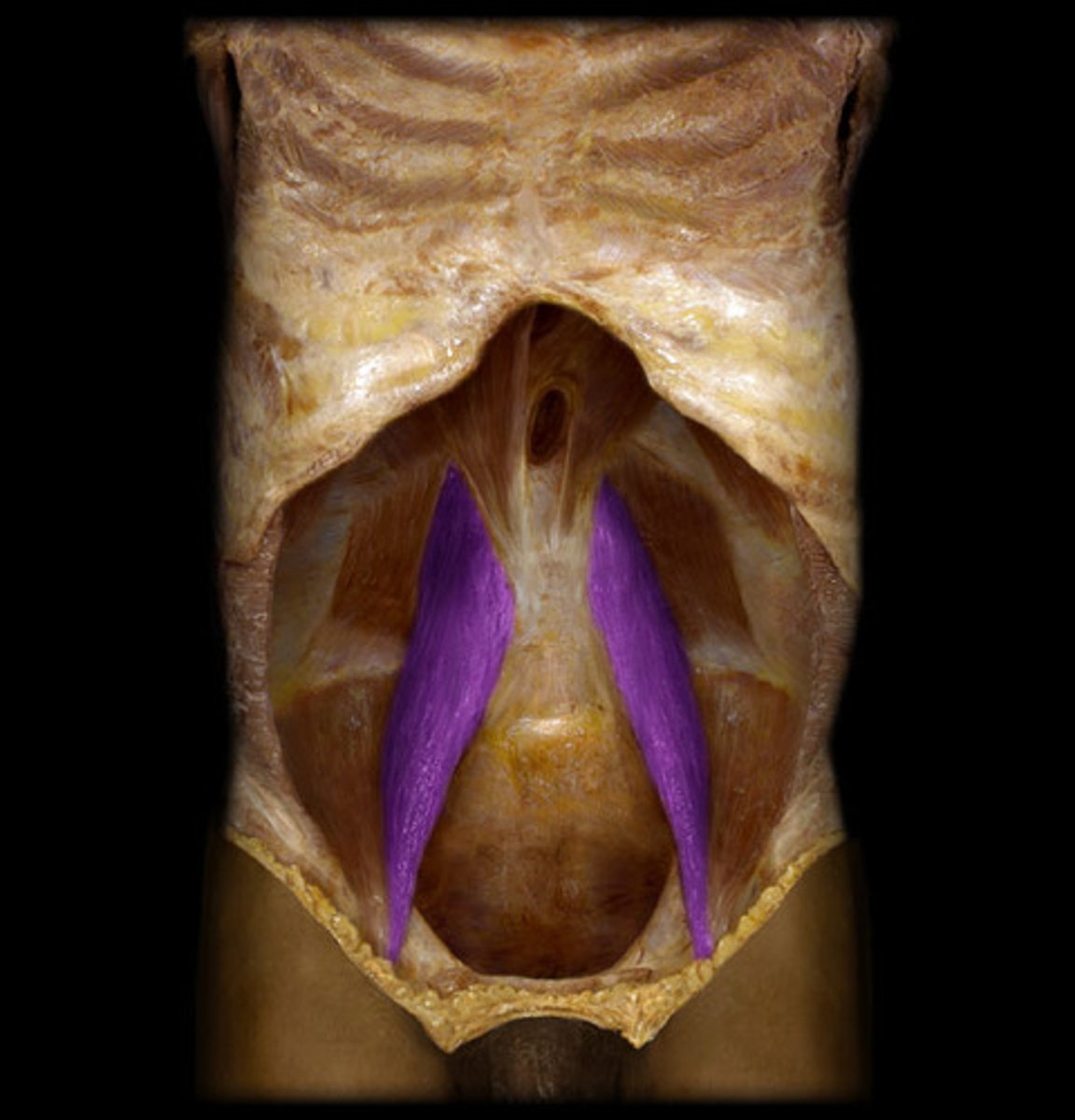
psoas minor m.
identify the structure
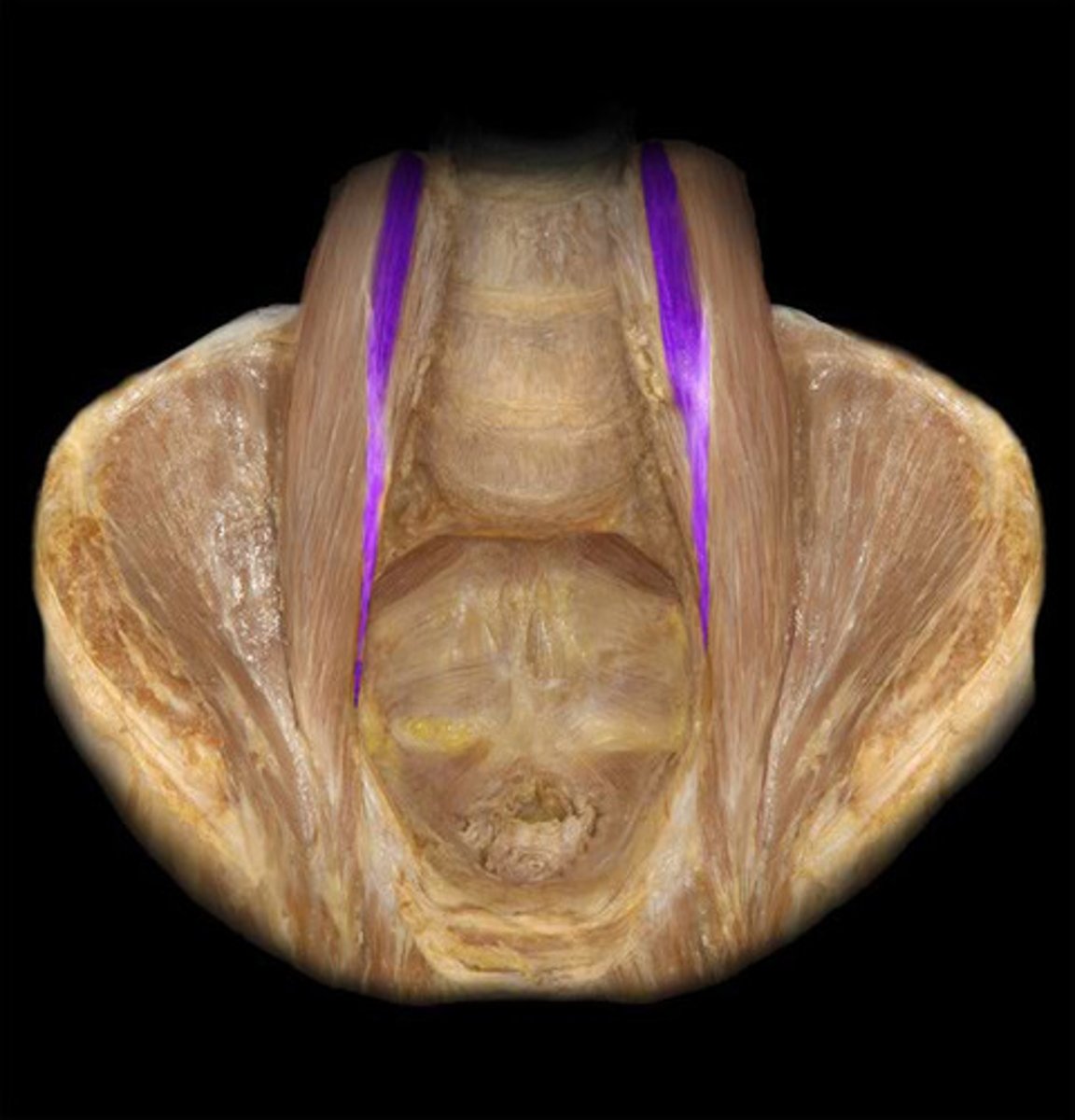
transversus abdominis m.
identify the structure
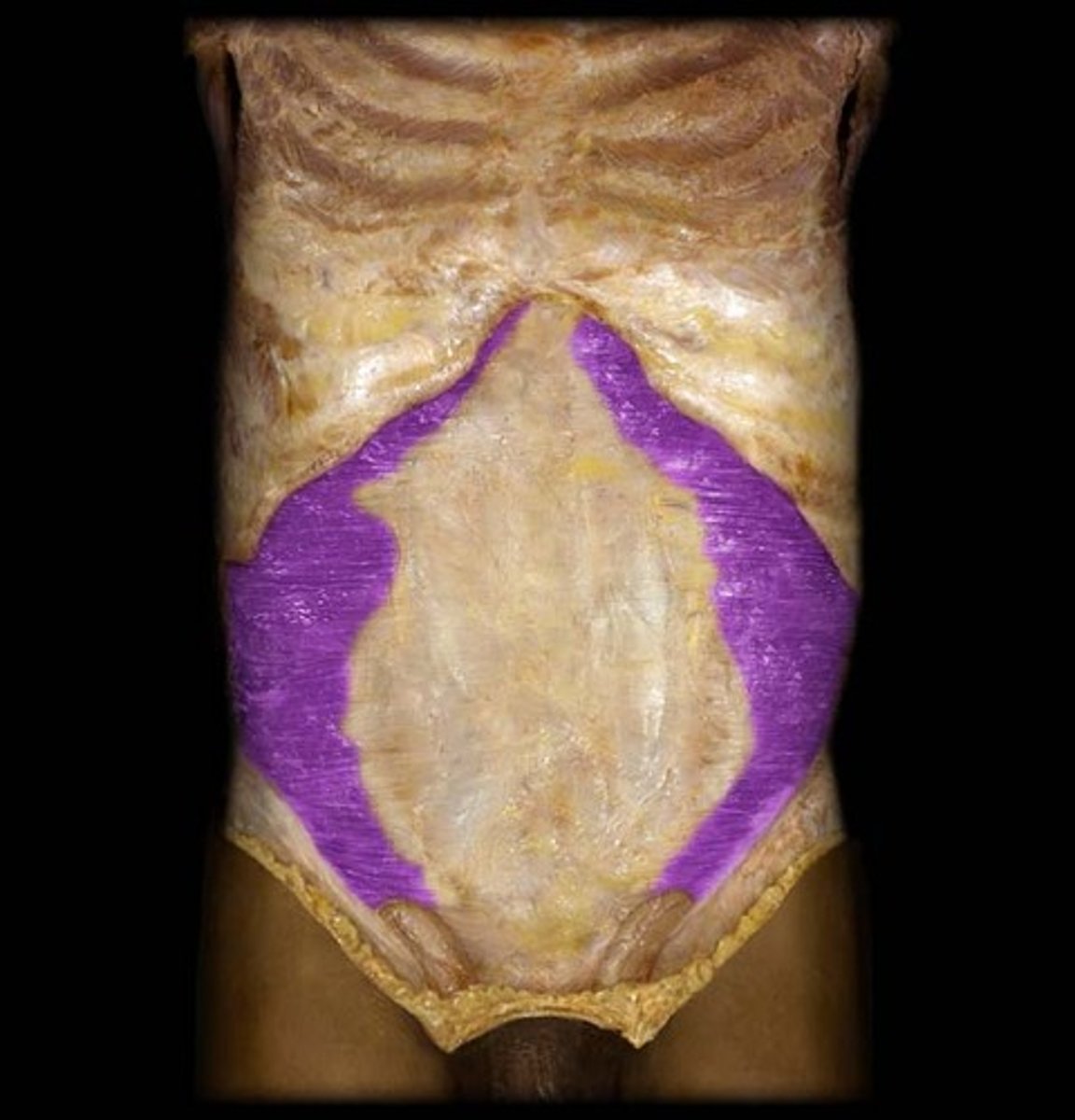
psoas abscess
identify the pathology
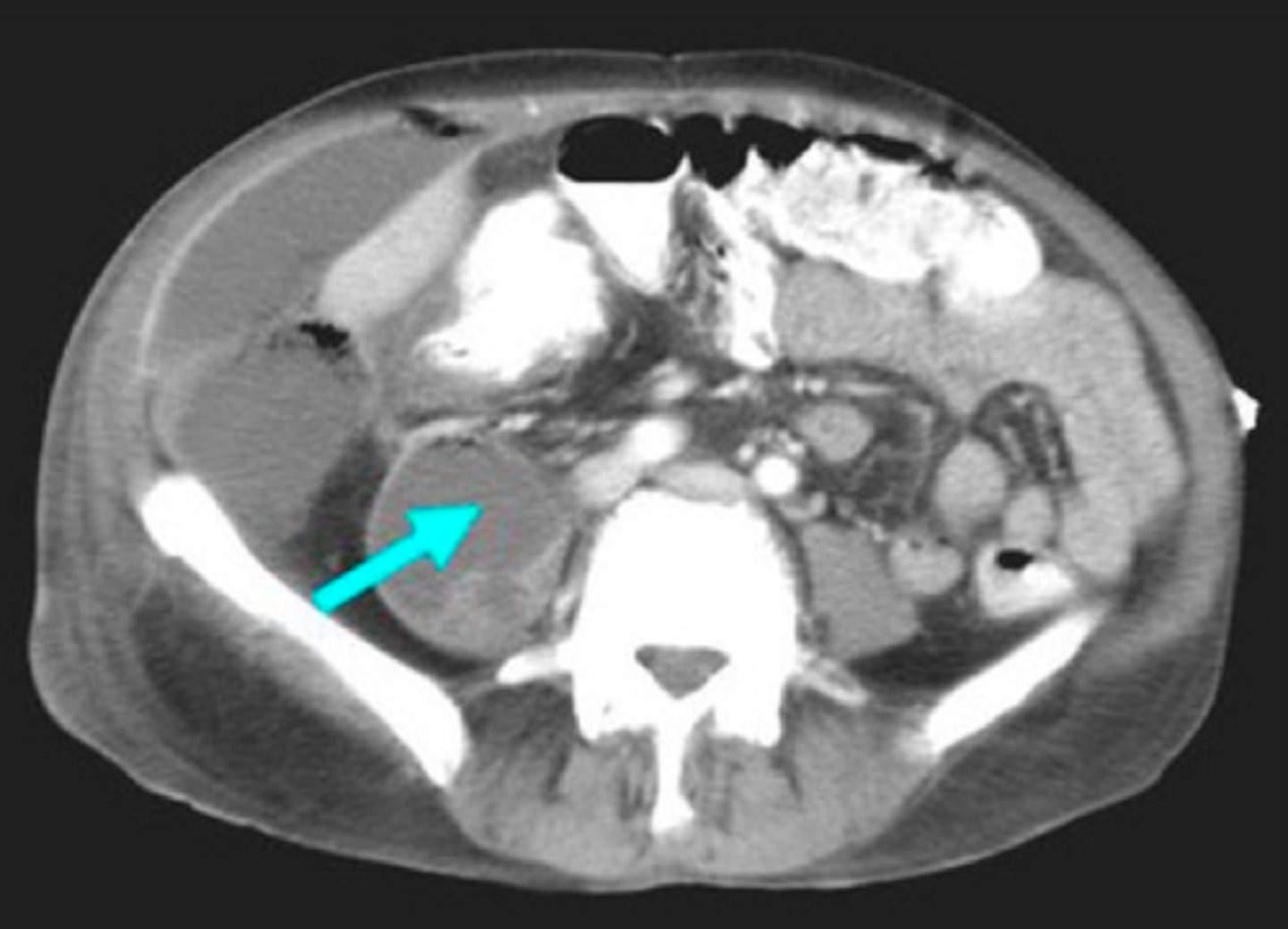
psoas abscess
identify the pathology
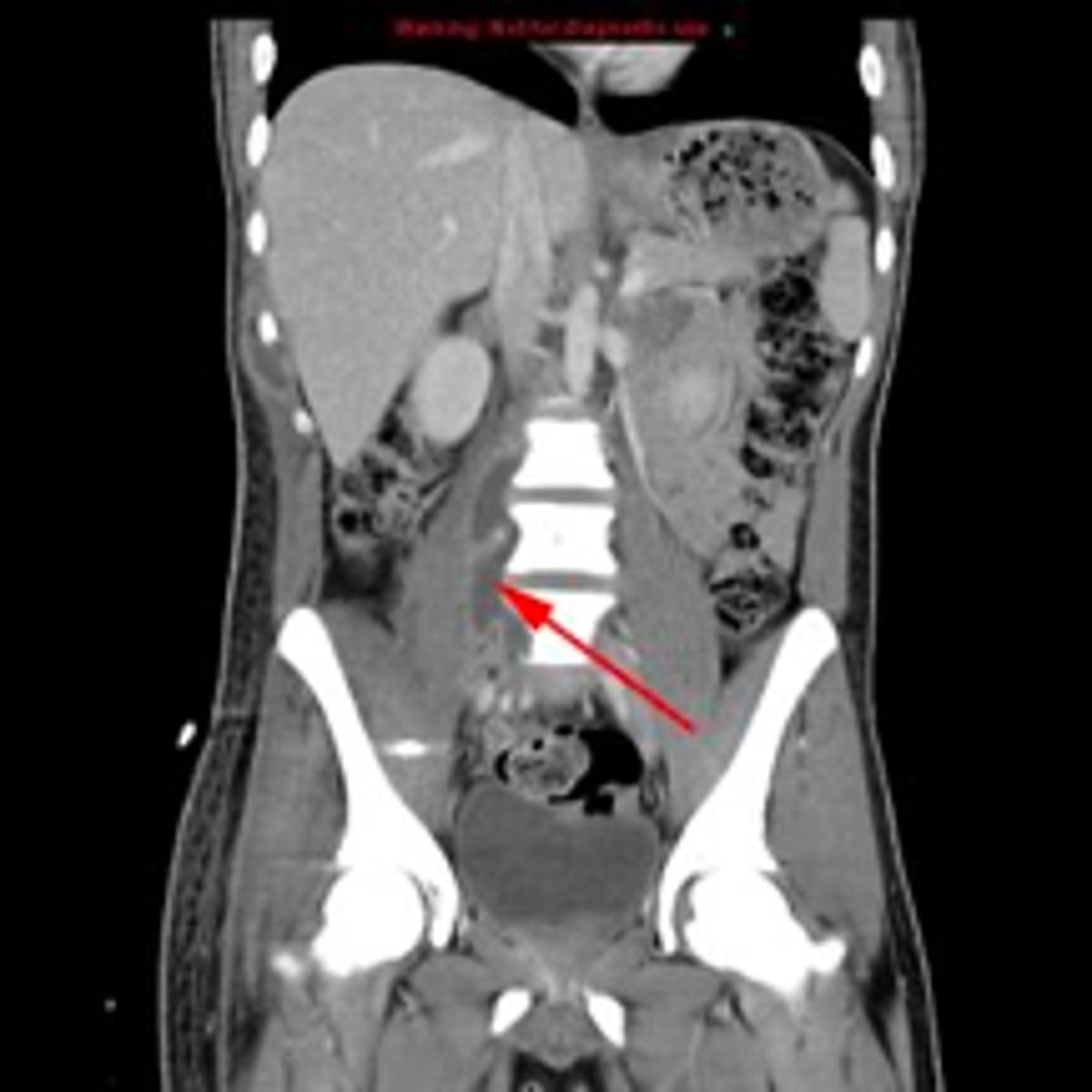
psoas abscess
patient presents with pain in the lower back and abdomen that sometimes radiates to the anterior thigh and hip. Patient is struggling to overcome a tuberculosis infection. What is the diagnosis?
inflamed appendix
patient presents with pain in the lower back, abdomen and right thigh during flexion and extension. What is the likely cause?
infected sigmoid colon
patient presents with pain in the lower back, abdomen and left thigh during flexion and extension. What is the likely cause?
IVC
what structures passes through the diaphragm at the T8 vertebrae level?
IVC
what structure pierces the central tendon of the diaphragm to enter the abdominal cavity?
esophagus
what structures passes through the diaphragm at the T10 vertebrae level?
abdominal aorta
what structures passes through the diaphragm at the T12 vertebrae level?
phrenic n.
innervation for diaphragm:
right crus
what part of the diaphragm forms the esophageal hiatus?
esophagus
what structure passes through the right crus?
T10
the right crus loops at what vertebral level?
abdominal aorta
what structure passes into the abdominal cavity through the right and left crura, posterior to the esophagus?
inferior phrenic aa.
what arteries supply the diaphragm at the level of T12?
L4
at what vertebral level does the abdominal aorta bifurcate into the right and left common iliac aa?
external iliac a.
which branch of the common iliac a. supples the lower limbs?
internal iliac a.
which branch of the common iliac a. supples the pelvic structures?
celiac trunk
superior mesenteric a.
inferior mesenteric a.
median sacral a.
name the 4 unpaired branches of the abdominal aorta:
inferior phrenic a.
middle suprarenal a.
renal a.
gonadal a.
lumbar aa.
name the 5 paired branches of the abdominal aorta:
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
identify the pathology
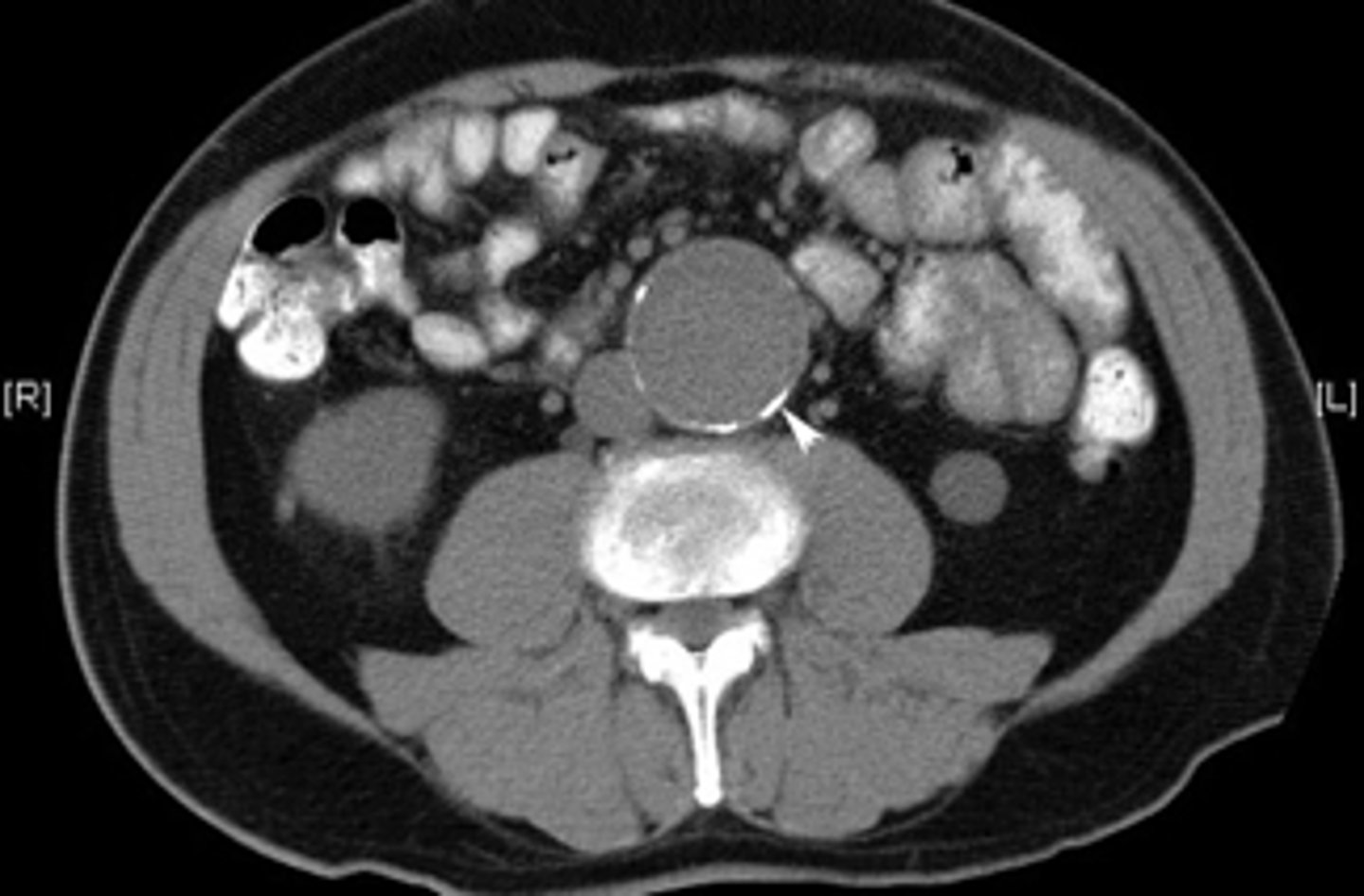
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
identify the pathology
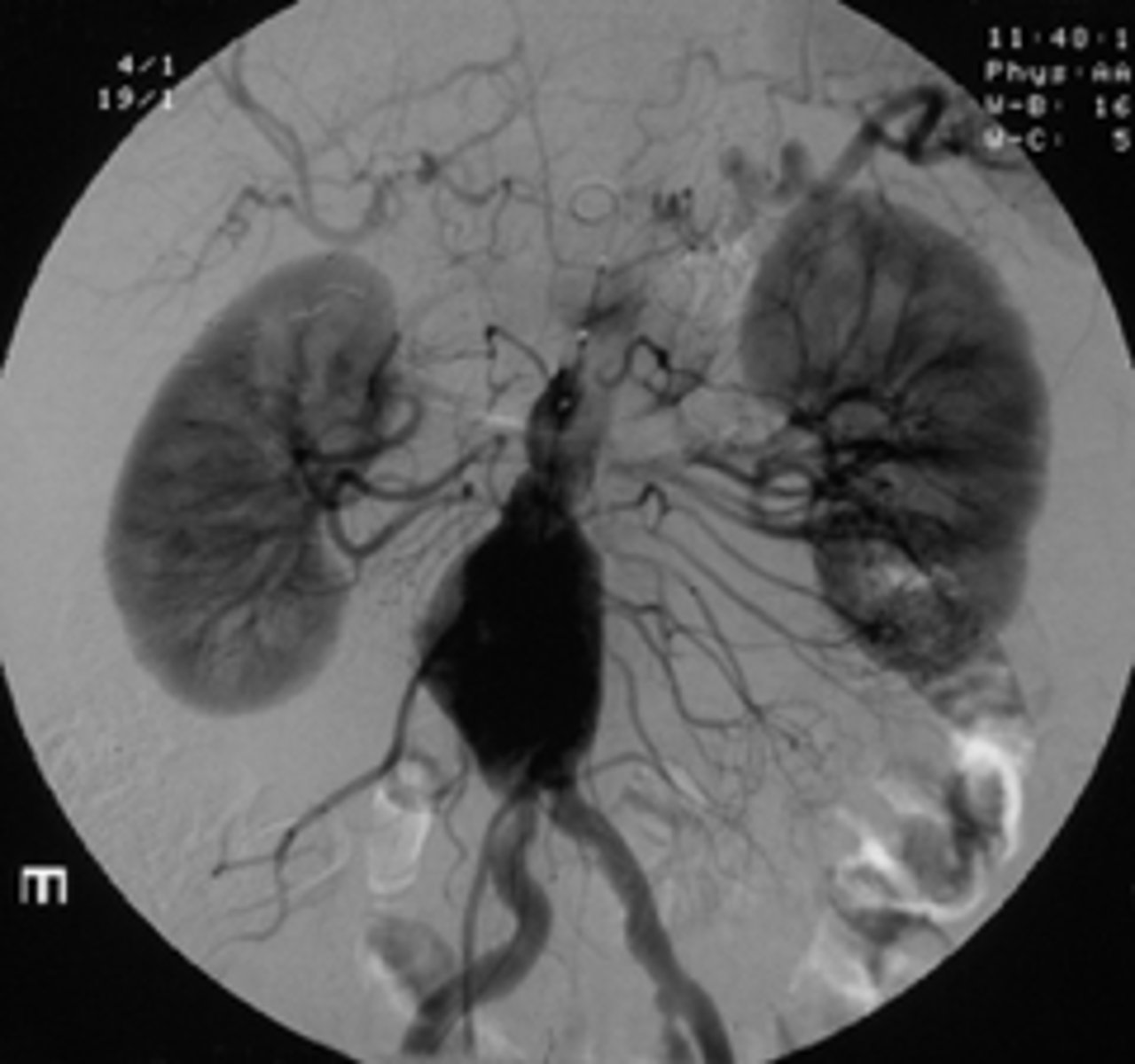
common iliac vv.
the IVC is formed by the conjunction of the:
IVC
the right inferior phrenic v. drains into the:
left renal v.
the left inferior phrenic v. drains into the:
IVC
the right suprarenal v drains into the:
left renal v.
the left suprarenal v drains into the:
IVC
the right gonadal vein drains into the:
left renal v.
the left gonadal vein drains into the:
left renal v.
what structure crosses directly anterioinferior to the superior mesenteric artery?
superior mesenteric a.
the paired renal arteries sit at the same level as what unpaired artery?
left psoas muscle
if there was a blockage in the left renal vein, what structures would not be affected:
- left kidney
- left testicle/ovary
- left adrenal gland
- left side of diaphragm
- left psoas muscle
genitofemoral n.
what nerve pierces through the psoas muscle?
genitofemoral n.
identify the structure
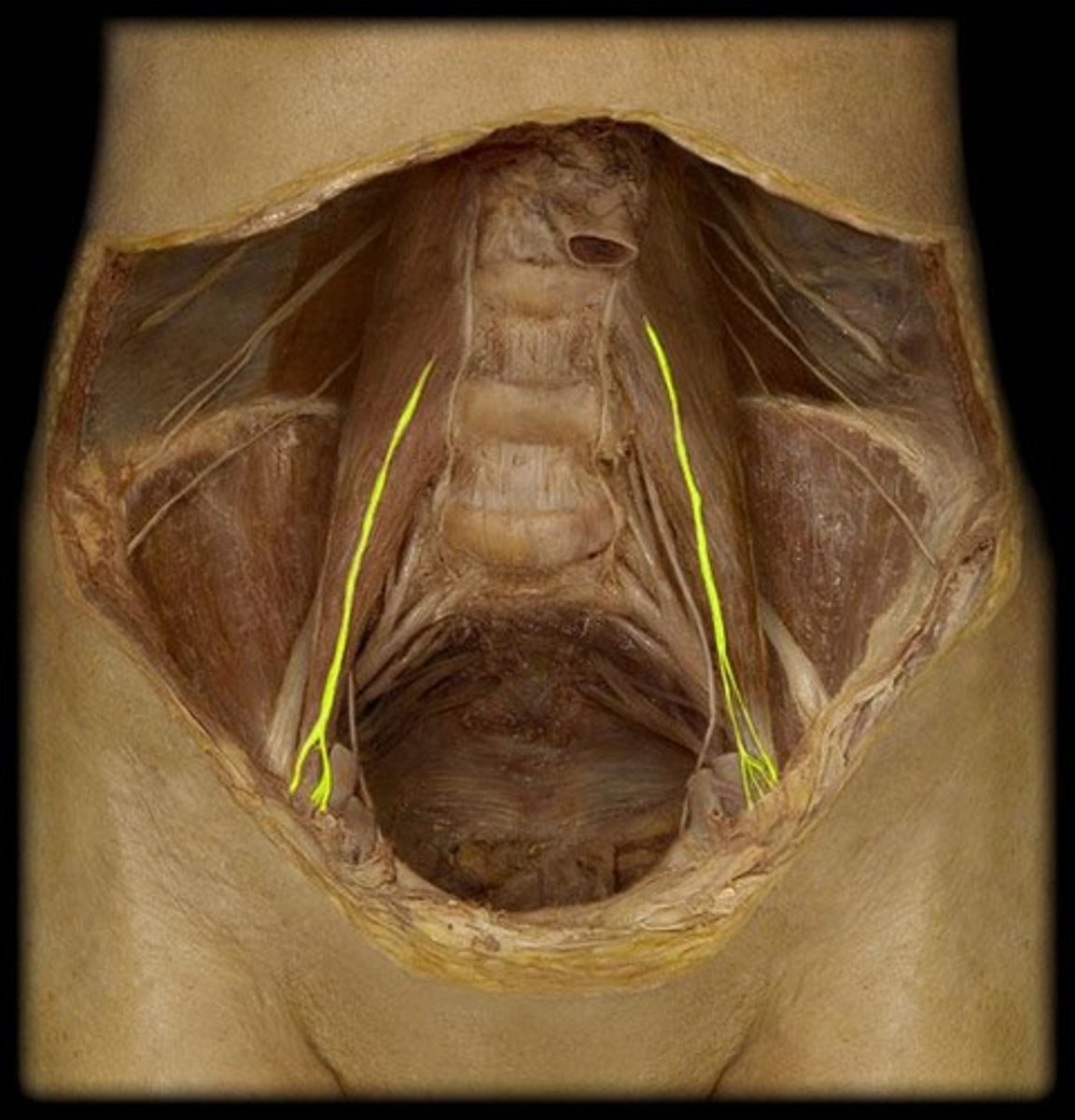
subcostal n.
identify the structure
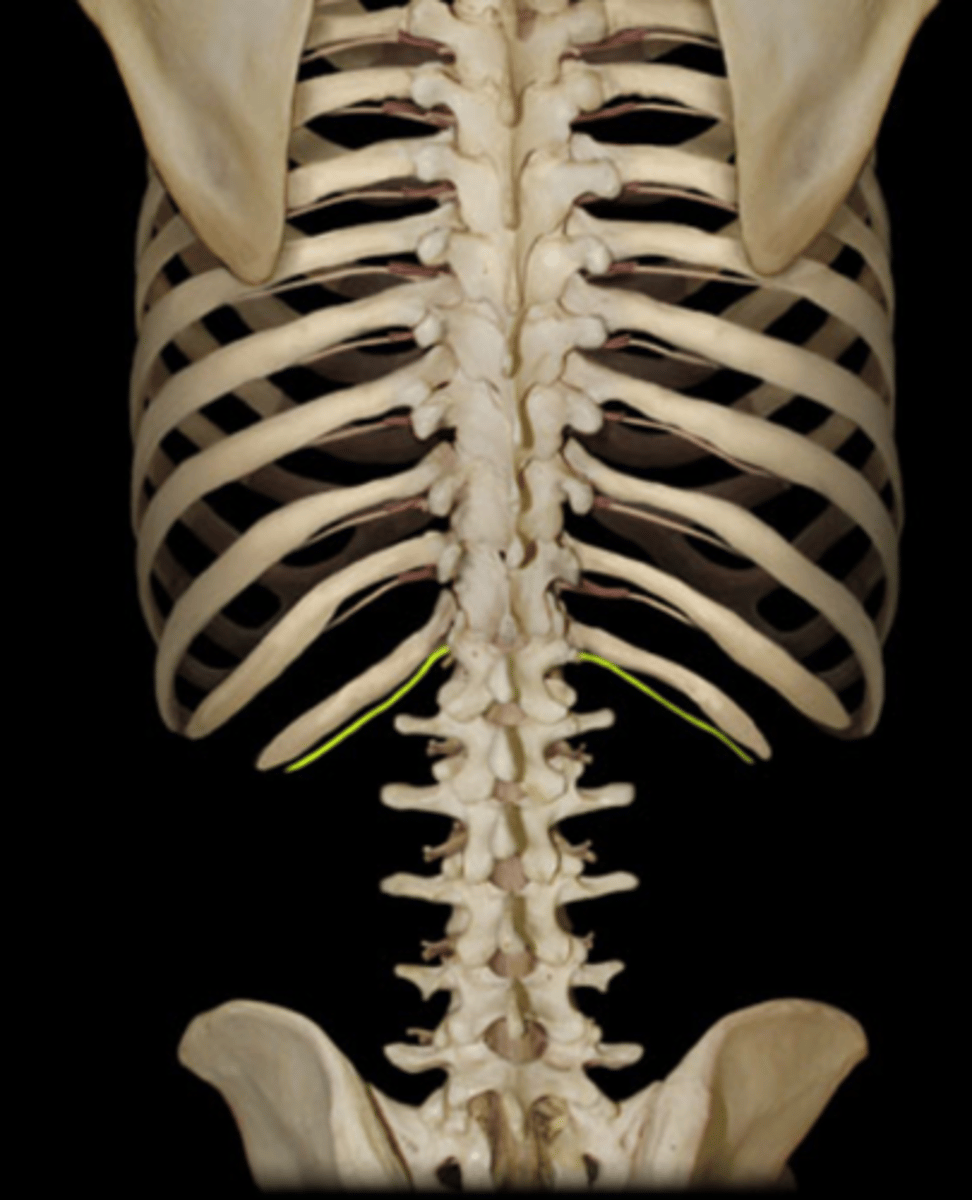
iliohypogastric n.
identify the structure
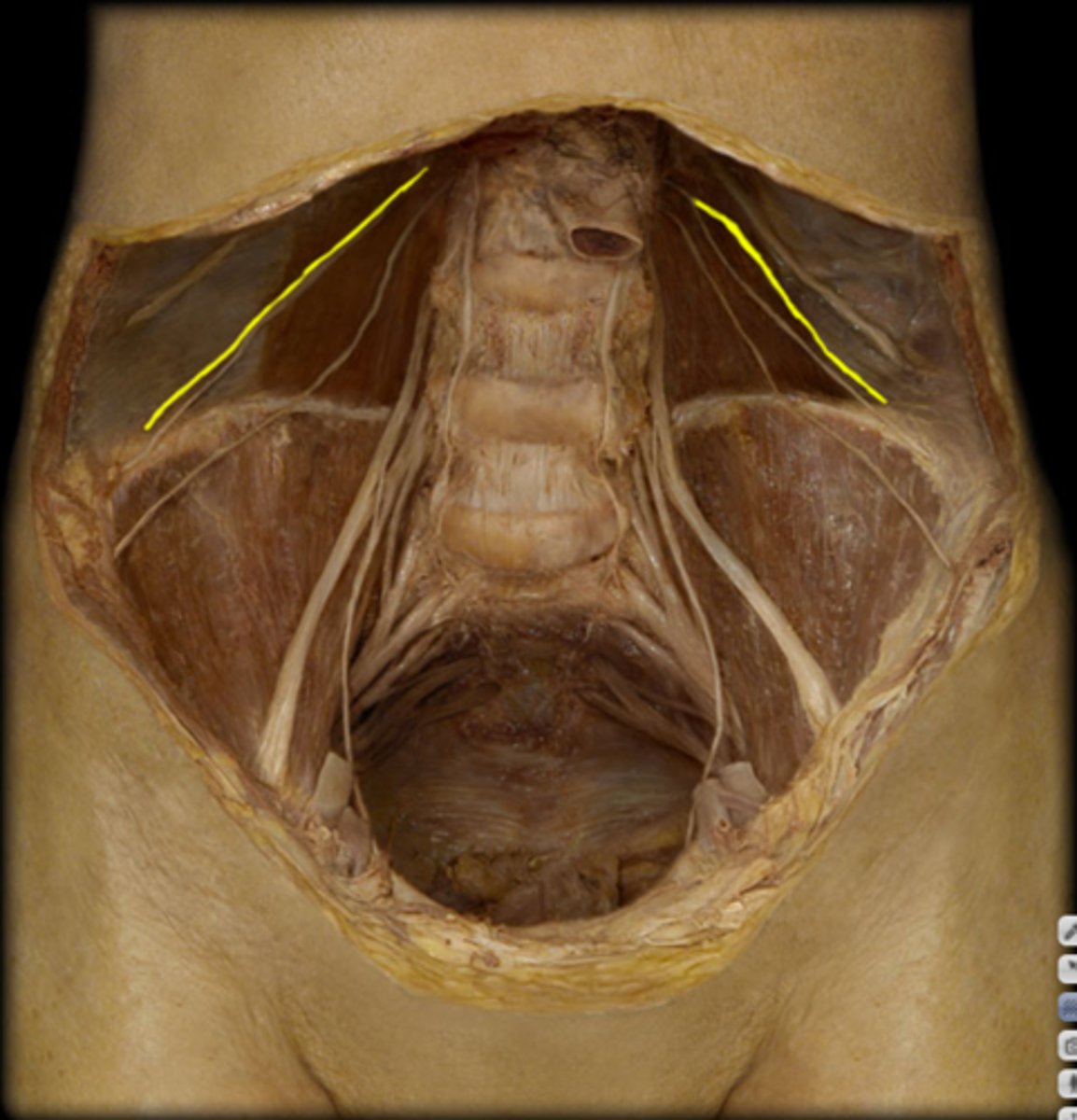
ilioinguinal n.
identify the structure
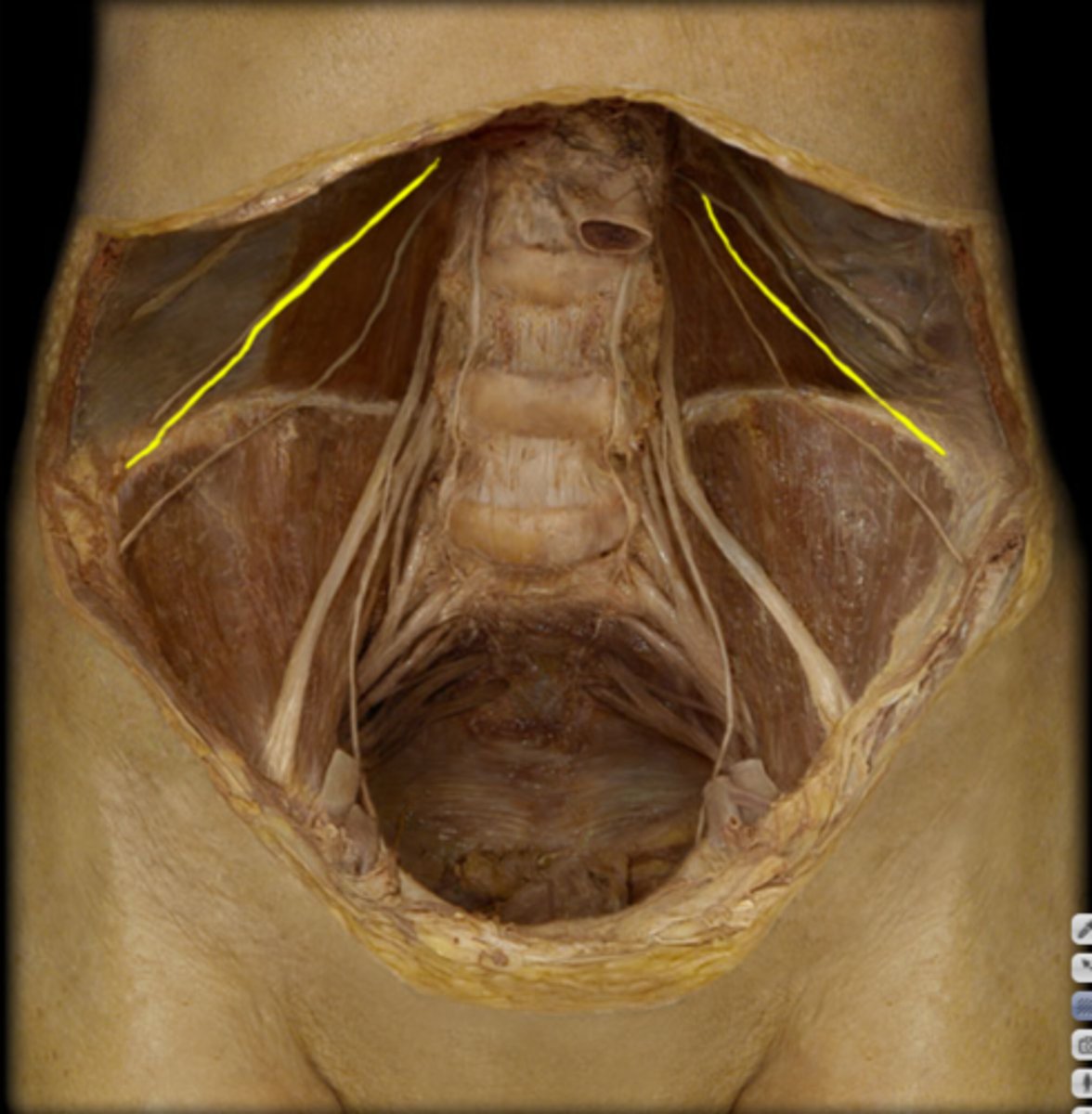
femoral n.
identify the structure
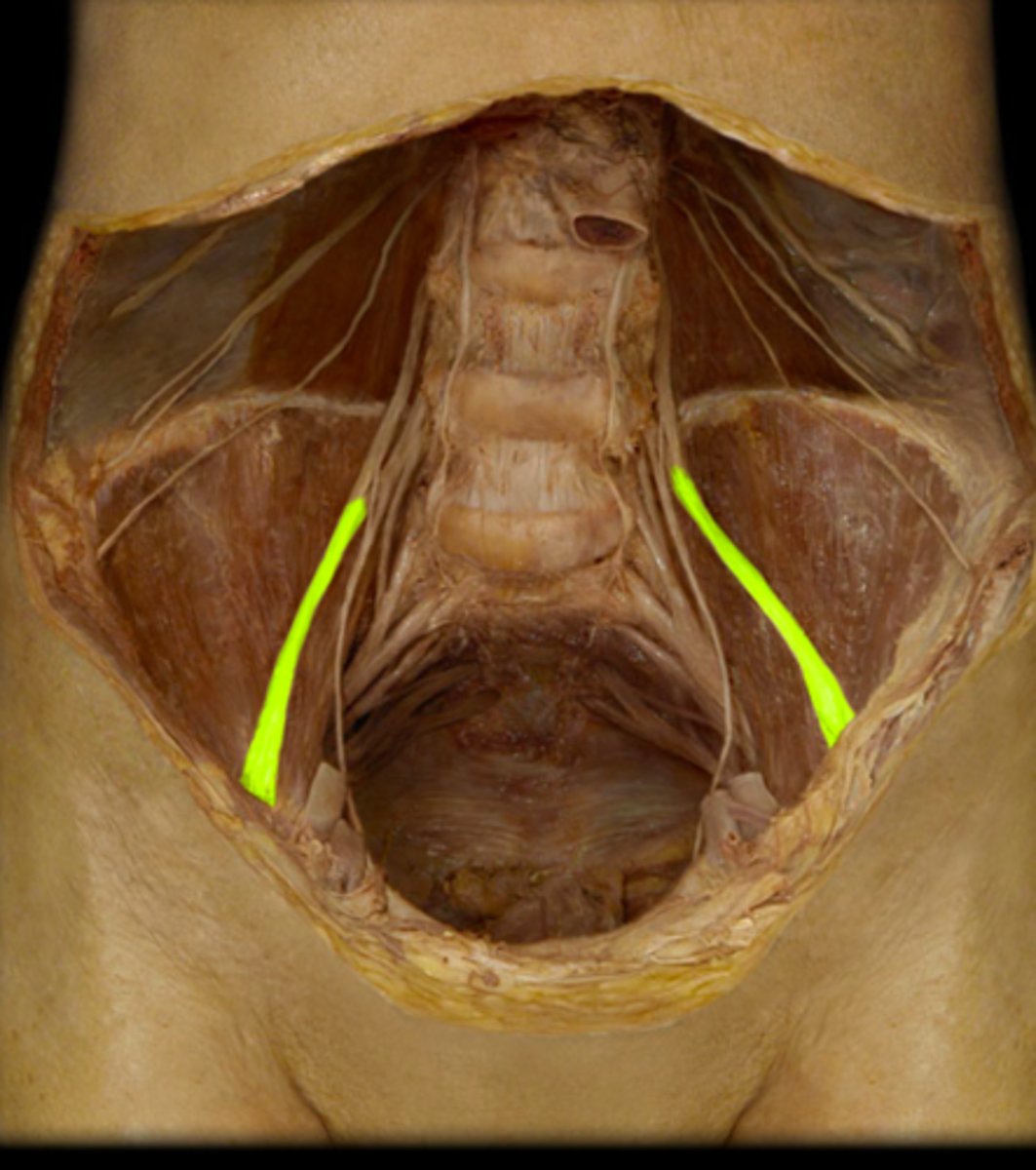
psoas major m.
the genitofemoral n. pierces through what muscle?
lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh
what nerve runs over the superior surface of the iliacus muscle?
femoral n.
what nerve runs over the inferior surface of the iliacus muscle?
subcostal n.
what nerve runs inferior to the 12th rib?
iliohypogastric n.
ilioinguinal n.
what nerves cross over the quadratus lumborum m.?
genital branch of genitofemoral nerve
what branch of the genitofemoral n. travels through the inguinal canal to provide efferent fibers to the cremaster m.?
femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve
what branch of the genitofemoral n. travels below the inguinal ligament to provide afferent fibers to the skin of the thigh?
T8 - T12
Skin of anterior abdominal wall supplied by lower intercostal nerves:
T12
the subcostal nerve arises from spinal nerve level:
L1
the iliohypogastric nerve arises from spinal nerve level:
L1
the ilioinguinal nerve arises from spinal nerve level:
L1-L2
the genitofemoral nerve arises from spinal nerve level:
L2-L3
the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh arises from spinal nerve level:
L2-L4
the femoral nerve arises from spinal nerve level:
L2-L4
the obturator nerve arises from spinal nerve level:
celiac ganglia
postsynaptic efferent sympathetic cell bodies from the greater splanchnic nerves are found at the:
aorticorenal ganglia
postsynaptic efferent sympathetic cell bodies from the least splanchnic nerves are found at the:
superior mesenteric ganglia
postsynaptic efferent sympathetic cell bodies from the lesser splanchnic nerves are found at the:
inferior mesenteric ganglia
postsynaptic efferent sympathetic cell bodies from the lumbar splanchnic nerves are found at the:
sypathetic chain ganglia
afferent fibers from abdominal viscera travel through:
pre-aortic lymph nodes
what type of lymph nodes drain the GI system?
lateral aortic lymph nodes
what type of lymph nodes drain the structures of the posterior abdominal wall, pelvis and lower limb?
lateral aortic lymph nodes
what lymph nodes would the kidneys drain into?
pre-aortic lymph nodes
what lymph nodes would the jejunum drain into?
T12
the cisterna chyle is located at what vertebral level?
cisterna chyli
what structure sits to the right of the aorta behind the right crus?