physics p1 - matter
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
* discovered electrons which are dotted around inside spheres of positive charge
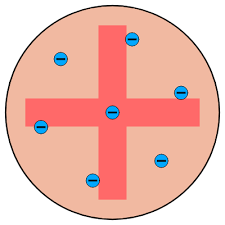
* nucleus surrounded by cloud of negative electrons so most of atom is empty space
* aimed beams of positively charged **alpha particles** at very thin gold foil.
* According to the plum pudding model, these particles should have passed straight through. However, many of them changed direction instead.
* this meant it had to have a small positively charged nucleus
* a **problem** with Rutherford's model - the **electrons** would eventually f**all into the nucleus** because they are negatively charged and so attracted to the positive nucleus.
* Niels Bohr improved Rutherford's model. Using mathematical ideas, he showed that electrons occupy **shells** around the nucleus.
what is an atom
a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons, with the nucleus size being much smaller than that of the atom and with the most mass in the nucleus
* Mass per unit volume
* denisty = mass/ volume so density must change too
* solids are most dense and gasses are least
* for volume do length x width x height
* mass / volume
how do you find the density of an object
find out mass by weighing it
for volume use a eurika beaker
mass / volume
* place measuring cylinder under spout and put object in water
* the volume of water collected in the measuring cyclinder is the volume of the object
* only vibrate as not much energy in kinetic energy stores
why is a solid denser than gas
because the particles are tightly packed in a regular structure whereas in a gas the particles are spread out
* particles can flow over each other to form irregular arrangement
* more energy in kinetic energy stores
* particles travel in random directions at high speeds
* have lots of energy in kinetic energy stores
because as particles vibrate more, some of the forces of attraction between them weaken causing the solid to melt into a liquid
\
how does a liquid become a gas
adding more heat energy breaks the bonds between the atoms completely
whats it called when a solid turns into a liquid
melting
whats it called when a liquid turns into a solid
freezing
whats it called when a liquid turns into a gas
evaporating
whats it called when a gas turns into a liquid
condensing
whats it called when a gas turns into a solid/ solid turns into a gas
sublimating
what 2 things can heating a substance do
raise its temperature
change the state of the substance