Unit 5 Ap Psychology
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Memory
learning that persists over time
information and or experiences that are encoded, stored and retrieved
Rehearsal
repetition of incoming information
Eideic Memory
rare ability in some people to recall images and sounds after short exposure.
Multistore model of memory
Information moves through multiple stores
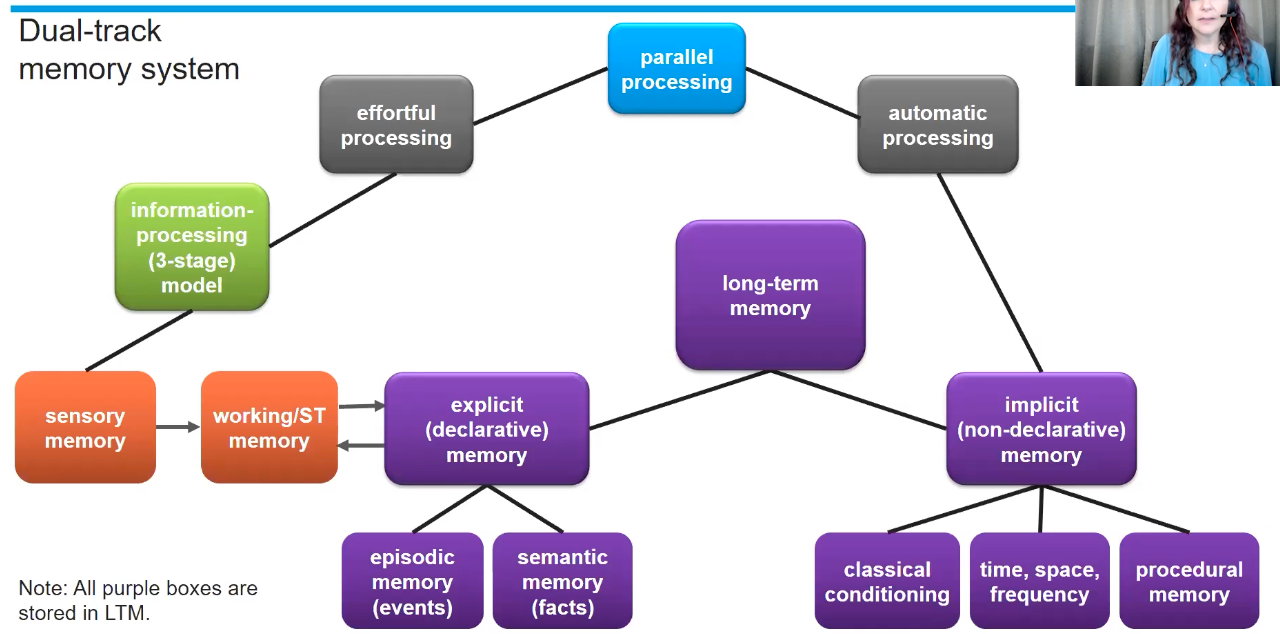
Atikinson and Shiffrin’s Information-processing Model
Similar to sequential computer processing
3 stage model of memory
sensory
short term (STM)
long term (LTM)
Baddeley
revised short-term memory, where we actively process information
working information
STM is like a shelf used temporarily
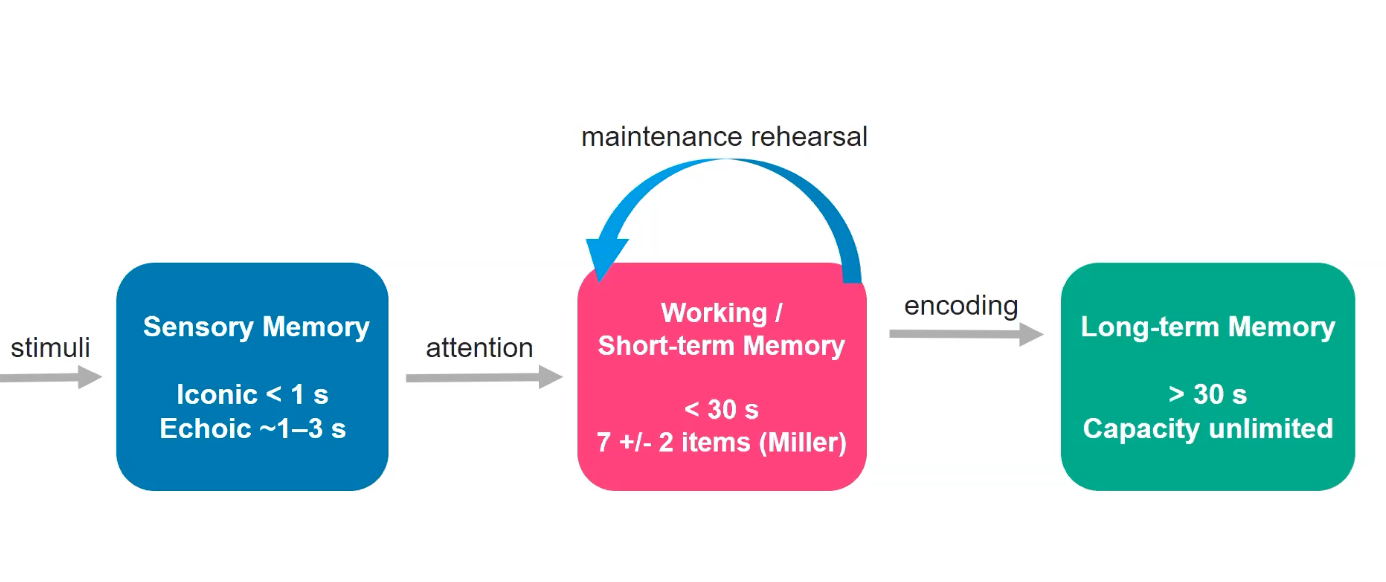
Information processing model ( 3 stage model
stimuli →
Sensory Memory (Iconic < 1s) (Echoic1-3s) →
attention→
Working/ Short-term Memory (30s) (7±2 items)
Miller
maintenance rehearsal
encoding →
Long-term memory 30s
capacity is unlimited
Sensory memory
brief high capacity store
Two types:
iconic 1s: visual
echoic 1-3s: sound
Working/ short term memory
lower capacity 30s
hold up to 7± 2 items
Maintenance rehearsal
Try to hold on to something in working memory
Like saying it in your head
Long Term Memory
By encoding information
unlimited
anything over 30 seconds
take it out by retrieval
Encoding
Put something in your long term memory
Retrieval
Take something out long term memory to working memory
two types
Recognition
Recall
Recognition
Identify previous learning
ex. Mcq of Ap exam
Recall
Retrieving or pulling out previous learning, decline with age
ex. giving a definition
Relearning
Improved retrieval with repeated learning
ex studying after three practice assignment for quicker retrieval
Overlearning
Practicing a skill to make it more resilient to forgetting
ex. after getting correct answers in a math assignments practice for 10 more minutes
Retrieval Cues
Serve as connection points to access a memory, such as smell, sounds, or visual elements.
Priming
Retrieval Cue
Activation of memory associations, sometimes unconscious
previous exposures may influence future thoughts
Context Dependent Memory
retrieval Cue
revisiting location of an experience
ex. you go into the kitchen for tape fut forget, when you come bak you see the ripped paper and remember
State Dependent memory
Retrieval Cue
What we experience in one state like a headache could be remembered better the next time we are in that state.
ex: mood congruent memories
Shallow Processing
little elaboration with a focus on superficial and or perceptual elements
superficial, less effective
ex. encoding a word by the type of font it is written with
Deep processing
focus on the meaning with deeper elaboration
semantic endocoding
ex. encoding a word by the meaning and connecting it o previous learning
leads to better retention
Visual encoding
encode by visual elements
ex.
Acustic encoding
encode by sound
ex. rhymes with
Semantic encoding
encode by meaning
used in deep processing
ex. what category does it belong to ?
Massed practice
Spacing effect
Try to encode all at one
ex. cramming
Distributed practice
Spacing effect
encode over multiple time periods; the longer the better
ex. daily review sessions
Spacing effect
Distributed practice → long term retention unlike massed practice
Testing Effect
retrieving info for assessments like practice tests
more powerful for memory than restudying and rereading
Serial Position effect
The middle items are the least remebered
Recency effect
last items in a list are remembered best after seen
probably because still in working memory
Primacy effect
The first items in a list are remembered best
probably lasting effect on long term memory
Chunking
organizing effect
clustering items into units, especially is meaningful
ex number chunks in phone number
Mnemonics
organizing effect
Memory devices that use association or imagery to remember
ex keyword
Hirchies
organizing effect
Creating categories with subdivisions
Serial Processing
Only one process occurs at any given time, one after another
Parallel Processing
Multiple tracks of brain processes occurring at the same time
not the same as multitasking
two types:
effortful processing
Automatic processing
ex. after walking and discussing something you remember temperature, time pasees, key points, etc.
Effortful Processing
explicit declarative memories like experiences and facts
explained through 3-stage model
Automatic Processing
Implicit non declarative memories encoded unconsciously
Like time, space, and frequency
include procedural memory and classical conditioning
Dual track memory system
How do we forget?
encoding: something is in our working memory but didn’t link memory to go to long term
storage decay
retrival failure
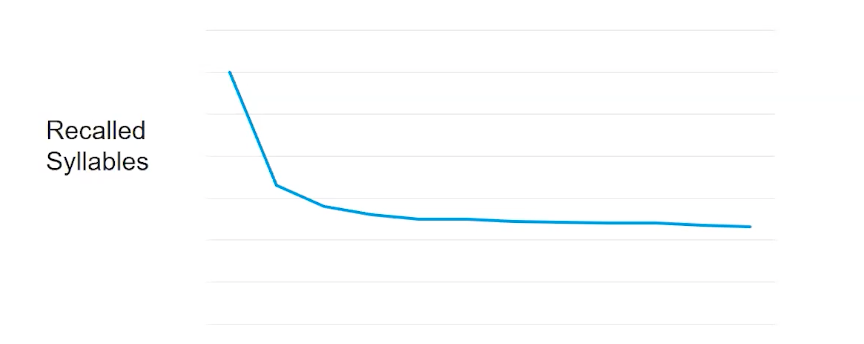
Storage decay
When a memory gets old therefore, it decays
Ebbunghoys forgetuc curev (1885)
memorized nonsense syllables like bix, lom
steep drop-off of recall initially, then levels out
Retrieval failure
when something is in our long term memory but we fail to retrieve it.
tip of the tongue phenomenon
stored but not accessible
can affect prospective memory ( looking back at previous info) or
ProsPective memory
Prospective memory
memory to do with something in the future
may be assisted with retrieval cues
like remembering to take daily medicine when looking at the medicine cabinet
Interference
some information blocks the recall of other info
two types
retroactive
proactive
Pro active interference
forward acting
prior information disrupts learning new information
while trying to learn new language old language interferes
Retroactive interference
backward-acting
new learning disrupts old information
when speaking old language new language keeps coming up
Amnesia
Temporary of permanent loss of memory types
retrograde
antograde
Source
Retrograde Amnesia
inability to remember past information or experiences
procedures remain intact, like walking
ex. blow to the head that leads to forgetting recent events
Anterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories
involves the Hippocampus
ex. HM got his hippocampus removed and was not able to form new memories
Source Amnesia
attributing an experience to the wrong source
ex. telling a joke to someone who told it to you
How to improve memory
make meaningful links and associations
distributed practice
activate retrieval cues
testing effect
chunking
mnemonic
sleep
Long Term potentiation
Increased efficiency in the synapse when repeatedly stimulated
neuron needs less activation
more connections between neurons
lasts from hours to weeks
Biology of Memory
Changes happen at a cellular level in the brain when learning happens
Long term potentiation
biology of Explicit memory
Memories of experiences and facts
associated with the hippocampus and frontal lobe
Hippocampus= hub through which complex neural memory networks are stored
biology of Implicit memories
memory for procedures, conditioning, and timing
cerebellum associated with classical conditioning.
basal ganglia in the deep brain associated with procedural motor skills. like riding a bike
Emotional memory
the limbic system is the center of the emotion in the brain including hippocampus and amygdala
Flashbulb memory
not immune to alteration
usually very personal experience.
like a first kiss
can be shared
more resistant to decay
Structures of thought
concept
prototype
exemplar
artificial concepot
Concept
Cluster of raw cognitive material
you either forget ut or join it with another piece of cognitive iinformation.
Prototype
a great, abstract example
not perfect but great
like when you think of a dog, you think of a labrador retriever
Exemplar
a great example from experience
but the experience is limited
like you are going to think about a dog you have met
Artificial Concept
a perfcet example
rare in real life
Functions of thoughts ( problem solving
Informal reasoning
fast thinking
thinking is slow when trying to evaluate multiple possibilities
we use
heuristics
top-down processing: already knowing about situation before having all details
schema: set of ideas used to view problem
mental seT
mental model
Formal reasoning
slow thinking
allows us to be sure of our answer, to lower the p-value
we use
algorithm
bottom-up processing: gathering many bits of data before conclusion
syllogism
artificial intelligence
Heuristics
thinking shortcuts based on experience
can lead us to the wrong answer
they are not always bad and are useful
process that leads to cognitive bias
representative
availability
anchoring bias
confirmation bias
hindsight bias
Mental set
similar to schema. way of thinking that has worked before
Mental model
Way of thinking about how things interact
Algorithm
Step by step process 1+__= 10
Syllogism
Using logic. if a=b and b=c them a=c. can be improved with practice
Diagnosis
Eliminate all wrong answers to get correct
Artificial Intelligence
Similar to algorithm. Facial recognition, auto-complete, or self driving cares use step by step processes to find patterns.
Cognitive biases
Result of using an imperfect thinking strategy
these results can be used to create even more wrong answers
there are many
fixedness
framing effect
illusory correlation
functional fixedness
belief perseverance
Concrete
examples not definitions
true understanding of concepts
Representativeness heuristic
Thinking that a new thing that has few characteristics of a schema, will fit nicely into that schema
Stereotyping
Availability heuristic
When strategy easily comes to mind
many students when they are stuck use study techniques that easily pop into they mind and don’t think about other strategies.
Anchoring bias
powerful emotional thought weighs down the rest of the minds
Confirmation bias
we watch and subscribe to things that support our oppinions
Hindsight bias
“i knew it all along”
before an event we are unsure of the outcome. after the outcome we think we did know it.
Fixedness
Not being able to se the problem from a different point of view
Framing effect
Words matter. How a problem is presented influences how we think
Illusory correlation
Just because things happen near each other does not mean there is a connection. Circumstantial evidence.
Funcional Fixedness
Not being able to see than an object can be used in different ways
Belief perseverance
Even when presented concrete evidence to the contrary, a person will hold their beliefs
Intelligence
opperantional definition:
abrstract
operationalized
Abstract Intelligence
Intelligence is the ability to think creatively
intelligence is the ability to apply knowledge to new situations
Operationalized intelligence
traditional tests were verbal tests
easy to grade and compara
Reductionism- reduce a concept like intelligence to a concept
Psychometrics
Measuring the minds
Speed of processing
easily measured and does seem to be correlated with intelligence
Fluid Intelligence
related to speed of processing
Fluid intelligence is your ability to process new information, learn, and solve problems
Crystalized Intelligence
heuristics
as we age we are slower
Crystallized intelligence is your stored knowledge, accumulated over the years.
Flynn Effects
over time, the average IQ of society rises
means that some tests need to be recalibrated
Savant Syndrome
Genius ability in a very narrow area
like being able to multiply large numbers instantly
It is related to Autism Spectrum Disorder
not all people with autism have savant and vise versa
Stereotype threat
members of a group who are thought to be “less than” in certain areas will often perform worse in that area than the members of a different group.
it is a confounding variable
Single Blind
to expose ST
intelligence testing
get a representative sample
Do not tell them that it is an intelligence test, have them take the test
Analyze the results and Racial differences will disappear.
Francis Galton (1822-1911)
First one to think that intelligence can be quantified. Psychometrics
his method, like Wundt’s introspection, wasn’t able to support his ideas
he wanted to correlate reaction times with intelligence
Charles Darwin Cousin
Believed in Eugenics,
believed that success was due to inherited mental traits
better people should have many children and less-able shouldn’t
Alfred Binet (1857-1911)
came up with the first test to classify mental abilities
originally used to help French schools identify children who are behind
gathered a lot of information about the abilities of children at each age. figured out what was normal for a child to do.
came up with mental age and Chronological age
MA/CA x 100= IQ 8/8 ×100= 100 (100 was the mean)
test was called the Binet-Simon test because he had a partner named Theodore Simon